Spring Cloud @RefreshScope 自动刷新Bean
目录
RefreshScope 代理过程
RefreshScope 刷新过程
在SpringCloud 中将组建添加 @RefreshScope 可以实现动态刷新,要实现自动更新,那么需要
- 当Bean更新的时获取到更新后的bean,那么这个Bean需要懒加载,即使用的时候再加载,需要代理
- 当Bean更新的时候获取最新的Bean,那么这个Bean需要重复加载,因此需要销毁原来生成的Bean,根据最新的信息创建新的Bean
RefreshScope 代理过程
SpringCloud 使用@RefreshScope 来解决动态刷新,查看注解, 以 @RefreshScope 声明的Bean将会被 org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.refresh.RefreshScope 代理
/**
* Convenience annotation to put a @Bean definition in
* {@link org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.refresh.RefreshScope refresh scope}.
* Beans annotated this way can be refreshed at runtime and any components that are using
* them will get a new instance on the next method call, fully initialized and injected
* with all dependencies.
* 这里意思是:以RefreshScope这种方式声明的bean将会在运行时被刷新,所有使用它的组件下一次方法调用的时候会得到一个初始化完整的bean,包含其依赖关系
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Scope("refresh")
@Documented
public @interface RefreshScope {
/**
* @see Scope#proxyMode()
*/
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode() default ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS;
}@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Scope {
@AliasFor("scopeName")
String value() default "";
/**
* singleton 表示该bean是单例的(默认)
* prototype 表示该bean是多例的,即每次使用该bean时都会新建一个对象
* request 在一次http请求中一个bean对应一个实例
* session 在一个httpSession中一个bean对应一个实例
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String scopeName() default "";
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT;
}@RefreshScope 是一个复合注解 ,并标识ScopedProxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS
1. ScopedProxyMode 枚举有4个属性
-
ScopedProxyMode .DEFAULT 默认值和ScopedProxyMode .NO 相同
-
ScopedProxyMode .NO 表示不需要代理,直接创建
-
ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES 表示通过JDK动态代理创建类
-
ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS 表示通过CGLIB动态代理方式创建类
2. @Scope 代表了Bean的作用域,sigleton 单例,prototype 多例,request 一次http请求对应一个实例, session 一个httpsession中一个bean对应一个实例
3. @Scope("refresh") 表示 @RefreshScope 是scopeName="refresh"的 @Scope
- RefreshScope 继承了了GenericScope 并且构造器中设置了名称为 "refresh" (代码片段1)
- 容器初始化时,RefreshScope注册到BeanFactory的scopes 中, key= "refresh" values=RefreshScope (代码片段2)
- BeanFactory对于Bean的加载是大致分为三种的,第一种:单例bean,Scope=Singleton,第二种:多例bean Scope=prototype ,这两种都是硬编码的方式实现定义,其他的属于第三种,由Scope管理,表示当Spring容器加载Bean的时候会将其bean定义由Scope管理 ,当获取BEAN的时候,通过scopeName=refresh m 找到注册的RefreshScope, 由RefreshScope 通过GCLIB动态代理的方式得到Bean , (代码片段3)
//代码片段1
@ManagedResource
public class RefreshScope extends GenericScope
implements ApplicationContextAware, Ordered {
private ApplicationContext context;
private BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private boolean eager = true;
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100;
// 初始化的时候设置了name属性为refresh
public RefreshScope() {
super.setName("refresh");
}
......
}
//代码片段2
public class GenericScope implements Scope, BeanFactoryPostProcessor,
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, DisposableBean {
private String name = "generic";
//默认名称是generic ,RefreshScope 将其修改成了"refresh"
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
//这里向BeanFactory注册Scope ,注册了refresh 名称和RefreshScope
beanFactory.registerScope(this.name, this);
setSerializationId(beanFactory);
}
}
//
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
//内置1个Map存储注册的Scope
private final Map scopes = new LinkedHashMap<>(8);
@Override
public void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope) {
Assert.notNull(scopeName, "Scope identifier must not be null");
Assert.notNull(scope, "Scope must not be null");
if (SCOPE_SINGLETON.equals(scopeName) || SCOPE_PROTOTYPE.equals(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot replace existing scopes 'singleton' and 'prototype'");
}
//注册后,保存到scopes中,这是1个map key=refresh ,values=RfreshScope
Scope previous = this.scopes.put(scopeName, scope);
if (previous != null && previous != scope) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Replacing scope '" + scopeName + "' from [" + previous + "] to [" + scope + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Registering scope '" + scopeName + "' with implementation [" + scope + "]");
}
}
}
} // 代码片段3
// AbstractBeanFactory# doGetBean 方法: 创建Bean实例的处理方式
protected T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
//...
