SpringBoot笔记
文章目录
- 一、SpringBoot简介
-
- 1.1、回顾Spring
- 1.2、Spring如何简化Java开发?
- 1.3、什么是SpringBoot?
- 1.4、Spring Boot的主要优点
- 二、第一个SpringBoot程序—Hello,World
-
- 2.1、准备工作
- 2.2、创建基础项目说明
- 2.3、pom.xml 分析
- 2.4、Web接口开发
- 2.5、将项目打成jar包
- 三、SpringBoot运行原理初探
-
- 3.1、pom.xml文件
-
- 3.1.1、父依赖
- 3.1.2、启动器 spring-boot-starter
- 3.2、主启动类注解
-
- 3.2.1、默认的主启动类
- 3.2.2、主启动类注解分析
-
- (1)@SpringBootApplication
- (2)@ComponentScan
- (3)@SpringBootConfiguration
- (4)@EnableAutoConfiguration
-
- ***@AutoConfigurationPackage :自动配置包***
- ***@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件***
- 3.3、SpringApplication
-
- 3.3.1、SpringApplication.run(...)方法分析
- 3.3.2、类SpringApplication作用
- 3.3.3、run方法流程分析
- 四、YAML配置注入与SpringBoot配置文件加载
-
- 4.1、SpringBoot配置文件
- 4.2、Yaml概述
- 4.3、Yaml基础语法
-
- 4.3.1、字面量
- 4.3.2、对象和Map(键值对)
- 4.3.3、数组( List、set )
- 4.3.4、在application.yaml中修改SpringBoot默认端口号
- 4.4、Yaml注入配置文件
- 4.5、SpringBoot加载指定的配置文件
- 4.6、配置文件占位符
- 4.7、回顾properties配置
- 4.6、SpringBoot注入实值各方式对比
- 五、JSR303数据校验及多环境切换
-
- 5.1、JSR303数据校验
-
- 5.1.1、注解@validated
- 5.1.2、常见参数
- 5.2、多环境切换
-
- 5.2.1、多配置文件
- 5.2.2、yaml的多文档块
- 5.2.3、配置文件加载位置
-
- 指定位置加载配置文件
- 六、自动配置原理
-
- 6.1、分析自动配置原理
- 6.2、SpringBoot自动配置流程
- 6.3、@Conditional
- 七、自定义starter启动器
-
- 7.1、starter启动器说明
- 7.2、编写启动器
- 7.3、新建项目测试测试上述自定义启动器
- 八、整合JDBC
-
- 8.1、SpringData简介
- 8.2、整合JDBC
-
- 8.2.1、创建测试项目并链接数据源
- 8.2.2、JDBCTemplate
- 8.2.3、测试
- 九、整合Druid
-
- 9.1、Druid简介
- 9.2、配置Druid数据源
- 9.3、配置Druid数据源监控
-
- 9.3.1、配置 Druid 的后台管理
- 9.3.2、配置 Druid web 监控 filter 过滤器
- 十、整合MyBatis
- 十一、Web开发——静态资源处理和首页处理
-
- 11.1、静态资源处理
-
- 11.1.1、第一种静态资源映射规则
- 11.1.2、第二种静态资源映射规则
- 11.1.3、自定义静态资源路径
- 11.2、首页处理
-
- 补充、关于web网站图标说明
- 十二、Web开发——Thymeleaf模板引擎
-
- 12.1、何为模板引擎?
- 12.2、引入Thymeleaf
- 12.3、Thymeleaf分析
- 12.4、Thymeleaf 语法学习
- 十三、MVC自动配置原理
-
- 13.1、官方文档阅读
- 13.2、ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
- 13.3、转换器和格式化器
- 13.3、修改SpringBoot的默认配置
- 13.4、全面接管SpringMVC
- 十四、集成Swagger
-
- 14.1、Swagger简介
- 14.2、SpringBoot集成Swagger
- 14.3、配置Swagger
- 14.4、配置扫描接口
- 14.5、配置Swagger开关
- 14.6、配置API分组
- 14.7、实体配置
- 14.8、常用注解
- 十五、Dubbo和Zookeeper集成
-
- 15.1、分布式理论
-
- 15.1.1、什么是分布式系统?
