springboot整合redis
一.springboot整合Redis
springboot整合redis时提供了两个模板工具类,StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate.
1.StringRedisTemplate
(1) 引入相关的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
(2)注入StringRedisTemplate该类对象
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;(3)使用StringRedisTemplate
该类把对每种数据类型的操作,单独封了相应的内部类。
package com.wt;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootRedis01ApplicationTests {
//里面所有的key还是value field 它的类型必须都是String类型
//因为key和value获取field它们使用的都是String的序列化方式
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//以hash方式对String操作
@Test
public void test01(){
HashOperations forHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
//以hash方式向Redis存储数据
forHash.put("k2","name","王戎");
forHash.put("k2","age","25");
forHash.put("k2","sex","男");
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","山涛");
map.put("age","23");
map.put("sex","男");
forHash.putAll("k3",map);
//通过hash获取指定的key下指定键的值
Object o = forHash.get("k3", "name");
System.out.println(o);
//获取K3下所有的键
Set 2. RedisTemplate
package com.wt;
import com.wt.entity.Dept;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@SpringBootTest
public class SprigbootRedis02 {
//当你存储的value类型为对象类型使用redisTemplate
//存储的value类型为字符串,StringRedisTemplate
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void test01(){
/在使用RedisTemplate前必须序列化,否则数据库会出现乱码
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); //给key添加序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class));//给value添加序列化
//对String类型操作类
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//如果不设置序列化,key和value默认采用jdk的序列化方式
forValue.set("k1","陈奕迅");
Object k1 = forValue.get("k1");
System.out.println(k1);
//如果不实现序列化,value默认采用jdk的序列化方式,可以给实体类加序列化接口
forValue.set("k3",new Dept(1,"刘念牛",23));
}
}
上面的RedisTemplate需要每次都指定key value以及field的序列化方式,所以我们可以写一个配置类,为RedisTemplate指定好序列化。以后再用就无需再指定。
package com.wt.conf;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @Author wt
* @Date 2022/8/2 19:56
* @PackageName:com.wt.conf
* @ClassName: RedisConfig
* @Description: RedisTemplate的序列化配置文件
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化 filed value
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
return template;
}
}
二. redis的使用场景
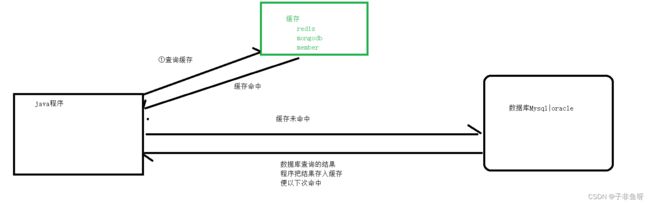
1.1 作为缓存
(1) 数据存储在内存中,数据查询速度快。可以分摊数据库压力
(2)什么样的数据适合放入缓存
查询频率比较高,修改频率比较低。
安全系数低的数据
(3) 使用redis作为缓存
引入相关依赖
mysql
mysql-connector-java
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.5.1
//如果使用@Autowired不使用@Resource则无需添加
org.eclipse.jetty.orbit
javax.annotation
1.1.0.v201108011116
实体类
package com.wt.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("tbl_user")
public class User {
@TableId("id")
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
}
mapper接口
package com.wt.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.wt.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
service接口
import com.wt.entity.User;
import com.wt.util.CommonResult;
public interface UserService {
CommonResult findById(Integer id);
CommonResult deleteById(Integer id);
CommonResult insertUser(User user);
CommonResult updateUser(User user);
}service层
package com.wt.service.impl;
import com.wt.dao.UserMapper;
import com.wt.entity.User;
import com.wt.service.UserService;
