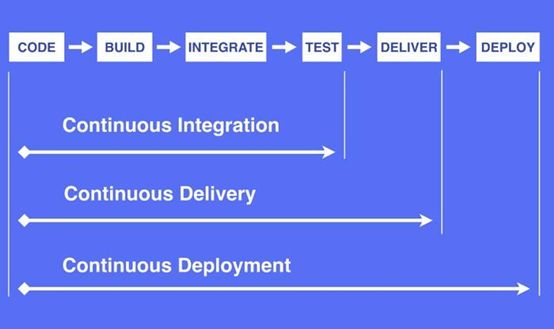
K8S部署&DevOps
k8s+kubesphere+devops
一、k8s 集群部署
1、k8s 快速入门
1)、简介
Kubernetes 简称 k8s。是用于自动部署,扩展和管理容器化应用程序的开源系统。
中文官网:https://kubernetes.io/zh/
中文社区:https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/
官方文档:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/home/
社区文档:http://docs.kubernetes.org.cn/
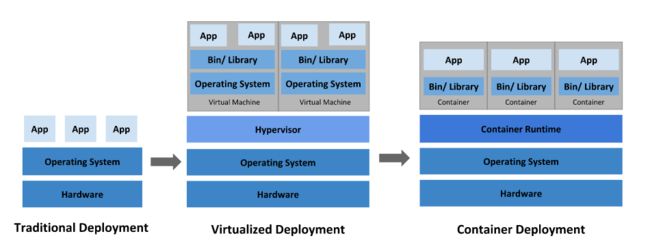
- 部署方式的进化
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/overview/
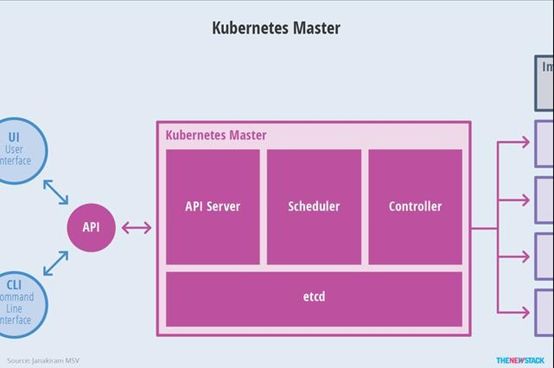
2)、架构
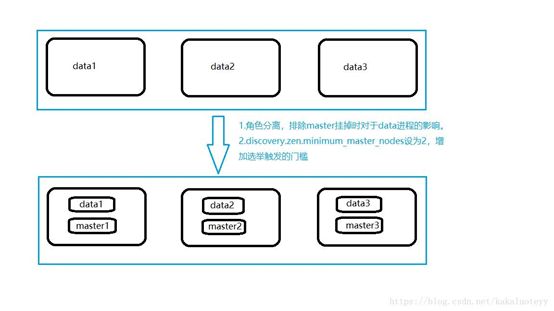
1、整体主从方式
一个服务器为主节点,其他的为node节点
2、Master 节点架构
-
kube-apiserver
- 对外暴露 K8S 的 api 接口,是外界进行资源操作的唯一入口
- 提供认证、授权、访问控制、API 注册和发现等机制
-
etcd
- etcd 是兼具一致性和高可用性的键值数据库,可以作为保存 Kubernetes 所有集群数据的后台数据库。
- Kubernetes 集群的 etcd 数据库通常需要有个备份计划
-
kube-scheduler
- 主节点上的组件,该组件监视那些新创建的未指定运行节点的 Pod,并选择节点 让 Pod 在上面运行。
- 所有对 k8s 的集群操作,都必须经过主节点进行调度
-
kube-controller-manager
- 在主节点上运行控制器的组件
- 这些控制器包括:
- 节点控制器(Node Controller): 负责在节点出现故障时进行通知和响应。
- 副本控制器(Replication Controller): 负责为系统中的每个副本控制器对象维护正确数量的 Pod。
- 端点控制器(Endpoints Controller): 填充端点(Endpoints)对象(即加入 Service 与 Pod) 。
- 服务帐户和令牌控制器(Service Account & Token Controllers): 为新的命名 空间创建默认帐户和 API 访问令牌
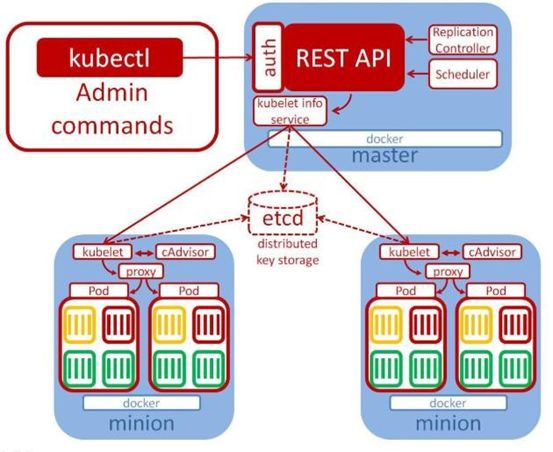
3、Node 节点架构
-
kubelet
- 一个在集群中每个节点上运行的代理。它保证容器都运行在 Pod 中。
- 负责维护容器的生命周期,同时也负责 Volume(CSI)和网络(CNI)的管理;
-
kube-proxy
- 负责为 Service 提供 cluster 内部的服务发现和负载均衡;
-
容器运行环境(Container Runtime)
- 容器运行环境是负责运行容器的软件。
- Kubernetes 支持多个容器运行环境: Docker、 containerd、cri-o、 rktlet 以及任何实现 Kubernetes CRI (容器运行环境接口)。
-
fluentd
- 是一个守护进程,它有助于提供集群层面日志集群层面的日志
3)、概念
-
Container:容器,可以是 docker 启动的一个容器
-
Pod:
- k8s 使用 Pod 来组织一组容器
- 一个 Pod 中的所有容器共享同一网络。
- Pod 是 k8s 中的最小部署单元
-
Volume
- 声明在 Pod 容器中可访问的文件目录
- 可以被挂载在 Pod 中一个或多个容器指定路径下
- 支持多种后端存储抽象(本地存储,分布式存储,云存储…)
![]()
-
Controllers:更高层次对象,部署和管理 Pod;
- ReplicaSet:确保预期的 Pod 副本数量
- Deplotment:无状态应用部署
- StatefulSet:有状态应用部署
- DaemonSet:确保所有 Node 都运行一个指定 Pod
- Job:一次性任务
- Cronjob:定时任务
-
Deployment:
- 定义一组 Pod 的副本数目、版本等
- 通过控制器(Controller)维持 Pod 数目(自动回 复失败的 Pod)
- 通过控制器以指定的策略控制版本(滚动升级,回滚等)
- Service
- 定义一组 Pod 的访问策略
- Pod 的负载均衡,提供一个或者多个 Pod 的稳定 访问地址
- 支持多种方式(ClusterIP、NodePort、LoadBalance)
- Label:标签,用于对象资源的查询,筛选
- Namespace:命名空间,逻辑隔离
- 一个集群内部的逻辑隔离机制(鉴权,资源)
- 每个资源都属于一个 namespace
- 同一个 namespace 所有资源名不能重复
- 不同 namespace 可以资源名重复
API:
我们通过 kubernetes 的 API 来操作整个集群
可以通过 kubectl、ui、curl 最终发送 http+json/yaml 方式的请求给 API Server,然后控制 k8s 集群。k8s 里的所有的资源对象都可以采用 yaml 或 JSON 格式的文件定义或描述
4)、快速体验
1、安装 minikube
https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases
下载 minikube-windows-amd64.exe 改名为 minikube.exe 打开 VirtualBox,打开cmd运行
minikube start --vm-driver=virtualbox --registry-mirror=https://registry.docker-cn.com
等待 20 分钟左右即可
2、体验 nginx 部署升级
提交一个nginx deployment
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment.yaml
升级nginx deployment
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment-update.yaml
扩容nginx deployment
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment-scale.yaml
5)、流程叙述
1、通过 Kubectl 提交一个创建RC(Replication Controller)的请求,该请求通过 APIServer被写入etcd 中
2、此时Controller Manager 通过API Server 的监听资源变化的接口监听到此RC 事件
3、分析之后,发现当前集群中还没有它所对应的Pod 实例,
4、于是根据RC 里的Pod 模板定义生成一个Pod 对象,通过APIServer 写入etcd
5、此事件被Scheduler 发现,它立即执行一个复杂的调度流程,为这个新 Pod 选定一 个落户的Node,然后通过 API Server 讲这一结果写入到 etcd 中,
6、目标 Node 上运行的 Kubelet 进程通过 APIServer 监测到这个“新生的”Pod,并按照它 的定义,启动该 Pod 并任劳任怨地负责它的下半生,直到Pod 的生命结束。
7、随后,我们通过Kubectl 提交一个新的映射到该 Pod 的Service 的创建请求
8、ControllerManager 通过Label 标签查询到关联的Pod 实例,然后生成Service 的 Endpoints 信息,并通过APIServer 写入到 etcd 中
9、接下来,所有 Node 上运行的 Proxy 进程通过 APIServer 查询并监听 Service 对象与 其对应的 Endpoints 信息,建立一个软件方式的负载均衡器来实现 Service 访问到后端 Pod 的流量转发功能。
k8s 里的所有的资源对象都可以采用yaml 或JSON 格式的文件定义或描述
2、k8s 集群安装
1、kubeadm
kubeadm 是官方社区推出的一个用于快速部署 kubernetes 集群的工具。 这个工具能通过两条指令完成一个 kubernetes 集群的部署:
# 创建一个 Master 节点
$ kubeadm init
# 将一个 Node 节点加入到当前集群中
$ kubeadm join <Master 节点的 IP 和端口 >
2、前置要求
一台或多台机器,操作系统 CentOS7.x-86_x64
硬件配置:2GB 或更多 RAM,2 个 CPU 或更多 CPU,硬盘 30GB 或更多
集群中所有机器之间网络互通
可以访问外网,需要拉取镜像
禁止 swap 分区
3、部署步骤
1.在所有节点上安装 Docker 和 kubeadm
2.部署 Kubernetes Master
3.部署容器网络插件
4.部署 Kubernetes Node,将节点加入 Kubernetes 集群中
5.部署 Dashboard Web 页面,可视化查看 Kubernetes 资源
4、环境准备
1、准备工作
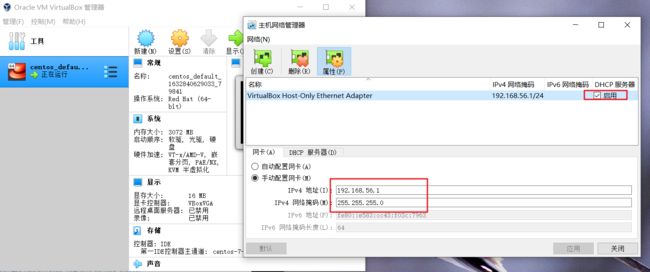
- 我们可以使用 vagrant 快速创建三个虚拟机。虚拟机启动前先设置 virtualbox 的主机网络。现全部统一为 192.168.56.1,以后所有虚拟机都是 56.x 的 ip 地址
- 设置虚拟机存储目录,防止硬盘空间不足
2、启动三个虚拟机
Vagrantfile:
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
(1..3).each do |i|
config.vm.define "k8s-node#{i}" do |node|
# 设置虚拟机的Box
node.vm.box = "centos/7"
# 设置虚拟机的主机名
node.vm.hostname="k8s-node#{i}"
# 设置虚拟机的IP
node.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.#{99+i}", netmask: "255.255.255.0"
# 设置主机与虚拟机的共享目录
# node.vm.synced_folder "~/Documents/vagrant/share", "/home/vagrant/share"
# VirtaulBox相关配置
node.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
# 设置虚拟机的名称
v.name = "k8s-node#{i}"
# 设置虚拟机的内存大小
v.memory = 4096
# 设置虚拟机的CPU个数
v.cpus = 4
end
end
end
end
-
使用我们提供的 vagrant 文件,复制到非中文无空格目录下,运行
vagrant up启动三个虚拟机。其实 vagrant 完全可以一键部署全部 k8s 集群。 https://github.com/rootsongjc/kubernetes-vagrant-centos-cluster http://github.com/davidkbainbridge/k8s-playground -
进入三个虚拟机,开启 root 的密码访问权限。
进去系统,如第一台k8s-node1
vagrant ssh k8s-node1su root #密码为 vagrantvi /etc/ssh/sshd_config修改
PasswordAuthentication yes
重启服务
systemctl restart sshd.service所有虚拟机设置为 4 核 4G
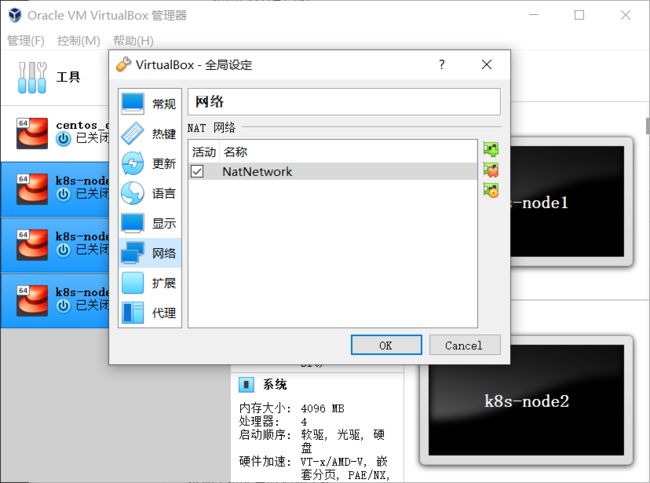
设置好 NAT 网络
关闭所有机器,全局设定设置net网络
每个机器设置网络连接方式为nat,界面名称为上述创建的NatNetwork,地址一定要随机在生成一个
3、设置 linux 环境(三个节点都执行)
关闭防火墙:
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
关闭selinux:
sed -i 's/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
set enforce 0
关闭 swap:
#关闭sawp分区 (可以不关闭,使用参数--ignore-preflight-errors=swap)
#临时关闭
swapoff -a
#永久
sed -ri 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab
#验证,swap 必须为 0;
free -g
添加主机名与IP 对应关系
cat > /etc/hosts << EOF
10.0.2.15 k8s-node1
10.0.2.4 k8s-node2
10.0..5 k8s-node3
EOF
#指定新的hostname
hostnamectl set-hostname <newhostname>
su 切换过来
将桥接的 IPv4 流量传递到 iptables 的链:
cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf << EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system
疑难问题:
遇见提示是只读的文件系统,运行如下命令
mount -o remount rw /
date 查看时间 (可选)
yum install -y ntpdate
同步最新时间
ntpdate time.windows.com
时间同步
echo '*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate -u ntp.api.bz' >>/var/spool/cron/root
systemctl restart crond.service
crontab -l
5、所有节点安装Docker、kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl
Kubernetes 默认 CRI(容器运行时)为 Docker,因此先安装 Docker。
1、安装 docker
1、卸载系统之前的 docker
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
2、安装 Docker-CE
源添加
#源添加
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
yum clean all
yum install -y bash-completion.noarch
安装必须的依赖,系统工具
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
设置 docker repo 的 yum 位置
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
可以查看版本安装
yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r
安装 docker,以及 docker-cli,可以指定一下版本
sudo yum install -y docker-ce-18.09.9-3.el7 docker-ce-cli-18.09.9-3.el7 containerd.io
3、配置 docker 加速
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
sudo echo -e "{\n \"registry-mirrors\": [\"https://5955cm2y.mirror.aliyuncs.com\"],\"exec-opts\": [\"native.cgroupdriver=systemd\"]\n}" > /etc/docker/daemon.json
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
4、启动 docker & 设置 docker 开机自启
systemctl enable docker
基础环境准备好,可以给三个虚拟机备份一下;为 node3 分配 16g,剩下的 3g。方便未来测试
2、添加阿里云 yum 源
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
拉取flanel镜像
docker pull lizhenliang/flannel:v0.11.0-amd64
3、安装 kubeadm,kubelet 和 kubectl
yum list|grep kube #检查是否有kube源
yum install -y kubelet-1.17.3 kubeadm-1.17.3 kubectl-1.17.3
systemctl enable kubelet #开机启动
systemctl start kubelet #启动
查看kubelet状态:systemctl status kubelet 发现启动不起来,因为其他配置未配置,这里先不管
6、部署k8s-master
1、master 节点初始化
先查看要成为master节点的默认网卡地址:ip addr
如图下面的设置为–apiserver-advertise-address=10.0.2.15
执行命令前可能失败先复制我们准备的master_images.sh文件
master_images.sh:
#!/bin/bash
images=(
kube-apiserver:v1.17.3
kube-proxy:v1.17.3
kube-controller-manager:v1.17.3
kube-scheduler:v1.17.3
coredns:1.6.5
etcd:3.4.3-0
pause:3.1
)
for imageName in ${images[@]} ; do
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName
# docker tag registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName k8s.gcr.io/$imageName
done