- 15.1.2、架构随流量演变
- 15.2、什么是RPC
- 15.3、测试环境搭建
- 15.3.1、Dubbo
-
- 15.3.2、Dubbo环境搭建
- 15.4、SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper
-
- 15.4.1、框架搭建
- 15.4.2、服务提供者
- 15.4.3、服务消费者
- 15.4.4、启动测试
- 补充
-
- Web开发——页面国际化
- SpringBoot实现异步、定时、邮件任务
- SpringBoot实现富文本编辑器
- SpringBoot集成SpringSecurity
- 参考博客—狂神说
一、SpringBoot简介
1.1、回顾Spring
- Spring是一个开源框架,是在03 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架。
- Spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建的,简化开发。
1.2、Spring如何简化Java开发?
为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采用了以下4种关键策略:
基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程,所有东西都是bean;
通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合;
基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程;
通过切面和模版减少样式代码,RedisTemplate,xxxTemplate。
1.3、什么是SpringBoot?
学过javaweb的同学就知道,开发一个web应用,从最初开始接触Servlet结合Tomcat, 跑出一个Hello Wolrld程序,是要经历特别多的步骤;后来就用了框架Struts,再后来是SpringMVC,到了现在的SpringBoot,过一两年又会有其他web框架出现;你们有经历过框架不断的演进,然后自己开发项目所有的技术也在不断的变化、改造吗?建议都可以去经历一遍;
言归正传,什么是SpringBoot呢,就是一个javaweb的开发框架,和SpringMVC类似,对比其他javaweb框架的好处,官方说是简化开发,约定大于配置, you can “just run”,能迅速的开发web应用,几行代码开发一个http接口。
所有的技术框架的发展似乎都遵循了一条主线规律:从一个复杂应用场景 衍生 一种规范框架,人们只需要进行各种配置而不需要自己去实现它,这时候强大的配置功能成了优点;发展到一定程度之后,人们根据实际生产应用情况,选取其中实用功能和设计精华,重构出一些轻量级的框架;之后为了提高开发效率,嫌弃原先的各类配置过于麻烦,于是开始提倡“约定大于配置”,进而衍生出一些一站式的解决方案。
是的这就是Java企业级应用->J2EE->spring->springboot的过程。
随着 Spring 不断的发展,涉及的领域越来越多,项目整合开发需要配合各种各样的文件,慢慢变得不那么易用简单,违背了最初的理念,甚至人称配置地狱。Spring Boot 正是在这样的一个背景下被抽象出来的开发框架,目的为了让大家更容易的使用 Spring 、更容易的集成各种常用的中间件、开源软件;
Spring Boot 基于 Spring 开发,Spirng Boot 本身并不提供 Spring 框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于 Spring 框架的应用程序。也就是说,它并不是用来替代 Spring 的解决方案,而是和 Spring 框架紧密结合用于提升 Spring 开发者体验的工具。Spring Boot 以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数 Spring Boot 应用只需要很少的 Spring 配置。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如 Redis、MongoDB、Jpa、RabbitMQ、Quartz 等等),Spring Boot 应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用。
简单来说就是SpringBoot其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架 。
Spring Boot 出生名门,从一开始就站在一个比较高的起点,又经过这几年的发展,生态足够完善,Spring Boot 已经当之无愧成为 Java 领域最热门的技术。
1.4、Spring Boot的主要优点
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
二、第一个SpringBoot程序—Hello,World
2.1、准备工作
目的:
学习如何快速的创建一个Spring Boot应用,并且实现一个简单的Http请求处理
环境准备:
java version “1.8.0_181”
Maven-3.6.1
SpringBoot 2.x 最新版
开发工具:
IDEA
2.2、创建基础项目说明
Spring官方提供了非常方便的工具(Spring Initializr)让我们快速构建应用。
项目创建方式一:使用Spring Initializr 的 Web页面创建项目
1、打开 https://start.spring.io/
2、填写项目信息
3、点击”Generate Project“按钮生成项目;下载此项目
4、解压项目包,并用IDEA以Maven项目导入,一路下一步即可,直到项目导入完毕。
5、如果是第一次使用,可能速度会比较慢,包比较多、需要耐心等待一切就绪。
项目创建方式二:使用 IDEA 直接创建项目
1、创建一个新项目
2、选择spring initalizr , 可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
