Spring 入门教程
Spring 入门教程
1、参考资料
- 尚硅谷-Spring5框架最新版教程(idea版)
- 雷丰阳spring、springmvc、mybatis、spring一站式学习
项目地址:Oneby / spring-learn
2、Spring 概述
2.1、Spring 框架概述
Spring 是轻量级的开源的 JavaEE 框架
Spring 为简化企业级开发而生,使用Spring,Javabean就可以实现很多以前要靠EJB才能实现的功能
Spring 有两个核心部分:IOC 和 AOP
- IOC(Inversion of Control,即控制反转)是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来降低计算机代码之间的耦合度,其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI)。Spring 就是采用依赖注入的方式,为我们管理容器中的 bean 实例对象
- AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,即面向切面)可以在不修改源代码的前提下,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理方式实现对原有代码的增强(添加新功能)
Spring的优良特性
- 非侵入式:基于Spring开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于Spring的API
- 依赖注入:DI——Dependency Injection,反转控制(IOC)最经典的实现
- 面向切面编程:Aspect Oriented Programming——AOP
- 容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
- 组件化:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在 Spring 中可以使用XML和Java注解组合这些对象。
- 一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(实际上Spring 自身也提供了表述层的SpringMVC和持久层的Spring JDBC)。
Spring 目前的版本
目前已经更新到 Spring 5.3.3 版本,不过我还是与老师使用同一个版本吧,老师讲课使用的是 Spring 5.2.6 版本
Spring jar 包下载地址
老师上课手动导入 jar 包的依赖,我们还是使用 maven 引入相关依赖吧~
Spring 模块
![]()
2.2、Spring 入门案例
0、入门案例的目标
目标:使用 Spring 创建 bean 实例对象,并为其属性赋值
1、创建 maven 工程
因为后续测试还会创建其他 maven 工程,因此我们先创建一个 maven 父工程(spring-learn),再创建本章对应的 maven 子工程(spring-getting-start)
2、引入相关依赖
在 spring-getting-start 工程中引入 spring-beans、spring-context、spring-core、spring-expression 的依赖,这四个依赖正是 Spring Core Container 所需的依赖,此外 Springn 还需依赖 commons-logging 实现日志功能
如下是 pom.xml 中引入的依赖配置,为了测试方便,我们引入了 spring-test 和 jupiter 相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-beansartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-coreartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-expressionartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logginggroupId>
<artifactId>commons-loggingartifactId>
<version>1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupitergroupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiterartifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
3、创建实体类
创建 Student 实体类
/**
* @ClassName Student
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:27
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Student {
private Integer stuId;
private String stuName;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer stuId, String stuName) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public Integer getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuId(Integer stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4、编写 Spring 配置文件
在 resources 包下点击鼠标右键,选择【New】–>【XML Configuration File】–>【Spring Config】,注:resource 包下的配置文件在执行时会被拷贝至类路径的根目录
添加如下配置:创建 Student 对象的实例,并注入属性的值
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="007"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
beans>
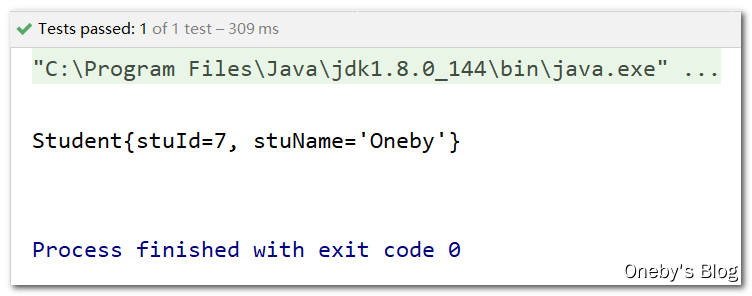
5、编写测试代码
测试代码:首先创建 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 对象,XML 配置文件的路径为类路径下的 getting-start.xml;然后获取容器中的 Student 对象,并打印此 Student 对象
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void gettingStart() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("getting-start.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Student student = (Student) iocContainer.getbean("student");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(student);
}
}
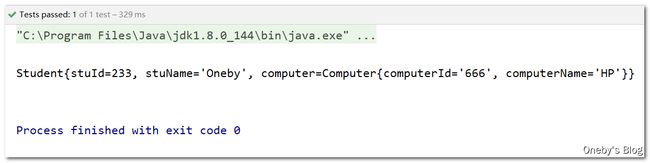
测试结果:从 Spring 容器中获取到的 Student 对象,其属性值已经被注入
关于 jupiter 更加拉风的写法
使用 @SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:getting-start.xml") 注解指明 Spring 单元测试的配置文件路径,再使用 @Autowired 注解自动装配容器中的 Student 对象
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:getting-start.xml")
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
public void gettingStart() {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
测试结果:为啥这个就输出了一大堆日志信息
![]()
测试结果:Spring 在创建 IOC 容器时,就已经完成了 bean 的创建和属性的赋值
3、IOC 容器和 bean 管理
3.1、IOC 和 DI 的关系
IOC(Inversion of Control):反转控制
早在2004年,Martin Fowler就提出了“哪些方面的控制被反转了?”这个问题。他总结出是依赖对象的获得被反转了,因为大多数应用程序都是由两个或是更多的类通过彼此的合作来实现企业逻辑,这使得每个对象都需要获取与其合作的对象(也就是它所依赖的对象)的引用。如果这个获取过程要靠自身实现,那么这将导致代码高度耦合并且难以维护和调试
在应用程序中的组件需要获取资源时,传统的方式是组件主动的从容器中获取所需要的资源,在这样的模式下开发人员往往需要知道在具体容器中特定资源的获取方式。比如 ClassA 中需要用到 ClassB 的对象,一般情况下,需要在 ClassA 的代码中显式的 new 一个 ClassB 的对象
反转控制的思想完全颠覆了应用程序组件获取资源的传统方式:反转了资源的获取方向——改由容器主动的将资源推送给需要的组件,开发人员不需要知道容器是如何创建资源对象的,只需要提供接收资源的方式即可。采用依赖注入技术之后,ClassA 的代码只需要定义一个私有的 ClassB 对象,不需要直接 new 来获得这个对象,而是通过相关的容器控制程序来将 ClassB 对象在外部 new 出来并注入到 A 类里的引用中。而具体获取的方法、对象被获取时的状态由配置文件(如 XML)来指定
DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
可以将 DI 看作是 IOC 的一种实现方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如:setter 方法)接受来自于容器的资源注入。相对于 IOC 而言,这种表述更直接
IOC容器在Spring中的实现
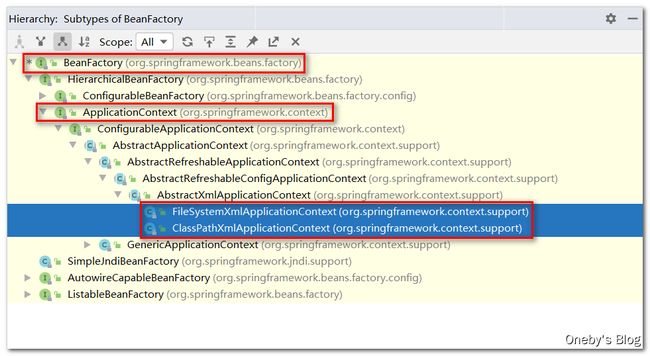
在通过IOC容器读取bean的实例之前,需要先将IOC容器本身实例化,Spring提供了IOC容器的两种实现方式:
beanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现,是Spring内部的基础设施,是面向Spring本身的,不是提供给开发人员使用的。ApplicationContext:beanFactory的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向Spring的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext而不是底层的beanFactory。
ApplicationContext的主要实现类
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:对应类路径下的XML格式的配置文件FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:对应文件系统中的XML格式的配置文件
在初始化时就创建单例的bean,也可以通过配置的方式指定创建的bean是多实例的
ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口
- 是
ApplicationContext的子接口,包含一些扩展方法 refresh()和close()让ApplicationContext具有启动、关闭和刷新上下文的能力
WebApplicationContext 接口
WebApplicationContext,是继承于ApplicationContext的一个接口,扩展了ApplicationContext,是专门为Web应用准备的,它允许从相对于Web根目录的路径中装载配置文件完成初始化
举例说明 IOC 为何可以降低代码的耦合度
1、原始方式:自己 new 对象
假设现在需要创建 Student 对象实例,原始方式则是直接 new Student() 对象,再通过 setter 方法注入器属性值
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setStuId(7);
stu.setStuName("Oneby");
结论:我们纯手动自己 new 对象,代码耦合度极高
2、进阶方式:通过工厂创建对象
可以先通过 XML 配置文件配置 bean 的属性
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="007"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
再通过工厂模式 + 反射的方法创建该对象的实例,并注入属性值
public class StudentFactory {
public static Student getStudent(){
String className = ...; // 通过 XML 解析获取全类名
String[] fieldNames = ..; // 通过 XML 解析获取字段名
String[] fieldValues = ...; // 通过 XML 解析获取字段值
Class clazz = Class.forName(className); // 通过反射创建对象实例
for (int i = 0; i < fieldNames.length; i++) {
// 依次为字段赋值
}
return clazz; // 返回创建的实例对象
}
}
结论:这种方式可以降低代码的耦合度,我们使用 Student 对象再不需要自己去 new,而是通过工厂获得,但是这种方式还是脱离不了我们自己去获取和管理 bean
3、最终方式:通过 Spring IOC 管理 bean
首先创建 Spring 配置文件
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="007"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
在通过 iocContainer.getbean("beanId") 方法或者 @Autowire 方式获取 bean 岂不美滋滋,这样我们可以将 bean 的创建与它们之间的依赖关系完全交给 Spring IOC 容器去管理,代码耦合程度极大降低
3.2、bean 对象的获取
获取 bean 对象的几种方式
在容器的顶级接口 beanFactory接口中,定义了如下几个方法,用于获取 bean 实例
Object getbean(String name) throws beansException;:通过 bean name 获取 bean 实例T getBean(Class requiredType) throws BeansException; T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
3.3、bean 属性的赋值
3.3.1、属性注入的方式
1、通过 bean 的 setter 方法注入属性
通过
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="007"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
测试结果
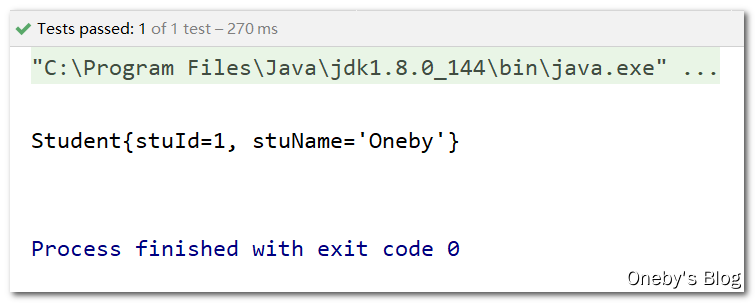
2、通过构造器注入属性值
通过 constructor-arg 标签为对象的属性赋值,通过 name 指定属性名,value 指定属性值
