修改 Zynq 7000 系列 CPU 主频到 800HMz(7045 和 7100)
目录
-
- 调频
- 分析
- 时钟树
- 修改
调频
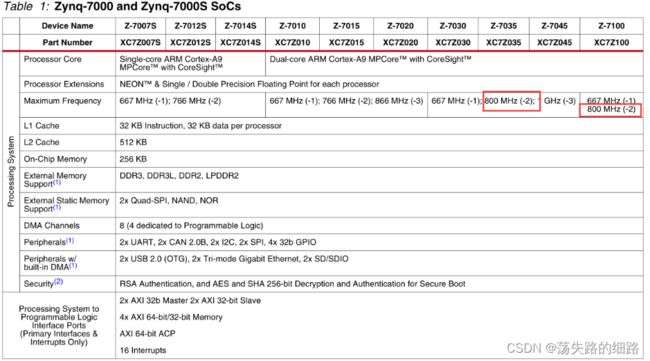
首先看Data Sheet进行确认,能不能配到800MHz的,是可以的
用Frequency scaling驱动的话,除了本身的驱动,还需要把CONFIG_CPUFREQ_DT编译进内核
进入文件系统,就可以在/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq目录调频
-
看一下当前频率
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq -
看一下当前模式
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor -
设置成333MHz
echo 333334 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed -
设置成666MHz
echo 666667 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed -
设置成
performance模式
echo performance > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
在设备树zynq-7000.dtsi修改 cpus节点,加多一个800MHz的选项
cpus {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
cpu0: cpu@0 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
device_type = "cpu";
reg = <0>;
clocks = <&clkc 3>;
clock-latency = <1000>;
cpu0-supply = <®ulator_vccpint>;
operating-points = <
/* kHz uV */
800000 1000000
666667 1000000
333334 1000000
>;
};
cpu1: cpu@1 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
device_type = "cpu";
reg = <1>;
clocks = <&clkc 3>;
};
};
然后直接 echo 800000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed,发现再cat出来,并没有改变主频。但是cat scaling_available_frequencies是有800MHz选项的。
再用cpufreq-info命令看,也是有到800HMz的
分析
当前是666MHz,执行 devmem2 0xF8000120 看一下 ARM_CLK_CTRL
/dev/mem opened.
Memory mapped at address 0xb6fd4000.
Read at address 0xF8000120 (0xb6fd4120): 0x1F000200
如果是333MHz的话
/dev/mem opened.
Memory mapped at address 0xb6f00000.
Read at address 0xF8000120 (0xb6f00120): 0x1F000400
看到其实是分频系数 2->4 了,实际是有变化的
猜想是时钟树分频设置的不对,导致设置不了800MHz
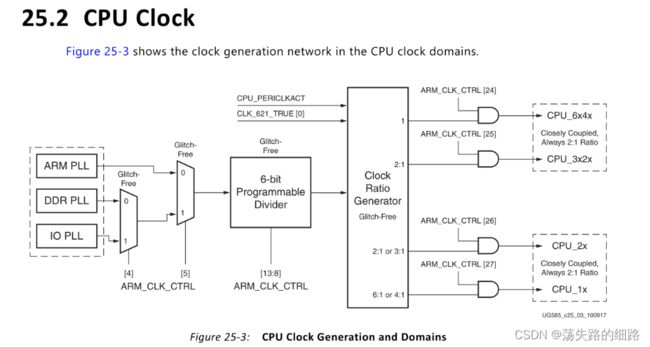
时钟树
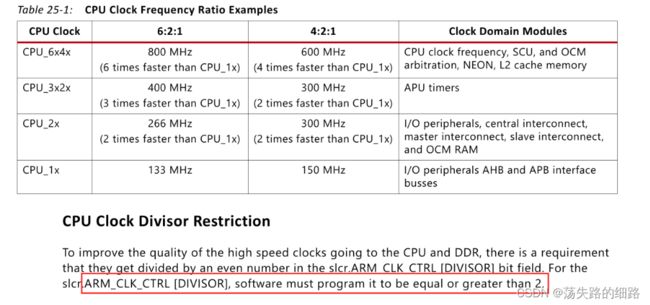
有6:2:1和4:2:1两种模式,两种模式的CPU_6x4x的频率是6:4。CPU_6x4x可以根据ARM PLL乘以分频系数ARM_CLK_CTRL [DIVISOR],分频系数注意要大于等于2
