面试题:深拷贝、浅拷贝、引用拷贝的区别
文章目录
-
- 引用拷贝
- 浅拷贝
- 深拷贝
- 小结
作者:小牛呼噜噜 | https://xiaoniuhululu.com
计算机内功、JAVA底层、面试相关资料等更多精彩文章在公众号「小牛呼噜噜 」
引用拷贝
引用拷贝: 引用拷贝不会在堆上创建一个新的对象,只 会在栈上生成一个新的引用地址,最终指向依然是堆上的同一个对象。
//实体类
public class Person{
public String name;//姓名
public int height;//身高
public StringBuilder something;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public StringBuilder getSomething() {
return something;
}
public void setSomething(StringBuilder something) {
this.something = something;
}
public Person(String name, int height, StringBuilder something) {
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
this.something = something;
}
}
//测试类
public class copyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("小张", 180, new StringBuilder("今天天气很好"));
Person p2 = p1;
System.out.println("对象是否相等:"+ (p1 == p2));
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
// change
p1.name="小王";
p1.height = 200;
p1.something.append(",适合出去玩");
System.out.println("...after p1 change....");
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
}
}
结果:
对象是否相等:true
p1 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
p2 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
…after p1 change…
p1 属性值=小王,200,今天天气很好,适合出去玩
p2 属性值=小王,200,今天天气很好,适合出去玩
before change:
after change:
我们可以看出 由于2个引用p1,p2 都是指向堆中同一个对象,所以2个对象是相等的,修改了对象p1,会影响到对象p2
需要注意的
- name属性,虽然她是引用类型,但她同时也是String类型,不可变,对其修改,JVM会默认在堆上创建新的内存空间,再重新赋值
int weight=180;是成员变量,存放在堆中,不是所有的基本类型变量 都存放在JVM栈中
注意与这篇文章得区分开来 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6qRspyLAsoBxttGwGtxsAA, int num1 = 10;是基本类型的局部变量,存放在栈中
浅拷贝
浅拷贝 :浅拷贝会在堆上创建一个新的对象,新对象和原对象不等,但是新对象的属性和老对象相同。
其中:
- 如果属性是基本类型(int,double,long,boolean等),拷贝的就是基本类型的值。
- 如果属性是引用类型(除了基本类型都是引用类型),拷贝的就是引⽤数据类型变量的地址值,⽽对于引⽤类型变量指向的堆中的对象不会拷贝。
如何实现浅拷贝呢?也很简单,就是在需要拷贝的类上实现Cloneable接口并重写其clone()方法。
@Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
在使用的时候直接调用类的clone()方法即可
//实体类 继承Cloneable
public class Person implements Cloneable{
public String name;//姓名
public int height;//身高
public StringBuilder something;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public StringBuilder getSomething() {
return something;
}
public void setSomething(StringBuilder something) {
this.something = something;
}
public Person(String name, int height, StringBuilder something) {
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
this.something = something;
}
@Override
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Person) super.clone();
}
}
//测试类
public class shallowCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p1 = new Person("小张", 180, new StringBuilder("今天天气很好"));
Person p2 = p1.clone();
System.out.println("对象是否相等:"+ (p1 == p2));
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
// change
p1.setName("小王");
p1.setHeight(200);
