利用短时傅里叶变换(STFT)对信号进行时频谱分析和去噪声
利用短时傅里叶变换(STFT)对信号进行时频谱分析和去噪声
1、背景
傅里叶变换(TF)对频谱的描绘是“全局性”的,不能反映时间维度局部区域上的特征,人们虽然从傅立叶变换能清楚地看到一整段信号包含的每一个频率的分量值,但很难看出对应于频率域成分的不同时间信号的持续时间和发射的持续时间,缺少时间信息使得傅立叶分析在更精密的分析中显得很无力。傅里叶变换只反映出信号在频域的特性,无法在时域内对信号进行分析。另外,傅里叶变换的相位对于噪声非常敏感,很长的数据中哪怕是很小一段出错,通过傅里叶变换得到的相位也会与真是的相位相差很多。
2、短时傅里叶变换(STFT)
短时傅里叶变换,又称窗傅里叶变换。在信号做傅里叶变换之前乘一个时间有限的窗函数 h(t),并假定非平稳信号在分析窗的短时间隔内是平稳的,通过窗函数 h(t)在时间轴上的移动,对信号进行逐段分析得到信号的一组局部“频谱”,即信号在时域内的每一瞬间的频谱。
获得信号时域内的频谱信息之后,就可以对信号进行滤波处理。在时域内的频谱信息中可以直观的找出信号的主要频率信息,从而去掉能够被认为是噪声的次要频率信息,再通过逆变换得到降噪之后的信号。
3、处理思路
1)原始信号转换成WAV格式的音频信号,通过音频来判断结果;
2)对数据进行短时傅里叶变换,获得原始信号时间分辨的频谱信号;
3)利用谱减法降噪。具体实现是通过鼠标选择原始信号时间分辨的频谱信号幅值部分需要保留的区域,通过矩阵掩模实现谱减法。掩模矩阵通过通过鼠标选取区域,区域内部的为1,外部为0,将掩模矩阵和原始信号时间分辨的频谱信号幅值矩阵对应位置元素相乘,得到降噪后的幅值矩阵;
4)使用短时傅里叶变换的相位和降噪后的幅值重构复信号的频域分布;
5)使用短时傅立叶变换逆变换重构完成滤波的时域信号;
6)将滤波的信号转换成WAV格式的音频信号,判断效果。
注:由于此处处理的信号是音频信号采样率比较高,通过观察时域波形很难判断效果的好坏,故采用转换成音频信号的方式来判断效果。对于常规的待处理信号,直接通过绘制时域波形来判断即可。
4、具体实现
这里以一段音频信息的背景噪声去除和主要声音的提取为例子。代码注释比较详细,具体实现不做过多赘述。
以下是原始音频:
原始音频链接
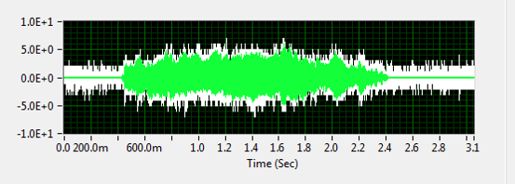
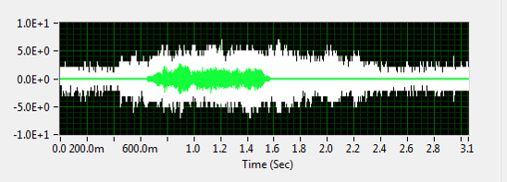
原始信号时域波形如下:
1)数组转换成WAV格式音频文件借助wave模块:
# 数组转换成WAV文件
def array2WAV(t, signal, wavName, savePath):
num_samples = len(signal)
amplitude = 50
sampling_rate = 1.0 / (t[1] - t[0])
nframes = num_samples
comptype = "NONE"
compname = "not compressed"
nchannels = 1
sampwidth = 2
wav_file = wave.open("{}/{}.wav".format(savePath, wavName), 'w')
wav_file.setparams((nchannels, sampwidth, int(sampling_rate), nframes,
comptype, compname))
for s in signal:
wav_file.writeframes(struct.pack('h', int(s * amplitude)))
2)STFT实现 首先创建一个M行L列的矩阵xmat,该矩阵的每一行代表一个0-Fe的频率,单位为Hz,每一列对应该段被窗函数截取的信号的FFT快速傅里叶变换。短时傅里叶变换实现如下:
# 短时傅里叶变换实现
# 函数输入六个参数,返回短时傅里叶变换的二维数据结果和横纵轴数据
# trame和Fe : 初始的数字信号和它的采样频率
# Nfft : 上文提到的离散傅里叶变换中,频域的采样个数M
# fenetre : 短时傅里叶变换中使用的窗函数,在接下来的实现中我都使用了汉明窗np.hamming。
# Nwin : 窗函数的长度(包含点的个数)
# Nhop : 窗函数每次滑动的长度,一般规定为Nwin/2,窗函数长度的一半
# 首先创建一个M行L列的矩阵xmat,该矩阵的每一行代表一个0-Fe的频率,单位为Hz,每一列对应该段被窗函数截取的信号的FFT快速傅里叶变换。
def TFCT(trame, Fe, Nfft, fenetre, Nwin, Nhop):
L = int((len(trame) - len(fenetre)) / Nhop) + 1
M = Nfft
xmat = np.zeros((M, L))
for j in range(L):
xmat[:, j] = np.fft.fft(trame[j * Nhop:Nwin + Nhop * j] * fenetre,
Nfft)
x_temporel = np.linspace(0, (1 / Fe) * len(trame), len(xmat[0]))
x_frequentiel = np.linspace(0, Fe / 2, len(xmat[:, 0]))
return xmat, x_temporel, x_frequentiel
原始信号的STFT结果如下图所示:
从图中可以看出,三条较长黄色谱线对应海豚的叫声(对应于一个主频和两个谐波分量)。仔细观察可以看出同时在这期间还有另一只小动物的叫声(在分析频段内只能看到主频和一次谐波分量,所以只有两块时频谱),犹豫这个声音比较小,因此在这个图中不明显。实际上,如果不进行STFT处理,这个小动物的声音很难发现。后续的处理只需要在这个图中分别取出两种叫声的主频和谐波分量,其余的全部舍弃,即可实现降噪滤波。
3)时频谱中感兴趣部分提取
为方便后续的边界识别,首先需要对时频谱进行矩阵平滑出理:
# 矩阵平滑
def smoothMatrix(toSolveMatrix):
for i in range(len(toSolveMatrix)):