复制到这个要成为master节点的机器中
当前文件可能没有执行的权限使用命令
chmod 700 master_images.sh
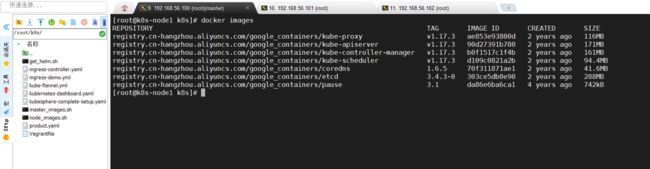
执行这个文件下砸镜像
./master_images.sh
等待几分钟下载完成,执行docker images查看下载情况
之后执行下面命令
kubeadm init \
--apiserver-advertise-address=10.0.2.15 \
--image-repository registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
--kubernetes-version v1.17.3 \
--service-cidr=10.96.0.0/16 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
可能提示swap的错误,关闭即可
或者提示
把这个设置为1即可
echo "1">/proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
echo "1">/proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-ip6tables
启动成功
![]()
由于默认拉取镜像地址k8s.gcr.io国内无法访问,这里指定阿里云镜像仓库地址。可以手动 按照我们的 images.sh 先拉取镜像,
地址变为 registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers 也可以。
科普:无类别域间路由(Classless Inter-Domain Routing、CIDR)是一个用于给用户分配 IP 地址以及在互联网上有效地路由 IP 数据包的对 IP 地址进行归类的方法。
拉取可能失败,需要下载镜像。
运行完成提前复制:加入集群的令牌,这会成功后先不要删除信息
2、测试 kubectl(主节点执行)
初始化成功后提示
执行一些配置文件
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
//todo
目前 master 状态为 notready。等待网络加入完成即可。
journalctl -u kubelet
7、 安装 Pod 网络插件(CNI)
$ kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
可能拉去失败,这里我用自己的
kube-flannel.yml
---
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: psp.flannel.unprivileged
annotations:
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: docker/default
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: docker/default
apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: runtime/default
apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: runtime/default
spec:
privileged: false
volumes:
- configMap
- secret
- emptyDir
- hostPath
allowedHostPaths:
- pathPrefix: "/etc/cni/net.d"
- pathPrefix: "/etc/kube-flannel"
- pathPrefix: "/run/flannel"
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
# Users and groups
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
# Privilege Escalation
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation: false
# Capabilities
allowedCapabilities: ['NET_ADMIN']
defaultAddCapabilities: []
requiredDropCapabilities: []
# Host namespaces
hostPID: false
hostIPC: false
hostNetwork: true
hostPorts:
- min: 0
max: 65535
# SELinux
seLinux:
# SELinux is unused in CaaSP
rule: 'RunAsAny'
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: flannel
rules:
- apiGroups: ['extensions']
resources: ['podsecuritypolicies']
verbs: ['use']
resourceNames: ['psp.flannel.unprivileged']
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/status
verbs:
- patch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: flannel
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: flannel
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: flannel
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: flannel
namespace: kube-system
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
data:
cni-conf.json: |
{
"name": "cbr0",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "flannel",
"delegate": {
"hairpinMode": true,
"isDefaultGateway": true
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {
"portMappings": true
}
}
]
}
net-conf.json: |
{
"Network": "10.244.0.0/16",
"Backend": {
"Type": "vxlan"
}
}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds-amd64
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- amd64
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-amd64
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-amd64
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds-arm64
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- arm64
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-arm64
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-arm64
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds-arm
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- arm
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-arm
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-arm
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds-ppc64le
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- ppc64le
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-ppc64le
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-ppc64le
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds-s390x
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- s390x
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-s390x
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-s390x
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
以上地址可能被墙, 大家获取上传我们下载好的 kube-flannel.yml 运行即可, 同时 kube-flannel.yml 中指定的 images 访问不到可以去 docker hub 找一个wget yml 的地址
vi 修改 yml 所有 amd64 的地址都修改了即可。
执行命令
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
等待大约 3 分钟
kubectl get pods -n kube-system 查看指定名称空间的 pods
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces 查看所有名称空间的 pods
$ ip link set cni0 down 如果网络出现问题, 关闭 cni0, 重启虚拟机继续测试
执行 watch kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide 监控 pod 进度
等 3-10 分钟, 完全都是 running 以后继续
获取所有节点
kubectl get nodes
8、加入Kubernetes Node
在 Node 节点执行。
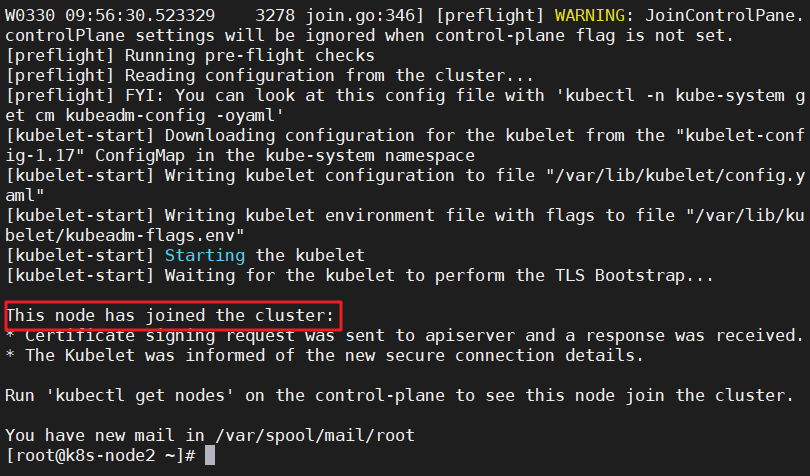
向集群添加新节点,执行在 kubeadm init 输出的 kubeadm join 命令:
kubeadm join 10.0.2.15:6443 --token 9g1a61.2a0407fj52gdfvfz \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:c3fdaf1e1c9e7230e3809a8a57223419f2cafddedc98085d8df3dbd1586bb59a
重启服务
systemctl restart docker.service
确保 node 节点成功
token 过期怎么办
#重新创建一个
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
#或者创建一个永久的token
kubeadm token create --ttl 0 --print-join-command
执行 watch kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide 监控 pod 进度
等 3-10 分钟,完全都是 running 以后使用kubectl get nodes检查状态
9、入门操作 kubernetes 集群
1、部署一个 tomcat
kubectl create deployment tomcat6 --image=tomcat:6.0.53-jre8
可以获取到 tomcat 信息,在哪个节点
kubectl get pods -o wide
此时如图部署在了node3节点上,如果node3宕机了会感知到然后重新部署到其他节点如node2
2、暴露 nginx 访问
kubectl expose deployment tomcat6 --port=80 --target-port=8080 --type=NodePort
80 映射容器的 8080;service 会代理 Pod 的 80
查看信息
kubectl get svc -o wide
访问测试,端口如上图,ip哪个机器都可以
http://192.168.56.102:30560/
3、动态扩容测试
kubectl get deployment
应用升级
kubectl set image (--help 查看帮助)
扩容
kubectl scale --replicas=3 deployment tomcat6
扩容了多份,所有无论访问哪个 node 的指定端口,都可以访问到 tomcat6
4、以上操作的 yaml 获取
参照 k8s 细节
5、删除
Kubectl get all
kubectl delete deploy/nginx
kubectl delete service/nginx-service
流程:创建 deployment 会管理 replicas,replicas 控制 pod 数量,有 pod 故障会自动拉起新的 pod
10、安装默认 dashboard(暂不使用)
1、部署 dashboard
$ kubectl apply -f \ https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v1.10.1/src/deploy/recommende
墙的原因可能不成功,就使用我们准备好的文件,自行上传 文件中无法访问的镜像,自行去 docker hub 找
kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
# Copyright 2017 The Kubernetes Authors.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ------------------- Dashboard Secret ------------------- #
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
namespace: kube-system
type: Opaque
---
# ------------------- Dashboard Service Account ------------------- #
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
---
# ------------------- Dashboard Role & Role Binding ------------------- #
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
rules:
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder' secret.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to get, update and delete Dashboard exclusive secrets.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder", "kubernetes-dashboard-certs"]
verbs: ["get", "update", "delete"]
# Allow Dashboard to get and update 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-settings"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
# Allow Dashboard to get metrics from heapster.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
resourceNames: ["heapster"]
verbs: ["proxy"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services/proxy"]
resourceNames: ["heapster", "http:heapster:", "https:heapster:"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
---
# ------------------- Dashboard Deployment ------------------- #
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
containers:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard
image: k8s.gcr.io/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.10.1
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
args:
