Introduction to computation
6.00 Introduction to Computer Science
and Programming
• Goal:
–Become skillful at making a computer do what you want it to do
– Learn computational modes of thinking
– Master the art of computational problem solving
What does a computer do?
• Fundamentally a computer:
– Performs calculations
– Remembers the results
• What calculations?
– Built in primitives
– Creating our own methods of calculating
(最关键的事情是如何创造我们自己的计算方法、如何获取计算机一样的思考,也就是计算思维,然后按照这样的方式思考,以便计算机能够提取它)
(计算思维模式意味着一切都可以看做是一个涉及到数字和公式的数学问题。)
Computational problem solving
• What is computation?
– What is knowledge?
– Declarative knowledge(陈述性知识)
• Statements of fact
– Imperative knowledge(程序性知识)
• “how to” methods or recipes
Declarative knowledge
• “The square root of a number x is a number y such that y*y = x”
•Can you use this to find the square root of a particular instance of x?
(答案是不能,所以虽然陈述性知识是许多知识基石,但他不是我们所需要的)
Imperative knowledge
• Here is a “recipe” for deducing a square root
Of a number x – attributed to Heron of
Alexandria in the first century AD
• Start with a guess, called g?
• If g*g is close enough to x, stop and say that g is the answer
• Otherwise make a new guess, by averaging g and x/g ?
• Using this new guess, repeat the process until we get close enough
(这就是程序性知识,寻找东西的方法)
How do we transform a recipe in a mechanical process?
• Build a machine to compute square roots
–Fixed Program Computers(固定程序计算机)
•Calculator
•Atanasoff and Berry’s (1941) computer for systems of linear equations
•Alan Turing’s (1940’s) bombe – decode Enigma codes
• Use a machine that stores and manipulates
Instructions(能存储和操作命令)
– Stored Program Computer
Stored program computer
• Sequence of instructions (program) stored inside computer
– Built from predefined set of primitive instructions
• Arithmetic and logic
• Simple tests
• Moving data
• Special program (interpreter) executes(执行) each
instruction in order
A basic machine architecture
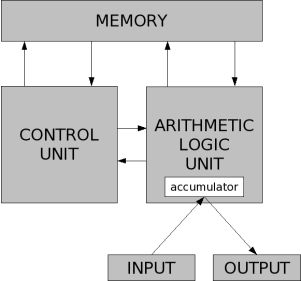 八根箭头代表着什么?
八根箭头代表着什么?
代码在内存中创造一套指令,这里有一个控制单元让我们按照指令顺序来执行,让数据通过ALU再回到内存中,有时还会执行测试指令跳转到代码的其他位置,它会一直不停做这些,直到OUTPUT最后结果。
(Turing showed 6种原语就能计算任何计算,还能写一些代码序列创造新的原语,然后加入原语集中供整个系统使用。原语集是预先设定好的,在ALU中让计算机工作的组件)
Where can things go wrong?
• Syntactic errors(句法的错误)
– Common but easily caught by computer
• Static semantic errors(静态语义错误)
– Some languages check carefully before running,
others check while interpreting the program
– If not caught, behavior of program unpredictable
• Programs don’t have semantic errors, but
meaning may not be what was intended(意思不明确)
– stops running
– Runs forever
– Produces an answer, but not programmer’s intent(意图)
Our goal
• Learn the syntax and semantics of a
programming language
• Learn how to use those elements to translate
“recipes” for solving a problem into a form
that the computer can use to do the work for us
• Computational modes of thought enable us to
use a suite of methods to solve problems