Pandas之Series和DateFrame详解
文章目录
- 1. 什么是Pandas?
- 2. 为什么要学习pandas
- 3. Series
-
- 3.1 Series的创建
-
- 3.1.1 通过列表或者一维数组创建
- 3.1.2 通过字典创建
- 3.2 Series的基本用法
- 4. DataFrame
-
- 4.1 DateFrame构建
-
- 4.1.1 字典类
-
- 1. 数组、列表或元组构成的字典构造dataframe
- 2. Series构成的字典构造dataframe
- 3. 字典构成的字典构造dataframe
- 4.1.2 列表类
-
- 1. ndarray 构造dataframe
- 2. 字典构成的列表构造dataframe
- 3. Series构成的列表构造dataframe
- 4.2 DataFrame的基本用法
-
- 4.2.1 .T转置
- 4.2.2 通过列索引获取列数据(Series类型)
- 4.2.3 增加列数据
- 4.2.4 删除列
- 4.3 DataFrame索引操作
- 4.4 DataFrame的切片操作
1. 什么是Pandas?
Pandas的名称来自于面板数据(panel data)
Pandas是一个强大的分析结构化数据的工具集,基于NumPy构建,提供了高级数据结构和数据操作工具,它是使Python成为强大而高效的数据分析环境的重要因素之一。
Pandas有以下几个特点:
- 是一个强大的分析和操作大型结构化数据集所需的工具集
- 基础是NumPy,提供了高性能矩阵的运算
- 提供了大量能够快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法
- 应用于数据挖掘,数据分析
- 提供数据清洗功能
2. 为什么要学习pandas
numpy已经能够帮助我们处理数据,能够结合matplotlib解决我们数据分析的问题,那么pandas学习的目的在什么地方呢?
numpy能够帮我们处理处理数值型数据,但是这还不够,很多时候,我们的数据除了数值之外,还有字符串,还有时间序列等。比如:我们通过爬虫获取到了存储在数据库中的数据,所以,pandas出现了。
pandas官网
首先先来认识pandas中的两个常用的类
-
- Series
-
- DataFrame
3. Series
3.1 Series的创建
Series是一个一维的结构
创建Series的语法:pd.Series();
常用的几个参数:
- index,用于指定新的索引,
例如pd.Series(arr1,index=[‘a’,‘b’,‘c’,‘d’,‘e’])以a,b,c,d,e作为行索引;- dtype,用于指定元素的数据类型;
3.1.1 通过列表或者一维数组创建
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 1. 通过list创建
s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5])
print(s1)
'''
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
dtype: int64
'''
# 2. 通过一维数组创建
x = np.arange(1,6)
s2 = pd.Series(x)
print(s2)
'''
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
dtype: int32
'''
3.1.2 通过字典创建
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':'李剑神','age':18,'class':'雪中一班'}
s3 = pd.Series(dict)
print(s3)
'''
name 李剑神
age 18
class 雪中一班
dtype: object
'''
# 也可以指定索引,索引和字典键相同才有效,否则默认为NaN
s4 = pd.Series(dict,index = ['name','age','class','sex'])
print(s4)
'''
name 李剑神
age 18
class 雪中一班
sex NaN
dtype: object
'''
3.2 Series的基本用法
Series的常用属性:
- shape 返回形状
- size 返回元素个数
- index 返回索引值
- values 返回值
- dtype 元素的类型
用法示例:
from pandas import Series
s = Series(data=[1,2,3,'four'],index=['a','b','c','d'])
print(s.dtype) # object
- Series和DataFrame中的索引都是Index对象
- 索引对象不可变,保证了数据的安全。
- 常见的Index种类:
Index,索引
Int64Index,整数索引
MultiIndex,层级索引
DatetimeIndex,时间戳类型
import pandas as pd
dic = {'name':'李剑神','age':18,'class':'雪中一班'}
s = pd.Series(dic)
print(s)
print('*'*20)
print(s[0])
print('-'*20)
print(s.age)
print('='*20)
print(s[0:2])
'''
name 李剑神
age 18
class 雪中一班
dtype: object
********************
李剑神
--------------------
18
====================
name 李剑神
age 18
dtype: object
'''
Series的常用方法:
- head(),tail()
- unique()
- isnull(),notnull()
- add() sub() mul() div()
import numpy as np
from pandas import Series
s = Series(data=np.random.randint(10,50,size=(10,)))
print(s)
print('-'*20)
print(s.head(3)) # 显示前3个数据
print('*'* 20)
print(s.tail(3)) # 显示后3个元素
print('='*20)
print(s.unique()) # 去重
print('#'*20)