3、填写项目信息
4、选择初始化的组件(初学勾选 Web 即可)
5、填写项目路径
6、等待项目构建成功
项目结构分析
通过上面步骤完成了基础项目的创建。就会自动生成以下文件:
1、程序的主启动类
2、一个 application.properties配置文件
3、一个 测试类
4、一个 pom.xml
2.3、pom.xml 分析
自动生成的pom.xml文件中存在Spring Boot项目的依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
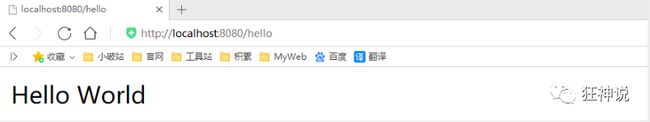
2.4、Web接口开发
- 在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
- 在包中新建一个HelloController类
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
Note:简单几步,就完成了一个web接口的开发,SpringBoot就是这么简单。所以我们常用它来建立我们的微服务项目!
2.5、将项目打成jar包
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<skipTests>trueskipTests>
configuration>
plugin>
三、SpringBoot运行原理初探
3.1、pom.xml文件
3.1.1、父依赖
- SpringBoot主要是依赖一个父项目,主要目的是管理项目的资源过滤及插件。该父依赖如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
- 点进去,发现上述父依赖还有一个父依赖,如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependenciesrelativePath>
parent>
这里才是真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,即SpringBoot的版本控制中心。
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了。
3.1.2、启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
- springboot-boot-starter-xxx:spring-boot的场景启动器
- spring-boot-starter-web:导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter(启动器),
只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 ,
我们要用什么功能仅需导入什么样的场景启动器即可;
我们未来也可以自己自定义 starter。
3.2、主启动类注解
3.2.1、默认的主启动类
//@SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类
//说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//以为是启动了一个方法,没想到启动了一个服务
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
一个简单的启动类并不简单,虽仅一个注解,可该注解的上层存在多个注解。
下一步我们来分析SpringBoot主启动类的注解@SpringBootApplication及其上层注解。
3.2.2、主启动类注解分析
(1)@SpringBootApplication
作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 ,SpringBoot就应该通过运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用。
进入这个注解后,可以看到其上层除标准注解外还有很多其他注解,如下:
import...
//标准注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
//SpringBoot独有注解
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// ......
}
(2)@ComponentScan
这个注解在Spring中很重要 ,它对应XML配置中的元素。
作用:自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中。
(3)@SpringBootConfiguration
作用:SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示该类这是一个SpringBoot的配置类。
继续进去这个注解查看,如下
// 点进去得到下面的 @Component
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {}
@Component
public @interface Configuration {}
- 这里的 @Configuration,说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件;
- 里面的 @Component 这就说明,启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用!
(4)@EnableAutoConfiguration
作用:开启自动配置功能。
以前我们需要自己配置的东西,而现在SpringBoot可以自动帮我们配置 ;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效。
继续进去这个注解查看,如下:
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import...