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<constructor-arg name="stuId" value="1" />
<constructor-arg name="stuName" value="Oneby" />
bean>
测试结果
3、通过级联属性赋值
准备工作
为了演示级联属性的赋值,我们添加 Computer 类
/**
* @ClassName Computer
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 23:09
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Computer {
String computerId;
String computerName;
public Computer() {
}
public Computer(String computerId, String computerName) {
this.computerId = computerId;
this.computerName = computerName;
}
public String getComputerId() {
return computerId;
}
public String getComputerName() {
return computerName;
}
public void setComputerId(String computerId) {
this.computerId = computerId;
}
public void setComputerName(String computerName) {
this.computerName = computerName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Computer{" +
"computerId='" + computerId + '\'' +
", computerName='" + computerName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
在 Student 类中添加 Computer 类型的字段
/**
* @ClassName Student
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:27
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Student {
private Integer stuId;
private String stuName;
private Computer computer;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer stuId, String stuName, Computer computer) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.computer = computer;
}
public Integer getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public Computer getComputer() {
return computer;
}
public void setStuId(Integer stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public void setComputer(Computer computer) {
this.computer = computer;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", computer=" + computer +
'}';
}
}
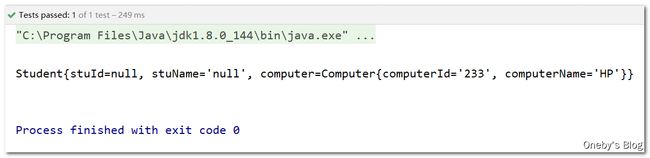
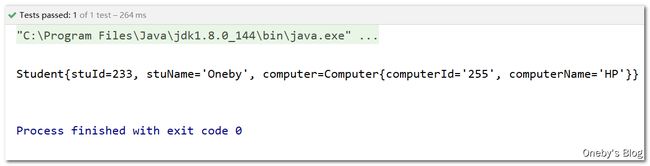
演示级联属性的赋值
在 student 对象中有一个名为 computer 的字段,该字段指向了一个 computer 对象,级联属性赋值的含义为:在 student bean 中的 computer.computerId 和 computer.computerName 的方式为 computer 对象中的 computerId 和 computerName 字段赋值
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="computer" ref="computer"/>
<property name="computer.computerId" value="233"/>
<property name="computer.computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer"/>
测试结果
4、通过 p 名称空间注入属性值
为了简化XML文件的配置,越来越多的XML文件采用属性而非子元素配置信息。Spring从2.5版本开始引入了一个新的p命名空间,可以通过
准备工作:在配置文件中引入 p 名称空间
对照着 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 这行改吧改吧
通过 p 名称空间注入属性值
其实 p 名称空间赋值就是
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" p:stuId="1" p:stuName="Oneby"/>
测试结果
![]()
3.3.2、属性赋值的类型
1、字面量
- 可以使用字符串表示的值,可以通过
value属性或value子节点的方式指定 - 基本数据类型及其封装类、
String等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式 - 若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用
把字面值包裹起来
演示字面量的使用
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
2、null 值
通过 null
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName">
<null/>
property>
<property name="computer">
<null/>
property>
bean>
测试结果
3、引用外部 bean
通过 ref 属性引用外部 bean
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="computer" ref="computer"/>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="255"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
测试结果
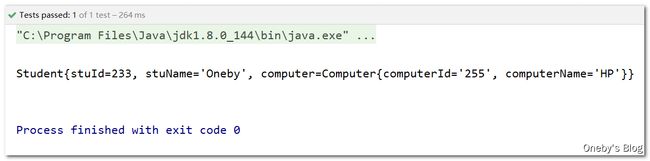
4、引用内部 bean
当bean实例仅仅给一个特定的属性使用时,可以将其声明为内部bean。内部bean声明直接包含在id或name属性,内部bean不能使用在任何其他地方
在 ref 属性引用外部 bean,而是直接定义一个 内部 bean
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="computer">
<bean class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="255"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
property>
bean>
测试结果
3.3.3、对集合属性赋值
在Spring中可以通过一组内置的XML标签来配置集合属性,比如:、util 名称空间来提取集合类型的 bean
0、准备工作
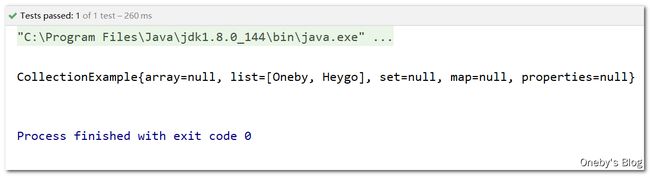
新建 CollectionExample 类,演示对集合属性的操作
/**
* @ClassName CollectionExample
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/15 20:51
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class CollectionExample {
private String[] array;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String,String> map;
private Properties properties;
public String[] getArray() {
return array;
}
public void setArray(String[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionExample{" +
"array=" + Arrays.toString(array) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
单元测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("collection-property-injection.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
CollectionExample collectionExample = (CollectionExample) iocContainer.getBean("collectionExample");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(collectionExample);
}
}
1、数组
通过 指定对其他bean的引用。通过
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>Onebyvalue>
<value>Heygovalue>
array>
property>
bean>
测试结果
![]()
2、List
通过 指定对其他bean的引用。通过
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>Onebyvalue>
<value>Heygovalue>
list>
property>
bean>
测试结果
3、Set
通过 指定对其他bean的引用。通过
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>Onebyvalue>
<value>Heygovalue>
set>
property>
bean>
测试结果
4、Map
Java.util.Map通过标签定义,标签里可以使用多个、key-value键值对可以使用key和value来定义;bean引用通过key-ref和value-ref属性定义。
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="name" value="Oneby">entry>
<entry key="hobby" value="code">entry>
map>
property>
bean>
测试代码
![]()
5、Properties
使用java.util.Properties,该标签使用多个key和value
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="name">Onebyprop>
<prop key="hobby">codeprop>
props>
property>
bean>
测试代码
6、集合类型的 bean
如果只能将集合对象配置在某个bean内部,则这个集合的配置将不能重用。我们需要将集合bean的配置拿到外面,供其他bean引用。
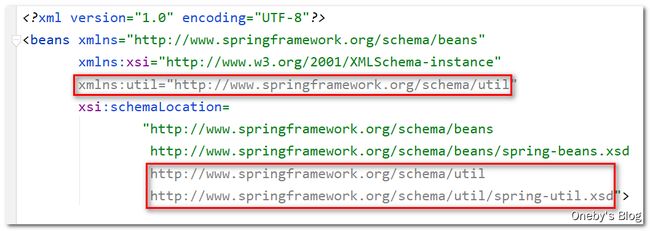
引入名称空间:配置集合类型的bean需要引入util名称空间
将 beans 名称空间对应的这两项 xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util 和 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd,将 beans 全部替换为 util 就行啦~
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
使用 id 属性,方便其他地方进行引用
<util:list id="list">
<value>Onebyvalue>
<value>Heygovalue>
util:list>
<bean id="collectionExample" class="com.oneby.entity.CollectionExample">
<property name="list" ref="list"/>
bean>
测试结果
![]()
3.4、通过工厂创建 bean
1、静态工厂
调用静态工厂方法创建bean是将对象创建的过程封装到静态方法中。当客户端需要对象时,只需要简单地调用静态方法,而不用关心创建对象的细节。
声明通过静态方法创建的bean需要在class属性里指定静态工厂类的全类名,同时在factory-method属性里指定工厂方法的名称。最后使用
2、实例工厂
实例工厂方法:将对象的创建过程封装到另外一个对象实例的方法里。当客户端需要请求对象时,只需要简单的调用该实例方法而不需要关心对象的创建细节。
实现方式
- 配置工厂类实例的bean
- 在
factory-method属性里指定该工厂方法的名称 - 使用
construtor-arg元素为工厂方法传递方法参数
3、FactoryBean 接口
以上两种方式通常用的不多,我们一般通过实现 FactoryBean 接口,并重写其中的方法来获得工厂类
- Spring中有两种类型的bean,一种是普通bean,另一种是工厂bean,即
FactoryBean - 工厂bean跟普通bean不同,其返回的对象不是指定类的一个实例,其返回的是该工厂bean的
getObject()方法所返回的对象 - 工厂bean必须实现
org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean接口
FactoryBean 接口
FactoryBean 接口中有如下三个方法,getObject() 方法负责将创建好的 bean 实例返回给 IOC 容器;getObjectType() 方法负责返回工厂生产的 bean 类型;isSingleton() 方法用于指示该 bean 实例是否为单例,默认是单例 bean
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
// Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object managed by this factory.
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
// Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, or null if not known in advance.
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
// Is the object managed by this factory a singleton?