//L313开始
//如果是单例:Bean配置成“singleton” 或者未配置的时候
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
}
//Bean配置成“prototype” 的时候
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
}
//配置成refesh分支的时候
else {
//Scope Bean实例交由Scope自己创建
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
//这里通过"refresh" 得到注册的RefreshScope
//通过RefreshScope 来创建Bean,前面说了RefreshScope 通过GCLIB动态代理创建BEAN
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
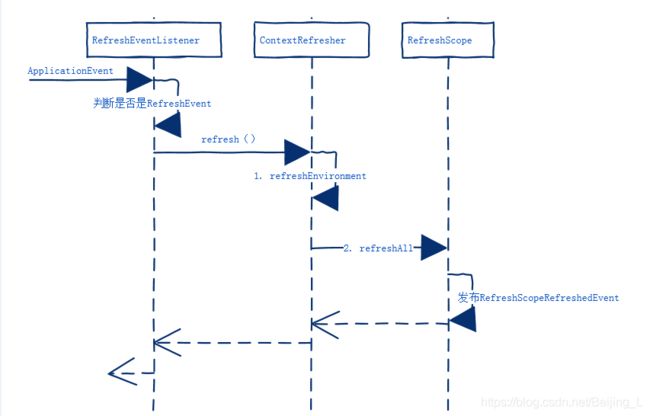
} RefreshScope 刷新过程
- RefreshEventListener 捕获事件 RefreshEvent
- ContextRefresher 对象先刷新环境,然后刷新 RefreshScope,
- RefreshScope刷新过程,清除refreshscope缓存幷销毁Bean,发布RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent 通知声明周期已经发生变更, 下次就会重新从BeanFactory获取一个新的实例,
public class RefreshEventListener {
private ContextRefresher refresh;
@EventListener
public void handle(RefreshEvent event) {
if (this.ready.get()) { // don't handle events before app is ready
log.debug("Event received " + event.getEventDesc());
//刷新
Set keys = this.refresh.refresh();
log.info("Refresh keys changed: " + keys);
}
}
}
//-----------------ContextRefresher ---------------------
public class ContextRefresher {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
private RefreshScope scope;
//.....
public synchronized Set refresh() {
//刷新环境
Set keys = refreshEnvironment();
//刷新 RefreshScope
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
public synchronized Set refreshEnvironment() {
Map before = extract(
this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());
addConfigFilesToEnvironment();
Set keys = changes(before,
extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();
this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(context, keys));
return keys;
}
//.....
}
//------------------RefreshScope --------------------
@ManagedResource
public class RefreshScope extends GenericScope
implements ApplicationContextAware, Ordered {
// 销毁RefreshScope 中的bean, 强制下一次执行的时候刷新
@ManagedOperation(description = "Dispose of the current instance of all beans in this scope and force a refresh on next method execution.")
public void refreshAll() {
//这里调用父类的方法销毁
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
}
//-----------------GenericScope ---------------------
public class GenericScope implements Scope, BeanFactoryPostProcessor,
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, DisposableBean {
private BeanLifecycleWrapperCache cache = new BeanLifecycleWrapperCache(
new StandardScopeCache());
//..
//销毁
@Override
public void destroy() {
List errors = new ArrayList();
// 清空缓存
Collection wrappers = this.cache.clear();
for (BeanLifecycleWrapper wrapper : wrappers) {
try {
Lock lock = locks.get(wrapper.getName()).writeLock();
lock.lock();
try {
wrapper.destroy(); //销毁
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
errors.add(e);
}
}
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
throw wrapIfNecessary(errors.get(0));
}
this.errors.clear();
}
//再次获取的时候重新通过工厂获取新值
@Override
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory objectFactory) {
BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name,
new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());
try {
return value.getBean();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
}
public Object getBean() {
if (this.bean == null) {
synchronized (this.name) {
if (this.bean == null) {
//bean不存在的时候创建
this.bean = this.objectFactory.getObject();
}
}
}
return this.bean;
}
}
下一篇:Nacos 配置中心原理(Nacos +SpringCloud)