- --auto-generate-certificates
# Uncomment the following line to manually specify Kubernetes API server Host
# If not specified, Dashboard will attempt to auto discover the API server and connect
# to it. Uncomment only if the default does not work.
# - --apiserver-host=http://my-address:port
volumeMounts:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
mountPath: /certs
# Create on-disk volume to store exec logs
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-volume
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTPS
path: /
port: 8443
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
secret:
secretName: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
- name: tmp-volume
emptyDir: {}
serviceAccountName: kubernetes-dashboard
# Comment the following tolerations if Dashboard must not be deployed on master
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
---
# ------------------- Dashboard Service ------------------- #
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
2、暴露 dashboard 为公共访问
默认 Dashboard 只能集群内部访问,修改 Service 为 NodePort 类型,暴露到外部:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1 metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard name: kubernetes-dashboard namespace: kube-system
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
nodePort: 30001 selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
访问地址:http://NodeIP:30001
3、创建授权账户
$ kubectl create serviceaccount dashboard-admin -n kube-system
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding dashboard-admin --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:dashboard-admin
$ kubectl describe secrets -n kube-system $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | awk '/dashboard-admin/{print $1}')
使用输出的 token 登录 Dashboard。
二、KubeSphere
默认的 dashboard 没啥用,我们用 kubesphere 可以打通全部的 devops 链路。 Kubesphere 集成了很多套件,集群要求较高
https://kubesphere.io/
Kuboard 也很不错,集群要求不高
https://kuboard.cn/support/
1、简介
KubeSphere 是一款面向云原生设计的开源项目,在目前主流容器调度平台 Kubernetes 之 上构建的分布式多租户容器管理平台,提供简单易用的操作界面以及向导式操作方式,在降 低用户使用容器调度平台学习成本的同时,极大降低开发、测试、运维的日常工作的复杂度。
2、安装
1、前提条件
https://kubesphere.io/docs/v2.1/zh-CN/installation/prerequisites/
2、安装前提环境
1、安装 helm(master 节点执行)
Helm 是 Kubernetes 的包管理器。包管理器类似于我们在 Ubuntu 中使用的 apt、Centos 中使用的 yum 或者 Python 中的 pip 一样,能快速查找、下载和安装软件包。Helm 由客 户端组件 helm 和服务端组件 Tiller 组成, 能够将一组 K8S 资源打包统一管理, 是查找、共享和使用为 Kubernetes 构建的软件的最佳方式。
1)、安装
curl -L https://git.io/get_helm.sh | bash
墙原因,这里使用离线安装
获取安装包,这个地址下载快一点
https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/helm/v2.16.3/
将解压后的linux-amd64/helm、linux-amd64/tiller两个文件放到/usr/local/bin/目录中
chmod 700 xxx #没有权限就使用这个命令更改一下
2)、验证版本
helm version #错误先不管
3、创建权限(master 执行)
创建 helm-rbac.yaml,写入如下内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: tiller
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: tiller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: tiller
namespace: kube-system
应用配置
kubectl apply -f helm-rbac.yaml
2、安装 Tiller(master 执行)
1、初始化
helm init --service-account=tiller --upgrade -i registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/tiller:v2.16.3 --stable-repo-url https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts
–tiller-image指定镜像,否则会被墙
等待节点上部署的 tiller 完成即可
2、测试(可跳过)
helm install stable/nginx-ingress --name nginx-ingress
helm ls
helm delete nginx-ingress
3、使用语法(可跳过)
#创建一个 chart 范例
helm create helm-chart
#检查 chart 语法
helm lint ./helm-chart
#使用默认 chart 部署到 k8s
helm install --name example1 ./helm-chart --set service.type=NodePort
#查看是否部署成功
kubectl get pod
3、安装 OpenEBS(master 执行)
https://v2-1.docs.kubesphere.io/docs/zh-CN/appendix/install-openebs/
确定 master 节点是否有 taint
kubectl describe node k8s-node1 | grep Taint
取消 taint
kubectl taint nodes k8s-node1 node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule-
创建 OpenEBS 的 namespace,OpenEBS 相关资源将创建在这个 namespace 下:
kubectl create ns openebs
安装 OpenEBS,以下列出两种方法,可参考其中任意一种进行创建
A. 若集群已安装了 Helm,可通过 Helm 命令来安装 OpenEBS:
helm install --namespace openebs --name openebs stable/openebs --version 1.5.0
B.除此之外 还可以通过 kubectl 命令安装:
kubectl apply -f https://openebs.github.io/charts/openebs-operator-1.5.0.yaml
以上两种官方说明的方式 第一种提示(hint: running helm repo update may help)我解决不了
第二种是下载一个yaml文件去应用,因为官方提供的地址找不到资源了,这里我们去docker找到对应的版本拉取,然后使用我们自己的yaml文件执行
docker pull openebs/m-apiserver:1.5.0
docker pull openebs/openebs-k8s-provisioner:1.5.0
docker pull openebs/snapshot-controller:1.5.0
docker pull openebs/snapshot-provisioner:1.5.0
docker pull openebs/node-disk-manager-amd64:v0.4.5
docker pull openebs/node-disk-operator-amd64:v0.4.5
docker pull openebs/admission-server:1.5.0
docker pull openebs/provisioner-localpv:1.5.0
openebs-operator-1.5.0.yaml
# This manifest deploys the OpenEBS control plane components, with associated CRs & RBAC rules
# NOTE: On GKE, deploy the openebs-operator.yaml in admin context
# Create the OpenEBS namespace
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openebs
---
# Create Maya Service Account
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: openebs-maya-operator
namespace: openebs
---
# Define Role that allows operations on K8s pods/deployments
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: openebs-maya-operator
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/proxy"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["namespaces", "services", "pods", "pods/exec", "deployments", "deployments/finalizers", "replicationcontrollers", "replicasets", "events", "endpoints", "configmaps", "secrets", "jobs", "cronjobs"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["statefulsets", "daemonsets"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["resourcequotas", "limitranges"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["ingresses", "horizontalpodautoscalers", "verticalpodautoscalers", "poddisruptionbudgets", "certificatesigningrequests"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["storageclasses", "persistentvolumeclaims", "persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["volumesnapshot.external-storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshots", "volumesnapshotdatas"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["apiextensions.k8s.io"]
resources: ["customresourcedefinitions"]
verbs: [ "get", "list", "create", "update", "delete", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "disks", "blockdevices", "blockdeviceclaims"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "cstorpoolclusters", "storagepoolclaims", "storagepoolclaims/finalizers", "cstorpoolclusters/finalizers", "storagepools"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "castemplates", "runtasks"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "cstorpools", "cstorpools/finalizers", "cstorvolumereplicas", "cstorvolumes", "cstorvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "cstorpoolinstances", "cstorpoolinstances/finalizers"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "cstorbackups", "cstorrestores", "cstorcompletedbackups"]
verbs: ["*" ]
- apiGroups: ["coordination.k8s.io"]
resources: ["leases"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list", "delete", "update", "create"]
- apiGroups: ["admissionregistration.k8s.io"]
resources: ["validatingwebhookconfigurations", "mutatingwebhookconfigurations"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "list", "delete", "update", "patch"]
- nonResourceURLs: ["/metrics"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: [ "upgradetasks"]
verbs: ["*" ]
---
# Bind the Service Account with the Role Privileges.
# TODO: Check if default account also needs to be there
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: openebs-maya-operator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: openebs-maya-operator
namespace: openebs
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: openebs-maya-operator
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: maya-apiserver
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: maya-apiserver
openebs.io/component-name: maya-apiserver
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: maya-apiserver
openebs.io/component-name: maya-apiserver
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
rollingUpdate: null
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: maya-apiserver
openebs.io/component-name: maya-apiserver
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: maya-apiserver
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: openebs/m-apiserver:1.5.0
ports:
- containerPort: 5656
env:
# OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG enables maya api service to connect to K8s
# based on this config. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for maya api server version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG
# value: "/home/ubuntu/.kube/config"
# OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER enables maya api service to connect to K8s
# based on this address. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for maya api server version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER
# value: "http://172.28.128.3:8080"
# OPENEBS_NAMESPACE provides the namespace of this deployment as an
# environment variable
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# OPENEBS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT provides the service account of this pod as
# environment variable
- name: OPENEBS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
# OPENEBS_MAYA_POD_NAME provides the name of this pod as
# environment variable
- name: OPENEBS_MAYA_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
# If OPENEBS_IO_CREATE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CONFIG is false then OpenEBS default
# storageclass and storagepool will not be created.
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CREATE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CONFIG
value: "true"
# OPENEBS_IO_INSTALL_DEFAULT_CSTOR_SPARSE_POOL decides whether default cstor sparse pool should be
# configured as a part of openebs installation.
# If "true" a default cstor sparse pool will be configured, if "false" it will not be configured.
# This value takes effect only if OPENEBS_IO_CREATE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CONFIG
# is set to true
- name: OPENEBS_IO_INSTALL_DEFAULT_CSTOR_SPARSE_POOL
value: "false"
# OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_TARGET_DIR can be used to specify the hostpath
# to be used for saving the shared content between the side cars
# of cstor volume pod.
# The default path used is /var/openebs/sparse
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_TARGET_DIR
# value: "/var/openebs/sparse"
# OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_POOL_SPARSE_DIR can be used to specify the hostpath
# to be used for saving the shared content between the side cars
# of cstor pool pod. This ENV is also used to indicate the location
# of the sparse devices.
# The default path used is /var/openebs/sparse
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_POOL_SPARSE_DIR
# value: "/var/openebs/sparse"
# OPENEBS_IO_JIVA_POOL_DIR can be used to specify the hostpath
# to be used for default Jiva StoragePool loaded by OpenEBS
# The default path used is /var/openebs
# This value takes effect only if OPENEBS_IO_CREATE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CONFIG
# is set to true
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_JIVA_POOL_DIR
# value: "/var/openebs"
# OPENEBS_IO_LOCALPV_HOSTPATH_DIR can be used to specify the hostpath
# to be used for default openebs-hostpath storageclass loaded by OpenEBS
# The default path used is /var/openebs/local
# This value takes effect only if OPENEBS_IO_CREATE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CONFIG
# is set to true
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_LOCALPV_HOSTPATH_DIR
# value: "/var/openebs/local"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_JIVA_CONTROLLER_IMAGE
value: "openebs/jiva:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_JIVA_REPLICA_IMAGE
value: "openebs/jiva:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_JIVA_REPLICA_COUNT
value: "3"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_TARGET_IMAGE
value: "openebs/cstor-istgt:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_POOL_IMAGE
value: "openebs/cstor-pool:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_POOL_MGMT_IMAGE
value: "openebs/cstor-pool-mgmt:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_VOLUME_MGMT_IMAGE
value: "openebs/cstor-volume-mgmt:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_VOLUME_MONITOR_IMAGE
value: "openebs/m-exporter:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_CSTOR_POOL_EXPORTER_IMAGE
###################################################################################################################
value: "openebs/m-exporter:1.5.0"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_HELPER_IMAGE
value: "openebs/linux-utils:1.5.0"
# OPENEBS_IO_ENABLE_ANALYTICS if set to true sends anonymous usage
# events to Google Analytics
- name: OPENEBS_IO_ENABLE_ANALYTICS
value: "true"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_INSTALLER_TYPE
value: "openebs-operator"
# OPENEBS_IO_ANALYTICS_PING_INTERVAL can be used to specify the duration (in hours)
# for periodic ping events sent to Google Analytics.
# Default is 24h.
# Minimum is 1h. You can convert this to weekly by setting 168h
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_ANALYTICS_PING_INTERVAL
# value: "24h"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /usr/local/bin/mayactl
- version
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /usr/local/bin/mayactl
- version
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: maya-apiserver-service
namespace: openebs
labels:
openebs.io/component-name: maya-apiserver-svc
spec:
ports:
- name: api
port: 5656
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5656
selector:
name: maya-apiserver
sessionAffinity: None
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: openebs-provisioner
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: openebs-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-provisioner
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: openebs-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-provisioner
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
rollingUpdate: null
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-provisioner
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: openebs-provisioner
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: openebs/openebs-k8s-provisioner:1.5.0
env:
# OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER enables openebs provisioner to connect to K8s
# based on this address. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER
# value: "http://10.128.0.12:8080"
# OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG enables openebs provisioner to connect to K8s
# based on this config. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG
# value: "/home/ubuntu/.kube/config"
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME provides the maya-apiserver K8s service name,
# that provisioner should forward the volume create/delete requests.
# If not present, "maya-apiserver-service" will be used for lookup.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.3-RC1 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME
# value: "maya-apiserver-apiservice"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pgrep
- ".*openebs"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: openebs-snapshot-operator
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: openebs-snapshot-operator
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-snapshot-operator
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: openebs-snapshot-operator
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-snapshot-operator
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-snapshot-operator
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-snapshot-operator
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: snapshot-controller
image: openebs/snapshot-controller:1.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pgrep
- ".*controller"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
# OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME provides the maya-apiserver K8s service name,
# that snapshot controller should forward the snapshot create/delete requests.
# If not present, "maya-apiserver-service" will be used for lookup.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.3-RC1 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME
# value: "maya-apiserver-apiservice"
- name: snapshot-provisioner
image: openebs/snapshot-provisioner:1.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME provides the maya-apiserver K8s service name,
# that snapshot provisioner should forward the clone create/delete requests.
# If not present, "maya-apiserver-service" will be used for lookup.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.3-RC1 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_MAYA_SERVICE_NAME
# value: "maya-apiserver-apiservice"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pgrep
- ".*provisioner"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
---
# This is the node-disk-manager related config.
# It can be used to customize the disks probes and filters
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: openebs-ndm-config
namespace: openebs
labels:
openebs.io/component-name: ndm-config
data:
# udev-probe is default or primary probe which should be enabled to run ndm
# filterconfigs contails configs of filters - in their form fo include
# and exclude comma separated strings
node-disk-manager.config: |
probeconfigs:
- key: udev-probe
name: udev probe
state: true
- key: seachest-probe
name: seachest probe
state: false
- key: smart-probe
name: smart probe
state: true
filterconfigs:
- key: os-disk-exclude-filter
name: os disk exclude filter
state: true
exclude: "/,/etc/hosts,/boot"
- key: vendor-filter
name: vendor filter
state: true
include: ""
exclude: "CLOUDBYT,OpenEBS"
- key: path-filter
name: path filter
state: true
include: ""
exclude: "loop,/dev/fd0,/dev/sr0,/dev/ram,/dev/dm-,/dev/md"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: openebs-ndm