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
演示 FactoryBean 接口的使用
创建 StudentFactory 类,该类实现了 FactoryBean 接口,并重写了其中的 getObject() 和 getObjectType() 方法
/**
* @ClassName StudentFactory
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/15 21:54
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class StudentFactory implements FactoryBean<Student> {
@Override
public Student getObject() throws Exception {
return new Student(233,"Oneby");
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Student.class;
}
}
在 Spring 配置文件中使用 StudentFactory 工厂创建 Student 对象
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.StudentFactory"/>
测试结果
3.5、bean 的高级配置
3.5.1、bean 的作用域
bean 的作用域
在Spring中,可以在scope属性里设置bean的作用域,以决定这个bean是单实例的还是多实例的。
默认情况下,Spring只为每个在IOC容器里声明的bean创建唯一一个实例(单例对象),整个IOC容器范围内都能共享该实例:所有后续的getBean()调用和bean引用都将返回这个唯一的bean实例。该作用域被称为singleton,它是所有bean的默认作用域
两种 bean 的作用域
singleton:在Spring IOC容器中仅存在一个bean实例,bean以单实例的方式存在
prototype:每次调用getBean()时都会返回一个新的实例
注:当bean的作用域为singleton时,Spring会在IOC容器对象创建时就创建bean的对象实例。而当bean的作用域为prototype时,IOC容器在获取bean的实例时创建bean的实例对象
单例模式:
scope="singleton"
其实 scope 属性默认就是 singleton,不写也没事儿
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" scope="singleton">
<property name="stuId" value="233" />
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby" />
bean>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Student student1 = (Student) iocContainer.getBean("student");
Student student2 = (Student) iocContainer.getBean("student");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
System.out.println(student1 == student2);
}
}
程序运行结果:调用两次 getBean() 方法得到的 Student 对象是同一个实例
![]()
原型模式:
scope="prototype"
将 Student 对象的 scope 属性配置为 prototype,表示每次获取时才创建对象
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" scope="prototype">
<property name="stuId" value="233" />
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby" />
bean>
程序运行结果:调用两次 getBean() 方法将得到不同的 Student 对象
![]()
3.5.2、bean 的生命周期
Spring IOC 管理下的 bean 生命周期
Spring IOC容器可以管理bean的生命周期,Spring允许在bean生命周期内特定的时间点执行指定的任务,Spring IOC容器对bean的生命周期进行管理的过程:
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建bean实例
- 为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用
- 调用bean的初始化方法
- bean可以使用了
- 当容器关闭时,调用bean的销毁方法
注:在配置bean时,通过init-method和destroy-method属性为bean指定初始化和销毁方法
代码演示
创建 Order 类,用于演示 bean 的生命周期
/**
* @ClassName Order
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/21 21:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Order {
private String name;
public Order() {
System.out.println("第一步:执行无参数构造创建 bean 实例");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("第二步:调用 setter 方法为属性赋值");
}
// init-method 初始化方法
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("第三步:执行 init-method 初始化方法");
}
// destroy-method 销毁方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("第五步:执行 destroy-method 初销毁方法");
}
}
在 order 对象的 init-method 方法(初始化方法)和 destroy-method 方法(销毁方法)
<bean id="order" class="com.oneby.entity.Order"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="name" value="iPad" />
bean>
测试代码:记得要关闭 IOC 容器才会执行 destroy-method 方法,并且接口类型需要上升到 ConfigurableApplicationContext 才会提供 close() 方法
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Order order = (Order) iocContainer.getBean("order");
//3.打印bean
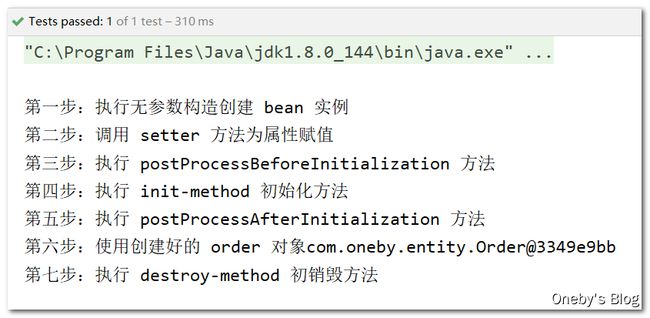
System.out.println("第四步:使用创建好的 order 对象" + order);
//4.关闭IOC容器
iocContainer.close();
}
}
程序运行结果
添加 BeanPostProcessor 后的 bean 生命周期
bean的后置处理器
- bean后置处理器允许在调用初始化方法前后对bean进行额外的处理
- bean后置处理器对IOC容器里的所有bean实例逐一处理,而非单一实例。其典型应用是:检查bean属性的正确性或根据特定的标准更改bean的属性。
- bean后置处理器时需要实现接口:
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor。在初始化方法被调用前后,Spring将把每个bean实例分别传递给上述接口的以下两个方法: postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object, String)postProcessAfterInitialization(Object, String)
添加bean后置处理器后bean的生命周期
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建bean实例
- 为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用
- 将bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法
- 调用bean的初始化方法
- 将bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
- bean可以使用了
- 当容器关闭时调用bean的销毁方法
代码演示
创建 MyBeanPost 类,继承自 MyBeanPost 类,并重写其中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法
/**
* @ClassName MyBeanPost
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/21 21:59
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第三步:执行 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:执行 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法");
return bean;
}
}
配置文件:在配置文件中实例化我们自定义的 MyBeanPost 后置处理器
<bean id="order" class="com.oneby.entity.Order"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="name" value="iPad" />
bean>
<bean id="myBeanPost" class="com.oneby.config.MyBeanPost"/>
测试代码:现在使用 order 对象变成了第六步
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Order order = (Order) iocContainer.getBean("order");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println("第六步:使用创建好的 order 对象" + order);
//4.关闭IOC容器
iocContainer.close();
}
}
程序运行结果
3.5.3、读取 properties 文件
为什么要使用外部的 properties 文件
当bean的配置信息逐渐增多时,查找和修改一些bean的配置信息就变得愈加困难。这时可以将一部分信息提取到bean配置文件的外部,以properties格式的属性文件保存起来,同时在bean的配置文件中引用properties属性文件中的内容,从而实现一部分属性值在发生变化时仅修改properties属性文件即可。这种技术多用于连接数据库的基本信息的配置。
准备工作:引入数据库依赖
引入 druid 和 mysql 的驱动
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.8version>
dependency>
直接数据库连接配置卸载 Spring 配置文件中
配置文件,指定数据库的用户名、用户密码、数据库连接地址、数据库驱动名称
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
bean>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) iocContainer.getBean("dataSource");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}
程序运行结果
引用外部 properties 配置文件单独存放数据库配置信息
引入 context 名称空间
将 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 和 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 复制,并将出现 beans 的位置全部替换为 context
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
![]()
代码测试
在类路径下创建 jdbc.properties 数据库配置文件
prop.userName=root
prop.password=root
prop.url=jdbc:mysql:///test
prop.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
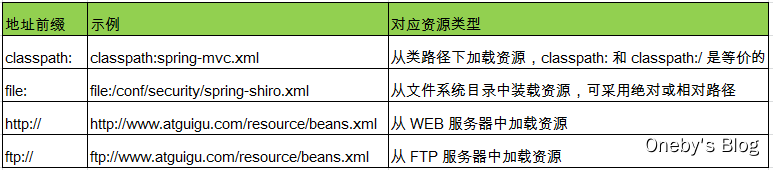
通过 location 来制定配置文件的路径,classpath: 表示该配置文件位于类路径下,并通过 ${prop.userName} 的方式来取出配置文件中的属性值
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"/>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"/>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"/>
bean>
程序运行结果
3.5.4、bean 的自动装配
自动装配的概念
[1]手动装配:以value或ref的方式明确指定属性值都是手动装配。
[2]自动装配:根据指定的装配规则,不需要明确指定,Spring自动将匹配的属性值注入bean中。
装配模式
[1]根据类型自动装配(byType):将类型匹配的bean作为属性注入到另一个bean中。若IOC容器中有多个与目标bean类型一致的bean,Spring将无法判定哪个bean最合适该属性,所以不能执行自动装配
[2]根据名称自动装配(byName):必须将目标bean的名称和属性名设置的完全相同
[3]通过构造器自动装配(constructor):当bean中存在多个构造器时,此种自动装配方式将会很复杂。不推荐使用。
选用建议
相对于使用注解的方式实现的自动装配,在XML文档中进行的自动装配略显笨拙,在项目中更多的使用注解的方式实现。
代码举例
通过 autowire="byType",指定 student 对象中的 bean 按照类型进行装配
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" autowire="byType">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="666"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
程序运行结果
![]()
3.5.5、配置信息的继承
配置信息的继承
Spring允许继承bean的配置,被继承的bean称为父bean,继承这个父bean的bean称为子bean
子bean从父bean中继承配置,包括bean的属性配置,子bean也可以覆盖从父bean继承过来的配置
准备工作:创建实体类
创建 CorporateSlave 类,其含义为社畜
/**
* @ClassName CorporateSlave
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/21 12:32
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class CorporateSlave {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String company;
private String hobby;
private String profession;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public String getProfession() {
return profession;
}
public void setProfession(String profession) {
this.profession = profession;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CorporateSlave{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", company='" + company + '\'' +
", hobby='" + hobby + '\'' +
", profession='" + profession + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
不使用继承配置 bean
喏,Oneby 和 Heygo 两位社畜的 company、hobby、profession 属性的值均相同,这样配置显得有些冗余
<bean id="corporateSlave1" class="com.oneby.entity.CorporateSlave">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="company" value="OneTech"/>
<property name="hobby" value="Code"/>
<property name="profession" value="Programer"/>
bean>
<bean id="corporateSlave2" class="com.oneby.entity.CorporateSlave">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="Heygo"/>
<property name="company" value="OneTech"/>
<property name="hobby" value="Code"/>
<property name="profession" value="Programer"/>
bean>
使用配置信息的继承配置 bean
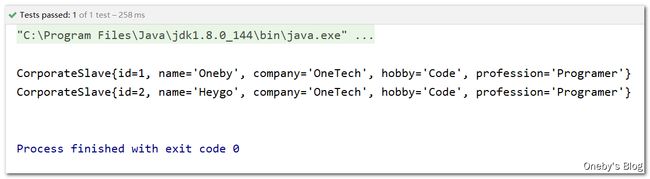
配置信息的继承:Heygo 的配置信息继承于 Oneby(指定 bean 的 parent 属性),自然就获得了 Oneby 社畜的所有配置信息,只需要重写自己不一样的配置信息即可
<bean id="corporateSlave1" class="com.oneby.entity.CorporateSlave">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="company" value="OneTech"/>
<property name="hobby" value="Code"/>
<property name="profession" value="Programer"/>
bean>
<bean id="corporateSlave2" parent="corporateSlave1">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="Heygo"/>
bean>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
CorporateSlave corporateSlave1 = (CorporateSlave) iocContainer.getBean("corporateSlave1");
CorporateSlave corporateSlave2 = (CorporateSlave) iocContainer.getBean("corporateSlave2");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(corporateSlave1);
System.out.println(corporateSlave2);
}
}
程序运行结果
注意事项:配置信息的继承
父bean可以作为配置模板,也可以作为bean实例。若只想把父bean作为模板,可以设置abstract 属性为true,这样Spring将不会实例化这个bean
3.5.6、bean 之间的依赖
bean 的作用域
有的时候创建一个bean的时候需要保证另外一个bean也被创建,这时我们称前面的bean对后面的bean有依赖。例如:要求创建Student对象的时候必须创建Computer。这里需要注意的是依赖关系不等于引用关系,Student即使依赖Computer也可以不引用它
举例一:
student对象依赖computer对象,但我们不创建computer对象
在配置文件呢中,我们只实例化 student 对象,并且执行其 depends-on 属性等于 computer,表示student 对象的创建依赖于 computer 对象的创建
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" depends-on="computer">
<property name="stuId" value="233" />
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby" />
bean>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-advance-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Student student = (Student) iocContainer.getBean("student");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(student);
}
}
程序运行结果:org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'student' defined in class path resource [spring-advance-config.xml]: 'student' depends on missing bean 'computer'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No bean named 'computer' available
报错信息已经很明显了:'student' depends on missing bean 'computer',说是缺少一个 computer 对象
举例二:
student对象依赖computer对象,我们就创建computer对象
既然 student 对象依赖 computer 对象,那么我们在配置文件中创建 computer 对象
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student" depends-on="computer">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer"/>
程序运行结果:再次证明了以来不一定要引用
3.6、SpEL 表达式语言
3.6.1、SpEL 简介
SpEL 是什么?