for j in range(len(toSolveMatrix[i])):
leftIndex = 0
rightIndex = 0
upIndex = 0
downIndex = 0
if i - 1 < 0:
leftIndex = 0
else:
leftIndex = -1
if j - 1 < 0:
upIndex = 0
else:
upIndex = -1
if i + 1 > len(toSolveMatrix) - 1:
rightIndex = 0
else:
rightIndex = 1
if j + 1 > len(toSolveMatrix[i]) - 1:
downIndex = 0
else:
downIndex = 1
toSolveMatrix[i][j] = (
toSolveMatrix[i][j] + toSolveMatrix[i + leftIndex][j + upIndex]
+ toSolveMatrix[i + leftIndex][j + downIndex] +
toSolveMatrix[i + rightIndex][j + upIndex] +
toSolveMatrix[i + rightIndex][j + upIndex]) / 5
return toSolveMatrix
通过鼠标绘制区域,获得时频谱中感兴趣的区域:
# 本程序用于通过鼠标来获得矩阵的掩模区域
# 一定要注意窗口的操作顺序
# 在程序运行之后,会出现矩阵的灰度图,在上面通过鼠标左键的拖动来选定区域
# 选定完成之后直接关掉这个灰度图从窗口
# 后面再依次关掉后续过程中出现的几个小窗口,直到下一次区域选定的矩阵灰度图出现为止
# 再继续重复上面的操作即可
import cv2
import numpy as np
import copy
import os
currentPath = os.path.dirname(__file__)
points = []
def on_mouse(event, x, y, flags, param):
global points, img, i, Cur_point, Start_point
copyImg = copy.deepcopy(img)
h, w = img.shape[:2]
mask_img = np.zeros([h + 2, w + 2], dtype=np.uint8)
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
Start_point = [x, y]
points.append(Start_point)
cv2.circle(img, tuple(Start_point), 1, (255, 255, 255), 0)
cv2.imshow("window1", img)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and flags == cv2.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON:
Cur_point = [x, y]
cv2.line(img, tuple(points[-1]), tuple(Cur_point), (255, 255, 255))
cv2.imshow("window1", img)
points.append(Cur_point)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
Cur_point = Start_point
cv2.line(img, tuple(points[-1]), tuple(Cur_point), (255, 255, 255))
cv2.circle(img, tuple(Cur_point), 1, (255, 255, 255))
ret, image, mask, rect = cv2.floodFill(img, mask_img, (x, y),
(255, 255, 255),
cv2.FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE)
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskImage.jpg".format(currentPath), img)
src = cv2.bitwise_and(img, image)
cv2.imwrite("{}/segImg.jpg".format(currentPath), src)
cv2.waitKey(0)
img = cv2.imread('{}/segImg.jpg'.format(currentPath))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 240, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.drawContours(copyImg, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow('RoiImg', copyImg) # 只显示零件外轮廓
cv2.waitKey(0)
cimg = np.zeros_like(img)
cimg[:, :, :] = 0
cv2.drawContours(cimg,
contours,
1,
color=(255, 255, 255),
thickness=-1)
cv2.imshow('maskImg', cimg) # 将零件区域像素值设为(255, 255, 255)
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskMatrix_{}.jpg".format(currentPath, i + 1), cimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
获得感兴趣区域之后,进行掩模处理,掩模矩阵的计算:
