工程(八)——yolov5可见光+红外双模态融合(代码)
目录
一、数据集融合
1.1 直接权重融合
1.2 TIF融合方法
二、结果集融合
2.1 整体代码框架
2.2 标定参数
2.3 选择最优检测框
2.3.1 检测框合并
2.3.2 重复检测框剔除
2.4 结果可视化
2.4.3 单目估计距离
2.4.4 结果参数可视化
三、特征集融合
目标检测的融合方法主要分为三种方式,下面将给出三种方法的思路和相关的代码。融合的前提是传感器的标定,不知道如何标定的小伙伴参见下方链接,本文直接使用标定后的图片。
可见光相机与红外相机标定_OrigamiSun的博客-CSDN博客_红外相机标定
一、数据集融合
工程难度:简单
将可见光和红外图像先融合再传入网络进行训练,网络结构不用改动。融合前需要对可见光相机和红外相机进行参数标定,这样才能进行融合。
1.1 直接权重融合
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
try:
import cv2
except:
import sys
sys.path.remove('/opt/ros/kinetic/lib/python2.7/dist-packages')
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import time
def weight_half_algo(p1_path, p2_path, weight=0.5):
# 两幅图像的加权平均
p1 = cv2.imread(p1_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # 按彩色图像读取
p2 = cv2.imread(p2_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # .astype(np.float)
p1 = p1.astype(np.float) # 转成float类型矩阵
p2 = p2.astype(np.float) # 转成float类型矩阵
p = weight * p1 + (1 - weight) * p2
return p
def flist():
"""
对文件夹下的示例图像批量进行计算。结果写入文件夹 rootdir_Res 中
:return:
"""
rootdir_IR = r'D:\Project\Python\ImageFusion\VIFB-master\input\IR' # 红外图像存放路径
rootdir_VI = r'D:\Project\Python\ImageFusion\VIFB-master\input\VI' # 可见光图像存放路径
rootdir_Res = r'D:\Project\Python\ImageFusion\VIFB-master\Res' # TIF算法处理后的图像存放路径
rootdir_Res_weight = r'D:\Project\Python\ImageFusion\VIFB-master\Res_weight' # 平均加权算法处理后的图像存放路径
fflist = os.listdir(rootdir_IR) # 列出文件夹下所有的目录与文件
# print(fflist)
for i in range(0, len(fflist)):
path1 = os.path.join(rootdir_IR, fflist[i])
path2 = os.path.join(rootdir_VI, fflist[i])
if os.path.isfile(path1) and os.path.isfile(path2):
p = weight_half_algo(path1, path2) # 采用两者平均加权的方法进行融合
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(rootdir_Res_weight, fflist[i]), p)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 程序开始时的时间
time_start = time.time()
# 1 图表示可见光;2 图表示红外
flist()
time_end = time.time()
#cv2.imwrite('./final_res.jpg', p)
print('程序运行花费时间', time_end - time_start)直接自己设置权重,权重为定值,融合效果有限
1.2 TIF融合方法
TIF算法是将图像分成基础层和细节层,之后再按加权相加。基础层,就是将图像进行均值滤波(文中用的是35),均值滤波后的图像就是基础层,原图减去基础层就是细节层。基础层的权重是0.5,细节层的权重按公式计算,是动态的。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
try:
import cv2
except:
import sys
sys.path.remove('/opt/ros/kinetic/lib/python2.7/dist-packages')
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import time
def TIF_algo(p1, p2, median_blur_value=3, mean_blur_value=35):
"""
通过TIF方法融合图像
:param p1_path: 图像1路径
:param p2_path: 图像2路径
:param median_blur_value: 中值滤波参数
:param mean_blur_value: 均值滤波参数
:return: 融合图像
"""
# median_blur_value = 3 # 中值滤波系数
# mean_blur_value = 35 # 均值滤波系数
# 均值滤波后(35,35)的图层,即基础层
p1_b = cv2.blur(p1, (mean_blur_value, mean_blur_value))
p1_b = p1_b.astype(np.float) # 转成float类型矩阵
p2_b = cv2.blur(p2, (mean_blur_value, mean_blur_value))
p2_b = p2_b.astype(np.float) # 转成float类型矩阵
# cv2.imshow('picture after mean blur p1_b', p1_b)
# cv2.imshow('picture after mean blur p2_b', p2_b)
# 均值滤波后的细节层
# p1_d = abs(p1.astype(np.float) - p1_b)
# p2_d = abs(p2.astype(np.float) - p2_b)
p1_d = p1.astype(np.float) - p1_b
p2_d = p2.astype(np.float) - p2_b
# cv2.imshow('detail layer p1', p1_d / 255.0)
# cv2.imshow('detail layer p2', p2_d / 255.0)
# 原图经过中值滤波后的图层
p1_after_medianblur = cv2.medianBlur(p1, median_blur_value)