print(s.isnull()) #用于判断每一个元素是否为空,为空返回True,否则返回False,notnull()与之相反
'''
0 24
1 11
2 37
3 32
4 43
5 16
6 38
7 22
8 40
9 44
dtype: int32
--------------------
0 24
1 11
2 37
dtype: int32
********************
7 22
8 40
9 44
dtype: int32
====================
[24 11 37 32 43 16 38 22 40 44]
####################
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 False
4 False
5 False
6 False
7 False
8 False
9 False
dtype: bool
'''
Series的算术运算:
法则:索引一致的元素进行算数运算否则补空
import numpy as np
from pandas import Series
s1 = Series(data=[1,2,3],index=['a','b','c'])
s2 = Series(data=[1,2,3],index=['a','d','c'])
s = s1 + s2
print(s)
'''
a 2.0
b NaN
c 6.0
d NaN
dtype: float64
'''
4. DataFrame
DataFrame是一个【表格型】的数据结构。DataFrame由按一定顺序排列的多列数据组成。设计初衷是将Series的使用场景从一维拓展到多维。
4.1 DateFrame构建
4.1.1 字典类
1. 数组、列表或元组构成的字典构造dataframe
示例:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
# 数组、列表或元组构成的字典构造dataframe
#构造一个字典
data = {'a':[1,2,3,4],
'b':(5,6,7,8),
'c':np.arange(9,13)}
#构造dataframe
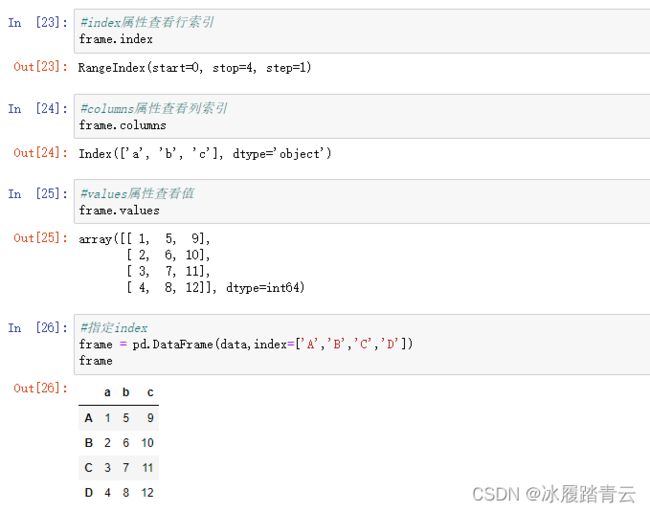
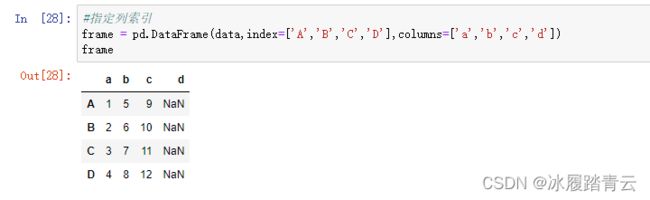
frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(frame)
'''
a b c
0 1 5 9
1 2 6 10
2 3 7 11
3 4 8 12
'''
DataFrame既有行索引,也有列索引。
行索引:index
列索引:columns
值:values
2. Series构成的字典构造dataframe
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
#2.Series构成的字典构造dataframe
pd1 = pd.DataFrame({'a':pd.Series(np.arange(3)),
'b':pd.Series(np.arange(3,5))})
print(pd1)
'''
a b
0 0 3.0
1 1 4.0
2 2 NaN
'''
3. 字典构成的字典构造dataframe
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
#3.字典构成的字典构造dataframe
#字典嵌套
data1 = {
'a':{'apple':3.6,'banana':5.6},
'b':{'apple':3,'banana':5},
'c':{'apple':3.2}
}
pd2 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
print(pd2)
'''
a b c
apple 3.6 3 3.2
banana 5.6 5 NaN
'''
小练习
题目:根据以下考试成绩表,创建一个DataFrame,命名为df:
张三 李四
语文 150 0
数学 150 0
英语 150 0
理综 300 0
参考代码:
from pandas import DataFrame
dic = {
'张三':[150,150,150,300],
'李四':[0,0,0,0]
}
df = DataFrame(data=dic,index=['语文','数学','英语','理综'])
print(df)
'''
张三 李四
语文 150 0
数学 150 0
英语 150 0
理综 300 0
'''
4.1.2 列表类
1. ndarray 构造dataframe
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
# 1. ndarray 构造dataframe
#构造二维数组对象
arr1 = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
frame1 = pd.DataFrame(arr1)
print(frame1)
'''
0 1 2
0 0 1 2
1 3 4 5
2 6 7 8
3 9 10 11
'''
2. 字典构成的列表构造dataframe
import pandas as pd
# 2. 字典构成的列表构造dataframe
l1 = [{'apple':3.6,'banana':5.6},{'apple':3,'banana':5},{'apple':3.2}]
pd3 = pd.DataFrame(l1)
print(pd3)
'''
apple banana
0 3.6 5.6
1 3.0 5.0
2 3.2 NaN
'''
3. Series构成的列表构造dataframe
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 3. Series构成的列表构造dataframe
l2 = [pd.Series(np.random.rand(3)),pd.Series(np.random.rand(2))]
pd4 = pd.DataFrame(l2)
print(pd4)
'''
0 1 2
0 0.057995 0.053132 0.694455
1 0.100159 0.143437 NaN
'''
4.2 DataFrame的基本用法
4.2.1 .T转置
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['a','c','b'],columns=['A','B','C'])