//标准注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
//独有注解
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
@AutoConfigurationPackage :自动配置包
Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
- @import 是Spring底层注解
作用:给容器中导入一个组件。- Registrar.class
作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器 。
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件
AutoConfigurationImportSelector :自动配置导入选择器,那么它会导入哪些组件的选择器呢?我们点击去这个类看源码:
- AutoConfigurationImportSelector类中有一个这样的方法——getCandidateConfigurations
// 获得候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
//这里的getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法
//返回的就是我们最开始看的启动自动导入配置文件的注解类;EnableAutoConfiguration
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
- 这个方法又调用了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
//这里它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
- 我们继续点击查看 loadSpringFactories 方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//获得classLoader , 我们返回可以看到这里得到的就是EnableAutoConfiguration标注的类本身
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//去获取一个资源 "META-INF/spring.factories"
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
//将读取到的资源遍历,封装成为一个Properties
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
- 发现一个多次出现的文件:spring.factories,全局搜索并打开它;看到了很多自动配置的文件,该文件即spring.factories就是自动配置根源所在。
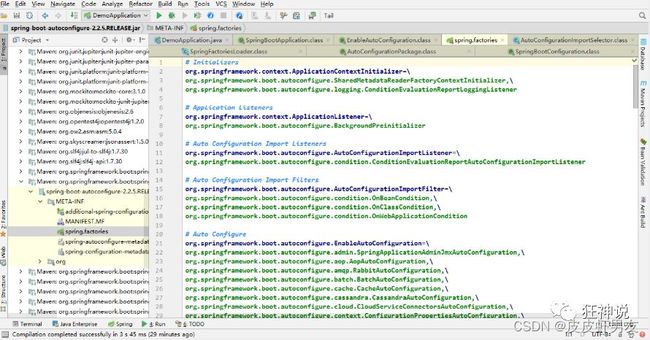 随便找一个打开的spring.factories文件中的自动配置类,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration
随便找一个打开的spring.factories文件中的自动配置类,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration
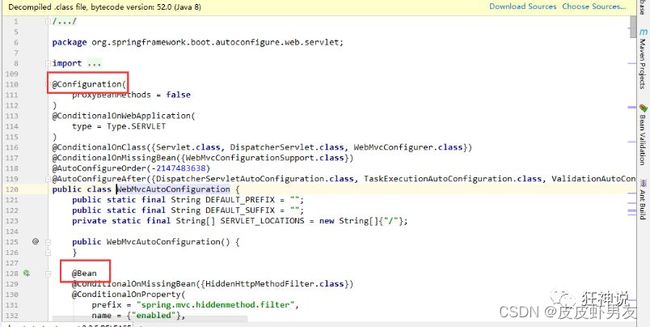
可以发现WebMvcAutoConfiguration是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean,其余的自动配置类也个个的都是JavaConfig配置类。
结论:自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
3.3、SpringApplication
3.3.1、SpringApplication.run(…)方法分析
//SpringbootApplication为主启动类名
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
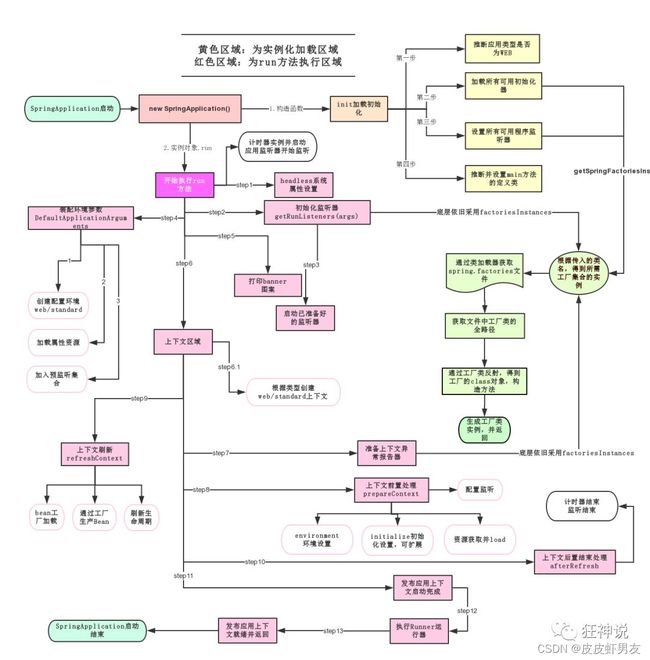
该方法主要分两部分:
一是SpringApplication的实例化,即传入该主启动类SpringbootApplication.class后,再对SpringApplication实例化。
二是run方法的执行。
3.3.2、类SpringApplication作用
- 推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
- 查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
- 找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
- 推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
查看构造器:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
// ......