import com.wt.util.CommonResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author wt
* @Date 2022/8/2 20:20
* @PackageName:com.wt.service.impl
* @ClassName: UserServiceImpl
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public CommonResult findById(Integer id) {
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//查询缓存
Object o = forValue.get("user::" + id);
//判断缓存是否命中
if (o!=null){
//缓存中若存在则直接调用缓存中的内容
return new CommonResult(2000,"查询成功",o);
}
User user = userMapper.selectById(id);
if (user!=null){
//存入缓存,并且设置缓存有效时间为2小时
forValue.set("user::"+id,user,2, TimeUnit.HOURS);
return new CommonResult(2000,"查询成功",user);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"查询失败",null);
}
public CommonResult deleteById(Integer id) {
redisTemplate.delete("user::"+id); //删除数据库内容前先删除缓存
int i = userMapper.deleteById(id);
if (i>0){
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
public CommonResult insertUser(User user) {
int i= userMapper.insert(user);
if (i>0){
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
public CommonResult updateUser(User user) {
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
if (i>0){
forValue.set("user"+user.getId(),user,2,TimeUnit.HOURS);
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
}
controller层
package com.wt.controller;
import com.wt.entity.User;
import com.wt.service.UserService;
import com.wt.util.CommonResult;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @Author wt
* @Date 2022/8/2 20:19
* @PackageName:com.wt.controller
* @ClassName: UserController
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("order")
public class UserController {
// @Autowired
// private UserService userService;
@Resource(name = "userServiceImplt")
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("findById/{id}")
public CommonResult findById(@PathVariable Integer id){
CommonResult result = userService.findById(id);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("delById/{id}")
public CommonResult delById(@PathVariable Integer id){
return userService.deleteById(id);
}
@GetMapping("inst")
public CommonResult insertUser(@PathVariable User user){
return userService.insertUser(user);
}
@GetMapping("pudd")
public CommonResult updeUser(@PathVariable User user){
return userService.updateUser(user);
}
}
查看的缓存: 前部分代码相同@before通知,后部分代码也相同后置通知。 我们可以AOP完成缓存代码和业务代码分离。
spring框架内置了相关的缓存注解。--使用注解即可完成。并进行解析。
1.2 使用springboot内置注解替换手动添加查询缓存
(1) 把缓存的配置类加入原先的手动缓存配置类中
package com.wt.conf;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @Author wt
* @Date 2022/8/2 19:56
* @PackageName:com.wt.conf
* @ClassName: RedisConfig
* @Description: RedisTemplate的序列化配置文件
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
//手动注解配置方法
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化 filed value
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
return template;
}
//springboot内置的注解配置方法
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题),过期时间600秒
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600)) //缓存过期10分钟 ---- 业务需求。
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))//设置key的序列化方式
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer)) //设置value的序列化
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
(2)使用开启缓存注解
@EnableCaching //开启缓存注解
(3) 使用注解
只需更改service层即可
package com.wt.service.impl;
import com.wt.dao.UserMapper;