p2_after_medianblur = cv2.medianBlur(p2, median_blur_value)
# 矩阵转换,换成float型,参与后面计算
p1_after_medianblur = p1_after_medianblur.astype(np.float)
p2_after_medianblur = p2_after_medianblur.astype(np.float)
# 计算均值和中值滤波后的误差
p1_subtract_from_median_mean = p1_after_medianblur - p1_b + 0.01 # 加0.01 保证结果非NAN
p2_subtract_from_median_mean = p2_after_medianblur - p2_b + 0.01
# cv2.imshow('subtract_from_median_mean p1_subtract_from_median_mean', p1_subtract_from_median_mean/255.0)
# cv2.imshow('subtract_from_median_mean p2_subtract_from_median_mean', p2_subtract_from_median_mean/255.0)
m1 = p1_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 0]
m2 = p1_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 1]
m3 = p1_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 2]
res = m1 * m1 + m2 * m2 + m3 * m3
# delta1 = np.sqrt(res)
delta1 = res
m1 = p2_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 0]
m2 = p2_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 1]
m3 = p2_subtract_from_median_mean[:, :, 2]
res = m1 * m1 + m2 * m2 + m3 * m3
# delta2 = np.sqrt(res) #采用平方和开根号做权重计算
# delta2 = res #采用平方和做权重计算
delta2 = abs(m1) # 由于图像2 红外图像是灰度图像,直接用像素差做权重计算
delta_total = delta1 + delta2 # 分母
psi_1 = delta1 / delta_total
psi_2 = delta2 / delta_total
psi1 = np.zeros(p1.shape, dtype=np.float)
psi2 = np.zeros(p2.shape, dtype=np.float)
psi1[:, :, 0] = psi_1
psi1[:, :, 1] = psi_1
psi1[:, :, 2] = psi_1
psi2[:, :, 0] = psi_2
psi2[:, :, 1] = psi_2
psi2[:, :, 2] = psi_2
# 基础层融合
p_b = 0.5 * (p1_b + p2_b)
# 细节层融合
p_d = psi1 * p1_d + psi2 * p2_d
# 整体融合
p = p_b + p_d
return p
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 程序开始时的时间
time_start = time.time()
# 1 图表示可见光;2 图表示红外
#flist()
p1_path = './rgb/000000.jpg' # 可见光图像
p1 = cv2.imread(p1_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)#.astype(np.float)
p2_path = './t/000000.jpg' # 红外图像
p2 = cv2.imread(p2_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)#.astype(np.float)
p = TIF_algo(p1, p2)
time_end = time.time()
cv2.imwrite('./dy_weight/000000.jpg', p)
print('程序运行花费时间', time_end - time_start)可以看到融合的图片细节更加清楚 。
将融合后的图像传入神经网络进行训练。
二、结果集融合
工程难度:中等
单独训练两个网络,得到两个权重。将detect改成ros节点,对应两个callback分别加载加载两个模型权重进行检测,得到结果进行融合,选择结果最好的。
2.1 整体代码框架
可以看到双模态的主要更改有
1、两个检测器
2、怎么选择最优目标
3、结果的可视化
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import rospy
import numpy as np
import time
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import threading
import argparse
from std_msgs.msg import Header
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
try:
import cv2
except ImportError:
import sys
sys.path.remove('/opt/ros/kinetic/lib/python2.7/dist-packages')
import cv2
from yolov5_detector import Yolov5Detector, draw_predictions
from mono_estimator import MonoEstimator
from functions import get_stamp, publish_image
from functions import display, print_info
from functions import simplified_nms
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Demo script for dual modal peception')
parser.add_argument('--print', action='store_true',
help='Whether to print and record infos.')
parser.add_argument('--sub_image1', default='/pub_rgb', type=str,
help='The image topic to subscribe.')