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances();
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
3.3.3、run方法流程分析
四、YAML配置注入与SpringBoot配置文件加载
4.1、SpringBoot配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 ,配置文件名称固定即application.xxx。
SpringBoot被创建时默认文件application.properties,但我们可以按照自己开发需求创建文件application.yaml。
- application.properties,properties文件语法结构 :key=value 。
- application.yaml,yaml文件语法结构 :key: value,即key:空格value。
配置文件的作用 :按照个人需求修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值。
比如在配置文件中修改Tomcat默认启动的端口号,仅需在默认文件application.properties中编写配置
server.port=8081
4.2、Yaml概述
YAML是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language”(YAML不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)
这种语言以数据作为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点!
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用xml文件来配置;我们对yaml文件和xml文件进行对比,比如一个简单的端口配置:
- 传统xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
server>
- yaml配置:
server:
prot: 8080
4.3、Yaml基础语法
Yaml语法要求严格
- 空格不能省略
- 以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
- 属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
4.3.1、字面量
字面量即基本值,如数字,布尔值,字符串
字面量直接写在key后面就可以即可
key: value
- 字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号
“ ”即双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符 , 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思。比如 :name: " lao \n ba " 输出 :lao 换行 ba' '即单引号,会转义特殊字符 , 特殊字符最终会变成和普通字符一样输出 比如 :name: ‘ lao \n ba’ 完全输出 : lao \n ba
4.3.2、对象和Map(键值对)
#对象、Map格式
Key: #对象,Map的名字
key1: value1 #属性1和值1
key2: value2 #属性2和值2
- 普通写法
起始行写对象的名字,在其下一行来写对象属性和值的关系,注意缩进。比如:
student:
name: qinjiang
age: 3
- 行内写法
student: {name: qinjiang,age: 3}
4.3.3、数组( List、set )
- 普通写法
用 - 值表示数组中的一个元素,比如:
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
- 行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
4.3.4、在application.yaml中修改SpringBoot默认端口号
配置文件中添加,端口号的参数,就可以切换端口:
server:
port: 8082
4.4、Yaml注入配置文件
yaml文件更强大的地方在于可以给我们的实体类直接注入匹配值。
- 在springboot项目中的resources目录下新建一个文件 application.yml
- 编写一个实体类 Dog;
package com.kuang.springboot.pojo;
@Component //注册bean到容器中
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法
}
- 思考:我们原来是如何利用注解@Value给bean注入属性值的?如下:
@Component //注册bean
public class Dog {
@Value("阿黄")
private String name;
@Value("18")
private Integer age;
}
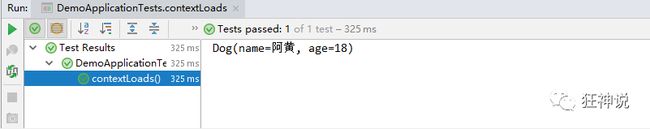
- 在SpringBoot的测试类下注入狗狗输出一下;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired //将狗狗自动注入进来
Dog dog;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dog); //打印看下狗狗对象
}
}
结果成功输出,@Value注入成功,这是我们原来的办法对吧。
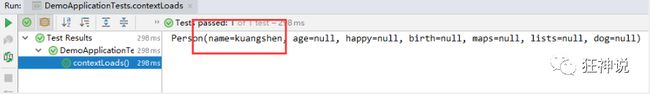
5、我们再编写一个复杂一点的实体类:Person 类
@Component //注册bean到容器中
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
//有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法
}
- 我们现在来使用yaml配置的方式进行注入,大家写的时候注意区别和优势,我们编写一个yaml配置,如下:
person:
name: qinjiang
age: 3
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 1
- 我们刚才已经把person这个对象的所有值都写好了,我们现在来注入到我们的类中!