# mask矩阵
def maskMatrixGet(savePath):
maskMatrixs = []
for i in range(3):
tempMaskMatrix = cv2.imread("{}/maskMatrix_{}.jpg".format(
savePath, i + 1))
# 因为maskMatrixs已经是二值图,因此读取之后灰度处理得到的就是二值图了
gray_tempMaskMatrix = cv2.cvtColor(tempMaskMatrix, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
maskMatrixs.append(gray_tempMaskMatrix)
rows, cols = maskMatrixs[0].shape
maskMatrix = np.zeros((rows, cols))
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
maskMatrix[i][j] = maskMatrixs[0][i][j] + \
maskMatrixs[1][i][j]+maskMatrixs[2][i][j]
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskMatrix.jpg".format(savePath), maskMatrix)
return maskMatrix
通过鼠标选取和掩模处理之后得到的海豚叫声的时频谱:
通过鼠标选取和掩模处理之后得到的未知小动物叫声的时频谱:
4)对提取出来的时频谱进行短时逆傅里叶变换重构相应的时域信号:
使用overlapp-add算法进行短时傅里叶变换的逆变换重构原信号:
# 使用overlapp-add算法进行短时傅里叶变换的逆变换重构原信号
# 函数有五个参数,返回重构的原信号的横轴和纵轴数据
# 第一步,对上一部分得出的矩阵xmat进行快速傅里叶变换的逆变换,得出同样规格M行L列的矩阵yl。
# 对yl矩阵的每一列平移 (l-1)Nhop,l ∈ \in∈ [1,L],例如第一列不变,第二列平移Nhop,第三列平移2Nhop,以此类推。之后将所有列的转置,叠加到总长度为Nfft +(L-1)*Nhop的向量yvect中。
def ITFD(xmat, Fe, Nfft, Nwin, Nhop):
window = np.hamming(Nwin)
# 采样周期
Te = 1 / Fe
# 信号重构
yvect = np.zeros(Nfft + (xmat.shape[1] - 1) * Nhop, dtype=complex)
t_vecteur = np.arange(0, Te * len(yvect), Te)
K = 0
L = xmat.shape[1]
yl = np.zeros(xmat.shape, dtype=complex)
for j in range(L):
yl[:, j] = np.fft.ifft(xmat[:, j])
# 平移和求和
for k in range(L):
yvect[Nhop * k:Nfft + Nhop * k] += yl[:, k]
# 标准化幅值
for n in range(Nwin - 1):
K += window[n]
K /= Nhop
yvect /= K
return t_vecteur, yvect
重构出来的海豚叫声的时域波形:
重构出来的未知小动物叫声的时域波形:
5)将提取出来的两个信号转换成WAV格式音频信号,判断效果,效果不佳则重新进行时频谱的区域选择
重构出来的海豚叫声的音频:
重构出来的海豚叫声的音频
重构出来的未知小动物叫声的音频:
重构出来的未知小动物叫声的音频
5、完整代码
整个代码分成两个单独的文件:
main.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import wave
import struct
from IPython.display import display, Audio
import cv2
import os
from time import *
currentPath = os.path.dirname(__file__)
# 短时傅里叶变换实现
# 函数输入六个参数,返回短时傅里叶变换的二维数据结果和横纵轴数据
# trame和Fe : 初始的数字信号和它的采样频率
# Nfft : 上文提到的离散傅里叶变换中,频域的采样个数M
# fenetre : 短时傅里叶变换中使用的窗函数,在接下来的实现中我都使用了汉明窗np.hamming。
# Nwin : 窗函数的长度(包含点的个数)
# Nhop : 窗函数每次滑动的长度,一般规定为Nwin/2,窗函数长度的一半
# 首先创建一个M行L列的矩阵xmat,该矩阵的每一行代表一个0-Fe的频率,单位为Hz,每一列对应该段被窗函数截取的信号的FFT快速傅里叶变换。
def TFCT(trame, Fe, Nfft, fenetre, Nwin, Nhop):
L = int((len(trame) - len(fenetre)) / Nhop) + 1
M = Nfft
xmat = np.zeros((M, L))
for j in range(L):
xmat[:, j] = np.fft.fft(trame[j * Nhop:Nwin + Nhop * j] * fenetre,
Nfft)
x_temporel = np.linspace(0, (1 / Fe) * len(trame), len(xmat[0]))
x_frequentiel = np.linspace(0, Fe / 2, len(xmat[:, 0]))
return xmat, x_temporel, x_frequentiel