parser.add_argument('--sub_image2', default='/pub_t', type=str,
help='The image topic to subscribe.')
parser.add_argument('--pub_image', default='/result', type=str,
help='The image topic to publish.')
parser.add_argument('--calib_file', default='../conf/calibration_image.yaml', type=str,
help='The calibration file of the camera.')
parser.add_argument('--modality', default='RGBT', type=str,
help='The modality to use. This should be `RGB`, `T` or `RGBT`.')
parser.add_argument('--indoor', action='store_true',
help='Whether to use INDOOR detection mode.')
parser.add_argument('--frame_rate', default=10, type=int,
help='Working frequency.')
parser.add_argument('--display', action='store_true',
help='Whether to display and save all videos.')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 在线程函数执行前,“抢占”该锁,执行完成后,“释放”该锁,则我们确保了每次只有一个线程占有该锁。这也是为什么能让RGB和T匹配的原因
image1_lock = threading.Lock() #创建锁
image2_lock = threading.Lock()
#3.1 获取RGB图像的时间戳和格式转化
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
def image1_callback(image):
global image1_stamp, image1_frame #多线程是共享资源的,使用全局变量
image1_lock.acquire() #锁定锁
image1_stamp = get_stamp(image.header) #获得时间戳
image1_frame = np.frombuffer(image.data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(image.height, image.width, -1)#图片格式转化
image1_lock.release() #释放
#3.2 获取红外图像的时间戳和格式转化
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
def image2_callback(image):
global image2_stamp, image2_frame
image2_lock.acquire()
image2_stamp = get_stamp(image.header)
image2_frame = np.frombuffer(image.data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(image.height, image.width, -1)
image2_lock.release()
#5.1 获取红外图像的时间戳和格式转化
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
def timer_callback(event):
#获得RGB的时间戳和图片
global image1_stamp, image1_frame
image1_lock.acquire()
cur_stamp1 = image1_stamp
cur_frame1 = image1_frame.copy()
image1_lock.release()
#获得T的时间戳和图片
global image2_stamp, image2_frame
image2_lock.acquire()
cur_stamp2 = image2_stamp
cur_frame2 = image2_frame.copy()
image2_lock.release()
global frame
frame += 1
start = time.time()
# 5.2获得预测结果
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
if args.indoor: #使用yolov5本身权重
labels, scores, boxes = detector.run(
cur_frame1, conf_thres=0.50, classes=[0]
) # person
else:
if args.modality.lower() == 'rgb': #用RGB图像权重
labels, scores, boxes = detector1.run(
cur_frame1, conf_thres=0.50, classes=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
) # pedestrian, cyclist, car, bus, truck
elif args.modality.lower() == 't': #用T图像权重
labels, scores, boxes = detector2.run(
cur_frame2, conf_thres=0.50, classes=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
) # pedestrian, cyclist, car, bus, truck
elif args.modality.lower() == 'rgbt': #双模态都用
#获取RGB的预测结果 类别、置信分数、检测框
labels1, scores1, boxes1 = detector1.run(
cur_frame1, conf_thres=0.50, classes=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
) # pedestrian, cyclist, car, bus, truck
#print("rgb",labels1, scores1, boxes1)
#获取T的预测结果
labels2, scores2, boxes2 = detector2.run(
cur_frame2, conf_thres=0.50, classes=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
) # pedestrian, cyclist, car, bus, truck
#print("T",labels2, scores2, boxes2)
# 确定最终结果
labels = labels1 + labels2 #合并类别数组
#print("labels",labels)
scores = scores1 + scores2 #合并分数数组
#print("scores",scores)
if boxes1.shape[0] > 0 and boxes2.shape[0] > 0: #如果可见光和红外都检测到目标
boxes = np.concatenate([boxes1, boxes2], axis=0) #链接两个检测框
#print("boxes",boxes)
# 排除重复的目标框
indices = simplified_nms(boxes, scores)
labels, scores, boxes = np.array(labels)[indices], np.array(scores)[indices], boxes[indices]
#print("result",labels, scores, boxes)
elif boxes1.shape[0] > 0: #如果只有可见光检测到
boxes = boxes1
#print("boxes",boxes)
elif boxes2.shape[0] > 0: #如果只有红外检测到
boxes = boxes2
#print("boxes",boxes)
else: #都没检测到
boxes = np.array([])
#print("boxes",boxes)
else:
raise ValueError("The modality must be 'RGB', 'T' or 'RGBT'.")