print(pd5)
print('*'*30)
print(pd5.T)
'''
A B C
a 0 1 2
c 3 4 5
b 6 7 8
******************************
a c b
A 0 3 6
B 1 4 7
C 2 5 8
'''
4.2.2 通过列索引获取列数据(Series类型)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['a','c','b'],columns=['A','B','C'])
print(pd5)
print('*'*30)
print(pd5['A']) # Series类型
'''
A B C
a 0 1 2
c 3 4 5
b 6 7 8
******************************
a 0
c 3
b 6
Name: A, dtype: int32
'''
4.2.3 增加列数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['a','c','b'],columns=['A','B','C'])
print(pd5)
print('*'*30)
pd5['D'] = [1,2,3]
print(pd5)
'''
A B C
a 0 1 2
c 3 4 5
b 6 7 8
******************************
A B C D
a 0 1 2 1
c 3 4 5 2
b 6 7 8 3
'''
4.2.4 删除列
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['a','c','b'],columns=['A','B','C'])
print(pd5)
print('*'*30)
del(pd5['C'])
print(pd5)
'''
A B C
a 0 1 2
c 3 4 5
b 6 7 8
******************************
A B
a 0 1
c 3 4
b 6 7
'''
DataFrame常用的属性
values、columns、index、shape
用法和series差不多直接调用即可
df.values
df.columns
df.index
df.shape
4.3 DataFrame索引操作
- 对列进行索引
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(50,100,size=(3,4)),columns=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('*'*20)
print(df['a']) # 取单列,如果df有显示的索引,通过索引机制去行或者列的时候只可以使用显示索引
print('='*20)
print(df[['a','c']]) #取多列
'''
a b c d
0 50 76 66 59
1 83 81 73 62
2 67 80 82 90
********************
0 50
1 83
2 67
Name: a, dtype: int32
====================
a c
0 50 66
1 83 73
2 67 82
'''
- 对行进行索引和对元素进行索引
iloc:
通过隐式索引取行
loc:
通过显示索引取行
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(50,100,size=(3,4)),columns=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('*'*20)
print(df.iloc[0]) # 取单行,这里的df行索引为隐式索引,用iloc或loc都可以
print('='*20)
# 取多行
print(df.iloc[[0,2]]) # 取第0行和第2行
print('-'*10)
#取单个元素
print(df.iloc[0,2]) # 第0行第2列的元素
print('*'*10)
print(df.loc[0,'a']) # 取0行a列元素
#取多个元素
print('*='*10)
print(df.iloc[[0,2],2]) # 取第0行和第2行的第二列元素
'''
a b c d
0 81 96 81 99
1 89 89 59 53
2 81 93 53 96
********************
a 81
b 96
c 81
d 99
Name: 0, dtype: int32
====================
a b c d
0 81 96 81 99
2 81 93 53 96
----------
81
**********
81
*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=
0 81
2 53
Name: c, dtype: int32
'''
4.4 DataFrame的切片操作
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(50,100,size=(3,4)),columns=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('*'*20)
#切行
print(df[0:2])
print('='*20)
#切列
print(df.iloc[:, 0:2])
'''
a b c d
0 84 78 70 81
1 79 66 70 80
2 96 65 89 85
********************
a b c d
0 84 78 70 81
1 79 66 70 80
====================
a b
0 84 78
1 79 66
2 96 65
'''
小结:
df索引和切片操作
索引:
df[col]:取列
df.loc[index]:取行
df.iloc[index,col]:取元素
切片:
df[index1:index3]:切行
df.iloc[:,col1:col3]:切列
好了,到这里,这篇博客也该跟大家说再见了,创作不易,如果本文对你有用,欢迎收藏加点赞,这真的是对我的肯定与鼓励,也是我坚持下去的动力。
生活就是久别重逢、失而复得、不期而遇、如约而至、还有未来可期。生活的热浪会把平凡的日子吹的蒸蒸日上,喜欢的歌慢慢听、喜欢的事慢慢做,喜欢的生活好好努力。在平凡的生活里,保持谦虚和努力,光芒再小,也要永远闪亮。