SpringBoot Spring Security 核心组件 认证流程 用户权限信息获取详细讲解
前言
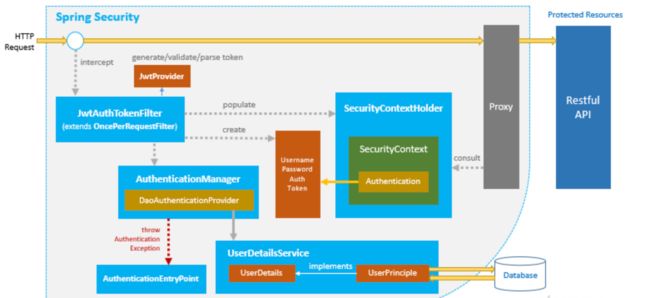
Spring Security 是一个安全框架, 可以简单地认为 Spring Security 是放在用户和 Spring 应用之间的一个安全屏障, 每一个 web 请求都先要经过 Spring Security 进行 Authenticate 和 Authoration 验证
核心组件
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder它持有的是安全上下文(security context)的信息。当前操作的用户是谁,该用户是否已经被认证,他拥有哪些角色权等等,这些都被保存在SecurityContextHolder中。SecurityContextHolder默认使用ThreadLocal 策略来存储认证信息。看到ThreadLocal 也就意味着,这是一种与线程绑定的策略。在web环境下,Spring Security在用户登录时自动绑定认证信息到当前线程,在用户退出时,自动清除当前线程的认证信息
看源码他有静态方法
//获取 上下文
public static SecurityContext getContext() {
return strategy.getContext();
}
//清除上下文
public static void clearContext() {
strategy.clearContext();
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal()
getAuthentication()返回了认证信息,getPrincipal()返回了身份信息
UserDetails便是Spring对身份信息封装的一个接口
SecurityContext
安全上下文,主要持有Authentication对象,如果用户未鉴权,那Authentication对象将会是空的。看源码可知
package org.springframework.security.core.context;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
Authentication getAuthentication();
void setAuthentication(Authentication var1);
}
Authentication
鉴权对象,该对象主要包含了用户的详细信息(UserDetails)和用户鉴权时所需要的信息,如用户提交的用户名密码、Remember-me Token,或者digest hash值等,按不同鉴权方式使用不同的Authentication实现
看源码可知道
package org.springframework.security.core;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Collection;
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean var1) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
-
Authentication是spring security包中的接口,直接继承自Principal类,而Principal是位于java.security包中的。可以见得,Authentication在spring security中是最高级别的身份/认证的抽象。由这个顶级接口,我们可以得到用户拥有的权限信息列表,密码,用户细节信息,用户身份信息,认证信息。 -
getAuthorities(),权限信息列表,默认是GrantedAuthority接口的一些实现类,通常是代表权限信息的一系列字符串。 -
getCredentials(),密码信息,用户输入的密码字符串,在认证过后通常会被移除,用于保障安全。 -
getDetails(),细节信息,web应用中的实现接口通常为 WebAuthenticationDetails,它记录了访问者的ip地址和sessionId的值。 -
getPrincipal(),敲黑板!!!最重要的身份信息,大部分情况下返回的是UserDetails接口的实现类,也是框架中的常用接口之一
注意
GrantedAuthority该接口表示了当前用户所拥有的权限(或者角色)信息。这些信息由授权负责对象AccessDecisionManager来使用,并决定最终用户是否可以访问某资源(URL或方法调用或域对象)。鉴权时并不会使用到该对象
UserDetails
这个接口规范了用户详细信息所拥有的字段,譬如用户名、密码、账号是否过期、是否锁定等。在Spring Security中,获取当前登录的用户的信息,一般情况是需要在这个接口上面进行扩展,用来对接自己系统的用户
看源码可知
package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
UserDetailsService
这个接口只提供一个接口loadUserByUsername(String username),这个接口非常重要,一般情况我们都是通过扩展这个接口来显示获取我们的用户信息,用户登陆时传递的用户名和密码也是通过这里这查找出来的用户名和密码进行校验,但是真正的校验不在这里,而是由AuthenticationManager以及AuthenticationProvider负责的,需要强调的是,如果用户不存在,不应返回NULL,而要抛出异常UsernameNotFoundException
看源码可知
package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String var1) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
Spring Security安全身份认证流程原理
-
用户名和密码被过滤器获取到,封装成
Authentication,通常情况下是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken这个实现类。 -
AuthenticationManager身份管理器负责验证这个Authentication -