labels_temp = labels.copy()
labels = []
for i in labels_temp:
labels.append(i if i not in ['pedestrian', 'cyclist'] else 'person')
print("boxes",boxes)
# 5.3单目估计距离
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
locations = mono.estimate(boxes)#获得目标框的世界坐标系
print("locations",locations)
indices = [i for i in range(len(locations)) if locations[i][1] > 0 and locations[i][1] < 200]
labels, scores, boxes, locations = \
np.array(labels)[indices], np.array(scores)[indices], boxes[indices], np.array(locations)[indices]
distances = [(loc[0] ** 2 + loc[1] ** 2) ** 0.5 for loc in locations] #估计距离
print("distances",distances)
cur_frame1 = cur_frame1[:, :, ::-1].copy() # to BGR
cur_frame2 = cur_frame2[:, :, ::-1].copy() # to BGR
# 5.4画检测框
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
for i in reversed(np.argsort(distances)):#reversed()函数用于对可迭代对象中的元素进行反向排列
cur_frame1 = draw_predictions(
cur_frame1, str(labels[i]), float(scores[i]), boxes[i], location=locations[i]
)
cur_frame2 = draw_predictions(
cur_frame2, str(labels[i]), float(scores[i]), boxes[i], location=locations[i]
)
# 5.5发布图像
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
result_frame = np.concatenate([cur_frame1, cur_frame2], axis=1) #合并图像
if args.display:
if not display(result_frame, v_writer, win_name='result'):
print("\nReceived the shutdown signal.\n")
rospy.signal_shutdown("Everything is over now.")
result_frame = result_frame[:, :, ::-1] # to RGB
publish_image(pub, result_frame)
delay = round(time.time() - start, 3)
if args.print:
print_info(frame, cur_stamp1, delay, labels, scores, boxes, locations, file_name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 初始化节点
rospy.init_node("dual_modal_perception", anonymous=True, disable_signals=True)
frame = 0
# 一、加载标定参数
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
if not os.path.exists(args.calib_file):
raise ValueError("%s Not Found" % (args.calib_file))
mono = MonoEstimator(args.calib_file, print_info=args.print)
# 二、初始化Yolov5Detector
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
if args.indoor:
detector = Yolov5Detector(weights='weights/coco/yolov5s.pt')
else:
if args.modality.lower() == 'rgb':
detector1 = Yolov5Detector(weights='weights/seumm_visible/yolov5s_100ep_pretrained.pt')
elif args.modality.lower() == 't':
detector2 = Yolov5Detector(weights='weights/seumm_lwir/yolov5s_100ep_pretrained.pt')
elif args.modality.lower() == 'rgbt': #双模态
detector1 = Yolov5Detector(weights='weights/yolov5s.pt')
detector2 = Yolov5Detector(weights='weights/yolov5s.pt')
else:
raise ValueError("The modality must be 'RGB', 'T' or 'RGBT'.")
# 三、进入回调函数
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
# 准备图像序列
image1_stamp, image1_frame = None, None
image2_stamp, image2_frame = None, None
#rgb回调函数
rospy.Subscriber(args.sub_image1, Image, image1_callback, queue_size=1,
buff_size=52428800)
#红外回调函数
rospy.Subscriber(args.sub_image2, Image, image2_callback, queue_size=1,
buff_size=52428800)
# 等待RGB和t图像都获得再进行下一次循环
while image1_frame is None or image2_frame is None:
time.sleep(0.1)
print('Waiting for topic %s and %s...' % (args.sub_image1, args.sub_image2))
print(' Done.\n')
# 四、功能选择
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
#如果在命令行中输入 python3 demo_dual_modal.py --print 则会运行下面代码
# 是否记录时间戳和检测结果
if args.print:
file_name = 'result.txt'
with open(file_name, 'w') as fob:
fob.seek(0)
fob.truncate()
# 是否保存视频
if args.display:
assert image1_frame.shape == image2_frame.shape, \
'image1_frame.shape must be equal to image2_frame.shape.'
