刘二大人 PyTorch深度学习实践 笔记 P10 卷积神经网络(基础篇)
刘二大人 PyTorch深度学习实践 笔记 P10 卷积神经网络(基础篇)
- 1、基本概念
- 2、卷积
-
- I 卷积运算过程
- II padding
- III stride=2 步长为2,有效降低图像的W H
- IV 下采样 max pooling layer 最大池化层,没有w,2 * 2的max pooling,默认stride=2
- V 运算迁移到GPU
- 3、一个简单的卷积神经网络示例:利用卷积神经网络来处理Minist数据集
- 4、作业:都变成3个,比较不同CNN之间的差别
1、基本概念
- 全连接网络: 像前几节中的用到的全是用线性层连接起来的网络层,称为全连接层。也就是线性层中的每一个输入结点都会参与下一层任何一个输出结点的计算上,这样的线性层叫做全连接层。如果整个网络都是用这种全连接层连接在一起的,那就称为全连接网络。
- 卷积神经网络: 需要根据输入的维度映射到对应的输出的维度上。
- 卷积: 保留图像的空间特征(全连接会丧失原有的一些空间信息)。
- 下采样: 通道数不变,图像的高度和宽度会发生改变,目的就是减少数据量,降低运算需求。
- 特征提取器: 包括卷积核下采样,通过卷积运算,找到某种特征。
- 全连接层: 变成一个向量,通过全连接,映射到10维即做分类。
- 总目标: 由12828的张量空间转换成输出10维的向量。
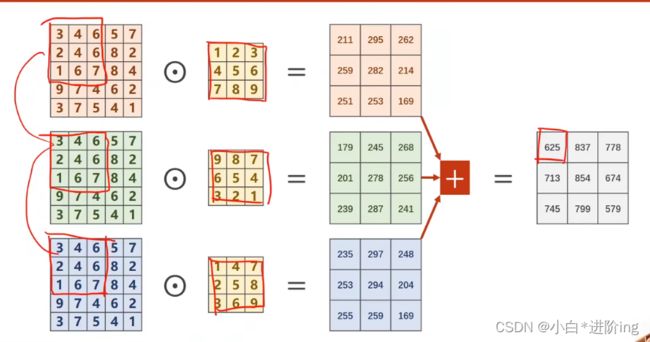
2、卷积
I 卷积运算过程
单通道: 从1 * 5 * 5 输入中拿出 3 * 3 框与核做卷积(数乘),对应元素相乘求和,得到第一个元素的结果,再将框移动,做相应的运算,以此类推。
三通道: 每一个通道匹配一个核,即核与通道的数量要一样。
多个垒起来,输入 n * w * h,输出 m * w * h,得到多个输出。
代码实现:
import torch
in_channels, out_channels = 5, 10 # n 输入的维度, m 输出的维度
width, height = 100, 100 # 图像大小
kernel_size = 3 # 卷积核的大小
batch_size = 1 # pytorch中输入必须是小批量的数据
# 卷积层对输入的通道数有要求
# 取随机数,随机采样
input = torch.randn(batch_size, in_channels, width, height)
# 卷积对象,torch.nn.Conv2d对由多个输入平面组成的输入信号进行二维卷积
# 三个参数,输入通道,输出通道,卷积核的大小
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size)
# 卷积层
output = conv_layer(input)
print(input.shape)
print(output.shape)
print(conv_layer.weight.shape)
输出:
torch.Size([1, 5, 100, 100])
torch.Size([1, 10, 98, 98])
torch.Size([10, 5, 3, 3]) # 输出通道 输入通道 卷积核大小
II padding
5 * 5 和 3 * 3 的卷积核 得到 3 * 3,但是希望图像大小不变,得到 5 * 5
把图像周围填充成 7 * 7 的,就可以了。
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,7,
2,4,6,8,2,
1,6,7,8,4,
9,7,4,6,2,
3,7,5,4,1]
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 5, 5) # B C W H
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
# 不需要偏置量,所以设置为False
kernel = torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]).view(1, 1, 3, 3) # O I W H
# 卷积层权重的初始化
conv_layer.weight.data = kernel.data
output = conv_layer(input)
print(output)
输出:
tensor([[[[ 91., 168., 224., 215., 127.],
[114., 211., 295., 262., 149.],
[192., 259., 282., 214., 122.],
[194., 251., 253., 169., 86.],
[ 96., 112., 110., 68., 31.]]]], grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>)
III stride=2 步长为2,有效降低图像的W H
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,7,
2,4,6,8,2,
1,6,7,8,4,
9,7,4,6,2,
3,7,5,4,1]
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 5, 5) # B C W H
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
kernel = torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]).view(1, 1, 3, 3) # O I W H
conv_layer.weight.data = kernel.data
output = conv_layer(input)
print(output)
输出:
tensor([[[[211., 262.],
[251., 169.]]]], grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>)
IV 下采样 max pooling layer 最大池化层,没有w,2 * 2的max pooling,默认stride=2
把 4 * 4 分成 2 * 2一组,拿出最大值拼成一个新的 2 * 2 输出,通道数量不变,图像大小变为原来的一半(长宽一半)。