SpEL的全称是 Spring Expression Language,即Spring表达式语言,简称SpEL,支持运行时查询并可以操作对象图,和JSP页面上的EL表达式、Struts2中用到的OGNL表达式一样,SpEL根据JavaBean风格的getXxx()、setXxx()方法定义的属性访问对象图,完全符合我们熟悉的操作习惯。
3.6.2、SpEL 使用
0、基本语法
SpEL使用#{…}作为定界符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是SpEL表达式
1、字面量
- 整数:
- 小数:
- 科学计数法:
- String类型的字面量可以使用单引号或者双引号作为字符串的定界符号
- Boolean:
2、引用其他 bean
在 value 属性中通过 #{对象名} 引用其他 bean,注意:不能使用 ref 属性
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="computer" value="#{computer}"/>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="666"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spel-test.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
Student student = (Student) iocContainer.getBean("student");
//3.打印bean
System.out.println(student);
}
}
程序运行结果
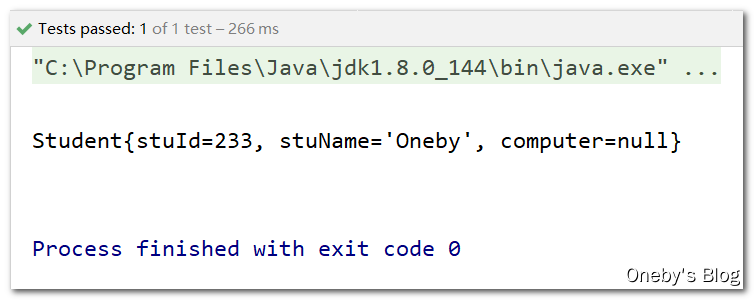
3、引用其他 bean 的属性
在 #{对象名.属性名} 引用其他 bean 的属性
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="computer" >
<bean class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="#{computer.computerId}"/>
<property name="computerName" value="#{computer.computerName}"/>
bean>
property>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="666"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
程序运行结果
![]()
4、调用非静态方法
通过 #{对象名.方法名} 调用对象的非静态方法
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="233"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
<property name="computer">
<bean class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="#{computer.getComputerId()}"/>
<property name="computerName" value="#{computer.getComputerName()}"/>
bean>
property>
bean>
<bean id="computer" class="com.oneby.entity.Computer">
<property name="computerId" value="666"/>
<property name="computerName" value="HP"/>
bean>
程序运行结果
5、调用静态方法
定义获取随机整数的方法,随机整数的范围为 [start,end]
/**
* @ClassName MathUtil
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 10:03
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class MathUtil {
public static int getRandomInt(int start, int end) {
return (int) (Math.random() * (end - start + 1) + start);
}
}
通过 T(静态类路径).方法名 调用静态方法
<bean id="student" class="com.oneby.entity.Student">
<property name="stuId" value="#{T(com.oneby.util.MathUtil).getRandomInt(0,255)}"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Oneby"/>
bean>
程序运行结果
6、运算符
①算术运算符:+、-、*、/、%、^
②字符串连接:+
③比较运算符:<、>、==、<=、>=、lt、gt、eq、le、ge
④逻辑运算符:and, or, not, |
⑤三目运算符:判断条件?判断结果为true时的取值:判断结果为false时的取值
⑥正则表达式:matches
3.7、注解方式配置 bean
3.7.1、注解的概述
注解方式对比 XML 方式
相对于XML方式而言,通过注解的方式配置bean更加简洁和优雅,而且和MVC组件化开发的理念十分契合,是开发中常用的使用方式。
3.7.2、标识组件
用于标识 bean 的四个注解
①普通组件:@Component,用于标识一个受Spring IOC容器管理的组件
②持久化层组件:@Respository,用于标识一个受Spring IOC容器管理的持久化层组件
③业务逻辑层组件:@Service,用于标识一个受Spring IOC容器管理的业务逻辑层组件
④表述层控制器组件:@Controller,用于标识一个受Spring IOC容器管理的表述层控制器组件
注意:事实上Spring并没有能力识别一个组件到底是不是它所标记的类型,即使将@Respository注解用在一个表述层控制器组件上面也不会产生任何错误,所以@Respository、@Service、@Controller这几个注解仅仅是为了让开发人员自己明确当前的组件扮演的角色。
组件命名规则
[1]默认情况:使用组件的简单类名首字母小写后得到的字符串作为bean的id
[2]使用组件注解的value属性指定bean的id
3.7.3、扫描组件
引入 AOP 依赖
引入 AOP 相关依赖,不然开启组件扫描时会报错:org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Unexpected exception parsing XML document from class path resource [annotation-config.xml]; nested exception is java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/aop/TargetSource
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aopartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
引入 context 名称空间
将 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 和 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 复制,并将出现 beans 的位置全部替换为 context
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
开启组件扫描
开启组件扫描,并指明要扫描的包路径
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
组件扫描的注意事项
组件扫描的详细说明
[1]base-package属性指定一个需要扫描的基类包,Spring容器将会扫描这个基类包及其子包中的所有类。
[2]当需要扫描多个包时可以使用逗号分隔。
[3]如果仅希望扫描特定的类而非基包下的所有类,可使用resource-pattern属性过滤特定的类,示例:
<context:component-scan
base-package="com.oneby"
resource-pattern="autowire/*.class"/>
包含与排除
use-default-filters属性配合使用才能够达到“仅包含某些组件”这样的效果。即:通过将use-default-filters属性设置为false,禁用默认过滤器,然后扫描的就只是include-filter中的规则指定的组件了。component-scan下可以拥有若干个include-filter和exclude-filter子节点
包扫描举例
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
过滤表达式
3.7.4、组件装配
组件装配的说明
项目中组件装配的需求
Controller组件中往往需要用到Service组件的实例,Service组件中往往需要用到Repository组件的实例。Spring可以通过注解的方式帮我们实现属性的装配。
组件扫描的原理
在指定要扫描的包时,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的实例。该后置处理器可以自动装配标记了@Autowired、@Resource或@Inject注解的属性
@Autowired注解
[1]根据类型实现自动装配。
[2]构造器、普通字段(即使是非public)、一切具有参数的方法都可以应用@Autowired注解
[3]默认情况下,所有使用@Autowired注解的属性都需要被设置。当Spring找不到匹配的bean装配属性时,会抛出异常。
[4]若某一属性允许不被设置,可以设置@Autowired注解的required属性为 false
[5]默认情况下,当IOC容器里存在多个类型兼容的bean时,Spring会尝试匹配bean的id值是否与变量名相同,如果相同则进行装配。如果bean的id值不相同,通过类型的自动装配将无法工作。此时可以在@Qualifier注解里提供bean的名称。Spring甚至允许在方法的形参上标注@Qualifiter注解以指定注入bean的名称。
[6]@Autowired注解也可以应用在数组类型的属性上,此时Spring将会把所有匹配的bean进行自动装配。
[7]@Autowired注解也可以应用在集合属性上,此时Spring读取该集合的类型信息,然后自动装配所有与之兼容的bean。
[8]@Autowired注解用在java.util.Map上时,若该Map的键值为String,那么 Spring将自动装配与值类型兼容的bean作为值,并以bean的id值作为键。
@Qualifier注解
通过类型的自动装配将无法工作。此时可以在@Qualifier注解里提供bean的名称,@Qualifier注解需要和上面@Autowired注解一起使用
@Autowired //根据类型进行注入
@Qualifier(value = "orderDao1") //根据bean名称进行注入
private OrderDao orderDao;
@Resource注解
@Resource注解要求提供一个bean名称的属性,若该属性为空,则自动采用标注处的变量或方法名作为bean的名称。@Resource是JDK提供的注解,咱还是尽量使用Spring提供的注解吧~
解释上面那句话:如果使用@Resource则表示按照类型进行注入,我觉得等同于@Autowire的效果吧;如果使用@Resource(name="Xxx")则表示根据bean的名称进行注入
//@Resource //根据类型进行注入
@Resource(name = "orderDao1") //根据bean名称进行注入
private OrderDao orderDao;
@Inject注解
@Inject和@Autowired注解一样也是按类型注入匹配的bean,但没有reqired属性。奇怪了,难道 Spring 5.2.6 版本该注解被移除了吗?
@Value注解
@Value注解用于注入普通属性的值,比如@Value(value = "Oneby")表示将"Oneby"字符串注入到属性中
@Value(value = "Oneby")
private String name;
组件装配的代码示例
DAO 层推荐使用 @Repository 注解标识 bean
/**
* @ClassName OrderDao
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 11:28
* @Version 1.0
*/
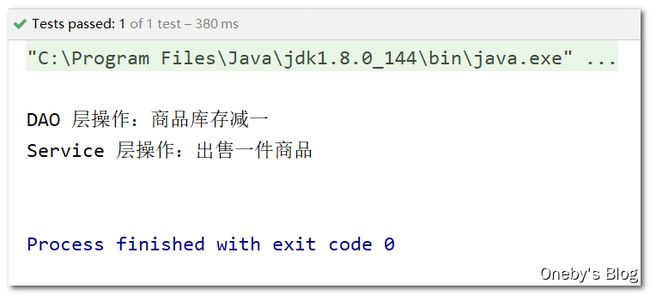
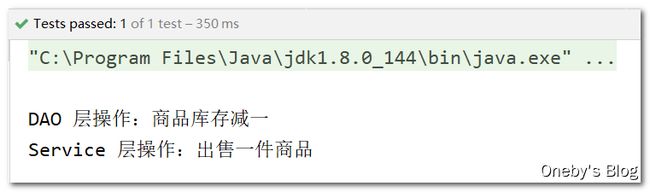
@Repository
public class OrderDao {
public void sell() {
System.out.println("DAO 层操作:商品库存减一");
}
}
Service 层推荐使用 @Service 注解标识 bean,并通过 @Autowired 注解标识
/**
* @ClassName OrderService
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/21 22:17
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderDao orderDao;
public void sell() {
orderDao.sell();
System.out.println("Service 层操作:出售一件商品");
}
}
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("annotation-config.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