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: openebs-ndm
openebs.io/component-name: ndm
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: openebs-ndm
openebs.io/component-name: ndm
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-ndm
openebs.io/component-name: ndm
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
# By default the node-disk-manager will be run on all kubernetes nodes
# If you would like to limit this to only some nodes, say the nodes
# that have storage attached, you could label those node and use
# nodeSelector.
#
# e.g. label the storage nodes with - "openebs.io/nodegroup"="storage-node"
# kubectl label node "openebs.io/nodegroup"="storage-node"
#nodeSelector:
# "openebs.io/nodegroup": "storage-node"
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: node-disk-manager
image: openebs/node-disk-manager-amd64:v0.4.5
imagePullPolicy: Always
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /host/node-disk-manager.config
subPath: node-disk-manager.config
readOnly: true
- name: udev
mountPath: /run/udev
- name: procmount
mountPath: /host/proc
readOnly: true
- name: sparsepath
mountPath: /var/openebs/sparse
env:
# namespace in which NDM is installed will be passed to NDM Daemonset
# as environment variable
- name: NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# pass hostname as env variable using downward API to the NDM container
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
# specify the directory where the sparse files need to be created.
# if not specified, then sparse files will not be created.
- name: SPARSE_FILE_DIR
value: "/var/openebs/sparse"
# Size(bytes) of the sparse file to be created.
- name: SPARSE_FILE_SIZE
value: "10737418240"
# Specify the number of sparse files to be created
- name: SPARSE_FILE_COUNT
value: "0"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pgrep
- ".*ndm"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: openebs-ndm-config
- name: udev
hostPath:
path: /run/udev
type: Directory
# mount /proc (to access mount file of process 1 of host) inside container
# to read mount-point of disks and partitions
- name: procmount
hostPath:
path: /proc
type: Directory
- name: sparsepath
hostPath:
path: /var/openebs/sparse
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: openebs-ndm-operator
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: openebs-ndm-operator
openebs.io/component-name: ndm-operator
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: openebs-ndm-operator
openebs.io/component-name: ndm-operator
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-ndm-operator
openebs.io/component-name: ndm-operator
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: node-disk-operator
image: openebs/node-disk-operator-amd64:v0.4.5
imagePullPolicy: Always
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- stat
- /tmp/operator-sdk-ready
initialDelaySeconds: 4
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 1
env:
- name: WATCH_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
# the service account of the ndm-operator pod
- name: SERVICE_ACCOUNT
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
- name: OPERATOR_NAME
value: "node-disk-operator"
- name: CLEANUP_JOB_IMAGE
value: "openebs/linux-utils:1.5.0"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: openebs-admission-server
namespace: openebs
labels:
app: admission-webhook
openebs.io/component-name: admission-webhook
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
rollingUpdate: null
selector:
matchLabels:
app: admission-webhook
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: admission-webhook
openebs.io/component-name: admission-webhook
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: admission-webhook
image: openebs/admission-server:1.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- -alsologtostderr
- -v=2
- 2>&1
env:
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: ADMISSION_WEBHOOK_NAME
value: "openebs-admission-server"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
namespace: openebs
labels:
name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
openebs.io/component-name: openebs-localpv-provisioner
openebs.io/version: 1.5.0
spec:
serviceAccountName: openebs-maya-operator
containers:
- name: openebs-provisioner-hostpath
imagePullPolicy: Always
image: openebs/provisioner-localpv:1.5.0
env:
# OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER enables openebs provisioner to connect to K8s
# based on this address. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_K8S_MASTER
# value: "http://10.128.0.12:8080"
# OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG enables openebs provisioner to connect to K8s
# based on this config. This is ignored if empty.
# This is supported for openebs provisioner version 0.5.2 onwards
#- name: OPENEBS_IO_KUBE_CONFIG
# value: "/home/ubuntu/.kube/config"
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: OPENEBS_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# OPENEBS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT provides the service account of this pod as
# environment variable
- name: OPENEBS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
- name: OPENEBS_IO_ENABLE_ANALYTICS
value: "true"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_INSTALLER_TYPE
value: "openebs-operator"
- name: OPENEBS_IO_HELPER_IMAGE
value: "openebs/linux-utils:1.5.0"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pgrep
- ".*localpv"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 60
---
执行命令应用
kubectl apply -f openebs-operator-1.5.0.yaml
稍等一会查看效果
kubectl get sc --all-namespaces
将 openebs-hostpath 设置为 默认的 StorageClass:
kubectl patch storageclass openebs-hostpath -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
至此,OpenEBS 的 LocalPV 已作为默认的存储类型创建成功。由于在文档开头手动去掉 了master 节点的 Taint,我们可以在安装完 OpenEBS 后将 master 节点 Taint 加上,避 免业务相关的工作负载调度到 master 节点抢占 master 资源,但是我个人测试这里不要加上,不然后面安装kubesphere的时候就会导致ks-gateway和api服务开启不了,所以忽略下面命令,后面有需要在看
kubectl taint nodes k8s-node1 node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoSchedule
3、最小化安装kubesphere
若您的集群可用的资源符合 CPU > 1 Core,可用内存 > 2 G,可以参考以下命令开启
KubeSphere 最小化安装:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/blob/v2.1.1/kubesphere-minimal.yaml
查看安装日志,请耐心等待安装成功。
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -f
4、完整化安装
若集群可用 CPU > 8 Core 且可用内存 > 16 G,可以使用以下命令完整安装 KubeSphere。
1、一条命令
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/v2.1.1/kubesphere-complete-setup.yaml
可以去我们的文件里面获取,上传到虚拟机,
参照 https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/tree/master 修改部分配置
2、查看进度
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -f
因为暂时我的机器内存有限,这里先使用最小安装,可能上述官方的地址失效,我找到一个kubesphere-minimal.yaml文件如下:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: kubesphere-system
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
ks-config.yaml: |
---
persistence:
storageClass: ""
etcd:
monitoring: False
endpointIps: 192.168.0.7,192.168.0.8,192.168.0.9
port: 2379
tlsEnable: True
common:
mysqlVolumeSize: 20Gi
minioVolumeSize: 20Gi
etcdVolumeSize: 20Gi
openldapVolumeSize: 2Gi
redisVolumSize: 2Gi
metrics_server:
enabled: False
console:
enableMultiLogin: False # enable/disable multi login
port: 30880
monitoring:
prometheusReplicas: 1
prometheusMemoryRequest: 400Mi
prometheusVolumeSize: 20Gi
grafana:
enabled: False
logging:
enabled: False
elasticsearchMasterReplicas: 1
elasticsearchDataReplicas: 1
logsidecarReplicas: 2
elasticsearchMasterVolumeSize: 4Gi
elasticsearchDataVolumeSize: 20Gi
logMaxAge: 7
elkPrefix: logstash
containersLogMountedPath: ""
kibana:
enabled: False
openpitrix:
enabled: False
devops:
enabled: True
jenkinsMemoryLim: 2Gi
jenkinsMemoryReq: 1000Mi
jenkinsVolumeSize: 8Gi
jenkinsJavaOpts_Xms: 512m
jenkinsJavaOpts_Xmx: 512m
jenkinsJavaOpts_MaxRAM: 2g
sonarqube:
enabled: True
postgresqlVolumeSize: 8Gi
servicemesh:
enabled: False
notification:
enabled: True
alerting:
enabled: True
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: ks-installer
namespace: kubesphere-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: ks-installer
namespace: kubesphere-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: ks-installer
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- rbac.authorization.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- apiregistration.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- apiextensions.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- tenant.kubesphere.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- certificates.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- devops.kubesphere.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- monitoring.coreos.com
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- logging.kubesphere.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- jaegertracing.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- storage.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- admissionregistration.k8s.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: ks-installer
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ks-installer
namespace: kubesphere-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: ks-installer
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ks-installer
namespace: kubesphere-system
labels:
app: ks-install
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ks-install
