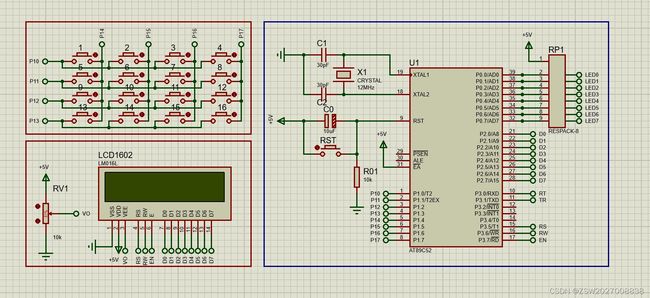
基于51单片机的矩阵键盘_Matrixkey---线反转法
1.矩阵键盘简介
矩阵键盘使用的方法与独立按键类似,但是比独立按键节省I/O,同时使用方法变得相对复杂了,首先展示硬件连接。
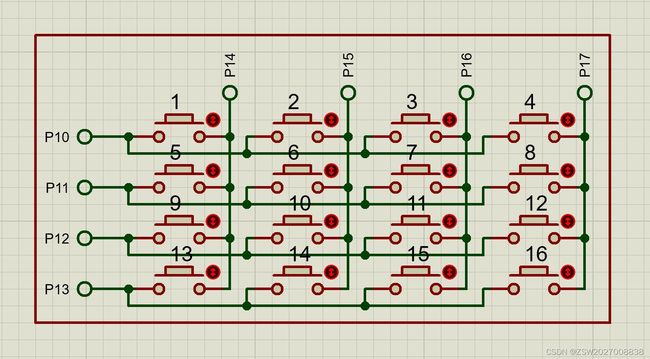
上图所示就是4X4矩阵键盘的常见接法,按行来看,每个按键的左端接在一起,按列来看,每个按键的右端接在一起,共占用8个I/O,接到51单片机的P1端口。
2.代码解释
对于矩阵键盘,常用的方法有两种,一个是线反转法,另一个是行列扫描法,本文介绍线反转法。首先插入模块化编程编程的内容,新建两个文件命名为keyboard.h与keyboard.c并添加到工程中,然后在h文件中定义一个宏,便于与硬件连接发生改变时而进行代码的修改。编程思路,首先给矩阵键盘的端口Matrixkey_Port赋值0x0F,意为行为1列为0,即0000 1111,对应上图就是P10,P11,P12,P13为1,P14,P15,P16,P17为0,那么此时如果第一行有按键按下,P10这一位的高电平必然被拉低,1 & 0 = 0,P1就会变成0X0E,第二,三,四行亦如此,然后进行反推,当检测到这些值的出现时就可以知道是哪一行有按键按下,记录下行值,row就是行值,再给矩阵键盘的端口Matrixkey_Port赋值0xF0,意为行为0列为1,即1111 0000,对应上图就是P10,P11,P12,P13为0,P14,P15,P16,P17为1,与第一次反推类似,可以得到列值col,在下文的程序中,只要将row,col进行运算就能得到1-16的返回值。row的值是1 2 3 4,col的值是1 2 3 4,而键盘编码如下:
/1 2 3 4/
/5 6 7 8/
/9 10 11 12/
/13 14 15 16/
显然,返回值1-16与行列的关系是(row-1)*4+col。
keyboard.h
#ifndef __KEYBOARD_H__
#define __KEYBOARD_H__
#define Matrixkey_Port P1
unsigned char Matrixkey_Scan(void);
#endif
keyboard.h
#include 3.完整工程
本次工程包含的文件如下:
main.c
#include delay.h
#ifndef __DELAY_H__
#define __DELAY_H__
//延时100us
void Delay_100us();
//x=1时,大约延时50us
void Delay_50xus(unsigned int x);
//x=1时,大约延时1ms
void Delay_xms(unsigned int x);
#endif
delay.c
#include "delay.h"
#include lcd1602.h
#ifndef __LCD1602_H__
#define __LCD1602_H__
//LCD1602写命令函数
void LCD1602_W_Cmd(unsigned char cmd);
//LCD1602写数据函数
void LCD1602_W_Dat(unsigned char dat);
//判忙函数,最高位位1即为忙
void LCD1602_BusyCheck();
//LCD1602初始化函数
void LCD1602_Init();
//LCD1602在指定位置显示字符hang:0-1,lie:0-15
void LCD1602_Dis_char(unsigned char hang,unsigned char lie,unsigned char ch);
//LCD1602在指定位置显示两位数据,比如20
void LCD1602_Dis_dat(unsigned char hang,unsigned char lie,unsigned char dat);
//LCD1602在指定位置显示字符串
void LCD1602_Dis_string(unsigned char hang,unsigned char lie,unsigned char *str);
#endif
lcd1602.c
#include