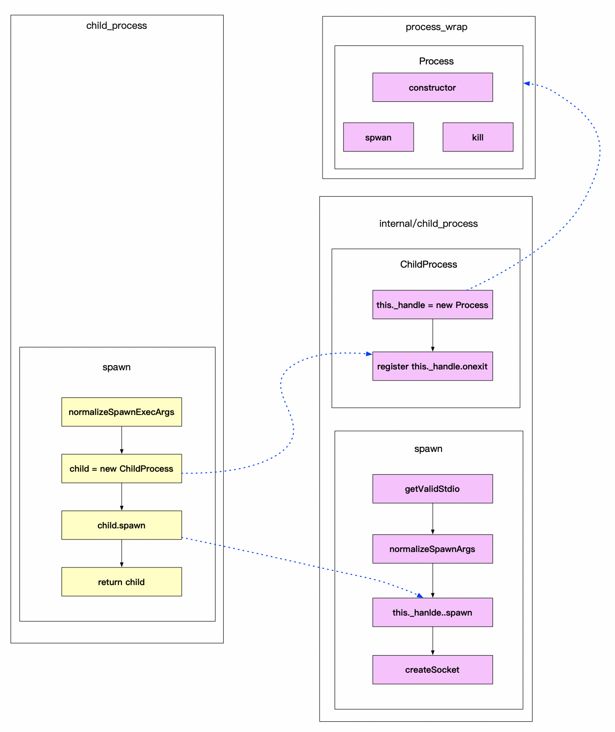
对应Node多进程exec方法执行流程源码分析 文章,exec/execFile/fork方法都是执行的spwan方法;这篇文章也是重点去梳理spawn方法的设计思路
源码分析
目前的源码是nodev12版本的;整体思路是差不多的,可供参考学习
core-modules/child_process.js
spawn方法
function spawn(file, args, options) {
const opts = .... // 标准化参数
const child = new ChildProcess();
....
child.spwan({
file: opts.file,
args: opts.args,
cwd: options.cwd,
....
});
return child;
}将按照执行流程,重点介绍这几个方法
ChildProcess.prototype.spawn方法
ChildProcess.prototype.spawn = function(options) {
let i =0;
if(options === null || typeof options !== 'object') { // options 如果不存在抛出异常
throw new ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE('options', 'Object', options)
}
let stdio = options.stdio || 'pipe'; // 标准的输出接口,通常采用pipe(管道)
stdio = getValidStdio(stdio, false); // pipe(管道)在这创建的;下面有getValidStdio方法源码的说明;
const ....
stdio = options.stdio = stdio.stdio;
// [
// {type: 'pipe', readable: true, writable: false, handle: Pipe},
// {type: 'pipe', readable: false, writable: true, handle: Pipe},
// {type: 'pipe', readable: false, wriatable: true, handle:Pipe}
// ];
....
const err = this._handle.spawn(options);
// 调用process_wrap进行实例化,创建子进程;err为0;表示子进程创建成功。
// 错误的err处理
if (err === UV_EACCES ||
err === UV_EAGAIN ||
.....
) {
process.nextTick(onErrorNT, this, err);
};
....
this.pid = this._handle.pid; // pid 为进程的id;
for (i = 0; i 0 );
// 得到socket实例;
};
};
};
...
// 输出流,输出流是i大于0
for (i>0 && this.pid!==0) {
...
stream.socket.on('close', ()=>{ // 绑定了close监听
maybeClose(this);
});
...
};
// 后续的错误流也会绑定colse监听
...