/*
@ConfigurationProperties作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应
*/
@Component //注册bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
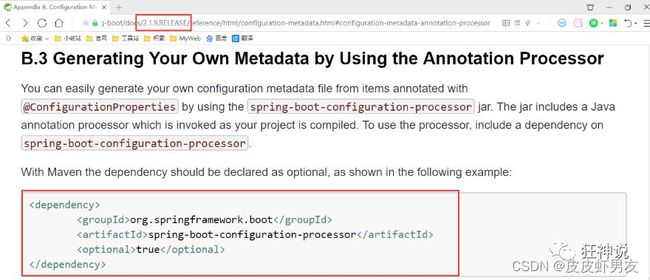
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
- 确认以上配置都OK之后,我们去测试类中测试一下:
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person; //将person自动注入进来
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person); //打印person信息
}
}
4.5、SpringBoot加载指定的配置文件
SpringBoot利用两个注解来加载配置文件:
@PropertySource :加载指定的配置文件。
@configurationProperties:默认从全局配置文件中获取值。
- 我们去在resources目录下新建一个person.properties文件
name=kuangshen
- 然后在我们的代码中指定加载person.properties文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties")
@Component //注册bean
public class Person {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
......
}
4.6、配置文件占位符
配置文件还可以编写占位符生成随机数,如下:
person:
name: qinjiang${random.uuid} # 随机uuid
age: ${random.int} # 随机int
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: ${person.hello:other}_旺财
age: 1
4.7、回顾properties配置
yaml配置文件是最简单,开发中最常用的,也是springboot所推荐的配置方式。但配置文件除了yaml还有SpringBoot默认的properties文件。
properties配置文件在写中文的时候,会有乱码 ,我们需要去IDEA中设置编码格式为UTF-8,需要再
settings-->FileEncodings中配置:
测试步骤:
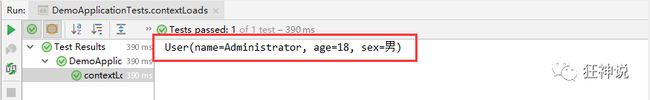
- 新建一个实体类User
@Component //注册bean
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
}
- 编辑配置文件 user.properties
user1.name=kuangshen
user1.age=18
user1.sex=男
- 我们在User类上使用@Value来进行注入!
@Component //注册bean
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties")
public class User {
//直接使用@value
@Value("${user.name}") //从配置文件中取值
private String name;
@Value("#{9*2}") // #{SPEL} Spring表达式
private int age;
@Value("男") // 字面量
private String sex;
}
4、Springboot测试
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
User user;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
4.6、SpringBoot注入实值各方式对比
@Value,作用:直接注入某一属性的实值。
@ConfigurationProperties,作用:注入配置文件(注入配置文件中已配置的实值)。
- @ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 , @Value则需要每个字段都添加,即需要为每个属性单独注解赋值。
- 松散绑定,比如我的yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是等价的, 即后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。
- JSR303数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性。
- 复杂类型封装,@ConfigurationProperties注入的yaml文件中可以封装对象 , 使用@value就不支持。
小结:
- 配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值 , 强烈推荐 yml;
- 如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value
- 如果说,我们专门编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行一一映射,就直接@configurationProperties,不要犹豫!
五、JSR303数据校验及多环境切换
5.1、JSR303数据校验
5.1.1、注解@validated
SpringBoot中可以用注解 @validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理。
例如下文代码中name只能支持Email格式:
@Component //注册bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated //数据校验
public class Person {
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误") //name必须是邮箱格式
private String name;
}
运行结果 :default message [不是一个合法的电子邮件地址]
![]()
使用数据校验,可以保证数据的正确性。
5.1.2、常见参数
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
.......等等
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则
5.2、多环境切换
5.2.1、多配置文件
参数profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活不同的环境版本,实现快速切换环境。
例如:
- application-test.properties 代表测试环境配置
- application-dev.properties代表开发环境配置
注意:Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.properties主配置文件
我们需要通过一个配置来选择需要激活的环境:
#比如在配置文件中指定使用dev环境,
#我们们可以通过设置不同的端口号进行测试;
