【42STL-函数对象使用详情】
文章目录
-
- 13 STL-函数对象
-
- 13.1 函数对象
-
- 13.1.1 函数对象概念
- 13.1.2 函数对象使用
- 13.2 谓词
-
- 13.2.1 谓词概念
- 13.2.2 一元谓词
- 13.2.3 二元谓词
- 13.3 内建函数对象
-
- 13.3.1 内建函数对象意义
- 13.3.2 关系仿函数
- 13.3.3 逻辑仿函数
13 STL-函数对象
13.1 函数对象
13.1.1 函数对象概念
概念:
- 重载函数调用重载符的类,其对象常称为函数对象
- 函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:
函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数
13.1.2 函数对象使用
特点:
- 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
- 函数对象可以作为参数传递
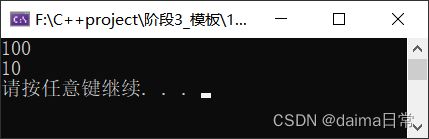
示例代码:
#include运行结果:
总结:
- 仿函数写法非常灵活,可以作为参数进行传递
13.2 谓词
13.2.1 谓词概念
概念:
- 返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
- 如果operator() 接收一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
- 如果operator()接受两个参数,那么叫做二元谓词
13.2.2 一元谓词
示例代码:
#include运行结果:
总结: 参数只有一个的谓词,称为一元谓词
13.2.3 二元谓词
示例代码:
#include总结: 参数只有两个的谓词,称为二元谓词
13.3 内建函数对象
13.3.1 内建函数对象意义
概念:
- STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
- 算术仿函数
- 关系仿函数
- 逻辑仿函数
用法:
- 这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同
- 使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件 #include
仿函数原型:
template//加法仿函数T plus template//减法仿函数T minus template//乘法仿函数T multiplies template//除法仿函数T divides template//取模仿函数T modulus template//取反仿函数T negate
示例代码:
#include运行结果:
总结: 使用内建函数对象是,需要引入头文件 #include
13.3.2 关系仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现关系对比
仿函数原型:
template//等于bool equal_to template//不等于bool not_equal_to template//大于bool greater template//大于等于bool greater_equal template//小于bool less template//小于等于bool less_equal
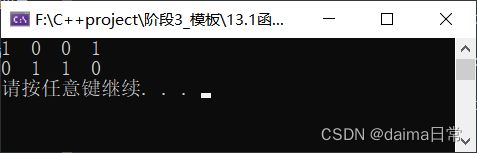
示例代码:
#include() 内建函数对象
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
总结: 关系仿函数中最常用的就是greater<> 大于
13.3.3 逻辑仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现逻辑运算
函数原型:
template//逻辑与bool logical_and template//逻辑或bool logical_or template//逻辑非bool logical_not
示例代码:
#include运行结果:
总结: 逻辑仿函数实际应用较少,了解即可。
如果对你有帮助的话,请不要忘了给我一点点点…支持 ( ^ o ^)/~