# 使用overlapp-add算法进行短时傅里叶变换的逆变换重构原信号
# 函数有五个参数,返回重构的原信号的横轴和纵轴数据
# 第一步,对上一部分得出的矩阵xmat进行快速傅里叶变换的逆变换,得出同样规格M行L列的矩阵yl。
# 对yl矩阵的每一列平移 (l-1)Nhop,l ∈ \in∈ [1,L],例如第一列不变,第二列平移Nhop,第三列平移2Nhop,以此类推。之后将所有列的转置,叠加到总长度为Nfft +(L-1)*Nhop的向量yvect中。
def ITFD(xmat, Fe, Nfft, Nwin, Nhop):
window = np.hamming(Nwin)
# 采样周期
Te = 1 / Fe
# 信号重构
yvect = np.zeros(Nfft + (xmat.shape[1] - 1) * Nhop, dtype=complex)
t_vecteur = np.arange(0, Te * len(yvect), Te)
K = 0
L = xmat.shape[1]
yl = np.zeros(xmat.shape, dtype=complex)
for j in range(L):
yl[:, j] = np.fft.ifft(xmat[:, j])
# 平移和求和
for k in range(L):
yvect[Nhop * k:Nfft + Nhop * k] += yl[:, k]
# 标准化幅值
for n in range(Nwin - 1):
K += window[n]
K /= Nhop
yvect /= K
return t_vecteur, yvect
# 数组转换成WAV文件
def array2WAV(t, signal, wavName, savePath):
num_samples = len(signal)
amplitude = 50
sampling_rate = 1.0 / (t[1] - t[0])
nframes = num_samples
comptype = "NONE"
compname = "not compressed"
nchannels = 1
sampwidth = 2
wav_file = wave.open("{}/{}.wav".format(savePath, wavName), 'w')
wav_file.setparams((nchannels, sampwidth, int(sampling_rate), nframes,
comptype, compname))
for s in signal:
wav_file.writeframes(struct.pack('h', int(s * amplitude)))
def dataRead(filePath):
data = np.loadtxt(filePath)
return data
# 矩阵平滑
def smoothMatrix(toSolveMatrix):
for i in range(len(toSolveMatrix)):
for j in range(len(toSolveMatrix[i])):
leftIndex = 0
rightIndex = 0
upIndex = 0
downIndex = 0
if i - 1 < 0:
leftIndex = 0
else:
leftIndex = -1
if j - 1 < 0:
upIndex = 0
else:
upIndex = -1
if i + 1 > len(toSolveMatrix) - 1:
rightIndex = 0
else:
rightIndex = 1
if j + 1 > len(toSolveMatrix[i]) - 1:
downIndex = 0
else:
downIndex = 1
toSolveMatrix[i][j] = (
toSolveMatrix[i][j] + toSolveMatrix[i + leftIndex][j + upIndex]
+ toSolveMatrix[i + leftIndex][j + downIndex] +
toSolveMatrix[i + rightIndex][j + upIndex] +
toSolveMatrix[i + rightIndex][j + upIndex]) / 5
return toSolveMatrix
# 矩阵预处理
def preproMatrix(toSolveMatrix, smoothNum):
for i in range(smoothNum):
toSolveMatrix = smoothMatrix(toSolveMatrix)
return toSolveMatrix
def nearestInList(x, aList):
diff = 100000000
resIndex = 0
for i in range(len(aList)):
if np.abs(aList[i] - x) < diff:
diff = np.abs(aList[i] - x)
resIndex = i
return resIndex
# mask矩阵
def maskMatrixGet(savePath):
maskMatrixs = []
for i in range(3):
tempMaskMatrix = cv2.imread("{}/maskMatrix_{}.jpg".format(
savePath, i + 1))
# 因为maskMatrixs已经是二值图,因此读取之后灰度处理得到的就是二值图了
gray_tempMaskMatrix = cv2.cvtColor(tempMaskMatrix, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
maskMatrixs.append(gray_tempMaskMatrix)
rows, cols = maskMatrixs[0].shape
maskMatrix = np.zeros((rows, cols))
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
maskMatrix[i][j] = maskMatrixs[0][i][j] + \
maskMatrixs[1][i][j]+maskMatrixs[2][i][j]