OrderService orderService = (OrderService) iocContainer.getBean("orderService");
//3.调用bean中的方法
orderService.sell();
}
}
程序运行结果
3.7.5、完全注解开发
创建 Spring 配置类
创建 SpringConfig 配置类,代替之前的 XML 配置文件
@Configuration标识这是一个配置类@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby")配置组件扫描@Bean用于向 IOC 容器中注入一个普通的 bean
/**
* @ClassName SpringConfig
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 19:26
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby")
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public OrderService getOrderService(){
return new OrderService();
}
}
完全注解的代码测试
测试代码:这次需要 new 一个 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 对象,并传入配置类的类型
@Test
public void testCompleteAnnotation() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
OrderService orderService = (OrderService) iocContainer.getBean("orderService");
//3.调用bean中的方法
orderService.sell();
}
程序运行结果
3.8、泛型依赖注入
泛型依赖注入的概述
Spring 4.x 中可以为子类注入子类对应的泛型类型的成员变量的引用
![]()
泛型依赖注入的实现
组件基类
BaseRepository
public class BaseRepository<T> {
public void save() {
System.out.println("Saved by BaseRepository");
}
}
BaseService
public class BaseService<T> {
@Autowired
private BaseRepository<T> repository;
public void add() {
repository.save();
}
}
组件实体类
UserRepository
@Repository
public class UserRepository extends BaseRepository<User>{
public void save() {
System.out.println("Saved by UserRepository");
}
}
UserService
@Service
public class UserService extends BaseService<User>{
}
模型实体类
User
public class User {
}
测试
测试代码
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("di.xml");
UserService us = (UserService) ioc.getBean("userService");
us.add();
}
执行结果
Saved by UserRepository
PS:看球不懂
3.9、配置文件整合
Spring 可以很方便地整合其他配置文件
- Spring允许通过
import元素的resource属性支持Spring的标准的路径资源
4、AOP
4.1、AOP 前奏
提出问题:数学计算器案例
计算器要求
①执行加减乘除运算
②日志:在程序执行期间追踪正在发生的活动
③验证:希望计算器只能处理正数的运算
计算器的常规实现
UML 类图
![]()
计算器的常规实现代码(这里为了形参类型为 int,无伤大雅)
常规实现存在的问题
代码混乱:越来越多的非业务需求(日志和验证等)加入后,原有的业务方法急剧膨胀。每个方法在处理核心逻辑的同时还必须兼顾其他多个关注点。
代码分散:以日志需求为例,只是为了满足这个单一需求,就不得不在多个模块(方法)里多次重复相同的日志代码。如果日志需求发生变化,必须修改所有模块。
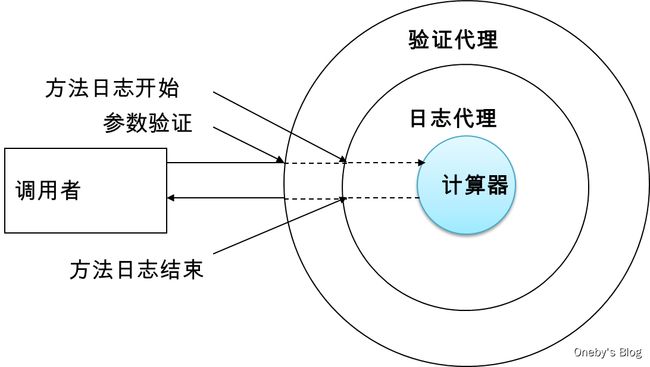
动态代理的介绍
代理设计模式的原理:使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后用该代理对象取代原始对象。任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理。代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。
数学计算器的改进
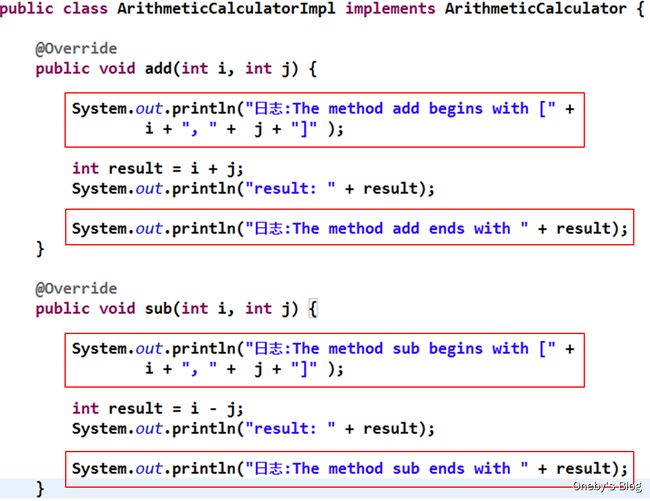
日志处理器
![]()
验证处理器
测试代码
4.2、AOP 概述
AOP 概述
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程):是一种新的方法论,是对传统OOP(Object-Oriented Programming,面向对象编程)的补充。
- AOP编程操作的主要对象是切面(aspect),而切面模块化横切关注点。
- 在应用AOP编程时,仍然需要定义公共功能,但可以明确的定义这个功能应用在哪里,以什么方式应用,并且不必修改受影响的类。这样一来横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的类里——这样的类我们通常称之为“切面”。
- AOP的好处:每个事物逻辑位于一个位置,代码不分散,便于维护和升级;业务模块更简洁,只包含核心业务代码
用通俗的话将:面向切面编程(方面),利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,可在不通过修改源代码方式,在主干功能里面添加新功能
AOP 相关术语
看不懂的专业术语
通知(Advice):就是你想要的功能,也就是上面说的日志处理、验证处理等。你给先定义好把,然后在想用的地方用一下。
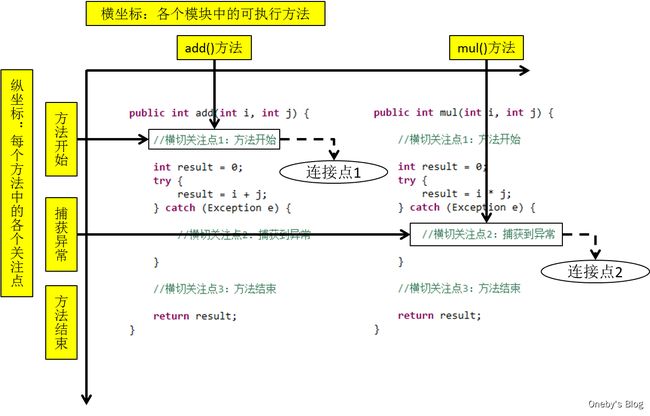
连接点(JoinPoint):这个更好解释了,就是Spring允许你使用通知的地方,那可真就多了,基本每个方法的前,后(两者都有也行),或抛出异常时都可以是连接点,spring只支持方法连接点.其他如aspectJ还可以让你在构造器或属性注入时都行,不过那不是咱关注的,只要记住,和方法有关的前前后后(抛出异常),都是连接点。
切入点(Pointcut):上面说的连接点的基础上,来定义切入点,你的一个类里,有15个方法,那就有几十个连接点了对把,但是你并不想在所有方法附近都使用通知(使用叫织入,以后再说),你只想让其中的几个,在调用这几个方法之前,之后或者抛出异常时干点什么,那么就用切点来定义这几个方法,让切点来筛选连接点,选中那几个你想要的方法。
切面(Aspect):切面是通知和切入点的结合。现在发现了吧,没连接点什么事情,连接点就是为了让你好理解切入点,搞出来的,明白这个概念就行了。通知说明了干什么和什么时候干(什么时候通过方法名中的before,after,around等就能知道),而切入点说明了在哪干(指定到底是哪个方法),这就是一个完整的切面定义。
引入(introduction):允许我们向现有的类添加新方法属性。这不就是把切面(也就是新方法属性:通知定义的)用到目标类中吗
目标(target):引入中所提到的目标类,也就是要被通知的对象,也就是真正的业务逻辑,他可以在毫不知情的情况下,被咱们织入切面。而自己专注于业务本身的逻辑。
代理(proxy):怎么实现整套aop机制的,都是通过代理。
织入(weaving):把切面应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。有3种方式,spring采用的是运行时。
用通俗的话讲
连接点:类里面哪些方法可以被增强,这些方法被称为连接点
切入点:实际被真正增强的方法,称为切入点
通知(增强):实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知(增强)。通知的类型:前置通知、后置通知、环绕通知、异常通知、最终通知
切面:把通知应用到切入点过程(是动作)
AspectJ 简介
AspectJ:Java社区里最完整最流行的AOP框架。在Spring2.0以上版本中,可以使用基于AspectJ注解或基于XML配置的AOP。
在 Spring 中使用 AspectJ 进行 AOP 操作
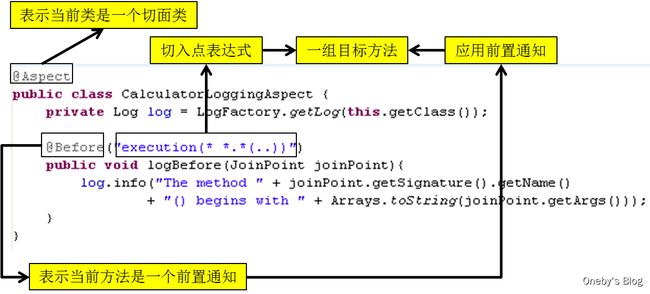
实现 AOP 操作的步骤
编写切面类(通过 @Aspect 注解标识这是一个切面类),并且不要忘记将切面类交给 Spring IOC 管理(Component 注解),并编写相应的通知方法与切入点表达式
在 Spring 配置文件中开启 aop 功能:通过
AspectJ支持5种类型的通知注解
[1]@Before:前置通知,在方法执行之前执行
[2]@After:后置通知,在方法执行之后执行
[3]@AfterRunning:返回通知,在方法返回结果之后执行
[4]@AfterThrowing:异常通知,在方法抛出异常之后执行
[5]@Around:环绕通知,围绕着方法执行
4.3、AOP 细节
准备工作:在 Spring 中使用 AspectJ
引入 maven 依赖:引入 aop 和 aspects 相关的依赖
<!-- spring-aop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-aspects -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aopalliance -->
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliance</groupId>
<artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- cglib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>com.springsource.net.sf.cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
编写 Spring 配置文件:引入 context 和 aop 名称空间;开启组件扫描,并指明包路径;开启自动代理功能
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
ArithmeticCalculator 接口:定义各种数学运算方法
/**
* @ClassName ArithmeticCalculator
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 22:00
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
void add(int i, int j);
void sub(int i, int j);
void mul(int i, int j);
void div(int i, int j);
}
ArithmeticCalculatorImpl 类:实现了 ArithmeticCalculator 接口中各种抽象的数学运算方法
/**
* @ClassName ArithmeticCalculatorImpl
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 22:02
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public void add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
}
切入点表达式的相关细节
切入点的作用:通过表达式的方式定位一个或多个具体的连接点(哪些方法需要被增强)
切入点表达式的语法格式:execution([权限修饰符] [返回值类型] [简单类名/全类名] [方法名]([参数列表]))
切入点表达式的举例一
表达式:execution(* com.atguigu.spring.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义:增强 ArithmeticCalculator 接口中声明的所有方法
解释说明:第一个“*”代表任意修饰符及任意返回值;第二个“*”代表任意方法;“…”匹配任意数量、任意类型的参数
注:若目标类、接口与该切面类在同一个包中可以省略包名
切入点表达式的举例二
表达式:execution(public * ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义: 增强 ArithmeticCalculator 接口的所有公有方法(TMD 接口中的方法不都是 public 吗)
切入点表达式的举例三
表达式:execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义:增强 ArithmeticCalculator 接口中返回double类型数值的方法
切入点表达式的举例四
表达式:execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, ..))
含义:第一个参数为double类型的方法。“…” 匹配任意数量、任意类型的参数
切入点表达式的举例五
表达式: execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, double))
含义:参数类型为double,double类型的方法
切入点表达式的举例六:在AspectJ中,切入点表达式可以通过 “&&”、“||”、“!”等操作符结合起来。
表达式:execution (* *.add(int,..)) || execution(* *.sub(int,..))