代码实现:
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,
2,4,6,8,
1,6,7,5,
9,7,4,6,
]
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 4, 4)
maxpooling_layer = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2) # 默认stride=2
output = maxpooling_layer(input)
print(output)
输出:
tensor([[[[4., 8.],
[9., 7.]]]])
V 运算迁移到GPU
1、模型迁移到GPU
model = Net()
# 将模型迁移到GPU上运行,cuda:0表示第0块显卡
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
model.to(device)
2、输入和数据迁移,数据要放在同一块显卡上
inputs, target = data
# 将要计算的张量也迁移到GPU上——输入和输出
inputs, target = inputs.to(device), target.to(device)
3、测试也迁移一下
images, labels = data
# 测试中的张量也迁移到GPU上
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
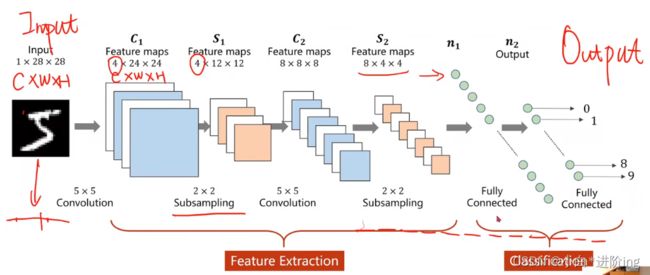
3、一个简单的卷积神经网络示例:利用卷积神经网络来处理Minist数据集
计算过程:
- 输入 1 * 28 * 28
- 卷积 28-5+1=24 得到 10 * 24 * 24
- 池化 10 * 12 * 12
- 卷积 12-5+1=8 得到 20 * 8 * 8
- 池化 20 * 4 * 4=320
- 全连接 映射到 10

把全连接网络改成卷积神经网络即可

代码实现:
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1、准备数据集
batch_size = 64
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307, ), (0.3081, ))
])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='dataset/mnist',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='dataset/mnist',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False)
# 2、建立模型
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(320, 10)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0) # x的第0维就是batch_size
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv1(x))) # 修正与池化顺序反了但是不影响
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
model = Net()
# 将模型迁移到GPU上运行,cuda:0表示第0块显卡
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# print(torch.cuda.is_available())
model.to(device)
# 3、建立损失函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
# 4、定义训练函数
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
inputs, target = data
# 将要计算的张量也迁移到GPU上——输入和输出
inputs, target = inputs.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前馈 反馈 更新
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, running_loss / 300))
running_loss = 0
# 5、定义测试函数
accuracy = []
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
images, labels = data
# 测试中的张量也迁移到GPU上
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
total += labels.size(0)
# 两个张量比较,得出的是其中相等的元素的个数(即一个批次中预测正确的个数)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy on test set: %d %%' % (100 * correct / total))
accuracy.append(100 * correct / total)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(10):
train(epoch)
test()
print(accuracy)
plt.plot(range(10), accuracy)
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.show()
输出:
[1, 300] loss: 0.556
[1, 600] loss: 0.185
[1, 900] loss: 0.134
Accuracy on test set: 96 %
[2, 300] loss: 0.107
[2, 600] loss: 0.094
[2, 900] loss: 0.087
Accuracy on test set: 97 %
[3, 300] loss: 0.077
[3, 600] loss: 0.075
[3, 900] loss: 0.071
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[4, 300] loss: 0.066
[4, 600] loss: 0.063
[4, 900] loss: 0.058
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[5, 300] loss: 0.058
[5, 600] loss: 0.054
[5, 900] loss: 0.056
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[6, 300] loss: 0.054
[6, 600] loss: 0.050
[6, 900] loss: 0.046
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[7, 300] loss: 0.044
[7, 600] loss: 0.046
[7, 900] loss: 0.045
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[8, 300] loss: 0.037
[8, 600] loss: 0.047
[8, 900] loss: 0.043
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[9, 300] loss: 0.039
[9, 600] loss: 0.042
[9, 900] loss: 0.036
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[10, 300] loss: 0.033
[10, 600] loss: 0.039
[10, 900] loss: 0.037
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[96.98, 97.46, 98.21, 98.03, 98.38, 98.53, 98.5, 98.4, 98.61, 98.89]
利用显卡加速运算过程,由错误率3%降到了2%。
4、作业:都变成3个,比较不同CNN之间的差别
计算过程:
- 输入 1 * 28 * 28
- 卷积 28-5+1=24 得到 16 * 24 * 24
- 池化 16 * 12 * 12
- 卷积 12-5+1=8 得到 32 * 8 * 8
- 池化 20 * 4 * 4
- 卷积 4-3+1=2 得到 64 * 2 * 2
- 池化 64 * 1 * 1
- 全连接 64 到 32 到 16 到 10
代码实现:
将网络模型更改成如下即可
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=5)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 32)
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(32, 16)
self.fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(16, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# x的第0维就是batch_size
batch_size = x.size(0)
x = self.pooling(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pooling(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pooling(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
输出:
[1, 300] loss: 2.268
[1, 600] loss: 1.135
[1, 900] loss: 0.331
Accuracy on test set: 89 %
[2, 300] loss: 0.198
[2, 600] loss: 0.165
[2, 900] loss: 0.133
Accuracy on test set: 96 %
[3, 300] loss: 0.107
[3, 600] loss: 0.106
[3, 900] loss: 0.095
Accuracy on test set: 97 %
[4, 300] loss: 0.081
[4, 600] loss: 0.077
[4, 900] loss: 0.078
Accuracy on test set: 97 %
[5, 300] loss: 0.063
[5, 600] loss: 0.063
[5, 900] loss: 0.065
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[6, 300] loss: 0.058
[6, 600] loss: 0.051
[6, 900] loss: 0.052
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[7, 300] loss: 0.040
[7, 600] loss: 0.051
[7, 900] loss: 0.046
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[8, 300] loss: 0.040
[8, 600] loss: 0.042
[8, 900] loss: 0.039
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[9, 300] loss: 0.040
[9, 600] loss: 0.038
[9, 900] loss: 0.036
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[10, 300] loss: 0.034
[10, 600] loss: 0.034
[10, 900] loss: 0.031
Accuracy on test set: 98 %
[89.86, 96.93, 97.7, 97.59, 98.44, 98.63, 98.31, 98.2, 98.77, 98.74]