p1.getSomething().append(",适合出去玩");
System.out.println("...after p1 change....");
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
}
}
结果:
对象是否相等:false
p1 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
p2 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
…after p1 change…
p1 属性值=小王,200,今天天气很好,适合出去玩
p2 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好,适合出去玩
before change:
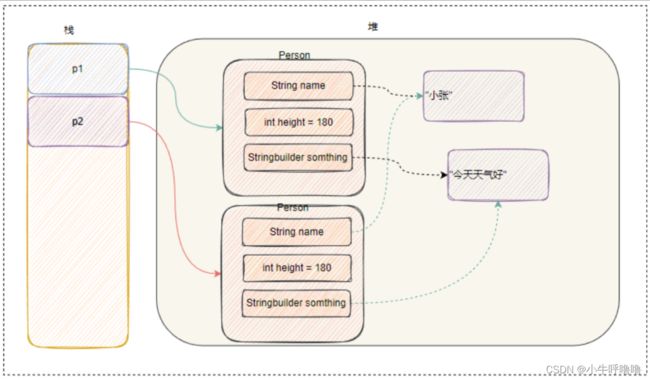
after change:
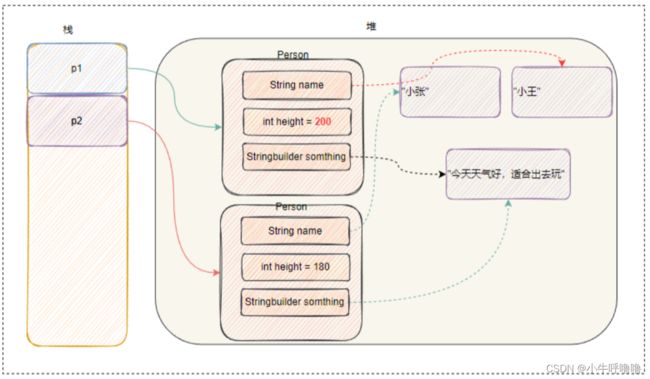
我们可以看出:
- 当我们修改对象p1的weight属性时,由于p2的height属性 是直接复制修改前的p1的height属性,所以还是180。
- 当我们修改对象p1的name属性 时,String name指向一个新的内存空间,但对象p2的name还是指向旧的内存空间,所以对象p2的name属性还是"小张"。
- 由于对象p1的something属性和对象p2的something属性指向是同一个内存空间,当我们修改对象p1的something属性,会影响到对象p2的something属性,所以对象p2的something属性变为"今天天气很好,适合出去玩"。
深拷贝
深拷贝 :完全拷贝⼀个对象,在堆上创建一个新的对象,拷贝被拷贝对象的成员变量的值,同时堆中的对象也会拷贝。
需要重写clone方法
@Override
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//return (Person) super.clone();
Person person = (Person) super.clone();
person.setSomething( new StringBuilder(person.getSomething()));//单独为引用类型clone
return person;
}
shallowCopyTest测试类的结果:
对象是否相等:false
p1 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
p2 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
…after p1 change…
p1 属性值=小王,200,今天天气很好,适合出去玩
p2 属性值=小张,180,今天天气很好
这时候对象p1和对象p2互不干扰了
before change:
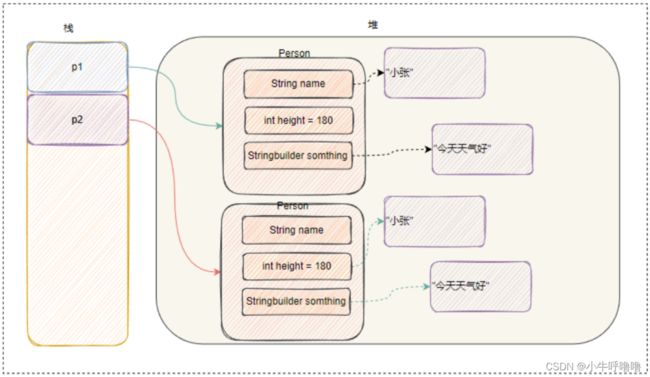
after change:
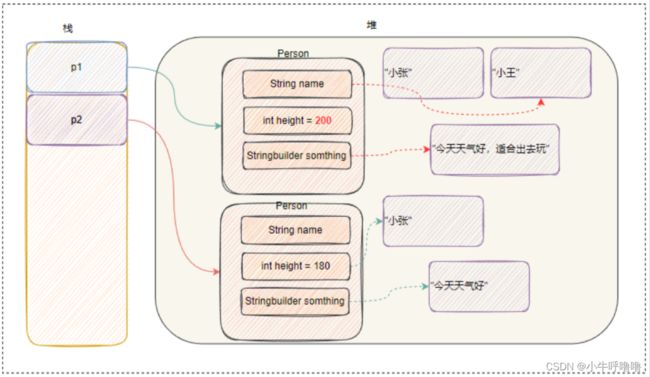
但这样也有个小问题,对象每有一个引用类型,我们都得重写其clone方法,这样会非常麻烦,因此我们还可以借助序列化来实现对象的深拷贝
//实体类 继承Cloneable
public class Person implements Serializable{
public String name;//姓名
public int height;//身高
public StringBuilder something;
...//省略 getter setter
public Object deepClone() throws Exception{
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
// 反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
//测试类,这边类名笔者就不换了,在之前的基础上改改
public class shallowCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Person p1 = new Person("小张", 180, new StringBuilder("今天天气很好"));
Person p2 = (Person)p1.deepClone();
System.out.println("对象是否相等:"+ (p1 == p2));
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
// change
p1.setName("小王");
p1.setHeight(200);
p1.getSomething().append(",适合出去玩");
System.out.println("...after p1 change....");
System.out.println("p1 属性值=" + p1.getName()+ ","+ p1.getHeight() + ","+ p1.getSomething());
System.out.println("p2 属性值=" + p2.getName()+ ","+ p2.getHeight() + ","+ p2.getSomething());
}
}
这样也会得到深拷贝的结果
小结
- 引用拷贝: 引用拷贝不会在堆上创建一个新的对象,只 会在栈上生成一个新的引用地址,最终指向依然是堆上的同一个对象。
- 浅拷贝 :浅拷贝会在堆上创建一个新的对象,新对象和原对象不等,但是新对象的属性和老对象相同。
其中:
- 如果属性是基本类型(int,double,long,boolean等),拷贝的就是基本类型的值。
- 如果属性是引用类型(除了基本类型都是引用类型),拷贝的就是引⽤数据类型变量的地址值,⽽对于引⽤类型变量指向的堆中的对象不会拷贝。
- 深拷贝 :完全拷贝⼀个对象,在堆上创建一个新的对象,拷贝被拷贝对象的成员变量的值,同时堆中的对象也会拷贝。
很感谢你能看到最后,如果喜欢的话,欢迎关注点赞收藏转发,谢谢!更多精彩的文章