含义:任意类中第一个参数为int类型的add方法或sub方法
将切入点表达式应用到实际的切面类中
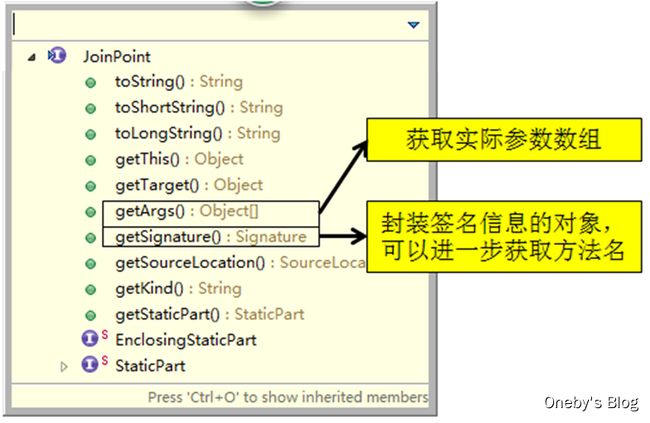
当前连接点的相关细节
切入点表达式通常都会是从宏观上定位一组方法,和具体某个通知的注解结合起来就能够确定对应的连接点。
那么就一个具体的连接点而言,我们可能会关心这个连接点的一些具体信息,例如:当前连接点所在方法的方法名、当前传入的参数值等等。这些信息都封装在JoinPoint接口的实例对象中
五种通知的相关细节
通知的概述
- 在具体的连接点上要执行的操作。
- 一个切面可以包括一个或者多个通知。
- 通知所使用的注解的值往往就是切入点表达式
前置通知
前置通知:在方法执行之前执行的通知,使用@Before注解
后置通知
后置通知:后置通知是在连接点完成之后执行的,即连接点返回结果或者抛出异常的时候,使用@After注解
返回通知
返回通知:无论连接点是正常返回还是抛出异常,后置通知都会执行。如果只想在连接点返回的时候记录日志,应使用返回通知代替后置通知。使用@AfterReturning注解
在返回通知中访问连接点的返回值:
- 在返回通知中,只要将returning属性添加到
@AfterReturning注解中,就可以访问连接点的返回值。该属性的值即为用来传入返回值的参数名称 - 必须在通知方法的签名中添加一个同名参数。在运行时Spring AOP会通过这个参数传递返回值
- 原始的切点表达式需要出现在
pointcut属性中
异常通知
异常通知:只在连接点抛出异常时才执行异常通知
将throwing属性添加到@AfterThrowing注解中,也可以访问连接点抛出的异常。Throwable是所有错误和异常类的顶级父类,所以在异常通知方法可以捕获到任何错误和异常。
如果只对某种特殊的异常类型感兴趣,可以将参数声明为其他异常的参数类型。然后通知就只在抛出这个类型及其子类的异常时才被执行
环绕通知
环绕通知是所有通知类型中功能最为强大的,能够全面地控制连接点,甚至可以控制是否执行连接点。
对于环绕通知来说,连接点的参数类型必须是ProceedingJoinPoint。它是 JoinPoint的子接口,允许控制何时执行,是否执行连接点。
在环绕通知中需要明确调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法来执行被代理的方法。如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了,但目标方法没有被执行。
注意:环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果,即调用 joinPoint.proceed();的返回值,否则会出现空指针异常。
![]()
4.4、AOP 注解方式
准备工作:在 Spring 中使用 AspectJ
引入 maven 依赖:引入 aop 和 aspects 相关的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aopartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.9.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliancegroupId>
<artifactId>aopallianceartifactId>
<version>1.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.cglibgroupId>
<artifactId>com.springsource.net.sf.cglibartifactId>
<version>2.2.0version>
dependency>
编写 Spring 配置文件:引入 context 和 aop 名称空间;开启组件扫描,并指明包路径;开启自动代理功能
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
目标类的定义
ArithmeticCalculator 接口:定义各种数学运算方法
/**
* @ClassName ArithmeticCalculator
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 22:00
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
void add(int i, int j);
void sub(int i, int j);
void mul(int i, int j);
void div(int i, int j);
}
ArithmeticCalculatorImpl 类:实现了 ArithmeticCalculator 接口中各种抽象的数学运算方法
/**
* @ClassName ArithmeticCalculatorImpl
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 22:02
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public void add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
@Override
public void div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("计算器计算得到的结果为: " + result);
}
}
切面类的定义
@Aspect注解标识这是一个切面类@Component注解将这个切面类对象交由 Spring IOC 进行管理execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))表示增强ArithmeticCalculator接口中的所有方法
/**
* @ClassName CalcLoggingAspect
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/22 21:57
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class CalculatorLoggingAspect {
@Before(value = "execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@Before 前置通知");
}
@After(value = "execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@After 后置通知");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@AfterReturning 返回后通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@AfterThrowing 异常通知");
}
@Around(value = "execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("@Around 环绕通知之前");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法
System.out.println("@Around 环绕通知之后");
}
}
代码测试
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop-test.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
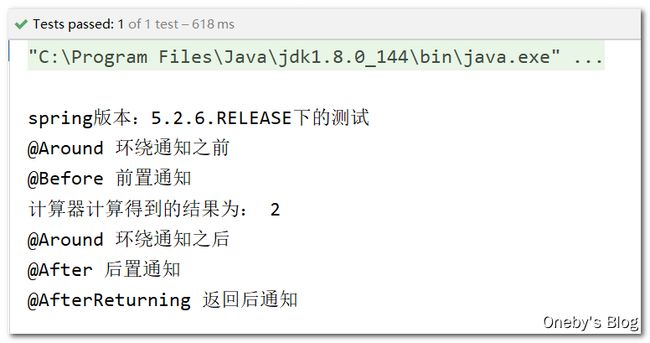
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.add(1, 1);
}
}
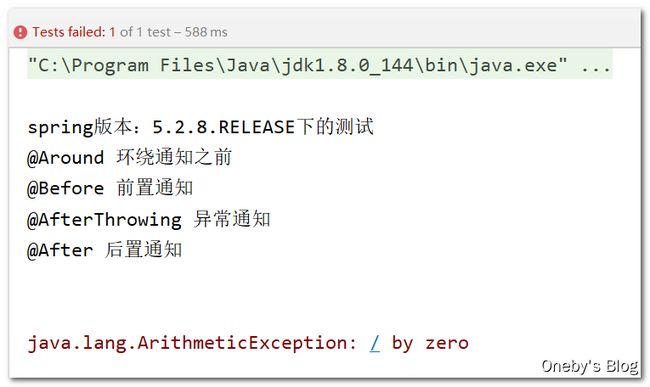
程序运行结果:我嘞个去,之前测试过 Spring 的通知执行顺序:第 4 章 Spring,不是说 Spring5 下的通知改进了吗?已经和 Spring4 下的通知执行顺序不一样了,咋还是和 Spring 的通知顺序一样
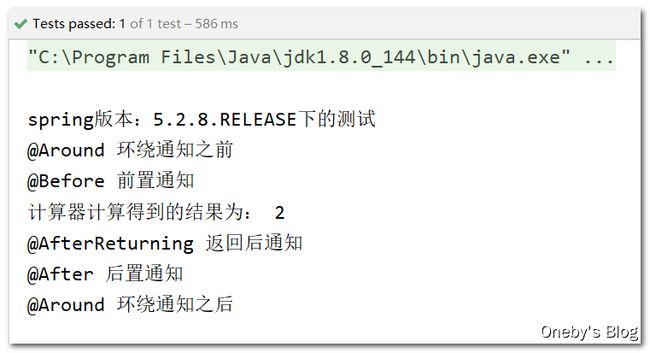
Spring 5.2.8 版本下的测试
还好之前跟着阳哥测试了一波,我将 Spring 版本改为 5.2.8 后,通知的执行顺序就正常啦:环绕通知包裹住其他通知;并且 @Atfer 在 @AfterReturning 之后执行
异常情况下的通知执行顺序
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop-test.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.div(1, 0);
}
}
程序运行结果:首先目标方法没有执行;没有 @AtferReturning 通知,之前 @AtferReturning 通知的地方变为了 @AtferThrowing ;Around 后置环绕通知也没有执行
完全使用注解方式进行 aop 开发
创建 SpringAopConfig 配置类:①@Configuration 表示这是一个配置类;②@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby") 配置包扫描路径为 com.oneby;③@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) 表示开启 AOP 自动代理
/**
* @ClassName SpringAopConfig
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 19:00
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class SpringAopConfig {
}
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringAopConfig.class);
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.div(1, 0);
}
}
程序运行结果
![]()
4.5、AOP 进阶操作
重用切入点定义
在编写AspectJ切面时,可以直接在通知注解中书写切入点表达式。但同一个切点表达式可能会在多个通知中重复出现。
在AspectJ切面中,可以通过@Pointcut注解将一个切入点声明成简单的方法。切入点的方法体通常是空的。
切入点方法的访问控制符同时也控制着这个切入点的可见性。如果切入点要在多个切面中共用,最好将它们集中在一个公共的类中。在这种情况下,它们必须被声明为public。在引入这个切入点时,必须将类名也包括在内。如果类没有与这个切面放在同一个包中,还必须包含包名。
其他通知可以通过方法名称引入该切入点
指定切面的优先级
在同一个连接点上应用不止一个切面时,除非明确指定,否则它们的优先级是不确定的。
切面的优先级可以通过实现Ordered接口或利用@Order注解指定。
实现Ordered接口,getOrder()方法的返回值越小,优先级越高。
若使用@Order注解,序号出现在注解中
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(0)
public class CalculatorValidationAspect {
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class CalculatorLoggingAspect {
4.6、AOP XML 方式
XML 配置概述
除了使用AspectJ注解声明切面,Spring也支持在bean配置文件中声明切面。这种声明是通过aop名称空间中的XML元素完成的。
正常情况下,基于注解的声明要优先于基于XML的声明。通过AspectJ注解,切面可以与AspectJ兼容,而基于XML的配置则是Spring专有的。由于AspectJ得到越来越多的 AOP框架支持,因此以注解风格编写的切面将会有更多重用的机会。
XML 配置细节
配置切面
在bean配置文件中,所有的Spring AOP配置都必须定义在
![]()
声明切入点
- 切入点使用
- 切入点必须定义在
- 定义在
- 定义在
- 基于XML的AOP配置不允许在切入点表达式中用名称引用其他切入点。
![]()
声明通知
- 在aop名称空间中,每种通知类型都对应一个特定的XML元素。
- 通知元素需要使用
method属性指定切面类中通知方法的名称
XML 配置细节
XML 配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="arithmeticCalculatorImpl" class="com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl"/>
<bean id="calculatorLoggingAspect" class="com.oneby.calc.CalculatorLoggingAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="calcPointcut" expression="execution(* com.oneby.calc.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="calculatorLoggingAspect">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="calcPointcut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="calcPointcut"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="calcPointcut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="calcPointcut"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="calcPointcut"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop-test.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.div(1, 0);
}
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringAopConfig.class);
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.div(1, 0);
}
@Test
public void testXml() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop-complete-xml.xml");
//2.根据id值获取bean实例对象
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = iocContainer.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3.调用bean中的方法
System.out.println("spring版本:" + SpringVersion.getVersion() + "下的测试");
arithmeticCalculator.div(1, 0);
}
}
程序运行结果
5、JdbcTemplate
5.1、概述
JDBC 概述
为了使JDBC更加易于使用,Spring在JDBC API上定义了一个抽象层,以此建立一个JDBC存取框架。
作为Spring JDBC框架的核心,JDBC模板的设计目的是为不同类型的JDBC操作提供模板方法,通过这种方式,可以在尽可能保留灵活性的情况下,将数据库存取的工作量降到最低。
可以将Spring的JdbcTemplate看作是一个小型的轻量级持久化层框架,和我们之前使用过的DBUtils风格非常接近。
5.2、环境准备
引入依赖
引入 jdbc 和 mysql 的相关依赖
<!-- spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-tx -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-orm -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.8</version>
</dependency>
编写配置文件
将数据库连接信息抽取到 jdbc.properties 配置文件中
prop.userName=root
prop.password=root
prop.url=jdbc:mysql:///test
prop.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Spring 配置文件
- 因为我们会用到
@Repository、@Service、@Controller之类的注解向 IOC 容器注入 bean 实例,因此需要开启组件扫描 - 使用
username、用户密码password、数据库连接地址url、驱动类名driverClassName - 使用
JdbcTemplate对象进行持久化操作,需要为其注入数据源dataSource
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"/>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"/>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"/>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
准备数据库表
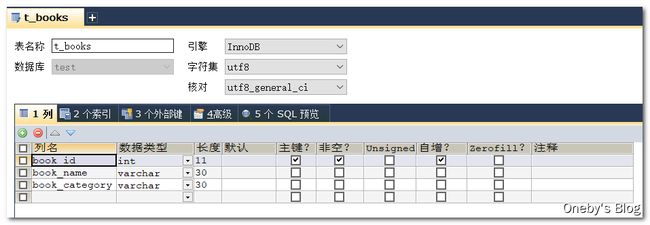
book_id 为图书编号,交由数据库维护;book_name 为书名;book_category 为书籍所属类别
创建实体类
Book 实体类
/**
* @ClassName Book
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 20:27