win_h, win_w = image1_frame.shape[0], image1_frame.shape[1] * 2
v_path = 'result.mp4'
v_format = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v")
v_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(v_path, v_format, args.frame_rate, (win_w, win_h), True)
# 五、预测结果与发布
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
# 启动定时检测线程
pub = rospy.Publisher(args.pub_image, Image, queue_size=1)
rospy.Timer(rospy.Duration(1 / args.frame_rate), timer_callback) #每frame_rate 秒调用一次timer_callback
# 与C++的spin不同,rospy.spin()的作用是当节点停止时让python程序退出
rospy.spin()
2.2 标定参数
要进行单目距离估计,引入相机标定参数,calibration_image.yaml 文件内容如下。
%YAML:1.0
---
ProjectionMat: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 4
dt: d
data: [859, 0, 339, 0, 0, 864, 212, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]
Height: 2.0 # the height of the camera (meter)
DepressionAngle: 0.0 # the depression angle of the camera (degree)2.3 选择最优检测框
2.3.1 检测框合并
想要选择最优检测框,首先要将所有框合并,一共四种情况,两路都检测到,各只有一路检测到,都没检测到
1、可见光和红外都检测到
# 可见光和红外检测出来的东西
rgb ['person'] [0.74] [[ 354 245 379 329]]
T ['person', 'person'] [0.77, 0.54] [[ 353 241 379 327]
[ 114 249 128 292]]
# 合并后的数组
labels ['person', 'person', 'person']
scores [0.74, 0.77, 0.54]
boxes [[ 354 245 379 329]
[ 353 241 379 327]
[ 114 249 128 292]]
2、只有可见光检测到
#各检测结果
rgb ['person'] [0.72] [[ 357 245 382 330]]
T [] [] []
# 合并
labels ['person']
scores [0.72]
boxes [[ 357 245 382 330]]
3、只有红外检测到
#各检测结果
rgb [] [] []
T ['person'] [0.72] [[ 357 245 382 330]]
# 合并
labels ['person']
scores [0.72]
boxes [[ 357 245 382 330]]
4、都没检测到
#各检测结果
rgb [] [] []
T [] [] []
# 合并
labels []
scores []
boxes [[]]2.3.2 重复检测框剔除
针对第一种情况,会出现同一目标同时被可见光和红外都检测到,那么到底用哪个检测框来表示是一个选择问题。
首先看一下效果,通过检测框坐标知道第1个person和第3个person是同一个目标,算法排除了第2个person目标,那么怎么选择最好的检测框呢?
NMS 把置信度(预测这个网格里是否有目标的置信度)最高的那个网格的边界箱作为极大边界箱,计算极大边界箱和其他几个网格的边界箱的IOU,如果超过一个阈值,例如0.5,就认为这两个网格实际上预测的是同一个物体,就把其中置信度比较小的删除。
#1、检测
rgb ['person', 'person'] [0.82, 0.6] [[ 373 244 401 333]
[ 110 259 123 299]]
T ['person'] [0.67] [[ 372 248 400 331]]
#2、合并
labels ['person', 'person', 'person']
scores [0.82, 0.6, 0.67]
boxes [[ 373 244 401 333]
[ 110 259 123 299]
[ 372 248 400 331]]
#3、选择
result ['person' 'person'] [ 0.82 0.6] [[ 373 244 401 333] [ 110 259 123 299]]
- 算法代码如下
def simplified_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres=0.5): #排除重复目标
'''
Args:
boxes: (n, 4), xyxy format
scores: list(float)
Returns:
indices: list(int), indices to keep
'''
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3] #获得每个检测框的对角坐标
area = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1) #所有检测框面积
#argsort()函数是将x中的元素从小到大排列,提取其对应的index(索引),使用[::-1],可以建立X从大到小的索引。
#1、置信度排序
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
idx = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] #置信度由大到小的索引排序
print("idx",idx)
indices = []
#2、循环数组筛选
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
while len(idx) > 0:
i = idx[0] #取最大置信度的索引
indices.append(i) #将这个索引放入indices中
print('indices',indices)
if len(idx) == 1: #如果就一个检测框