// 分别 创建输入流、输出流、错误流;下面是整理好后的结果
// socket 通信被创建完成
this.stdin = stdio.length >= 1 && stdio[0].socket !== undefined ? stdio[0].socket : null;
this.stdout = stdio.length > 2 &&stdio[1].socket!== undefined ? stdio[1].socket : null;
this.stderr = stdio.length >= 3 && stdio[2].socket !== undefined ? stdio[2].socket : null;
// stdio对象:从输入输出流中拿到socket对象
// [
// {type: 'pipe', readable: true, writable: false, handle: Pipe, socket: Socket},
// {type: 'pipe', readable: false, writable: true, handle: Pipe, socket: Socket},
// {type: 'pipe', readable: false, wriatable: true, handle:Pipe, socket:Socket}
// ];
// 将数组中的每一项的socket拿出来赋值到stdin、stdout、stderr;在返回回调函数中,我们会使用 stdout.on(‘data’, function
()=>{});".on"的方式来调用是因为,返回的是一个socket对象,socket对象的使用方法就是采用on的方式。
...
this.stdio = [];
if (i=0; i getValidStdio方法
function getValiStdio(stdio, sync) {
var ipc;
var ipcFd;
if(typeof stdio === 'string') {
stdio = stdioStringToArray(stdio); // 转化为数组 ['pipe', 'pipe', 'pipe'] [输入流、输出流、错误流];
}else if(!Array.isArray(stdio)){
throw new ..... //错误输出
}
}
while(stdio.length < 3)stdio.push(undefined);
stdio = stdio.reduce((acc, stdio, i) => {
if (stdio == null) {
...
};
if(stdio === 'ignore') {
// 传递的值是ignore,输入输出流不会创建,执行这个命令,不会收到反馈,静默方式去执行子进程。
...
}else if(stdio === 'pipe' || typeof stdio === 'number' && stdio < 0) {
// 对不同的管道进行不同的输入设置:
// 输入管道:子进程只能读不能写;
// 输出管道:子进程只能写不能读;
// 从这可以看出是单向的管道,不是双向的
var a = {
tyep:'pipe',
readable: i === 0,
writable: i !== 0
};
if(!sync) {
a.handle = new pipe (PipeConstants.SOCKET); // Pipe = internalBinding('pipe_warp);引入的c++源码;用于创建管道
}
....
// 以上方式在创建输出管道
return {
stdio, // Array;pipe的特性,如上添加的ver a ;输入和输出管道;
ipc, // fork中的双向通信管道,ipc通信;
ipcFd
};
})createSocket
function createSocket (pipe, readable) { // 调用了net下面的Socket方法
return net.Socket({handle: pipe, readable, writable: !readable});
// 这个方法后续会在callback的时候详细详解,和C++中有交互;先看返回结果,一个socket实例、创建了callback函数;
}总结
child.spawn方法的实现
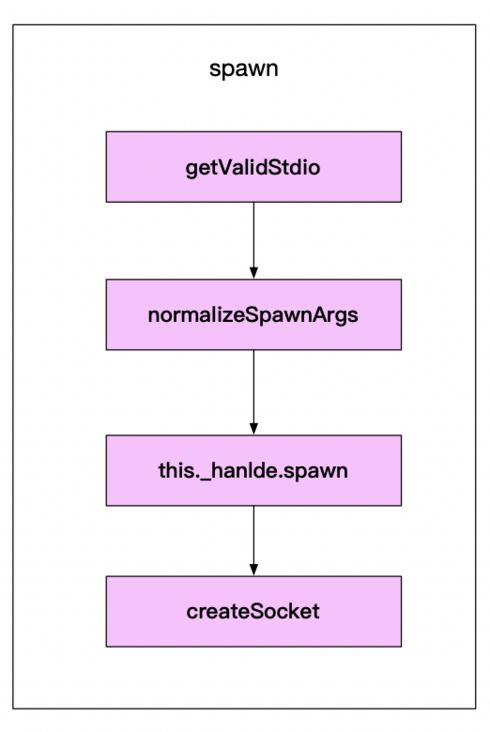
- 通过
getValidStdio来生成pipe(管道)创建管道实例;有三个分别是:输入管道、输出管道、error管道;没有创建socket通信; normalizeSpawnArgs进行参数的校验this._handle.spawn创建子进程- 调用
createSocket方法,将上面创建好的pipe和子进程当中的socket进行绑定;每一个pipe对应一个socket,用于父子进程通信;写入就用写入的pipe,读取就用读取的pipe,有异常存在就用异常的pipe;