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ks-install
spec:
serviceAccountName: ks-installer
containers:
- name: installer
image: kubesphere/ks-installer:v2.1.1
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
复制到机器中使用命令:
kubectl apply -f kubesphere-minimal.yaml
启动成功
3、解决问题重启 installer
kubectl delete pod ks-apigateway-78bcdc8ffc-fcfqb -n kubesphere-system
4、metrics-server 部署
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount metadata:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
template:
metadata:
name: metrics-server
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
serviceAccountName: metrics-server
volumes:
# mount in tmp so we can safely use from-scratch images and/or read-only containers
-name: tmp-dir
emptyDir: {}
containers:
-name: metrics-server
# image: k8s.gcr.io/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.6
image: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.6
args:
---cert-dir=/tmp
---secure-port=4443
---kubelet-insecure-tls
---kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,Hostname,InternalDNS,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP
ports:
- name: main-port
containerPort: 4443
protocol: TCP
securityContext:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- name: tmp-dir
mountPath: /tmp
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
3、角色管理
示例
1、创建一个角色(负责用户管理的)
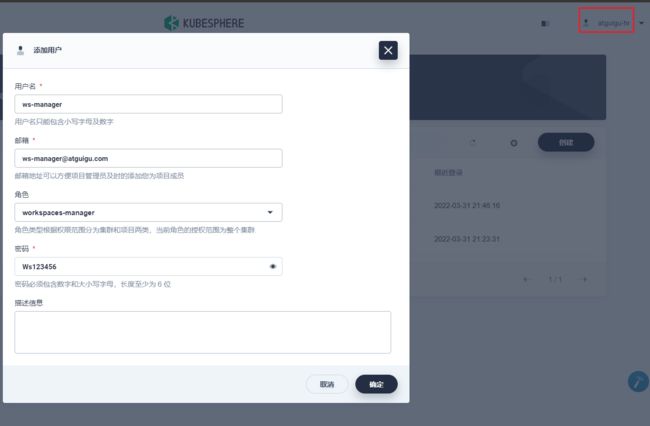
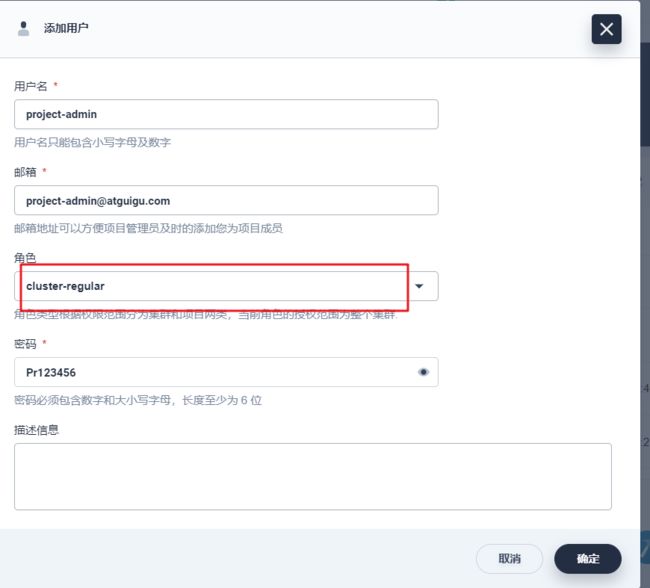
2、创建一个账号
3、使用创建的hr的账号分配一个集群工作空间的管理员
4、创建的hr的账号分配一个集群的普通用户
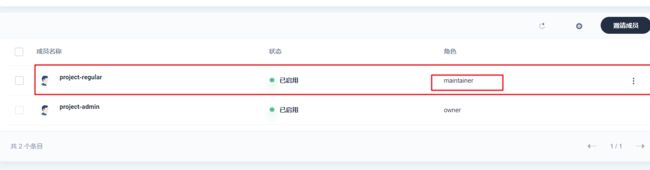
5、创建一个项目的管理用户
6、创建一个项目的普通用户
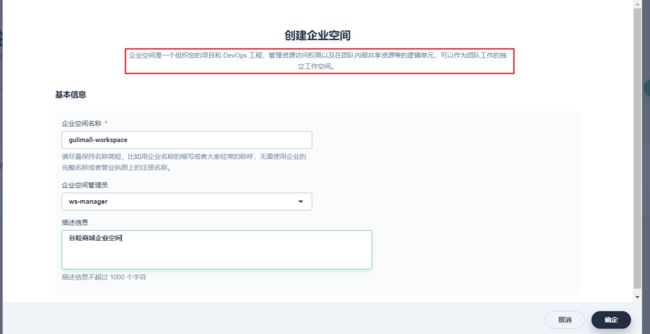
7、登录ws-manager用户(管理工作空间的)
创建一个项目空间
分配该项目空间的管理员
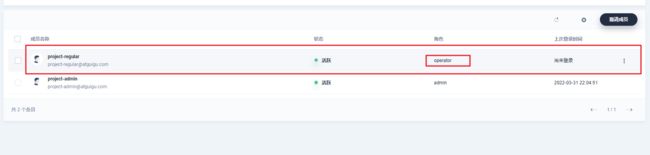
8、登录ws-admin(项目的管理员)
邀请两个成员,一个是项目的管理员,一个只能观看的普通用户
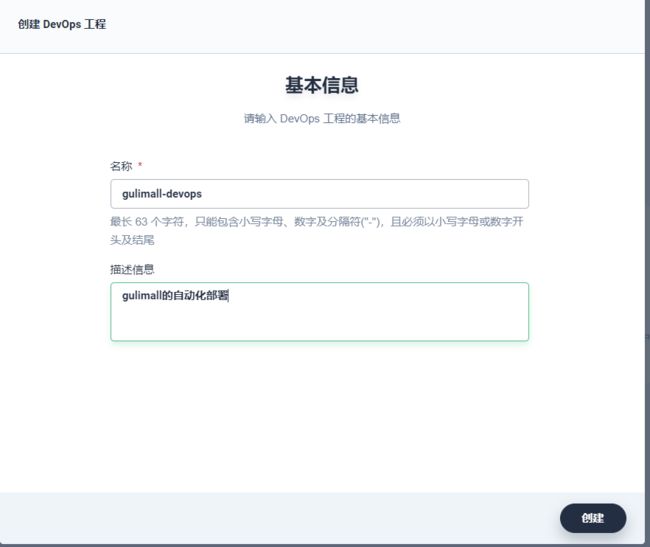
9、登录project-admin
创建一个资源项目,如谷粒商城后台项目、前端项目…
邀请一个开发人员
创建一个devops项目
邀请一个流水线维护人员
4、创建密钥
详情见https://v2-1.docs.kubesphere.io/docs/zh-CN/quick-start/wordpress-deployment/
5、创建凭证
https://v2-1.docs.kubesphere.io/docs/zh-CN/devops/credential/#%E5%88%9B%E5%BB%BA%E5%87%AD%E8%AF%81
6、等等。。。。。。
三、Docker 深入
1、Dockerfile
在 Docker 中创建镜像最常用的方式,就是使用 Dockerfile。Dockerfile 是一个 Docker 镜像 的描述文件,我们可以理解成火箭发射的 A、B、C、D…的步骤。Dockerfile 其内部包含了一 条条的指令,每一条指令构建一层,因此每一条指令的内容,就是描述该层应当如何构建。
1、示例
#基于 centos 镜像
FROM centos
#维护人的信息
MAINTAINER My CentOS <534096094@qq.com>
#安装 httpd 软件包
RUN yum -y update
RUN yum -y install httpd
#开启 80 端口
EXPOSE 80
#复制网站首页文件至镜像中 web 站点下
ADD index.html /var/www/html/index.html
#复制该脚本至镜像中,并修改其权限
ADD run.sh /run.sh
RUN chmod 775 /run.sh
#当启动容器时执行的脚本文件
CMD ["/run.sh"]
官方文档:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/#from
复杂一点的示例
#在 centos 上安装 nginx
FROM centos
#标明著作人的名称和邮箱
MAINTAINER xxx [email protected]
#测试一下网络环境
RUN ping -c 1 www.baidu.com
#安装 nginx 必要的一些软件
RUN yum -y install gcc make pcre-devel zlib-devel tar zlib
#把 nginx 安装包复制到/usr/src/目录下,如果是压缩包还会自动解压,是网络路径会自动 下载
ADD nginx-1.15.8.tar.gz /usr/src/
#切换到/usr/src/nginx-1.15.8 编译并且安装
nginx RUN cd /usr/src/nginx-1.15.8 \
&& mkdir /usr/local/nginx \
&& ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx && make && make install \
&& ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ \
&& nginx
#删除安装 nginx 安装目录
RUN rm -rf /usr/src/nginx-nginx-1.15.8
#对外暴露 80 端口
EXPOSE 80
#启动 nginx
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
2、常用指令
| 类型 | 命令 |
|---|---|
| 基础镜像信息 | FROM |
| 维护者信息 | MAINTAINER |
| 镜像操作指令 | RUN、COPY、ADD、EXPOSE、WORKDIR、 ONBUILD、USER、VOLUME 等 |
| 容器启动时执行指令 | CMD、ENTRYPOINT |
2、镜像操作
1、创建项目 dockerfile
2、上传项目到服务器。
3、进入项目,构建镜像到本地仓库;
-
(1)
docker build -t nginx:GA-1.0 -f ./Dockerfile .别忘了最后的小数点。 -
(2)
docker images查看镜像 -
(3)
docker exec -it 容器id /bin/bash进入容器,修改容器 -
(4)
docker commit -a “leifengyang” -m “nginxxx” 容器 id mynginx:GA-2.0- docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
- OPTIONS 说明:
- -a :提交的镜像作者;
- -c :使用 Dockerfile 指令来创建镜像;
- -m :提交时的说明文字;
- -p :在 commit 时,将容器暂停。
-
(5)
docker login: 登陆到一个 Docker 镜像仓库,如果未指定镜像仓库地址,默认为官 方仓库 Docker Hubdocker login -u 用户名 -p 密码
-
(6)
docker logout: 登出一个 Docker 镜像仓库,如果未指定镜像仓库地址,默认为官 方仓库 Docker Hub
4、推送镜像到 docker hub
(1)标记镜像
docker tag local-image:tagname username/new-repo:tagname
(2)上传镜像
docker push username/new-repo:tagname
5、保存镜像,加载镜像
(1)可以保存镜像为 tar,使用 u 盘等设备复制到任意 docker 主机,再次加载镜像
(2)保存
docker save spring-boot-docker -o /home/spring-boot-docker.tar
(3)加载
docker load -i sping-boot-docker.tar
6、阿里云操作
(1)登录阿里云,密码就是开通镜像仓库时的密码
docker login --username=chenfl**** registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
(2)拉取镜像
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/chenfl_docker/gulimall:[镜像版本号]
(3)推送镜像
$ docker login --username=chenfl0126 registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
$ docker tag [ImageId] registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/chenfl_docker/gulimall:[镜像版本号]
$ docker push registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/chenfl_docker/gulimall:[镜像版本号]
四、K8S 细节
1、kubectl
1、kubectl 文档
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/
2、资源类型
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/#%E8%B5%84%E6%BA%90%E7%B1%BB%E5%9E%8B
3、格式化输出
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/#%E6%A0%BC%E5%BC%8F%E5%8C%96%E8%BE%93%E5%87%BA
4、常用操作
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/#%E7%A4%BA%E4%BE%8B-%E5%B8%B8%E7%94%A8%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C
5、命令参考
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands
2、yaml 语法
1、yml 模板
2、yaml 字段解析
参照官方文档
3、入门操作
1、Pod 是什么,Controller 是什么
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/#pods-and-controllers
Pod 和控制器
控制器可以为您创建和管理多个 Pod,管理副本和上线,并在集群范围内提供自修复能力。 例如,如果一个节点失败,控制器可以在不同的节点上调度一样的替身来自动替换 Pod。 包含一个或多个 Pod 的控制器一些示例包括:
Deployment
StatefulSet
DaemonSet
控制器通常使用您提供的 Pod 模板来创建它所负责的 Pod
2、Deployment&Service 是什么
3、Service 的意义
1、部署一个 nginx
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
2、暴露 nginx 访问
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort
统一应用访问入口;
Service 管理一组 Pod。
防止 Pod 失联(服务发现)、定义一组 Pod 的访问策略
现在 Service 我们使用 NodePort 的方式暴露,这样访问每个节点的端口,都可以访问到这 个 Pod,如果节点宕机,就会出现问题。
4、labels and selectors
5、Ingress
通过 Service 发现 Pod 进行关联。基于域名访问。
通过 Ingress Controller 实现 Pod 负载均衡
支持 TCP/UDP 4 层负载均衡和 HTTP 7 层负载均衡
步骤:
1)、部署 Ingress Controller
2)、创建 Ingress 规则
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: web
spec:
rules:
- host: tomcat6.atguigu.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: tomcat6
servicePort: 80
如果再部署了 tomcat8;看效果;
kubectl create deployment tomcat8 --image=tomcat:8.5.51-jdk8
kubectl expose deployment tomcat8 --port=88 --target-port=8080 --type=NodePort
删除指定资源
kubectl delete xxx
随便配置域名对应哪个节点,都可以访问 tomcat6/8;因为所有节点的 ingress-controller 路由表是同步的。
6、网络模型
Kubernetes 的网络模型从内至外 由四个部分组成:
-
1、Pod 内部容器所在的网络
-
2、Pod 所在的网络
-
3、Pod 和 Service 之间通信的网络
-
4、外界与 Service 之间通信的网络
4、项目部署
项目部署流程
制作项目镜像(将项目制作为 Docker 镜像,要熟悉 Dockerfile 的编写)
控制器管理 Pod(编写 k8s 的 yaml 即可)
暴露应用
日志监控
五、MySQL 集群
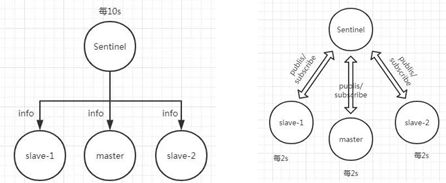
1、集群原理
以上可以作为企业中常用的数据库解决方案;
- MySQL-MMM 是 Master-Master Replication Manager for MySQL(mysql 主主复制管理 器)的简称,是 Google 的开源项目(Perl 脚本)。MMM 基于 MySQL Replication 做的扩展架构,主要用 来监控 mysql 主主复制并做失败转 移。其原理是将真实数据库节点的 IP(RIP)映射为虚拟 IP(VIP)集。 mysql-mmm 的监管端会提供多个 虚拟 IP(VIP),包括一个可写 VIP 多个可读 VIP,通过监管的管理,这 些 IP 会绑定在可用 mysql 之上,当 某一台 mysql 宕机时,监管会将 VIP 迁移至其他 mysql。在整个监管过 程中,需要在 mysql 中添加相关授 权用户,以便让 mysql 可以支持监 理机的维护。授权的用户包括一个mmm_monitor 用户和一个 mmm_agent 用户,如果想使用 mmm 的备份工具则还要添 加一个 mmm_tools 用户。
-
MHA(Master High Availability)目前在 MySQL 高可用方面是一个相对成熟的解决方案, 由日本 DeNA 公司 youshimaton(现就职于 Facebook 公司)开发,是一套优秀的作为 MySQL 高可用性环境下故障切换和主从提升的高可用软件。在MySQL 故障切换过程中, MHA 能做到在 0~30 秒之内自动完成数据库的故障切换操作(以 2019 年的眼光来说太 慢了),并且在进行故障切换的过程中,MHA 能在最大程度上保证数据的一致性,以 达到真正意义上的高可用。
-
InnoDB Cluster 支持自动 Failover、强一致性、读写分离、读库高可用、读请求负载均 衡,横向扩展的特性,是比较完备的一套方案。但是部署起来复杂,想要解决 router 单点问题好需要新增组件,如没有其他更好的方案可考虑该方案。 InnoDB Cluster 主 要由 MySQL Shell、MySQL Router 和 MySQL 服务器集群组成,三者协同工作,共同为 MySQL 提供完整的高可用性解决方案。MySQL Shell 对管理人员提供管理接口,可以 很方便的对集群进行配置和管理,MySQL Router 可以根据部署的集群状况自动的初始 化,是客户端连接实例。如果有节点 down 机,集群会自动更新配置。集群包含单点写 入和多点写入两种模式。在单主模式下,如果主节点 down 掉,从节点自动替换上来, MySQL Router 会自动探测,并将客户端连接到新节点。
2、Docker 安装模拟 MySQL 主从复制集群
1、下载mysql 镜像
2、创建Master 实例并启动
docker run -p 3307:3306 --name mysql-master \
-v /mydata/mysql/master/log:/var/log/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/master/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/master/conf:/etc/mysql \
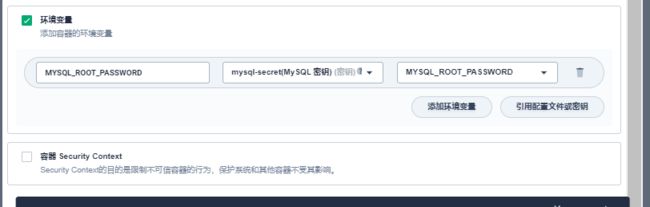
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \
-d mysql:5.7
参数说明
-p 3307:3306:将容器的 3306 端口映射到主机的 3307 端口
-v /mydata/mysql/master/conf:/etc/mysql:将配置文件夹挂在到主机
-v /mydata/mysql/master/log:/var/log/mysql:将日志文件夹挂载到主机
-v /mydata/mysql/master/data:/var/lib/mysql/:将配置文件夹挂载到主机
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root:初始化 root 用户的密码
修改master基本配置
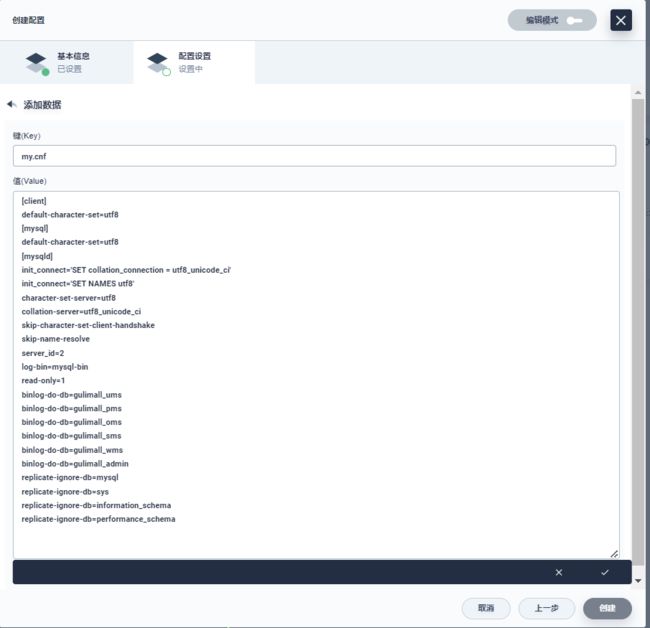
vim /mydata/mysql/master/conf/my.cnf
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
init_connect='SET collation_connection = utf8_unicode_ci'
init_connect='SET NAMES utf8'
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci
skip-character-set-client-handshake
skip-name-resolve
注意:skip-name-resolve 一定要加,不然连接 mysql 会超级慢
添加 master 主从复制部分配置,在上述后面加上
server_id=1
log-bin=mysql-bin
read-only=0
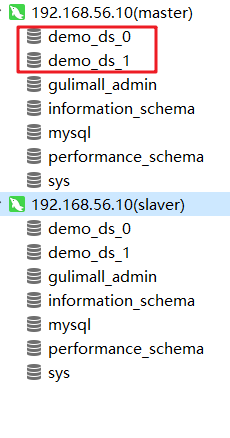
binlog-do-db=gulimall_ums
binlog-do-db=gulimall_pms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_oms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_sms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_wms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_admin