break
idx = idx[1:] #意思是去掉列表中第一个元素,对后面的元素进行操作
print('idx[1:]',idx)
#3、与最大置信度框的重合度来判断是否是重复检测框
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
xx1 = np.clip(x1[idx], a_min=x1[i], a_max=np.inf) #截取数组中小于或者大于某值的部分 np.inf表示无穷大
yy1 = np.clip(y1[idx], a_min=y1[i], a_max=np.inf)
xx2 = np.clip(x2[idx], a_min=0, a_max=x2[i])
yy2 = np.clip(y2[idx], a_min=0, a_max=y2[i])
w, h = np.clip((xx2 - xx1), a_min=0, a_max=np.inf), np.clip((yy2 - yy1), a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
inter = w * h
union = area[i] + area[idx] - inter
iou = inter / union #计算iou 越大越好最大为1
print('iou',iou)
#4、将重合度小的即不同目标保存到idx再次循环
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
idx = idx[iou < iou_thres] #框重合度小视为不同目标
print("idx",idx)
return indices #返回合并后的索引- 变量输出如下
重复目标
#1、检测
rgb ['person'] [0.81] [[ 365 248 392 332]]
T ['person'] [0.82] [[ 364 243 392 329]]
#2、合并
labels ['person', 'person']
scores [0.81, 0.82]
boxes [[ 365 248 392 332]
[ 364 243 392 329]]
#3、置信度排序选择
idx [1 0]
indices [1]
#4、对剩下的目标与置信度最大的目标进行iou计算,来判断是否是同一目标
idx[1:] [0]
iou [ 0.87867] #iou为0.87 高度重合,所以是同一目标
idx [] #没有待选目标了,循环结束
不重复目标
# 1、检测
rgb ['person'] [0.78] [[ 363 246 390 329]]
T ['person', 'person'] [0.84, 0.52] [[ 362 245 391 332]
[ 113 250 135 295]]
# 2、合并
labels ['person', 'person', 'person']
scores [0.78, 0.84, 0.52]
boxes [[ 363 246 390 329]
[ 362 245 391 332]
[ 113 250 135 295]]
# 3、排序
idx [1 0 2]
indices [1]
# 4、计算iou排除重复目标
idx[1:] [0 2]
iou [ 0.88823 0] #0表示不重合,为不同的目标,对应索引保存到indices
idx [2]
indices [1, 2]
result ['person' 'person'] [ 0.84 0.52] [[ 362 245 391 332]
[ 113 250 135 295]]
2.4 结果可视化
2.4.3 单目估计距离
# 5.3单目估计距离
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
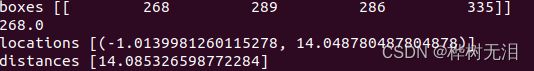
locations = mono.estimate(boxes)#获得目标框的世界坐标系
print("locations",locations)
indices = [i for i in range(len(locations)) if locations[i][1] > 0 and locations[i][1] < 200]
labels, scores, boxes, locations = \
np.array(labels)[indices], np.array(scores)[indices], boxes[indices], np.array(locations)[indices]
distances = [(loc[0] ** 2 + loc[1] ** 2) ** 0.5 for loc in locations] #估计距离
print("distances",distances)
cur_frame1 = cur_frame1[:, :, ::-1].copy() # to BGR
cur_frame2 = cur_frame2[:, :, ::-1].copy() # to BGR单目估计距离算法的代码如下
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import math
import cv2
from math import sin, cos
class MonoEstimator():
def __init__(self, file_path, print_info=True):
fs = cv2.FileStorage(file_path, cv2.FileStorage_READ)
mat = fs.getNode('ProjectionMat').mat()
self.fx = int(mat[0, 0])
self.fy = int(mat[1, 1])
self.u0 = int(mat[0, 2])
self.v0 = int(mat[1, 2])
self.height = fs.getNode('Height').real()
self.depression = fs.getNode('DepressionAngle').real() * math.pi / 180.0
if print_info:
print('Calibration of camera:')
print(' Parameters: fx(%d) fy(%d) u0(%d) v0(%d)' % (self.fx, self.fy, self.u0, self.v0))
print(' Height: %.2fm' % self.height)
print(' DepressionAngle: %.2frad' % self.depression)
print()
def uv_to_xyz(self, u, v):