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Book {
private Integer bookId;
private String bookName;
private String bookCategory;
public Book() {
}
public Book(String bookName, String bookCategory) {
this.bookName = bookName;
this.bookCategory = bookCategory;
}
public Book(Integer bookId, String bookName, String bookCategory) {
this.bookId = bookId;
this.bookName = bookName;
this.bookCategory = bookCategory;
}
public Integer getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(Integer bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getBookCategory() {
return bookCategory;
}
public void setBookCategory(String bookCategory) {
this.bookCategory = bookCategory;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"bookId=" + bookId +
", bookName='" + bookName + '\'' +
", bookCategory='" + bookCategory + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
5.3、持久化操作
增删改
增删改用这个函数:public int update(String sql, @Nullable Object... args) throws DataAccessException,通过 sql 指明要执行的 SQL 语句,并通过可变长参数 args 指明 SQL 语句的参数
查询某个值或对象(查询单行)
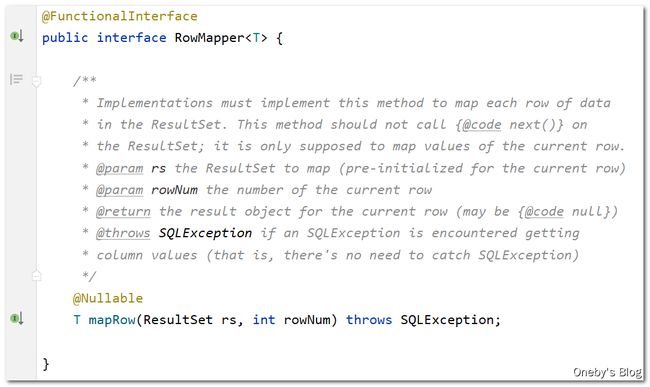
查询某个值或对象用这个函数:public ,通过 sql 指明要执行的 SQL 语句,通过 RowMapper 对象指明从数据库查询出来的参数应该如何封装到指定的对象中,并通过可变长参数 args 指明 SQL 语句的参数
RowMapper 接口
RowMapper 接口是一个函数式接口,其中只有一个方法:T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException,该方法的具体作用是将查询得到的每行数据映射到 ResultSet 中
BeanPropertyRowMapper 类
BeanPropertyRowMapper 类实现了 RowMapper 接口,其功能是:将查询得到的结果集的值,注入到对象属性中
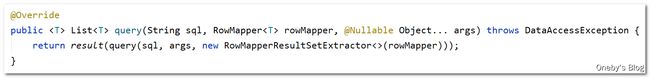
查询对象集合(查询多行)
查询对象集合使用这个函数:public ,通过 sql 指明要执行的 SQL 语句,通过 RowMapper 对象指明从数据库查询出来的参数应该如何封装到指定的对象中,并通过可变长参数 args 指明 SQL 语句的参数
批量操作
批量操作包括批量增加、批量更新、批量删除操作,这些操作都可以使用 public int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List 函数完成:通过 sql 指明要执行的 SQL 语句,并通过参数 batchArgs 指明批处理 SQL 语句的参数
5.4、持久化代码
使用
JdbcTemplate操作数据库,进行持久化操作
BookDao 接口的定义
/**
* @ClassName BookDao
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 20:24
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface BookDao {
// 添加一本图书
public int addBook(Book book);
// 删除一本图书
public int deleteBook(String bookId);
// 更新一本图书的信息
public int updateBook(Book book);
// 查询一本图书
public Book findBookInfo(int bookId);
// 查询所有图书的数量
public int findBookCount();
// 查询所有图书的集合
public List<Book> findAllBookInfo();
// 批量添加图书
public int[] batchAddBook(List<Book> books);
// 批量修改图书信息
public int[] batchUpdateBook(List<Book> books);
// 批量删除图书
public int[] batchDeleteBook(List<Integer> bookId);
}
BookDaoImpl 实现类的定义
- 增删改使用
update()方法 - 查询某个值或对象
queryForObject()方法 - 查询对象集合使用
query()方法 - 批量处理使用
batchUpdate()方法
/**
* @ClassName BookDaoImpl
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 20:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
// 注入 JdbcTemplate 对象
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public int addBook(Book book) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "insert into t_books (book_name, book_category) values (?, ?) ";
// SQL 语句参数
Object[] args = {book.getBookName(), book.getBookCategory()};
// 执行 SQL 语句
int insertRows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
return insertRows;
}
@Override
public int deleteBook(String bookId) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "delete from t_books where book_id = ?";
// 执行 SQL 语句
int deleteRows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, bookId);
return deleteRows;
}
@Override
public int updateBook(Book book) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "update t_books set book_name = ?, book_category = ? where book_id = ?";
// SQL 语句参数
Object[] args = {book.getBookName(), book.getBookCategory(), book.getBookId()};
// 执行 SQL 语句
int insertRows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
return insertRows;
}
@Override
public Book findBookInfo(int bookId) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "select * from t_books where book_id = ?";
// 执行 SQL 语句
Book book = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Book.class), bookId);
return book;
}
@Override
public int findBookCount() {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "select count(*) from t_books";
// 执行 SQL 语句
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
return count;
}
@Override
public List<Book> findAllBookInfo() {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "select * from t_books";
// 执行 SQL 语句
List<Book> books = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class));
return books;
}
@Override
public int[] batchAddBook(List<Book> books) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "insert into t_book (book_name, book_category) values (?, ?)";
// 构造参数
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
for (Book book : books) {
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{book.getBookName(), book.getBookCategory()});
}
// 批量执行
int[] batchAffectedRows = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
return batchAffectedRows;
}
@Override
public int[] batchUpdateBook(List<Book> books) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "update t_books set book_name = ?, book_category = ? where book_id = ?";
// 构造参数
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
for (Book book : books) {
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{book.getBookName(), book.getBookCategory(), book.getBookId()});
}
// 批量执行
int[] batchAffectedRows = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
return batchAffectedRows;
}
@Override
public int[] batchDeleteBook(List<Integer> bookIds) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "delete from t_books where book_id = ?";
// 构造参数
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer bookId : bookIds) {
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{bookId});
}
// 批量执行
int[] batchAffectedRows = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
return batchAffectedRows;
}
}
6、声明式事务管理
6.1、事务概述
事务概述与其 ACID 属性
在JavaEE企业级开发的应用领域,为了保证数据的完整性和一致性,必须引入数据库事务的概念,所以事务管理是企业级应用程序开发中必不可少的技术。
事务就是一组由于逻辑上紧密关联而合并成一个整体(工作单元)的多个数据库操作,这些操作要么都执行,要么都不执行。
事务的四个关键属性(ACID)
原子性(atomicity):“原子”的本意是“不可再分”,事务的原子性表现为一个事务中涉及到的多个操作在逻辑上缺一不可。事务的原子性要求事务中的所有操作要么都执行,要么都不执行。
一致性(consistency):“一致”指的是数据的一致,具体是指:所有数据都处于满足业务规则的一致性状态。一致性原则要求:一个事务中不管涉及到多少个操作,都必须保证事务执行之前数据是正确的,事务执行之后数据仍然是正确的。如果一个事务在执行的过程中,其中某一个或某几个操作失败了,则必须将其他所有操作撤销,将数据恢复到事务执行之前的状态,这就是回滚。
隔离性(isolation):在应用程序实际运行过程中,事务往往是并发执行的,所以很有可能有许多事务同时处理相同的数据,因此每个事务都应该与其他事务隔离开来,防止数据损坏。隔离性原则要求多个事务在并发执行过程中不会互相干扰。
持久性(durability):持久性原则要求事务执行完成后,对数据的修改永久的保存下来,不会因各种系统错误或其他意外情况而受到影响。通常情况下,事务对数据的修改应该被写入到持久化存储器中。
6.2、Spring 事务管理
之前的方式:编程式事务管理
使用原生的JDBC API进行事务管理
- 获取数据库连接Connection对象
- 取消事务的自动提交
- 执行操作
- 正常完成操作时手动提交事务
- 执行失败时回滚事务
- 关闭相关资源
编程式事务管理的缺点
使用原生的JDBC API实现事务管理是所有事务管理方式的基石,同时也是最典型的编程式事务管理。编程式事务管理需要将事务管理代码嵌入到业务方法中来控制事务的提交和回滚。在使用编程的方式管理事务时,必须在每个事务操作中包含额外的事务管理代码。相对于核心业务而言,事务管理的代码显然属于非核心业务,如果多个模块都使用同样模式的代码进行事务管理,显然会造成较大程度的代码冗余
现在的方式:声明式事务管理
大多数情况下声明式事务比编程式事务管理更好:它将事务管理代码从业务方法中分离出来,以声明的方式来实现事务管理。
事务管理代码的固定模式作为一种横切关注点,可以通过AOP方法模块化,进而借助Spring AOP框架实现声明式事务管理。
Spring在不同的事务管理API之上定义了一个抽象层,通过配置的方式使其生效,从而让应用程序开发人员不必了解事务管理API的底层实现细节,就可以使用Spring的事务管理机制。
Spring既支持编程式事务管理,也支持声明式的事务管理。
Spring提供的事务管理器
Spring从不同的事务管理API中抽象出了一整套事务管理机制,让事务管理代码从特定的事务技术中独立出来。开发人员通过配置的方式进行事务管理,而不必了解其底层是如何实现的。
Spring的核心事务管理抽象是PlatformTransactionManager。它为事务管理封装了一组独立于技术的方法。无论使用Spring的哪种事务管理策略(编程式或声明式),事务管理器都是必须的。
事务管理器可以以普通的bean的形式声明在Spring IOC容器中。
事务管理器的主要实现
① DataSourceTransactionManager:在应用程序中只需要处理一个数据源,而且通过JDBC存取。
② JtaTransactionManager:在JavaEE应用服务器上用JTA(Java Transaction API)进行事务管理
③ HibernateTransactionManager:用Hibernate框架存取数据库
![]()
6.3、事务代码示例
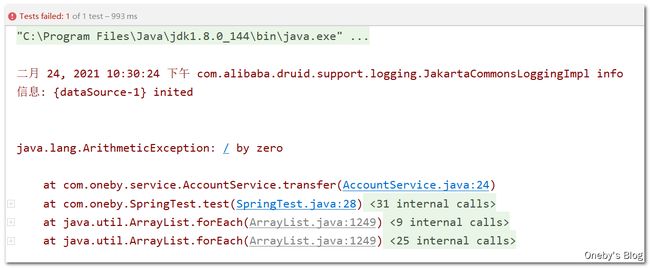
引入依赖
依赖见上节
准备数据库表
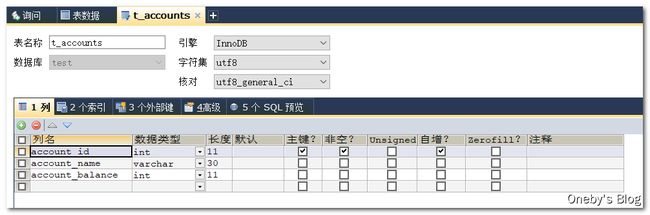
account_id 为账户 id,交由数据库维护;account_name 为账户名称;account_balance 为账户余额
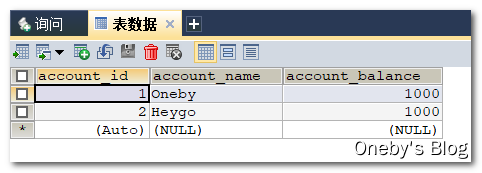
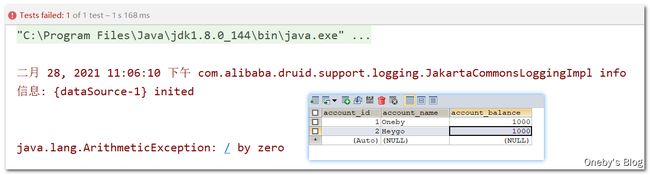
数据库初始数据:Oneby 和 Heygo 分别由 1000 大洋
编写实体类
创建与数据库表对应的实体类
/**
* @ClassName Account
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 23:51
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Account {
private Integer accountId;
private String accountName;
private Integer accountBalance;
public Integer getAccountId() {
return accountId;
}
public void setAccountId(Integer accountId) {
this.accountId = accountId;
}
public String getAccountName() {
return accountName;
}
public void setAccountName(String accountName) {
this.accountName = accountName;
}
public Integer getAccountBalance() {
return accountBalance;
}
public void setAccountBalance(Integer accountBalance) {
