POJ-3241 Object Clustering 曼哈顿最小生成树
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3241
题意:平面上有n个点集,现在把他们分成k个集合,使得每个集合中的每个点都至少有一个本集合的点之间的曼哈顿距离不大于X,求最小的X。
题目要求划分集合之后,每个集合的曼哈顿最小生成树的最长边不超过X,那么容易想到就是整个点集的曼哈顿最小生成树的第n-k条边。。
那么主要就是求曼哈顿最小生树的问题了,有O(logn)的算法可以轻松解决建图的问题,主要是利用到了环切的性质,考虑到很多边其实都是没有用的:对于某个点,以他为中心的区域分为8个象限,对于每一个象限,只会取距离最近的一个点连边。。
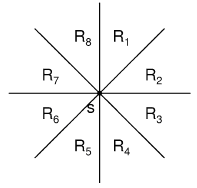
如果这样建立边的话需要建立8次,但是考虑到对称性,实际上我们只要建立4次就够了,R1,R2,R3,R4。再来看看R1和R2区域点集需要满足的条件,
R1:1. x≥xk 2.y-x>yk-xk R2:1.x≥xk 2.y-x<yk-xk
这里只是一个>和<小于的区别,因此我们完全只需要两次就够了。。。
还可以用坐标变化来求,R1:y-x>yk-xk R2:y-x<yk-xk R3:y+x>yk+xk R4:y+x<yk+xk
R1->R2:关于y=x对称,swap(x,y)
R2->R3:考虑到代码的方便性,我们考虑R2->R7,x=-x。
R7->R4:因为上面求的是R2->R7,因此这里还是关于y=x对称。。
然后用个BIT维护就可以了,不要问我BIT是什么Binary Indexed Trees。。
1 //STATUS:C++_AC_79MS_884KB 2 #include <functional> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <iostream> 5 //#include <ext/rope> 6 #include <fstream> 7 #include <sstream> 8 #include <iomanip> 9 #include <numeric> 10 #include <cstring> 11 #include <cassert> 12 #include <cstdio> 13 #include <string> 14 #include <vector> 15 #include <bitset> 16 #include <queue> 17 #include <stack> 18 #include <cmath> 19 #include <ctime> 20 #include <list> 21 #include <set> 22 #include <map> 23 using namespace std; 24 //#pragma comment(linker,"/STACK:102400000,102400000") 25 //using namespace __gnu_cxx; 26 //define 27 #define pii pair<int,int> 28 #define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) 29 #define lson l,mid,rt<<1 30 #define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1 31 #define PI acos(-1.0) 32 //typedef 33 typedef __int64 LL; 34 typedef unsigned __int64 ULL; 35 //const 36 const int N=10010; 37 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 38 const int MOD=100000,STA=8000010; 39 const LL LNF=1LL<<60; 40 const double EPS=1e-8; 41 const double OO=1e15; 42 const int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0}; 43 const int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1}; 44 const int day[13]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 45 //Daily Use ... 46 inline int sign(double x){return (x>EPS)-(x<-EPS);} 47 template<class T> T gcd(T a,T b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;} 48 template<class T> T lcm(T a,T b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;} 49 template<class T> inline T lcm(T a,T b,T d){return a/d*b;} 50 template<class T> inline T Min(T a,T b){return a<b?a:b;} 51 template<class T> inline T Max(T a,T b){return a>b?a:b;} 52 template<class T> inline T Min(T a,T b,T c){return min(min(a, b),c);} 53 template<class T> inline T Max(T a,T b,T c){return max(max(a, b),c);} 54 template<class T> inline T Min(T a,T b,T c,T d){return min(min(a, b),min(c,d));} 55 template<class T> inline T Max(T a,T b,T c,T d){return max(max(a, b),max(c,d));} 56 // 57 58 struct Point{ 59 int x,y,id; 60 bool operator<(const Point p)const{ 61 return x!=p.x?x<p.x:y<p.y; 62 } 63 }p[N]; 64 struct BIT{ 65 int min_val,pos; 66 void init(){ 67 min_val=INF; 68 pos=-1; 69 } 70 }bit[N]; 71 struct Edge{ 72 int u,v,d; 73 bool operator<(const Edge e)const{ 74 return d<e.d; 75 } 76 }e[N<<2]; 77 int T[N],hs[N]; 78 int n,mt,pre[N]; 79 80 void adde(int u,int v,int d) 81 { 82 e[mt].u=u,e[mt].v=v; 83 e[mt++].d=d; 84 } 85 86 int find(int x) 87 { 88 return pre[x]=(x==pre[x]?x:find(pre[x])); 89 } 90 int dist(int i,int j) 91 { 92 return abs(p[i].x-p[j].x)+abs(p[i].y-p[j].y); 93 } 94 95 inline int lowbit(int x) 96 { 97 return x&(-x); 98 } 99 100 void update(int x,int val,int pos) 101 { 102 for(int i=x;i>=1;i-=lowbit(i)) 103 if(val<bit[i].min_val) 104 bit[i].min_val=val,bit[i].pos=pos; 105 } 106 107 int query(int x,int m) 108 { 109 int min_val=INF,pos=-1; 110 for(int i=x;i<=m;i+=lowbit(i)) 111 if(bit[i].min_val<min_val) 112 min_val=bit[i].min_val,pos=bit[i].pos; 113 return pos; 114 } 115 116 int Manhattan_minimum_spanning_tree(int n,Point *p,int K) 117 { 118 int i,w,dir,fa,fb,pos,m; 119 //Build graph 120 mt=0; 121 for(dir=0;dir<4;dir++){ 122 //Coordinate transform - reflect by y=x and reflect by x=0 123 if(dir==1||dir==3){ 124 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 125 swap(p[i].x,p[i].y); 126 } 127 else if(dir==2){ 128 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 129 p[i].x=-p[i].x; 130 } 131 } 132 //Sort points according to x-coordinate 133 sort(p,p+n); 134 //Discretize 135 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 136 T[i]=hs[i]=p[i].y-p[i].x; 137 } 138 sort(hs,hs+n); 139 m=unique(hs,hs+n)-hs; 140 //Initialize BIT 141 for(i=1;i<=m;i++) 142 bit[i].init(); 143 //Find points and add edges 144 for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ 145 pos=lower_bound(hs,hs+m,T[i])-hs+1; //BIT中从1开始' 146 w=query(pos,m); 147 if(w!=-1) 148 adde(p[i].id,p[w].id,dist(i,w)); 149 update(pos,p[i].x+p[i].y,i); 150 } 151 } 152 //Kruskal - 找到第K小的边 153 sort(e,e+mt); 154 for(i=0;i<n;i++)pre[i]=i; 155 for(i=0;i<mt;i++){ 156 fa=find(e[i].u),fb=find(e[i].v); 157 if(fa!=fb){ 158 K--;pre[fa]=fb; 159 if(K==0)return e[i].d; 160 } 161 } 162 } 163 164 int main(){ 165 // freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 166 int i,j,k; 167 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)) 168 { 169 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 170 scanf("%d%d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); 171 p[i].id=i; 172 } 173 printf("%d\n",Manhattan_minimum_spanning_tree(n,p,n-k)); 174 } 175 return 0; 176 }