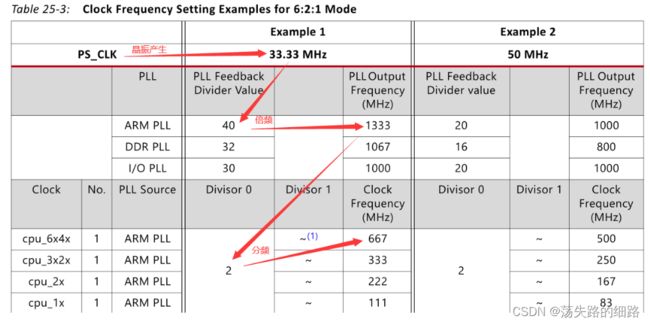
如上图,目前最终得到的最大主频是667MHz,分频只能大于等于2,分不出800MHz的频率,只能从倍频入手。
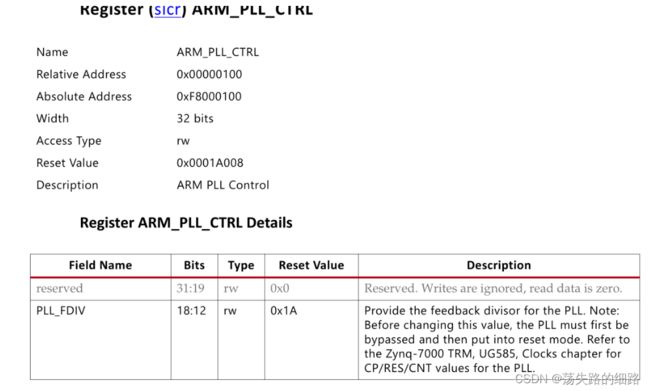
ARM_PLL_CTRL 倍频系数是7位的,最大可以到127,如果需要800MHz,反推出来倍频系数应该是48。
修改
尝试直接在内核修改寄存器
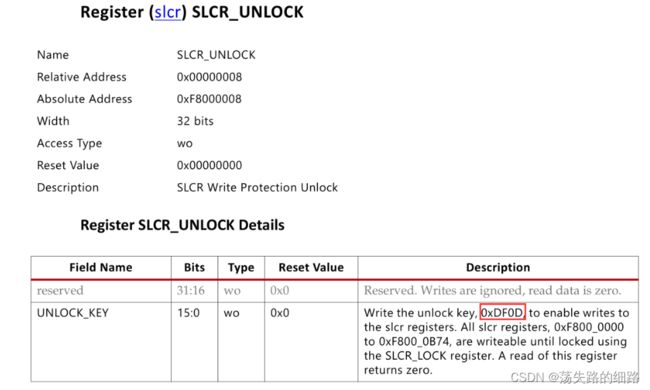
需要先unlock寄存器写权限
devmem2 0xF8000008 w 0xDF0D
然后直接修改
devmem2 0xF8000100 w 0x00030000
没有反应,重新ehco也不行,看到寄存器说明,修改的话要先设置成bypass和reset,但是尝试了下设置成reset,系统直接卡死了
只能看源码了,希望能找到在哪里设置倍频系数。
在设备树看到slcr节点,那么应该就是这个驱动设置倍频和分频系数了,但是看了驱动文档,没有倍频和分频的设置
slcr: slcr@f8000000 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-slcr", "syscon", "simple-mfd";
reg = <0xF8000000 0x1000>;
ranges;
clkc: clkc@100 {
#clock-cells = <1>;
compatible = "xlnx,ps7-clkc";
fclk-enable = <0xf>;
clock-output-names = "armpll", "ddrpll", "iopll", "cpu_6or4x",
"cpu_3or2x", "cpu_2x", "cpu_1x", "ddr2x", "ddr3x",
"dci", "lqspi", "smc", "pcap", "gem0", "gem1",
"fclk0", "fclk1", "fclk2", "fclk3", "can0", "can1",
"sdio0", "sdio1", "uart0", "uart1", "spi0", "spi1",
"dma", "usb0_aper", "usb1_aper", "gem0_aper",
"gem1_aper", "sdio0_aper", "sdio1_aper",
"spi0_aper", "spi1_aper", "can0_aper", "can1_aper",
"i2c0_aper", "i2c1_aper", "uart0_aper", "uart1_aper",
"gpio_aper", "lqspi_aper", "smc_aper", "swdt",
"dbg_trc", "dbg_apb";
reg = <0x100 0x100>;
};
rstc: rstc@200 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-reset";
reg = <0x200 0x48>;
#reset-cells = <1>;
syscon = <&slcr>;
};
pinctrl0: pinctrl@700 {
compatible = "xlnx,pinctrl-zynq";
reg = <0x700 0x200>;
syscon = <&slcr>;
};
};
分别看了 drivers/clk/zynq/pll.c和drivers/clk/zynq/clk.c,都只是看到代码在读倍频系数进行设置而已,没有看到在哪里配置倍频系数的。如果不是在内核设置,会是在uboot吗
在uboot的arch/arm/mach-zynq/clk.c看到zynq_clk_early_init函数(在arch/arm/mach-zynq/cpu.c调用),也只是读倍频系数,再往前追踪,并没有更多发现。
那会是在FSBL吗
直接进入目录看cd /embeddedsw/lib/sw_apps/zynq_fsbl/src里面的文件,果然发现了ps7_init.c就有设置倍频系数。
