【OpenCV图像处理】 图像拼接技术
目录
一:图像拼接技术 需求分析
二:图像拼接技术 具体步骤
三:图像拼接技术 代码实现
一:图像拼接技术 需求分析
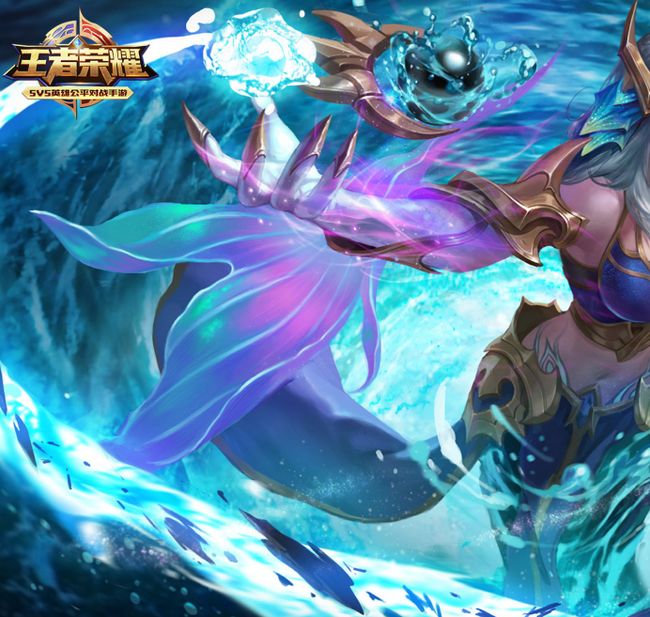
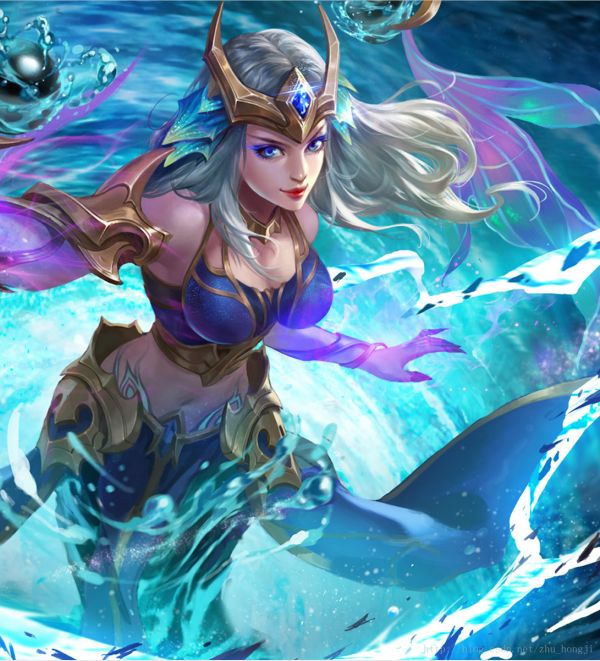
将下面两张图像进行拼接
拼接得到一张完整的图像
二:图像拼接技术 具体步骤
1.选择特征点
//1、选择特征点
//左图 右图 识别特征点 是Mat对象 用c d保存
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存 特征点为中心点区域比对
vector matches;
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序从小到大 找到特征点连线
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end()); 2.保存最优的特征点对象
//2、保存最优的特征点对象
vectorgood_matches;
int ptrpoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for (int i = 0;i < ptrpoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//2-1、画线 最优的特征点对象连线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
//imshow("outimg",outimg); 3.特征点匹配
//3、特征点匹配
vectorimagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for (int i= 0 ;i < good_matches.size();i++)
{
//查找特征点可连接处 变形
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
//查找特征点可连接处 查找基准线
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
} 4.透视转换 图像融合
//4、透视转换 图形融合
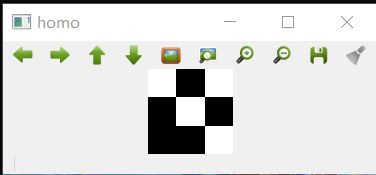
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
//imshow("homo",homo);
//根据透视转换矩阵进行计算 四个坐标
CalcCorners(homo,right);
//接收透视转换结果
Mat imageTransForm;
//透视转换
warpPerspective(right,imageTransForm,homo,
Size(MAX(corners.right_top.x,corners.right_bottom.x),left.rows));
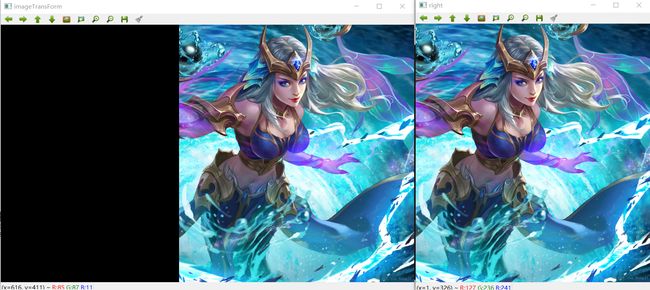
//右图透视变换 由于本次图片材料是自己截图拼接的 因此看不出透视变换的明显特征
//imshow("imageTransForm",imageTransForm);
//结果进行整合
int dst_width = imageTransForm.cols;
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTransForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTransForm.cols,imageTransForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));右图的透视转换,由于图像材料是自己截图拼接的,因此看不出透视变换的明显特征,但根据上图可知已经做出透视变换图像处理操作
左图与右图的透视转换结果 拼接 【这里只是将窗口移动测试看下前面步骤是否正确】
可以看出左图与右图的透视转换结果 是可以进行接下来的图像融合操作的
5.优化图像 进行最终的结果展示
//5、优化图像
OptimizeSeam(left,imageTransForm,dst);
//最终图像拼接结果
imshow("dst",dst);可以看出 顺利完成 两张图像拼接的图像处理操作
三:图像拼接技术 代码实现
#include
#include
#include //图像融合
#include //拼接算法
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
typedef struct
{
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
//图像融合的去裂缝处理操作
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst)
{