replicate-ignore-db=mysql
replicate-ignore-db=sys
replicate-ignore-db=information_schema
replicate-ignore-db=performance_schema
重启 master
3、 创建 Slave 实例并启动
docker run -p 3317:3306 --name mysql-slaver-01 \
-v /mydata/mysql/slaver/log:/var/log/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/slaver/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/slaver/conf:/etc/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \
-d mysql:5.7
修改 slave 基本配置
vim /mydata/mysql/slaver/conf/my.cnf
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
init_connect='SET collation_connection = utf8_unicode_ci'
init_connect='SET NAMES utf8'
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci
skip-character-set-client-handshake
skip-name-resolve
添加 master 主从复制部分配置,在上述后面加上
server_id=2
log-bin=mysql-bin
read-only=1
binlog-do-db=gulimall_ums
binlog-do-db=gulimall_pms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_oms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_sms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_wms
binlog-do-db=gulimall_admin
replicate-ignore-db=mysql
replicate-ignore-db=sys
replicate-ignore-db=information_schema
replicate-ignore-db=performance_schema
重启 slaver
4、 为 master 授权用户来他的同步数据
1、 进入 master 容器
docker exec -it mysql /bin/bash
2、 进入 mysql 内部 (mysql –uroot -p)(或者直接使用工具连接)
1) 、 授权 root 可以远程访问( 主从无关, 为了方便我们远程连接 mysql)
grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root' with grant option;
flush privileges;
2) 、 添加用来同步的用户
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'backup'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
3、 查看 master 状态
show master status;
5、 配置 slaver 同步 master 数据
1、 进入 slaver 容器
docker exec -it mysql-slaver-01 /bin/bash
2、 进入 mysql 内部(mysql –uroot -p)
1) 、 授权 root 可以远程访问( 主从无关, 为了方便我们远程连接 mysql)
grant all privileges on . to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root' with grant option;
flush privileges;
2) 、 设置主库连接,告诉mysql需要同步哪个节点
change master to master_host='192.168.56.10',master_user='backup',master_password='123456',master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=0,master_port=3307;
master_log_file:master中的File
master_host:master的主机地址
master_port:master的端口
3) 、 启动从库同步
start slave;
4) 、 查看从库状态
show slave status
至此主从配置完成;
总结:
1) 、 主从数据库在自己配置文件中声明需要同步哪个数据库, 忽略哪个数据库等信息。
并且 server-id 不能一样
2) 、 主库授权某个账号密码来同步自己的数据
3) 、 从库使用这个账号密码连接主库来同步数据
3、 MyCat 或者 ShardingSphere
shardingSphere: http://shardingsphere.apache.org/index_zh.html
auto_increment_offset: 1 从几开始增长
auto_increment_increment: 2 每次的步长
0、简介
Apache ShardingSphere 由 JDBC、Proxy 和 Sidecar(规划中)这 3 款既能够独立部署,又支持混合部署配合使用的产品组成。 它们均提供标准化的基于数据库作为存储节点的增量功能,可适用于如 Java 同构、异构语言、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。
关系型数据库当今依然占有巨大市场份额,是企业核心系统的基石,未来也难于撼动,我们更加注重在原有基础上提供增量,而非颠覆。
1、 下载安装 Sharding-Proxy
镜像方式
docker pull apache/shardingsphere-proxy
docker run -d -v /${your_work_dir}/conf:/opt/shardingsphere-proxy/conf -v
/mydata/sharding-proxy/lib:/opt/sharding-proxy/lib -e PORT=3308 -p13308:3308 apache/shardingsphere-proxy:latest
压缩包下载 https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/downloads/
这里我是下载的,下载后解压
然后下载mysql驱动放到上述解压下的lib包下
2、 配置数据分片+读写分离
数据分片config-sharding.yaml文件设置如下
schemaName: sharding_db
#
dataSources:
ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3307/demo_ds_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
ds_1:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3317/demo_ds_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
#
shardingRule:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_${order_id % 2}
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_item_${order_id % 2}
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_item_id
bindingTables:
- t_order,t_order_item
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmExpression: ds_${user_id % 2}
defaultTableStrategy:
none:
config-master_slave.yaml设置如下
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
######################################################################################################
#
# Here you can configure the rules for the proxy.
# This example is configuration of master-slave rule.
#
# If you want to use master-slave, please refer to this file;
# if you want to use sharding, please refer to the config-sharding.yaml.
#
######################################################################################################
#
schemaName: sharding_db_1
#
dataSources:
master_0_ds:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3307/demo_ds_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
slave_ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3317/demo_ds_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
masterSlaveRule:
name: ms_ds
masterDataSourceName: master_0_ds
slaveDataSourceNames:
- slave_ds_0
######################################################################################################
#
# If you want to connect to MySQL, you should manually copy MySQL driver to lib directory.
#
######################################################################################################
#schemaName: master_slave_db
#
#dataSources:
# master_ds:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_master?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
# slave_ds_0:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_slave_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
# slave_ds_1:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_slave_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
#
#masterSlaveRule:
# name: ms_ds
# masterDataSourceName: master_ds
# slaveDataSourceNames:
# - slave_ds_0
# - slave_ds_1
在创建一个文件为config-master_slave2.yaml,内容为
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
######################################################################################################
#
# Here you can configure the rules for the proxy.
# This example is configuration of master-slave rule.
#
# If you want to use master-slave, please refer to this file;
# if you want to use sharding, please refer to the config-sharding.yaml.
#
######################################################################################################
#
schemaName: sharding_db_2
#
dataSources:
master_1_ds:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3307/demo_ds_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
slave_ds_1:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3317/demo_ds_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
masterSlaveRule:
name: ms_ds_1
masterDataSourceName: master_1_ds
slaveDataSourceNames:
- slave_ds_1
######################################################################################################
#
# If you want to connect to MySQL, you should manually copy MySQL driver to lib directory.
#
######################################################################################################
#schemaName: master_slave_db
#
#dataSources:
# master_ds:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_master?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
# slave_ds_0:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_slave_0?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
# slave_ds_1:
# url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_ds_slave_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
# username: root
# password:
# connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
# idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
# maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
# maxPoolSize: 50
#
#masterSlaveRule:
# name: ms_ds
# masterDataSourceName: master_ds
# slaveDataSourceNames:
# - slave_ds_0
# - slave_ds_1
3、 conf目录下打开server.yaml 文件,设置如下
authentication:
users:
root:
password: root
sharding:
password: sharding
authorizedSchemas: sharding_db
4、加入这两个同步的库
-
先停止这两个mysql容器
docker stop mysql-master mysql-slaver-01 -
编辑两个myslq容器的配置文件加上同步的库
vi /mydata/mysql/master/conf/my.cnfvi /mydata/mysql/slaver/conf/my.cnf都加上这连个库:
binlog-do-db=demo_ds_0 binlog-do-db=demo_ds_1 -
启动容器
docker start mysql-master mysql-slaver-01
5、创建好我们需要的库
在master节点mysql上创建这两个库,这样slaver-01上也会同步有这两个库
6、启动
start.bat 3388 #自己指定端口,比如3388
连接测试
创建测试表
CREATE TABLE `t_order` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`status` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin;
CREATE TABLE `t_order_item` (
`order_item_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`content` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`status` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_item_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin;
注意:
启动时报什么vmxxx什么的,就在这个start.bat文件中删除这个-xx XXXX什么的
一定要把解压后的文件放在没有中文的目录下
lib下有很多的文件名都错了,需要更正,如有些的后缀名少了.jar
4、 k8s 有状态服务部署
可以使用 kubesphere, 快速搭建 MySQL 环境。
- 有状态服务抽取配置为 ConfigMap
- 有状态服务必须使用 pvc 持久化数据
- 服务集群内访问使用 DNS 提供的稳定域名
1、mysql主节点
1、创建配置
2、创建存储卷
3、创建有状态服务
2、mysql的slaver
1、创建存储卷
2、创建配置
3、创建有状态服务
其他设置类型主节点…
3、为 master 授权用户来他的同步数据
1、进入master容器组里的终端
添加用来同步的用户
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'backup'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
查看 master 状态
show master status;
2、 进入 slaver 容器
1) 、 授权 root 可以远程访问( 主从无关, 为了方便我们远程连接 mysql)
grant all privileges on . to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root' with grant option;
flush privileges;
2) 、 设置主库连接,告诉mysql需要同步哪个节点