import com.wt.entity.User;
import com.wt.service.UserService;
import com.wt.util.CommonResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author wt
* @Date 2022/8/2 20:20
* @PackageName:com.wt.service.impl
* @ClassName: UserServiceImpl
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImplt implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//使用查询注解:cacheNames表示缓存的名称 key 唯一标识 ---该注解的名字为 cacheNames::key---->user::1
//先从缓存中查看key为cacheNames::key 是否存在,如果存在则不会执行下面的方法体,如果不存在则执行方法体并把方法的返回值存入到缓存中
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"user"},key = "#id")
public CommonResult findById(Integer id) {
User user = userMapper.selectById(id);
if (user!=null){
return new CommonResult(2000,"查询成功",user);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"查询失败",null);
}
//删除方法对应的缓存注解先删除缓存再执行方法体
@Override
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "user",key = "#id")
public CommonResult deleteById(Integer id) {
int i = userMapper.deleteById(id);
if (i>0){
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
@Override
public CommonResult insertUser(User user) {
int i= userMapper.insert(user);
if (i>0){
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
//修改对应的注解会确保方法被执行,同时方法的返回值也被记录到缓存中,实现缓存与数据库的同步更新
@Override
@CachePut(cacheNames = {"user"},key = "#user.id")
public CommonResult updateUser(User user) {
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
if (i>0){
return new CommonResult(2000,"成功",i);
}
return new CommonResult(5000,"失败",null);
}
}
2. 分布式锁
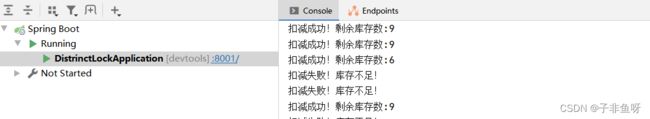
使用压测工具测试高并发下带来线程安全问题
可以看到同一个库存被使用了n次。数据库中库存变为负数。 线程安全问题出现。
解决方案:
(1) 使用 synchronized 或者lock锁
package com.wt.service.impl;
import com.wt.dao.ProductStockDao;
import com.wt.service.ProductStockService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ProductStockServiceImpl2 implements ProductStockService {
@Autowired
private ProductStockDao productStockDao;
@Override
public String decreaseStock(Integer productId) {
synchronized (this) {
//查看该商品的库存数量
Integer stock = productStockDao.findStockByProductId(productId);
if (stock > 0) {
//修改库存每次-1
productStockDao.updateStockByProductId(productId);
System.out.println("扣减成功!剩余库存数:" + (stock - 1));
return "success";
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败!库存不足!");
return "fail";
}
}
}
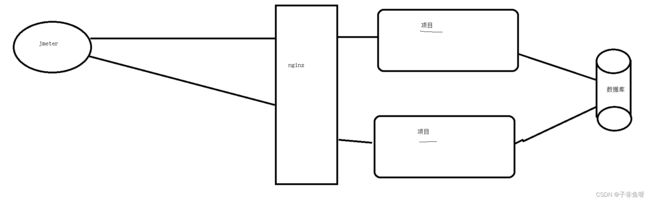
}使用synchronized 或者lock锁 如果我们搭建了项目集群,那么该锁无效。
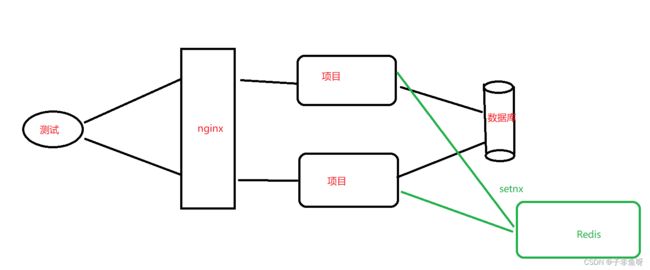
(2) 使用redis作为线程安全锁
使用idea开集群项目
搭建完成后同时开启两个项目,使用之前的自动锁或手动锁
发现又出现: 重复数字以及库存为负数。
使用redis作为锁
dao接口
package com.wt.dao;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface ProductStockDao {
public Integer findStockByProductId(Integer id);
public void updateStockByProductId(Integer id);
}mapper映射文件.xml
update tbl_stock set num=num-1 where productId=#{productId}
service接口
package com.wt.service;
public interface ProductStockService {
//减少库存
public String decreaseStock( Integer productId);
}service层
package com.wt.service.impl;
import com.wt.dao.ProductStockDao;
import com.wt.service.ProductStockService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ProductStockServiceImpl_redis implements ProductStockService {
@Autowired
private ProductStockDao productStockDao;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public String decreaseStock(Integer productId) {