int start = MIN(corners.left_top.x, corners.left_bottom.x);//开始位置,即重叠区域的左边界
double processWidth = img1.cols - start;//重叠区域的宽度
int rows = dst.rows;
int cols = img1.cols; //注意,是列数*通道数
double alpha = 1;//img1中像素的权重
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
uchar* p = img1.ptr(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//左图
Mat left = imread("D:/00000000000003jieduanshipincailliao/a1.png");
//右图
Mat right = imread("D:/00000000000003jieduanshipincailliao/a2.png");
//左右图显示
imshow("left",left);
imshow("right",right);
//创建SURF对象
Ptr surf;
//create 函数参数 海森矩阵阀值 800特征点以内
surf = SURF::create(800);
//创建一个暴力匹配器 用于特征点匹配
BFMatcher matcher;
//特征点容器 存放特征点KeyPoint
vectorkey1,key2;
//保存特征点
Mat c,d;
//1、选择特征点
//左图 右图 识别特征点 是Mat对象 用c d保存
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存 特征点为中心点区域比对
vector matches;
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序从小到大 找到特征点连线
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end());
//2、保存最优的特征点对象
vectorgood_matches;
int ptrpoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for (int i = 0;i < ptrpoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//2-1、画线 最优的特征点对象连线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
//imshow("outimg",outimg);
//3、特征点匹配
vectorimagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for (int i= 0 ;i < good_matches.size();i++)
{
//查找特征点可连接处 变形
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
//查找特征点可连接处 查找基准线
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
}
//4、透视转换 图形融合
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
//imshow("homo",homo);
//根据透视转换矩阵进行计算 四个坐标
CalcCorners(homo,right);
//接收透视转换结果
Mat imageTransForm;
//透视转换
warpPerspective(right,imageTransForm,homo,
Size(MAX(corners.right_top.x,corners.right_bottom.x),left.rows));
//右图透视变换 由于本次图片材料是自己截图拼接的 因此看不出透视变换的明显特征
//imshow("imageTransForm",imageTransForm);
//结果进行整合
int dst_width = imageTransForm.cols;
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTransForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTransForm.cols,imageTransForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));
//5、优化图像
OptimizeSeam(left,imageTransForm,dst);
//最终图像拼接结果
imshow("dst",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}