change master to master_host='gulimall-mysql-master.gulimall',master_user='backup',master_password='123456',master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=0,master_port=3306;
master_log_file:master中的File
master_host:master的主机地址
master_port:master的端口
master_host为服务的域名见下图:
3) 、 启动从库同步
start slave;
4) 、 查看从库状态
show slave status
至此主从配置完成;
总结:
1) 、 主从数据库在自己配置文件中声明需要同步哪个数据库, 忽略哪个数据库等信息。
并且 server-id 不能一样
2) 、 主库授权某个账号密码来同步自己的数据
3) 、 从库使用这个账号密码连接主库来同步数据
4、测试
进入mysql主节点修改数据库看从库有没有同步
六、Redis 集群
1、redis 集群形式
1、数据分区方案
1、客户端分区
客户端分区方案 的代表为 Redis Sharding,Redis Sharding 是 Redis Cluster 出来之前,业 界普遍使用的 Redis 多实例集群 方法。Java 的 Redis 客户端驱动库 Jedis,支持 Redis Sharding 功能,即 ShardedJedis 以及 结合缓存池 的 ShardedJedisPool。
优点
不使用 第三方中间件,分区逻辑可控,配置简单,节点之间无关联,容易 线性扩展,灵 活性强。
缺点
客户端 无法 动态增删服务节点,客户端需要自行维护 分发逻辑,客户端之间 无连接共享, 会造成连接浪费。
2、代理分区
代理分区常用方案有 Twemproxy 和 Codis。
3、redis-cluster
2、高可用方式
1、Sentinel( 哨兵机制)支持高可用
前面介绍了主从机制,但是从运维角度来看,主节点出现了问题我们还需要通过人工干预的 方式把从节点设为主节点,还要通知应用程序更新主节点地址,这种方式非常繁琐笨重, 而 且主节点的读写能力都十分有限,有没有较好的办法解决这两个问题,哨兵机制就是针对第 一个问题的有效解决方案,第二个问题则有赖于集群!哨兵的作用就是监控 Redis 系统的运 行状况,其功能主要是包括以下三个:
-
监控(Monitoring): 哨兵(sentinel) 会不断地检查你的 Master 和 Slave 是否运作正常。
-
提醒(Notification): 当被监控的某个 Redis 出现问题时, 哨兵(sentinel) 可以通过 API 向管理员或者其他应用程序发送通知。
-
自动故障迁移(Automatic failover): 当主数据库出现故障时自动将从数据库转换为主数 据库。
哨兵的原理
Redis 哨兵的三个定时任务,Redis 哨兵判定一个 Redis 节点故障不可达主要就是通过三个定 时监控任务来完成的:
- 每隔 10 秒每个哨兵节点会向主节点和从节点发送"info replication" 命令来获取最新的 拓扑结构
-
每隔 2 秒每个哨兵节点会向 Redis 节点的_sentinel_:hello 频道发送自己对主节点是否故 障的判断以及自身的节点信息,并且其他的哨兵节点也会订阅这个频道来了解其他哨兵 节点的信息以及对主节点的判断
-
每隔 1 秒每个哨兵会向主节点、从节点、其他的哨兵节点发送一个 “ping” 命令来做心 跳检测
如果在定时 Job3 检测不到节点的心跳,会判断为“主观下线”。如果该节点还是主节点那么 还会通知到其他的哨兵对该主节点进行心跳检测,这时主观下线的票数超过了数 时,那么这个主节点确实就可能是故障不可达了,这时就由原来的主观下线变为了“客观下 线”。
故障转移和 Leader 选举
如果主节点被判定为客观下线之后,就要选取一个哨兵节点来完成后面的故障转移工作,选 举出一个 leader,这里面采用的选举算法为 Raft。选举出来的哨兵 leader 就要来完成故障转 移工作,也就是在从节点中选出一个节点来当新的主节点,这部分的具体流程可参考引用《深入理解 Redis 哨兵搭建及原理》
2、redis-cluster
详见下章
2、Redis-Cluster
https://redis.io/topics/cluster-tutorial/
Redis 的官方多机部署方案,Redis Cluster。一组 Redis Cluster 是由多个 Redis 实例组成,官 方推荐我们使用 6 实例,其中 3 个为主节点,3 个为从结点。一旦有主节点发生故障的时候, Redis Cluster 可以选举出对应的从结点成为新的主节点,继续对外服务,从而保证服务的高 可用性。那么对于客户端来说,知道知道对应的 key 是要路由到哪一个节点呢?Redis Cluster 把所有的数据划分为 16384 个不同的槽位,可以根据机器的性能把不同的槽位分配给不同 的 Redis 实例,对于 Redis 实例来说,他们只会存储部分的 Redis 数据,当然,槽的数据是 可以迁移的,不同的实例之间,可以通过一定的协议,进行数据迁移。
1、槽
Redis 集群的功能限制;Redis 集群相对 单机 在功能上存在一些限制,需要 开发人员 提前 了解,在使用时做好规避。JAVA CRC16 校验算法
-
key 批量操作 支持有限。
- 类似 mset、mget 操作,目前只支持对具有相同 slot 值的 key 执行批量操作。 对于映射为不同 slot 值的 key 由于执行 mget、mget 等操作可能存在于多个节点上,因此不被支持。
-
key 事务操作 支持有限。
- 只支持多 key 在 同一节点上的事务操作,当多个 key 分布在 不同 的节点上 时 无法 使用事务功能。
-
key 作为 数据分区的最小粒度
-
不能将一个 大的键值对象如 hash、list 等映射到不同的节点。
-
不支持多数据库空间
- 单机下的 Redis 可以支持 16 个数据库(db0 ~ db15),集群模式 下只能使用一 个数据库空间,即 db0。
-
复制结构 只支持一层
- 从节点只能复制主节点,不支持嵌套树状复制结构。
-
命令大多会重定向,耗时多
2、一致性hash
一致性哈希 可以很好的解决稳定性问题,可以将所有的存储节点 排列在收尾相接的Hash环上,每个 key 在计算 Hash 后会顺时针找到临接的存储节点存放。而当有节点加入或退出时,仅影响该节点在 Hash 环上顺时针相邻的后续节点。
Hash 倾斜
如果节点很少,容易出现倾斜,负载不均衡问题。一致性哈希算法,引入了虚拟节点,在整 个环上,均衡增加若干个节点。比如 a1,a2,b1,b2,c1,c2,a1 和 a2 都是属于 A 节点 的。解决 hash 倾斜问题
3、部署 Cluster
1、创建 6 个 redis 节点
3 主 3 从方式,从为了同步备份,主进行 slot 数据分片
for port in $(seq 7001 7006); \
do \
mkdir -p /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf
touch /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
cat << EOF > /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
port ${port}
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
cluster-announce-ip 192.168.56.10
cluster-announce-port ${port}
cluster-announce-bus-port 1${port}
appendonly yes
EOF
docker run -p ${port}:${port} -p 1${port}:1${port} --name redis-${port} \
-v /mydata/redis/node-${port}/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d redis:5.0.7 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf; \
done
docker stop $(docker ps -a |grep redis-700 | awk '{ print $1}')
docker rm $(docker ps -a |grep redis-700 | awk '{ print $1}')
2、使用 redis 建立集群
docker exec -it redis-7001 bash
redis-cli --cluster create 192.168.56.10:7001 192.168.56.10:7002 192.168.56.10:7003 192.168.56.10:7004 192.168.56.10:7005 192.168.56.10:7006 --cluster-replicas 1
3、测试集群效果
随便进入某个 redis 容器
docker exec -it redis-7002 /bin/bash
使用 redis-cli 的 cluster 方式进行连接
redis-cli -c -h 192.168.56.10 -p 7001
cluster info; 获取集群信息
cluster nodes; 获取集群节点
Get/Set 命令测试,将会重定向
节点宕机, slave 会自动提升为 master, master 开启后变为 slave
4、k8s 部署 redis
参照有状态部署即可
七、Elasticsearch 集群
1、集群原理
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/distributed-cluster.html
elasticsearch 是天生支持集群的,他不需要依赖其他的服务发现和注册的组件,如 zookeeper 这些,因为他内置了一个名字叫 ZenDiscovery 的模块,是 elasticsearch 自己实现的一套用 于节点发现和选主等功能的组件,所以 elasticsearch 做起集群来非常简单,不需要太多额外 的配置和安装额外的第三方组件。
1、单节点
-
一个运行中的 Elasticsearch 实例称为一个节点,而集群是由一个或者多个拥有相同
cluster.name配置的节点组成, 它们共同承担数据和负载的压力。当有节点加入集群 中或者从集群中移除节点时,集群将会重新平均分布所有的数据 -
当一个节点被选举成为 主节点时, 它将负责管理集群范围内的所有变更,例如增加、 删除索引,或者增加、删除节点等。 而主节点并不需要涉及到文档级别的变更和搜索 等操作,所以当集群只拥有一个主节点的情况下,即使流量的增加它也不会成为瓶颈。 任何节点都可以成为主节点。我们的示例集群就只有一个节点,所以它同时也成为了主节点。
-
作为用户,我们可以将请求发送到 集群中的任何节点 ,包括主节点。 每个节点都知道任意文档所处的位置,并且能够将我们的请求直接转发到存储我们所需文档的节点。 无论我们将请求发送到哪个节点,它都能负责从各个包含我们所需文档的节点收集回数 据,并将最终结果返回給客户端。 Elasticsearch 对这一切的管理都是透明的。
2、集群健康
Elasticsearch 的集群监控信息中包含了许多的统计数据,其中最为重要的一项就是集群健 康 , 它 在 status 字 段中展示为 green 、 yellow 或者 red 。
GET /_cluster/health
status 字段指示着当前集群在总体上是否工作正常。它的三种颜色含义如下:
green:所有的主分片和副本分片都正常运行。
yellow:所有的主分片都正常运行,但不是所有的副本分片都正常运行。
red:有主分片没能正常运行。
3、分片
-
一个 分片是一个底层的工作单元 ,它仅保存了全部数据中的一部分。我们的文档被 存储和索引到分片内,但是应用程序是直接与索引而不是与分片进行交互。分片就认为 是一个数据区
-
一个分片可以是 主 分片或者 副本 分片。索引内任意一个文档都归属于一个主分片, 所以主分片的数目决定着索引能够保存的最大数据量。
-
在索引建立的时候就已经确定了主分片数,但是副本分片数可以随时修改。
-
让我们在包含一个空节点的集群内创建名为 blogs 的索引。 索引在默认情况下会被分 配 5 个主分片, 但是为了演示目的,我们将分配 3 个主分片和一份副本(每个主分片 拥有一个副本分片):
PUT /blogs{ "settings" : {
"number_of_shards" : 3,
"number_of_replicas" : 1
}}
此时集群的健康状况为 yellow 则表示全部 主分片都正常运行(集群可以正常服务所有请 求),但是 副本 分片没有全部处在正常状态。实际上,所有 3 个副本分片都是 unassigned
—— 它们都没有被分配到任何节点。在同一个节点上既保存原始数据又保存副本是没有意 义的,因为一旦失去了那个节点,我们也将丢失该节点上的所有副本数据
当前我们的集群是正常运行的,但是在硬件故障时有丢失数据的风险。
4、新增节点
当你在同一台机器上启动了第二个节点时,只要它和第一个节点有同样的 cluster.name 配 置,它就会自动发现集群并加入到其中。 但是在不同机器上启动节点的时候,为了加入到 同一集群,你需要配置一个可连接到的单播主机列表。 详细信息请查看最好使用单播代替组播
此时,cluster-health 现在展示的状态为 green ,这表示所有 6 个分片(包括 3 个主分片和 3 个副本分片)都在正常运行。我们的集群现在不仅仅是正常运行的,并且还处于 始终可 用的状态。
5、水平扩容-启动第三个节点
Node 1 和 Node 2 上各有一个分片被迁移到了新的 Node 3 节点,现在每个节点上都拥 有 2 个分片,而不是之前的 3 个。 这表示每个节点的硬件资源(CPU, RAM, I/O)将被更少 的分片所共享,每个分片的性能将会得到提升。
在运行中的集群上是可以动态调整副本分片数目的,我们可以按需伸缩集群。让我们把副本 数从默认的 1 增加到 2
PUT /blogs/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas" : 2
}
blogs 索引现在拥有 9 个分片:3 个主分片和 6 个副本分片。 这意味着我们可以将集群扩 容到 9 个节点,每个节点上一个分片。相比原来 3 个节点时,集群搜索性能可以提升 3 倍。
6、应对故障
-
我们关闭的节点是一个主节点。而集群必须拥有一个主节点来保证正常工作,所以发生 的第一件事情就是选举一个新的主节点: Node 2 。
-
在我们关闭 Node 1 的同时也失去了主分片 1 和 2 ,并且在缺失主分片的时候索引 也不能正常工作。 如果此时来检查集群的状况,我们看到的状态将会为 red :不是所 有主分片都在正常工作。
-
幸运的是,在其它节点上存在着这两个主分片的完整副本, 所以新的主节点立即将这 些分片在 Node 2 和 Node 3 上对应的副本分片提升为主分片, 此时集群的状态将会 为 yellow 。 这个提升主分片的过程是瞬间发生的,如同按下一个开关一般。
-
为什么我们集群状态是 yellow 而不是 green 呢? 虽然我们拥有所有的三个主分片, 但是同时设置了每个主分片需要对应 2 份副本分片,而此时只存在一份副本分片。 所 以集群不能为 green 的状态,不过我们不必过于担心:如果我们同样关闭了 Node 2 , 我们的程序 依然 可以保持在不丢任何数据的情况下运行,因为 Node 3 为每一个分 片都保留着一份副本。
-
如果我们重新启动 Node 1 ,集群可以将缺失的副本分片再次进行分配。如果 Node 1依然拥有着之前的分片,它将尝试去重用它们,同时仅从主分片复制发生了修改的数据 文件。
7、问题与解决
1、主节点
主节点负责创建索引、删除索引、分配分片、追踪集群中的节点状态等工作。Elasticsearch 中的主节点的工作量相对较轻,用户的请求可以发往集群中任何一个节点,由该节点负责分 发和返回结果,而不需要经过主节点转发。而主节点是由候选主节点通过 ZenDiscovery 机 制选举出来的,所以要想成为主节点,首先要先成为候选主节点
2、候选主节点
在 elasticsearch 集群初始化或者主节点宕机的情况下,由候选主节点中选举其中一个作为主 节点。指定候选主节点的配置为:node.master: true
当主节点负载压力过大,或者集中环境中的网络问题,导致其他节点与主节点通讯的时候, 主节点没来的及响应,这样的话,某些节点就认为主节点宕机,重新选择新的主节点,这样 的话整个集群的工作就有问题了,比如我们集群中有 10 个节点,其中 7 个候选主节点,1 个候选主节点成为了主节点,这种情况是正常的情况。但是如果现在出现了我们上面所说的 主节点响应不及时,导致其他某些节点认为主节点宕机而重选主节点,那就有问题了,这剩 下的 6 个候选主节点可能有 3 个候选主节点去重选主节点,最后集群中就出现了两个主节点 的情况,这种情况官方成为“脑裂现象”;
集群中不同的节点对于 master 的选择出现了分歧,出现了多个 master 竞争,导致主分片 和副本的识别也发生了分歧,对一些分歧中的分片标识为了坏片
3、数据节点
数据节点负责数据的存储和相关具体操作,比如 CRUD、搜索、聚合。所以,数据节点对机 器配置要求比较高,首先需要有足够的磁盘空间来存储数据,其次数据操作对系统 CPU、 Memory 和 IO 的性能消耗都很大。通常随着集群的扩大,需要增加更多的数据节点来提高 可用性。指定数据节点的配置:node.data: true。
elasticsearch 是允许一个节点既做候选主节点也做数据节点的,但是数据节点的负载较重, 所以需要考虑将二者分离开,设置专用的候选主节点和数据节点,避免因数据节点负载重导 致主节点不响应。
4、客户端节点
客户端节点就是既不做候选主节点也不做数据节点的节点,只负责请求的分发、汇总等等, 但是这样的工作,其实任何一个节点都可以完成,因为在 elasticsearch 中一个集群内的节点 都可以执行任何请求,其会负责将请求转发给对应的节点进行处理。所以单独增加这样的节 点更多是为了负载均衡。指定该节点的配置为:
node.master: false
node.data: false
5、脑裂”问题可能的成因
1.网络问题:集群间的网络延迟导致一些节点访问不到 master,认为 master 挂掉了从而选 举出新的 master,并对 master 上的分片和副本标红,分配新的主分片
2.节点负载:主节点的角色既为 master 又为 data,访问量较大时可能会导致 ES 停止响应造 成大面积延迟,此时其他节点得不到主节点的响应认为主节点挂掉了,会重新选取主节点。
3.内存回收:data 节点上的 ES 进程占用的内存较大,引发 JVM 的大规模内存回收,造成 ES 进程失去响应。
- 脑裂问题解决方案:
- **角色分离:**即 master 节点与 data 节点分离,限制角色;数据节点是需要承担存储 和搜 索的工作的,压力会很大。所以如果该节点同时作为候选主节点和数据节点, 那么一旦选上它作为主节点了,这时主节点的工作压力将会非常大,出现脑裂现象 的概率就增加了。
- **减少误判:**配置主节点的响应时间,在默认情况下,主节点 3 秒没有响应,其他节点就认为主节点宕机了, 那我们可以把该时间设置的长一点, 该配置是: discovery.zen.ping_timeout: 5
- **选举触发:**discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes:1(默认是 1),该属性定义的是 为了形成一个集群,有主节点资格并互相连接的节点的最小数目。
- 一个有10节点的集群 , 且每个节点都有成为主节点的资格, discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes 参数设置为 6。
- 正常情况下,10 个节点,互相连接,大于 6,就可以形成一个集群。
- 若某个时刻,其中有 3 个节点断开连接。剩下 7 个节点,大于 6,继续运行之 前的集群。而断开的 3 个节点,小于 6,不能形成一个集群。
- 该参数就是为了防止”脑裂”的产生。
- 建议设置为(候选主节点数 / 2) + 1
8、集群结构
以三台物理机为例。在这三台物理机上,搭建了 6 个 ES 的节点,三个 data 节点,三个 master 节点(每台物理机分别起了一个 data 和一个 master),3 个 master 节点,目的是达到(n/2)+1 等于 2 的要求,这样挂掉一台 master 后(不考虑 data),n 等于 2,满足参数,其他两个 master 节点都认为 master 挂掉之后开始重新选举
master 节点上
node.master = true
node.data = false
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes = 2
data 节点上
node.master = false
node.data = true
2、集群搭建
所有之前先运行:
sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
我们只是测试,所以临时修改。永久修改使用下面
#防止 JVM 报错