EMIT_MASKWRITE(0XF8000100, 0x0007F000U ,0x00028000U),
// .. .. .. FINISH: UPDATE FB_DIV
// .. .. .. START: BY PASS PLL
// .. .. .. PLL_BYPASS_FORCE = 1
// .. .. .. ==> 0XF8000100[4:4] = 0x00000001U
// .. .. .. ==> MASK : 0x00000010U VAL : 0x00000010U
// .. .. ..
这里的MASK是[18:12],对应的值是40,改为48,即0x00030000U。重新编译,发现值又被改会了40。
重新看了文件头才发现这居然是This file is automatically generated。
查看Makefile,发现这个文件是由lib/sw_apps/zynq_fsbl/misc/zc702/ps7_init.c拷贝过去的,于是在这个文件里面改,可以改为48,编译后烧到SD卡。
启动后发现默认已经配成了800HMz了
==> cpufreq-info
cpufrequtils 008: cpufreq-info (C) Dominik Brodowski 2004-2009
Report errors and bugs to [email protected], please.
analyzing CPU 0:
driver: cpufreq-dt
CPUs which run at the same hardware frequency: 0 1
CPUs which need to have their frequency coordinated by software: 0 1
maximum transition latency: 1000 ns.
hardware limits: 167 MHz - 800 MHz
available frequency steps: 167 MHz, 222 MHz, 333 MHz, 667 MHz, 800 MHz
available cpufreq governors: conservative, ondemand, userspace, powersave, performance
current policy: frequency should be within 167 MHz and 800 MHz.
The governor "performance" may decide which speed to use
within this range.
current CPU frequency is 800 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
analyzing CPU 1:
driver: cpufreq-dt
CPUs which run at the same hardware frequency: 0 1
CPUs which need to have their frequency coordinated by software: 0 1
maximum transition latency: 1000 ns.
hardware limits: 167 MHz - 800 MHz
available frequency steps: 167 MHz, 222 MHz, 333 MHz, 667 MHz, 800 MHz
available cpufreq governors: conservative, ondemand, userspace, powersave, performance
current policy: frequency should be within 167 MHz and 800 MHz.
The governor "performance" may decide which speed to use
within this range.
current CPU frequency is 800 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).