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskMatrix.jpg".format(savePath), maskMatrix)
return maskMatrix
# 谱减法的核心思路非常简单,顾名思义,谱减法是一种频域上的信号处理方法
# 其基本思路就是提取出信号本身的频谱以及噪音的频谱,通过两者之差获取降噪后信号的频谱,最后利用傅立叶变换逆变换重构初始信号。
# 要使用谱减法来进行信号处理,显然我们首先需要计算出信号的频谱以及噪音的频谱。
# 主方法入口
def main():
startTime = time()
# 原始数据读取与处理
data = dataRead("{}/data.txt".format(currentPath))
t = data[:, 0]
mix = data[:, 1]
array2WAV(t, mix * 50, "originalSignal", currentPath)
# 计算采样率
Fe = 1.0 / (t[1] - t[0])
Te = 1.0 / Fe
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot(t, mix)
plt.xlabel('t(s)')
plt.ylabel('amplitude(V)')
plt.title('representation of the original signal in time domain')
plt.show()
display(Audio(mix, rate=Fe))
# 短时傅里叶变换
Nfft = 256
Nwin = 256
Nhop = 128
window = np.hamming(Nwin)
xmat_sound, tvect, fvect = TFCT(mix, Fe, Nfft, window, Nwin, Nhop)
module_tf_xmat = abs(xmat_sound)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
xlim = int(module_tf_xmat.shape[0] / 2)
plt.imshow(20 * np.log10(module_tf_xmat[0:xlim, :]),
extent=[0, Te * len(mix), 0, Fe / 2],
aspect='auto')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('time(s)')
plt.ylabel('frequence(Hz)')
plt.title('spectrogram of the originql signal')
plt.show()
# 谱减法降噪
module_tf_xmat = abs(xmat_sound)
angle_tf_xmat = np.angle(xmat_sound)
module_tf_bruit = module_tf_xmat[:, 0]
module_reconstruit = np.zeros(module_tf_xmat.shape)
for n in range(module_tf_xmat.shape[1]):
module_reconstruit[:, n] = module_tf_xmat[:, n] - module_tf_bruit
cv2.imwrite("{}/spectrogramOfOriSig.jpg".format(currentPath),
module_reconstruit[0:xlim, :])
# 运行clickGetEare.py获取想要保留的二维频谱部分
os.system("python {}/clickGetEare.py".format(currentPath))
# 获取掩模矩阵
maskMatrix = maskMatrixGet(currentPath)
# 掩模运算
rows, cols = maskMatrix.shape
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
module_reconstruit[i][j] *= maskMatrix[i][j]
plt.imshow(20 * np.log10(module_reconstruit[0:xlim, :]),
extent=[0, Te * len(mix), 0, Fe / 2],
aspect='auto')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('time(s)')
plt.ylabel('frequence(Hz)')
plt.title('spectrogram of the denoised signal')
plt.show()
# 将相位和降噪后的幅值重构复信号的频域分布
tf_reconstruit = np.zeros(module_tf_xmat.shape, dtype=complex)
for i in range(module_tf_xmat.shape[0]):
for j in range(module_tf_xmat.shape[1]):
tf_reconstruit[i, j] = module_reconstruit[i, j] * \
np.exp(angle_tf_xmat[i, j]*1j)
# 使用短时傅立叶变换逆变换重构时域内的信号
t, yvect = ITFD(tf_reconstruit, Fe, Nfft, Nwin, Nhop)
array2WAV(t, yvect, "denoisedSignal", currentPath)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot(t.real, yvect.real)
plt.xlabel('t(s)')
plt.ylabel('amplitude(V)')
plt.title('representation of the denoised signal in time domain')