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean flag = forValue.setIfAbsent("aaa::" + productId, "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
if(flag) {
try {
//查看该商品的库存数量
Integer stock = productStockDao.findStockByProductId(productId);
if (stock > 0) {
//修改库存每次-1
productStockDao.updateStockByProductId(productId);
System.out.println("扣减成功!剩余库存数:" + (stock - 1));
return "success";
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败!库存不足!");
return "fail";
}
}finally {
redisTemplate.delete("aaa::" + productId);
}
}
return "服务器正忙,请稍后在试......";
}
}
controller层
package com.wt.controller;
import com.wt.service.ProductStockService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("productStock")
public class ProductStockController {
@Autowired
private ProductStockService productStockService;
//减库存
@RequestMapping("decreaseStock/{productId}")
public String decreaseStock(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId){
return productStockService.decreaseStock(productId);
}
}
3. redis的解决分布式锁的bug
 可以使用:redission依赖,redission解决redis超时问题的原理。
可以使用:redission依赖,redission解决redis超时问题的原理。
为持有锁的线程开启一个守护线程,守护线程会每隔10秒检查当前线程是否还持有锁,如果持有则延迟生存时间。
使用:
(1) 引入相关依赖
org.redisson
redisson
3.13.4
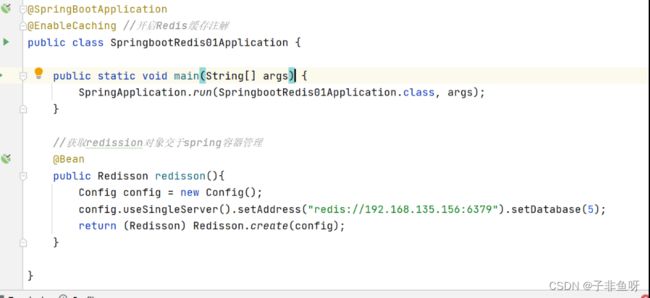
(2) 获取redission对象交于spring容器管理
//获取redission对象并交于spring容器管理
@Bean
public Redisson redisson(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.135.156:6379").setDatabase(5);
return (Redisson) Redisson.create(config);
}(3)修改service层
package com.wt.service.impl;
import com.wt.dao.ProductStockDao;
import com.wt.service.ProductStockService;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class ProductStockServiceImpl_redist implements ProductStockService {
@Autowired
private ProductStockDao productStockDao;
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
@Override
public String decreaseStock(Integer productId) {
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("ppp::"+productId);
try {
lock.lock(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//查看该商品的库存数量
Integer stock = productStockDao.findStockByProductId(productId);
if (stock > 0) {
//修改库存每次-1
productStockDao.updateStockByProductId(productId);
System.out.println("扣减成功!剩余库存数:" + (stock - 1));
return "success";
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败!库存不足!");
return "fail";
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
三.redis中常见的面试题
1. 什么是缓存穿透?怎么解决?
1. 数据库中没有该记录,缓存中也没有该记录,这时由人恶意大量访问这样的数据。这样就会导致该请求绕过缓存,直接访问数据,从而造成数据库压力过大。
2.解决办法:
[1]在controller加数据校验。
[2]我们可以在redis中存入一个空对象,而且要设置过期时间不能太长。超过5分钟
[3]我们使用布隆过滤器。底层:有一个bitmap数组,里面存储了该表的所有id.
//伪代码
String get(String key) { //布隆过滤器钟存储的是数据库表钟对应的id
String value = redis.get(key); //先从缓存获取。
if (value == null) { //缓存没有命中
if(!bloomfilter.mightContain(key)){//查看布隆过滤器钟是否存在
return null;
}else{
value = db.get(key); //查询数据库
redis.set(key, value);
}
}
return value;
}2. 什么是缓存雪崩?如何解决?
缓存雪崩是指缓存中数据大批量到过期时间,而查询数据量巨大,引起数据库压力过大甚至down机。和缓存击穿不同的是, 缓存击穿指并发查同一条数据,缓存雪崩是不同数据都过期了,很多数据都查不到从而查数据库。
1.什么下会发生缓存雪崩:
[1]项目刚上线,缓存中没有任何数据
[2]缓存出现大量过期。
[3]redis宕机
2.解决办法:
1.上线前预先把一些热点数据放入缓存。
2.设置过期时间为散列值
3.搭建redis集群
3. 什么是缓存击穿?如何解决?
缓存击穿是指缓存中没有但数据库中有的数据(一般是缓存时间到期),这时由于并发用户特别多,同时读缓存没读到数据,又同时去数据库去取数据,引起数据库压力瞬间增大,造成过大压力。
缓存击穿解决方案:
1.设置永久不过期。【这种只适合内存】
2.使用互斥锁(mutex key)业界比较常用的做法。
4. Redis 淘汰策略有哪些?