echo vm.max_map_count=262144 >> /etc/sysctl.conf sysctl -p
0、准备docker 网络
Docker 创建容器时默认采用 bridge 网络,自行分配 ip,不允许自己指定。
在实际部署中,我们需要指定容器 ip,不允许其自行分配 ip,尤其是搭建集群时,固定 ip 是必须的。
我们可以创建自己的 bridge 网络 : mynet,创建容器的时候指定网络为 mynet 并指定 ip 即可。
查看网络模式
docker network ls
创建一个新的 bridge 网络
docker network create --driver bridge --subnet=172.18.12.0/16 --gateway=172.18.1.1 mynet
查看网络信息
docker network inspect mynet
以后使用--network=mynet --ip 172.18.12.x 指定 ip
1、3-Master 节点创建
for port in $(seq 1 3); \
do \
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/config
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/data
chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}
cat << EOF > /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/config/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-es #集群的名称,同一个集群该值必须设置成相同的
node.name: es-master-${port} #该节点的名字
node.master: true #该节点有机会成为master节点
node.data: false #该节点可以存储数据
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.host: 0.0.0.0 #所有http均可访问
http.port: 920${port}
transport.tcp.port: 930${port}
discovery.zen.ping_timeout: 10s #设置集群中自动发现其他节点时ping连接的超时时间
discovery.seed_hosts: ["172.18.1.21:9301","172.18.1.22:9302","172.18.1.23:9303"]
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["172.18.1.21"] #新集群初始时的候选主节点,es7的新增配置
EOF
docker run --name elasticsearch-node-${port} \
-p 920${port}:920${port} -p 930${port}:930${port} \
--network=mynet --ip 172.18.1.2${port} \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms300m -Xmx300m" \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/master-${port}/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
-d elasticsearch:7.4.2
done
docker stop $(docker ps -a |grep elasticsearch-node- | awk '{ print $1}')
docker rm $(docker ps -a |grep elasticsearch-node- | awk '{ print $1}')
2、3-Data-Node 创建并启动
for port in $(seq 4 6); \
do \
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/config
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/data
chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}
cat << EOF > /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/config/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-es #集群的名称,同一个集群该值必须设置成相同的
node.name: es-node-${port} #该节点的名字
node.master: false #该节点有机会成为master节点
node.data: true #该节点可以存储数据
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.host: 0.0.0.0 #所有http均可访问
http.port: 920${port}
transport.tcp.port: 930${port}
discovery.zen.ping_timeout: 10s #设置集群中自动发现其他节点时ping连接的超时时间
discovery.seed_hosts: ["172.18.1.21:9301","172.18.1.22:9302","172.18.1.23:9303"]
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["172.18.1.21"] #新集群初始时的候选主节点,es7的新增配置
EOF
docker run --name elasticsearch-node-${port} \
-p 920${port}:920${port} -p 930${port}:930${port} \
--network=mynet --ip 172.18.1.2${port} \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms300m -Xmx300m" \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/node-${port}/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
-d elasticsearch:7.4.2
done
3、测试集群
http://192.168.56.10:9201/_nodes/process?pretty 查看节点状况
http://192.168.56.10:9201/_cluster/stats?pretty 查看集群状态
http://192.168.56.10:9201/_cluster/health?pretty 查看集群健康状况
http://192.168.56.10:9202/_cat/nodes 查看各个节点信息
$ curl localhost:9200/_cat
/_cat/allocation
/_cat/shards
/_cat/shards/{index}
/_cat/master
/_cat/nodes
/_cat/indices
/_cat/indices/{index}
/_cat/segments
/_cat/segments/{index}
/_cat/count
/_cat/count/{index}
/_cat/recovery
/_cat/recovery/{index}
/_cat/health
/_cat/pending_tasks
/_cat/aliases
/_cat/aliases/{alias}
/_cat/thread_pool
/_cat/plugins
/_cat/fielddata
/_cat/fielddata/{fields}
/_cat/nodeattrs
/_cat/repositories
/_cat/snapshots/{repository}
3、k8s 上部署
有状态服务
jvm.options
-Xms100m
-Xmx512m
八、RabbitMQ 集群
1、集群形式
RabbiMQ 是用 Erlang 开发的,集群非常方便,因为 Erlang 天生就是一门分布式语言,但其 本身并不支持负载均衡。
RabbitMQ 集群中节点包括内存节点(RAM)、磁盘节点(Disk,消息持久化),集群中至少有 一个 Disk 节点
-
普通模式(默认)
对于普通模式,集群中各节点有相同的队列结构,但消息只会存在于集群中的一个节 点。对于消费者来说,若消息进入 A 节点的 Queue 中,当从 B 节点拉取时,RabbitMQ 会 将消息从 A 中取出,并经过 B 发送给消费者。
应用场景:该模式各适合于消息无需持久化的场合,如日志队列。当队列非持久化,且 创建该队列的节点宕机,客户端才可以重连集群其他节点,并重新创建队列。若为持久化, 只能等故障节点恢复。
-
镜像模式
与普通模式不同之处是消息实体会主动在镜像节点间同步,而不是在取数据时临时拉 取,高可用;该模式下,mirror queue 有一套选举算法,即 1 个 master、n 个 slaver,生产 者、消费者的请求都会转至 master。
应用场景:可靠性要求较高场合,如下单、库存队列。
缺点:若镜像队列过多,且消息体量大,集群内部网络带宽将会被此种同步通讯所消耗。
1、镜像集群也是基于普通集群,即只有先搭建普通集群,然后才能设置镜像队列。
2、若消费过程中,master 挂掉,则选举新 master,若未来得及确认,则可能会重复消费。
1、搭建集群
mkdir /mydata/rabbitmq
cd rabbitmq/
mkdir rabbitmq01 rabbitmq02 rabbitmq03
docker run -d --hostname rabbitmq01 --name rabbitmq01 -v /mydata/rabbitmq/rabbitmq01:/var/lib/rabbitmq -p 15673:15672 -p 5673:5672 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='atguigu' rabbitmq:management
docker run -d --hostname rabbitmq02 --name rabbitmq02 -v /mydata/rabbitmq/rabbitmq02:/var/lib/rabbitmq -p 15674:15672 -p 5674:5672 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='atguigu' --link rabbitmq01:rabbitmq01 rabbitmq:management
docker run -d --hostname rabbitmq03 --name rabbitmq03 -v /mydata/rabbitmq/rabbitmq03:/var/lib/rabbitmq -p 15675:15672 -p 5675:5672 -e RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE='atguigu' --link rabbitmq01:rabbitmq01 --link rabbitmq02:rabbitmq02 rabbitmq:management
–hostname 设置容器的主机名
RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE 节点认证作用, 部署集成时需要同步该值
2、 节点加入集群
进入第一个节点
docker exec -it rabbitmq01 /bin/bash
rabbitmqctl stop_app
rabbitmqctl reset
rabbitmqctl start_app
exit
进入第二个节点
docker exec -it rabbitmq02 /bin/bash
rabbitmqctl stop_app
rabbitmqctl reset
rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@rabbitmq01
rabbitmqctl start_app
exit
进入第三个节点
docker exec -it rabbitmq03 /bin/bash
rabbitmqctl stop_app
rabbitmqctl reset
rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@rabbitmq01
rabbitmqctl start_app
exit
不成功就多执行几次就好了
3、 实现镜像集群
docker exec -it rabbitmq01 bash
rabbitmqctl set_policy -p / ha "^" '{"ha-mode":"all","ha-sync-mode":"automatic"}'
可以使用 rabbitmqctl list_policies -p / 查看 vhost/下面的所有 policy
在 cluster 中任意节点启用策略, 策略会自动同步到集群节点
策略模式 all 即复制到所有节点, 包含新增节点, 策略正则表达式为 “^” 表示所有匹配所有队列名称。 “^hello”表示只匹配名为 hello 开始的队列
2、集群测试
随便在 mq 上创建一个队列,发送一个消息,保证整个集群其他节点都有这个消息。如果 master 宕机,其他节点也能成为新的 master
3、k8s 上部署
参照有状态部署
九、DevOps
1、项目开发需要考虑的维度
Dev:怎么开发?
Ops:怎么运维?
高并发:怎么承担高并发
高可用:怎么做到高可用
2、什么是DevOps
微服务,服务自治。
DevOps: Development 和 Operations 的组合
-
DevOps 看作开发(软件工程)、技术运营和质量保障(QA)三者的交集。
-
突出重视软件开发人员和运维人员的沟通合作,通过自动化流程来使得软件构建、测试、 发布更加快捷、频繁和可靠。
-
DevOps 希望做到的是软件产品交付过程中 IT 工具链的打通,使得各个团队减少时间损 耗,更加高效地协同工作。专家们总结出了下面这个 DevOps 能力图,良好的闭环可以大大 增加整体的产出。
3、什么是CI&CD
1、持续集成(Continuous Integration)
-
持续集成是指软件个人研发的部分向软件整体部分交付,频繁进行集成以便更快地发现 其中的错误。“持续集成”源自于极限编程(XP),是 XP 最初的 12 种实践之一。
-
CI 需要具备这些:
- 全面的自动化测试。这是实践持续集成&持续部署的基础,同时,选择合适的 自动化测试工具也极其重要;
- 灵活的基础设施。容器,虚拟机的存在让开发人员和 QA 人员不必再大费周折;
- 版本控制工具。如 Git,CVS,SVN 等;
- 自动化的构建和软件发布流程的工具,如 Jenkins,flow.ci;
- 反馈机制。如构建/测试的失败,可以快速地反馈到相关负责人,以尽快解决 达到一个更稳定的版本。
2、持续交付(Continuous Delivery)
持续交付在持续集成的基础上,将集成后的代码部署到更贴近真实运行环境的「类生产环境」
(production-like environments)中。持续交付优先于整个产品生命周期的软件部署,建立 在高水平自动化持续集成之上。
灰度发布。
持续交付和持续集成的优点非常相似:
-
快速发布。能够应对业务需求,并更快地实现软件价值。
-
编码->测试->上线->交付的频繁迭代周期缩短,同时获得迅速反馈;
-
**高质量的软件发布标准。**整个交付过程标准化、可重复、可靠,
-
整个交付过程进度可视化,方便团队人员了解项目成熟度;
-
**更先进的团队协作方式。**从需求分析、产品的用户体验到交互 设计、开发、测试、运 维等角色密切协作,相比于传统的瀑布式软件团队,更少浪费。
3、持续部署(Continuous Deployment)
持续部署是指当交付的代码通过评审之后,自动部署到生产环境中。持续部署是持续交付的 最高阶段。这意味着,所有通过了一系列的自动化测试的改动都将自动部署到生产环境。它 也可以被称为“Continuous Release”。
“开发人员提交代码,持续集成服务器获取代码,执行单元测试,根据测 试结果决定是否部署到预演环境,如果成功部署到预演环境,进行整体 验 收测试,如果测试通过,自动部署到产品环境,全程自动化高效运转。”
持续部署主要好处是, 可以相对独立地部署新的功能, 并能快速地收集真实用户的反馈。
“You build it, you run it”, 这是 Amazon 一年可以完成 5000 万次部署,
平均每个工程师每天部署超过 50 次的核心秘籍。
下图是由 Jams Bowman 绘制的持续交付工具链图
4、落地方案
Maven+Github+Jenkins(Hudson[现由甲骨文维护])+Docker
自动化部署
十、附录
1、Jenkins
官方文档 https://jenkins.io/zh/doc/pipeline/tour/getting-started/
Jenkins 是开源 CI&CD 软件领导者, 提供超过 1000 个插件来支持构建、部署、自动化,满足任何项目的需要。
![]()
2、Jenkins 流水线
https://jenkins.io/zh/doc/book/pipeline/
3、k8s 部署 nacos
docker run --env MODE=standalone --name nacos \
-v /mydata/nacos/conf:/home/nacos/conf -d -p 8848:8848 nacos/nacos-server:1.1.4
4、k8s 部署 sentinel
可以制作一个镜像并启动它,暴露访问
docker run --name sentinel -d -p 8858:8858 -d bladex/sentinel-dashboard:1.6.3
5、k8s 部署 zipkin
docker run -d -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin
或者
docker run --env STORAGE_TYPE=elasticsearch --env ES_HOSTS=192.168.56.10:9200 openzipkin/zipkin
6、业务代码 CICD
1、参数化构建
2、并行任务&嵌套 stage
7、流程
1、DockerFile文件
FROM java:11
EXPOSE 8080
VOLUME /tmp
ADD target/*.jar /app.jar
RUN bash -c 'touch /app.jar'
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar","--spring.profiles.active=prod"]
2、deploy部署文件
#gulimall-xxx需要根据自己的服务名称改变
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: gulimall-auth-server
namespace: gulimall
labels:
app: gulimall-auth-server
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gulimall-auth-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gulimall-auth-server
spec:
containers:
- name: gulimall-auth-server
image: $REGISTRY/$DOCKERHUB_NAMESPACE/$APP_NAME:$TAG_NAME
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 500Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 10Mi
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 25%
maxSurge: 25%
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: gulimall-auth-server
namespace: gulimall
labels:
app: gulimall-auth-server
spec:
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
#这里需要根据服务自己改变
nodePort: 20001
selector:
app: gulimall-auth-server
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: None