# Compute (x, y, z) coordinates in the real world, according to (u, v) coordinates in the image.
# X axis - on the right side of the camera
# Z axis - in front of the camera
u = int(u)
v = int(v)
fx, fy = self.fx, self.fy
u0, v0 = self.u0, self.v0
h = self.height
t = self.depression
denominator = fy * sin(t) + (v - v0) * cos(t)
if denominator != 0:
z = (h * fy * cos(t) - h * (v - v0) * sin(t)) / denominator
if z > 1000: z = 1000
else:
z = 1000
x = (z * (u - u0) * cos(t) + h * (u - u0) * sin(t)) / fx
y = h
return x, y, z
def estimate(self, boxes):#单目估计距离
locations = []
if boxes.shape[0] > 0: #判断目标个数是否大于1
for box in boxes:
print(box[0])
u, v = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2, box[3]
x, y, z = self.uv_to_xyz(u, v)
locations.append((x, z))
return locationslocations是世界坐标系的xy坐标,distances是距离
2.4.4 结果参数可视化
# 5.4画检测框
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
for i in reversed(np.argsort(distances)):#reversed()函数用于对可迭代对象中的元素进行反向排列
cur_frame1 = draw_predictions(
cur_frame1, str(labels[i]), float(scores[i]), boxes[i], location=locations[i] #两个图像上的数据显示一样
)
cur_frame2 = draw_predictions(
cur_frame2, str(labels[i]), float(scores[i]), boxes[i], location=locations[i]
)
# 5.5发布图像
#×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
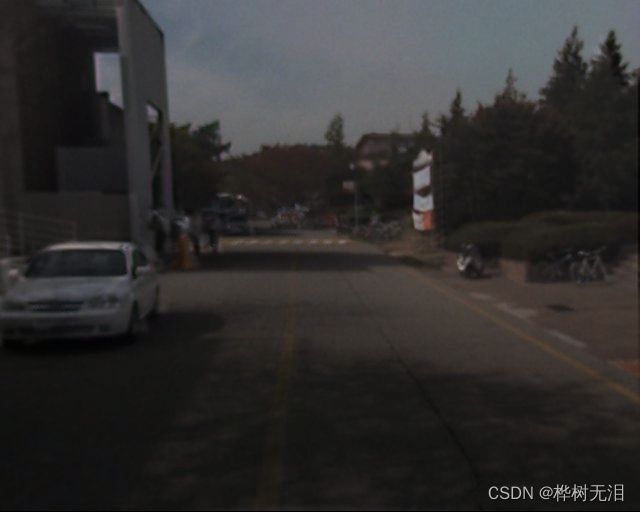
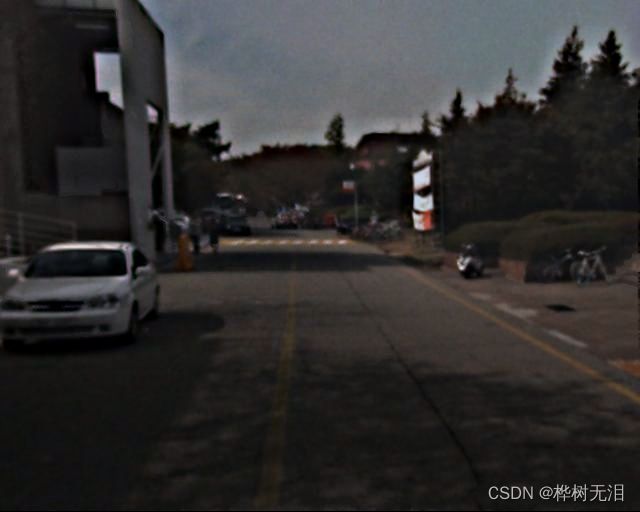
result_frame = np.concatenate([cur_frame1, cur_frame2], axis=1) #合并图像最后的效果如下
三、特征集融合
工程难度:困难
同时训练可见光和红外图片,需要改动网络的结构,对每层的特征进行融合。
同时需要对图片质量进行评价,给出自适应的融合权重。
3.1 双模态数据集制作
yaml文件配置
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
train1: /home/cxl/dual_yolo/dual_model_conv_yolov5/modules/yolov5-test/data/dual_data/train1/
train2: /home/cxl/dual_yolo/dual_model_conv_yolov5/modules/yolov5-test/data/dual_data/train2/
val: /home/cxl/dual_yolo/dual_model_conv_yolov5/modules/yolov5-test/data/dual_data/label/
# Classes
nc: 7 # number of classes
names: ['pedestrian','cyclist','car','bus','truck','traffic_light','traffic_sign'] # class names3.2 train.py修改
加载两个数据集