this.accountBalance = accountBalance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"accountId=" + accountId +
", accountName='" + accountName + '\'' +
", accountBalance=" + accountBalance +
'}';
}
}
编写配置文件
- 需要在 Spring 配置文件中引入
context名称空间和tx名称空间 - 注意:事务管理器的名字一定要叫
transactionManager,不然会抛异常:org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No bean named 'transactionManager' available: No matching TransactionManager bean found for qualifier 'transactionManager' - neither qualifier match nor bean name match! - 最后记得要使用
@Transactional注解)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"/>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"/>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"/>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
beans>
编写 DAO 层
AccountDao 接口
/**
* @ClassName AccountDao
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 23:56
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface AccountDao {
public int tranfer(String accountName, int money);
}
AccountDaoImpl 实现类:从名为 accountName 的账户中转走 money 元大洋
/**
* @ClassName AccountDaoImpl
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/23 23:58
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
// 注入 JdbcTemplate 对象
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public int tranfer(String accountName, int money) {
// 创建 SQL 语句
String sql = "update t_accounts set account_balance = account_balance - ? where account_name = ?";
// SQL 语句参数
Object[] args = {money, accountName};
// 执行 SQL 语句
int insertRows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
return insertRows;
}
}
编写 Service 层:没有添加事务
AccountService 类:从名为 srcAccountName 的账户转钱到名为 destAccountName 的账户,转账金额为 money 元大洋,但是在两个转账操作中间手动制造了一个异常
/**
* @ClassName AccountService
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/24 21:03
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(String srcAccountName, String destAccountName, int money) {
accountDao.tranfer(srcAccountName, money);
int i = 10 / 0; // 手动制造异常
accountDao.tranfer(destAccountName, -money);
System.out.println(srcAccountName + " 向 " + destAccountName + " 转账 " + money + " 元");
}
}
测试代码:Heygo 给 Oneby 转账 1000 大洋
/**
* @ClassName com.com.oneby.SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("transaction-test.xml");
//2.获取AccountService对象
AccountService accountService = iocContainer.getBean(AccountService.class);
//3.执行数据库操作
accountService.transfer("Heygo", "Oneby", 100);
}
}
程序抛出异常
Heygo 账户莫名其妙少了 100 块钱
![]()
编写 Service 层:添加声明式事务
AccountService 类:也没啥,就加了一个 @Transactional 注解,表示为 AccountService 类中的所有方法都开启事务控制
/**
* @ClassName AccountService
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/24 21:03
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Service
@Transactional
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(String srcAccountName, String destAccountName, int money) {
accountDao.tranfer(srcAccountName, money);
int i = 10 / 0; // 手动制造异常
accountDao.tranfer(destAccountName, -money);
System.out.println(srcAccountName + " 向 " + destAccountName + " 转账 " + money + " 元");
}
}
程序抛出异常
![]()
Oneby 账户和 Heygo 账户余额都没有改变呢
6.4、事务相关参数
6.4.1、事务传播行为
事务的传播行为概述
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播。例如:方法可能继续在现有事务中运行,也可能已经开启了一个新事务。事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定。Spring定义了7种类传播行为
REQUIRED 和 REQUIRES_NEW 传播行为
测试环境
REQUIRED 传播行为
当bookService的purchase()方法被另一个事务方法checkout()调用时,它默认会在现有的事务内运行。这个默认的传播行为就是REQUIRED。因此在checkout()方法的开始和终止边界内只有一个事务。这个事务只在checkout()方法结束的时候被提交,结果用户一本书都买不了
REQUIRES_NEW 传播行为
表示该方法必须启动一个新事务,并在自己的事务内运行。如果有事务在运行,就应该先挂起它
Spring 中配置事务的传播行为
1、注解方式
事务传播属性可以在@Transactional注解的propagation属性中定义
2、XML 方式
通过 propagation 属性设置事务的传播行为
6.4.2、事务隔离级别
数据库事务并发问题
假设现在有两个事务:Transaction01和Transaction02并发执行。
① 脏读
[1]Transaction01将某条记录的AGE值从20修改为30。
[2]Transaction02读取了Transaction01更新后的值:30。
[3]Transaction01回滚,AGE值恢复到了20。
[4]Transaction02读取到的30就是一个无效的值。
② 不可重复读
[1]Transaction01读取了AGE值为20。
[2]Transaction02将AGE值修改为30。
[3]Transaction01再次读取AGE值为30,和第一次读取不一致。
③ 幻读
[1]Transaction01读取了STUDENT表中的一部分数据。
[2]Transaction02向STUDENT表中插入了新的行。
[3]Transaction01读取了STUDENT表时,多出了一些行。
数据库的隔离级别
数据库系统必须具有隔离并发运行各个事务的能力,使它们不会相互影响,避免各种并发问题。一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为隔离级别。SQL标准中规定了多种事务隔离级别,不同隔离级别对应不同的干扰程度,隔离级别越高,数据一致性就越好,但并发性越弱。
①读未提交:READ UNCOMMITTED,允许Transaction01读取Transaction02未提交的修改。
②读已提交:READ COMMITTED,要求Transaction01只能读取Transaction02已提交的修改。
③可重复读:REPEATABLE READ,确保Transaction01可以多次从一个字段中读取到相同的值,即Transaction01执行期间禁止其它事务对这个字段进行更新。
④串行化:SERIALIZABLE,确保Transaction01可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在Transaction01执行期间,禁止其它事务对这个表进行添加、更新、删除操作。可以避免任何并发问题,但性能十分低下。
各个隔离级别解决并发问题的能力见下表
| 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| READ COMMITTED | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| REPEATABLE READ | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 无 | 无 | 无 |
各种数据库产品对事务隔离级别的支持程度
| Oracle | MySQL | |
|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED | × | √ |
| READ COMMITTED | √ | √ |
| REPEATABLE READ | × | √(默认) |
| SERIALIZABLE | √ | √ |
在Spring中指定事务隔离级别
1、注解方式
可以在@Transactional的isolation属性中设置隔离事务的级别
2、XML 方式
通过 isolation 属性设置传播事务的隔离级别
6.4.3、事务是否回滚
事务回滚的默认触发条件
捕获到RuntimeException或Error时回滚,而捕获到编译时异常不回滚。
在Spring中设置事务的回滚
1、注解方式:@Transactional 注解
[1]rollbackFor属性:指定遇到时必须进行回滚的异常类型,可以为多个
[2]noRollbackFor属性:指定遇到时不回滚的异常类型,可以为多个
2、XML 方式
通过 rollback-for 和 no-rollback-for 属性设置事务的回滚
![]()
6.4.4、事务超时时间
超时事务属性
超时事务属性:事务在强制回滚之前可以保持多久。这样可以防止长期运行的事务占用资源。
在Spring中设置事务的超时时间
1、注解方式:
通过 @Transactional 注解的 timeout 属性设置事务的超时时间,单位为 s
2、XML 方式
通过 timeout 属性设置事务的超时时间,单位为 s
![]()
6.4.5、事务只读属性
事务的优化:事务的只读属性
由于事务可以在行和表上获得锁,因此长事务会占用资源,并对整体性能产生影响。如果一个事物只读取数据但不做修改,数据库引擎可以对这个事务进行优化。
只读事务属性:表示这个事务只读取数据但不更新数据, 这样可以帮助数据库引擎优化事务。
在Spring中设置事务的只读属性
1、注解方式
通过 @Transactional 注解的 readOnly 属性设置事务是否只读
2、XML 方式
通过 read-only 属性设置事务是否只读
6.5、完全注解开发
创建 Spring 配置类
@Configuration标识这是一个配置类;@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby")配置包扫描路径;@EnableTransactionManagement开启注解事务管理;@PropertySource(value = "classpath:jdbc.properties")标识 properties 配置文件的路径- 使用
@Value注解读取 jdbc.properties 配置文件中的内容,并用于配置数据库连接池DataSource - 后面配置
JdbcTemplate和DataSourceTransactionManager都需要向其指定属性中注入DataSource对象
/**
* @ClassName TransactionConfig
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/24 22:39
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.oneby")
@EnableTransactionManagement
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class TransactionConfig {
@Value("${prop.userName}")
private String userName;
@Value("${prop.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${prop.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${prop.driverClass}")
private String driverClass;
// 数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
// 创建 JdbcTemplate 对象
// DataSource:IOC 容器会自动为我们注入类型为 DataSource 的 bean
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
// 创建事务管理器
// DataSource:IOC 容器会自动为我们注入类型为 DataSource 的 bean
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
代码测试
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName com.com.oneby.SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TransactionConfig.class);
//2.获取AccountService对象
AccountService accountService = iocContainer.getBean(AccountService.class);
//3.执行数据库操作
accountService.transfer("Heygo", "Oneby", 100);
}
}
程序执行抛出异常
![]()
转账操作未成功,Oneby 和 Heygo 账户中的前分文未动,证明声明式事务配置成功
![]()
6.6、XML 事务管理
XML 事务管理的配置文件
XML 方式配置事务就三步:① 配置切入点表达式;② 配置通知与事务参数;③ 将切入点表达式与通知联系起来
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.oneby"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"/>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"/>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"/>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointCut" expression="execution(* com.oneby.service.AccountService.*(..))"/>
aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut"/>
aop:config>
beans>
测试代码
/**
* @ClassName com.com.oneby.SpringTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author Oneby
* @Date 2021/2/13 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//1.创建IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainer =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xml-transaction-config.xml");
//2.获取AccountService对象
AccountService accountService = iocContainer.getBean(AccountService.class);
//3.执行数据库操作
accountService.transfer("Heygo", "Oneby", 100);
}
}
程序运行结果:程序运行后抛出异常,但 Oneby 和 Heygo 账户的余额一分不少,一分不多