GhostNet详解及代码实现
Ghost Net
1. Introduction
上图是由ResNet-50中的第一个残差块生成的某些中间特征图的可视化。从图中我们可以看出,这里面有很多特征图是具有高度相似性的(在图中分别用不同的颜色示意),换句话说,就是存在许多的冗余特征图。所以从另一个角度想,我们是不是可以利用一系列的线性变化,以很小的代价生成许多能从原始特征发掘所需信息的“幻影”特征图呢?这个便是整篇文章的核心思想。
2. Approach
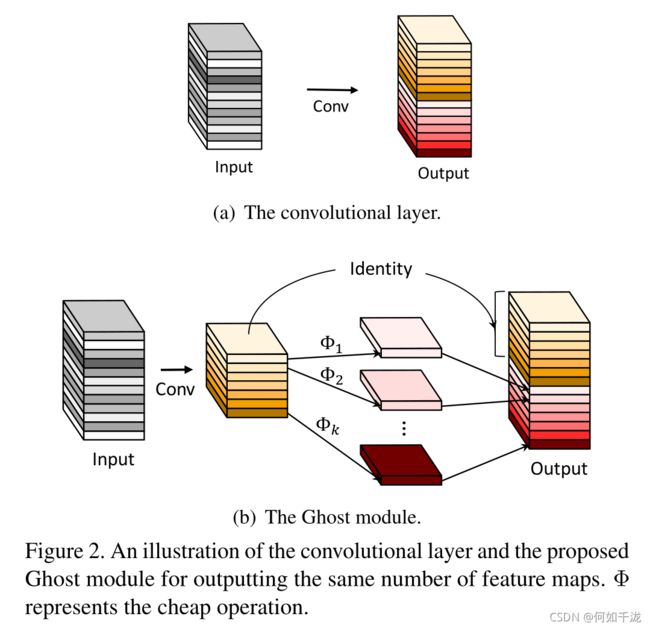
Ghost module:
- 先通过
conv生成一些特征图 - 然后对生成的特征图进行
cheap操作(Dwise conv)生成冗余特征图 - 最后将
conv生成的特征图与cheap操作生成的特征图进行concat操作
3. GhostNet
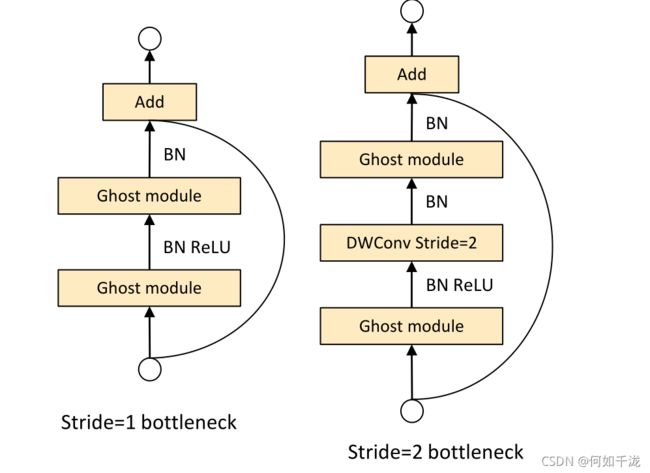
3.1 Ghost Bottlenecks
第一层Ghost module充当扩展层用于增加通道的数目
第二层Ghost module减少通道的数目来满足shortcut path
3.2 网络结构
4. Pytorch实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class DWConv3x3BNReLU(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride, groups):
super(DWConv3x3BNReLU, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
)
class SqueezeAndExcite(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, divide=4):
super(SqueezeAndExcite, self).__init__()
mid_channel = in_channel // divide
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.SEblock = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=in_channel, out_features=mid_channel),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=mid_channel, out_features=out_channel),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
out = self.pool(x)
out = torch.flatten(out, start_dim=1)
out = self.SEblock(out)
out = out.view(b, c, 1, 1)
return out * x
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, s=2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, use_relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
intrinsic_channel = out_channel // s
ghost_channel = intrinsic_channel * (s - 1)
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=intrinsic_channel, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=(kernel_size-1)//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(intrinsic_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if use_relu else nn.Sequential()
)
self.cheap_op = DWConv3x3BNReLU(in_channel=intrinsic_channel, out_channel=ghost_channel, stride=stride, groups=intrinsic_channel)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_op(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)
return out
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, mid_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride, use_se):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.bottleneck = nn.Sequential(
GhostModule(in_channel=in_channel, out_channel=mid_channel, use_relu=True),
DWConv3x3BNReLU(in_channel=mid_channel, out_channel=mid_channel, stride=stride, groups=mid_channel) if self.stride > 1 else nn.Sequential(),
SqueezeAndExcite(in_channel=mid_channel, out_channel=mid_channel) if use_se else nn.Sequential(),
GhostModule(in_channel=mid_channel, out_channel=out_channel, use_relu=False)
)
if self.stride > 1:
self.shortcut = DWConv3x3BNReLU(in_channel=in_channel, out_channel=out_channel, stride=stride, groups=1)
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.bottleneck(x)
residual = self.shortcut(x)
out += residual
return out
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
self.first_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
)
ghost_model_setting = [
# in, mid, out, kernel, stride, use_se
[16, 16, 16, 3, 1, False],
[16, 48, 24, 3, 2, False],
[24, 72, 24, 3, 1, False],
[24, 72, 40, 5, 2, True],
[40, 120, 40, 5, 1, True],
[40, 240, 80, 3, 2, False],
[80, 200, 80, 3, 1, False],
[80, 184, 80, 3, 1, False],
[80, 184, 80, 3, 1, False],
[80, 480, 112, 3, 1, True],
[112, 672, 112, 3, 1, True],
[112, 672, 160, 5, 2, True],
[160, 960, 160, 5, 1, False],
[160, 960, 160, 5, 1, True],
[160, 960, 160, 5, 1, False],
[160, 960, 160, 5, 1, True],
]
layers = []
for in_channel, mid_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride, use_se in ghost_model_setting:
layers.append(GhostBottleneck(in_channel=in_channel, mid_channel=mid_channel, out_channel=out_channel, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, use_se=use_se))
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.last_stage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=160, out_channels=960, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(960),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=960, out_channels=1280, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(in_features=1280, out_features=num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.first_conv(x)
x = self.features(x)
x = self.last_stage(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
model = GhostNet()
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
out = model(input)
print(out.size())
上一篇:ShuffleNet系列
完整代码