认证成功后,
AuthenticationManager身份管理器返回一个被填充满了信息的(包括上面提到的权限信息,身份信息,细节信息,但密码通常会被移除)Authentication实例。 -
SecurityContextHolder安全上下文容器将第3步填充了信息的Authentication,通过SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication()方法,设置到其中。
AuthenticationManager
初次接触Spring Security的朋友相信会被AuthenticationManager,ProviderManager ,AuthenticationProvider …这么多相似的Spring认证类搞得晕头转向,但只要稍微梳理一下就可以理解清楚它们的联系和设计者的用意。
AuthenticationManager(接口)是认证相关的核心接口,也是发起认证的出发点,因为在实际需求中,我们可能会允许用户使用用户名+密码登录,同时允许用户使用邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录,甚至,可能允许用户使用指纹登录(还有这样的操作?没想到吧),所以说AuthenticationManager一般不直接认证,
AuthenticationManager接口的常用实现类ProviderManager 内部会维护一个List列表,存放多种认证方式,实际上这是委托者模式的应用(Delegate)。
也就是说,核心的认证入口始终只有一个:AuthenticationManager,不同的认证方式:用户名+密码(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken),邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录则对应了三个AuthenticationProvider。这样一来就好理解多了
UserDetails和UserDetailsService
UserDetails
上面不断提到了UserDetails这个接口,它代表了最详细的用户信息,这个接口涵盖了一些必要的用户信息字段,我们一般都需要对它进行必要的扩展。
它和Authentication接口很类似,比如它们都拥有username,authorities,区分他们也是本文的重点内容之一。
Authentication的getCredentials()与UserDetails中的getPassword()需要被区分对待,前者是用户提交的密码凭证,后者是用户正确的密码,认证器其实就是对这两者的比对。Authentication中的getAuthorities()实际是由UserDetails的getAuthorities()传递而形成的。还记得Authentication接口中的getUserDetails()方法吗?其中的UserDetails用户详细信息便是经过了AuthenticationProvider之后被填充的。
UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService和AuthenticationProvider两者的职责常常被人们搞混,UserDetailsService只负责从特定的地方加载用户信息,可以是数据库、redis缓存、接口等
全局获取用户信息方式
- 通过注入 Principal 接口获取用户信息
在运行过程中,Spring 会将 Username、Password、Authentication、Token 注入到 Principal 接口中,我们可以直接在controller获取使用
@GetMapping("/home")
@ApiOperation("用户中心")
public Result getUserHome(Principal principal) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken=(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)principal;
return ResultResponse.success(usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.getPrincipal());
}
- 使用 @AuthenticationPrincipal 注解参数的方式
@GetMapping("/home")
@ApiOperation("用户中心")
public Result getUserHome(@AuthenticationPrincipal cn.soboys.kmall.security.entity.User user ) {
return ResultResponse.success(user);
}
- 全局上下文获取
由于获取当前用户的用户名是一种比较常见的需求,其实 Spring Security 在 Authentication 中的实现类中已经为我们做了相关实现,所以获取当前用户的用户名有如下更简单的方式
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "当前登录用户:" + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName();
}
}
- 获取当前登录用户的 UserDetails 实例,然后再转换成自定义的用户实体类 User,这样便能获取用户的 ID 等信息
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
User user = (User)principal;
return "当前登录用户信息:" + user.toString();
}
}
- 异步方法中获取用户信息
Spring Security在默认情况下无法在使用@Async注解的方法中获取当前登录用户的。若想在@Async方法中获取当前登录用户,则需要调用SecurityContextHolder.setStrategyName方法并设置相关的策略
参考
- Spring Security在@Async异步方法中获取登录用户
- Spring Security