plt.show()
data_denoised = np.transpose([t.real, yvect.real])
np.savetxt("{}/data_denoised.txt".format(currentPath), data_denoised)
endTime = time()
print("程序运行时间:{} s.".format(endTime - startTime))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
clickGetEare.py
# 本程序用于通过鼠标来获得矩阵的掩模区域
# 一定要注意窗口的操作顺序
# 在程序运行之后,会出现矩阵的灰度图,在上面通过鼠标左键的拖动来选定区域
# 选定完成之后直接关掉这个灰度图从窗口
# 后面再依次关掉后续过程中出现的几个小窗口,直到下一次区域选定的矩阵灰度图出现为止
# 再继续重复上面的操作即可
import cv2
import numpy as np
import copy
import os
currentPath = os.path.dirname(__file__)
points = []
def on_mouse(event, x, y, flags, param):
global points, img, i, Cur_point, Start_point
copyImg = copy.deepcopy(img)
h, w = img.shape[:2]
mask_img = np.zeros([h + 2, w + 2], dtype=np.uint8)
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
Start_point = [x, y]
points.append(Start_point)
cv2.circle(img, tuple(Start_point), 1, (255, 255, 255), 0)
cv2.imshow("window1", img)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and flags == cv2.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON:
Cur_point = [x, y]
cv2.line(img, tuple(points[-1]), tuple(Cur_point), (255, 255, 255))
cv2.imshow("window1", img)
points.append(Cur_point)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
Cur_point = Start_point
cv2.line(img, tuple(points[-1]), tuple(Cur_point), (255, 255, 255))
cv2.circle(img, tuple(Cur_point), 1, (255, 255, 255))
ret, image, mask, rect = cv2.floodFill(img, mask_img, (x, y),
(255, 255, 255),
cv2.FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE)
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskImage.jpg".format(currentPath), img)
src = cv2.bitwise_and(img, image)
cv2.imwrite("{}/segImg.jpg".format(currentPath), src)
cv2.waitKey(0)
img = cv2.imread('{}/segImg.jpg'.format(currentPath))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 240, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.drawContours(copyImg, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow('RoiImg', copyImg) # 只显示零件外轮廓
cv2.waitKey(0)
cimg = np.zeros_like(img)
cimg[:, :, :] = 0
cv2.drawContours(cimg,
contours,
1,
color=(255, 255, 255),
thickness=-1)
cv2.imshow('maskImg', cimg) # 将零件区域像素值设为(255, 255, 255)
cv2.imwrite("{}/maskMatrix_{}.jpg".format(currentPath, i + 1), cimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
for i in range(3):
path = '{}/spectrogramOfOriSig.jpg'.format(currentPath)
img = cv2.imread(path)
cv2.namedWindow("window1", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("window1", img)
cv2.setMouseCallback("window1", on_mouse, 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("window1", 1280, 960)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()