#我们启动SpringBoot,就可以看到已经切换到dev下的配置了;
spring.profiles.active=dev
5.2.2、yaml的多文档块
yaml配置和properties配置文件中一样,但是使用yml去实现多环境配置不需要创建多个配置文件,仅需将多个环境配置在一个yaml文件中实现。
server:
port: 8081
#选择要激活那个环境块
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev #配置环境的名称
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #配置环境的名称
注意:如果yaml和properties同时都配置了端口,并且没有激活其他环境,默认会使用properties配置文件的,即properties配置文件优先级高于yaml配置文件。
5.2.3、配置文件加载位置
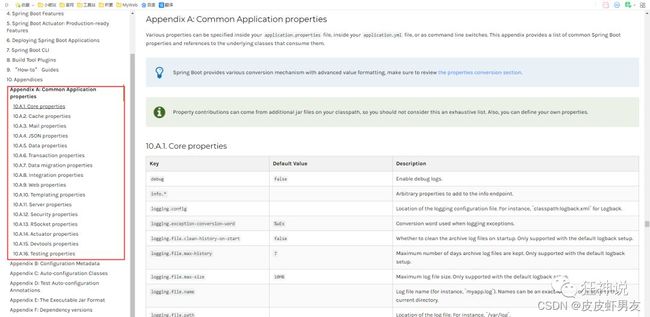
官方外部配置文件说明参考文档:
![]()
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件:
优先级1:项目路径下的config文件夹配置文件
优先级2:项目路径下配置文件
优先级3:资源路径下的config文件夹配置文件
优先级4:资源路径下配置文件
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置。
指定位置加载配置文件
我们可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置,如下:
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;这种情况,一般是后期运维做的多,相同配置,外部指定的配置文件优先级最高
java -jar spring-boot-config.jar --spring.config.location=F:/applicatio
六、自动配置原理
SpringBoot官方文档中有大量的配置,我们不可能手动注入这些配置(过于麻烦低效),因此SpringBoot提供自动配置这些配置文件的能力,仅需在需要配置的类上加上
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "下述配置的名字")
6.1、分析自动配置原理
以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理:
//表示这是一个配置类,和以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件;
@Configuration
//启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;
//进入这个HttpProperties查看,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来;
//并把HttpProperties加入到ioc容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})
//Spring底层@Conditional注解
//根据不同的条件判断,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效;
//这里的意思就是判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})
//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置:spring.http.encoding.enabled;
//如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.http.encoding",
value = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final Encoding properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
//给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
//。。。。。。。
}
总结 :根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效。
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着;
- 配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
例如:自动配置spring.http
//从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
public class HttpProperties {
// .....
}
6.2、SpringBoot自动配置流程
- SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
- 我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
- 我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
- 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类,给容器中添加组件。
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性。
6.3、@Conditional
自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效。
@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效。
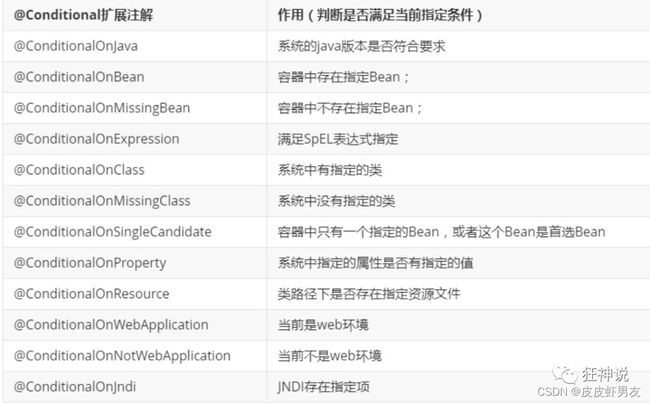
那么多的自动配置类,必须在一定的条件下才能生效;也就是说,我们加载了这么多的配置类,但不是所有的都生效了。
Q: 我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效?
A: 我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效:
#开启springboot的调试类
debug=true
结果如下:
Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的:正匹配) Negative
matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类:负匹配)
Unconditional classes: (没有条件的类)
七、自定义starter启动器
7.1、starter启动器说明
starter启动器模块是一个 空 jar 文件,仅提供辅助性依赖管理,这些依赖可能用于自动装配或者其他类库。
starter启动器命名规范:
- 官方命名:spring-boot-starter-xxx,例如:spring-boot-starter-web
- 自定义命名:xxx-spring-boot-starter,例如:MyStarter-spring-boot-starter
7.2、编写启动器
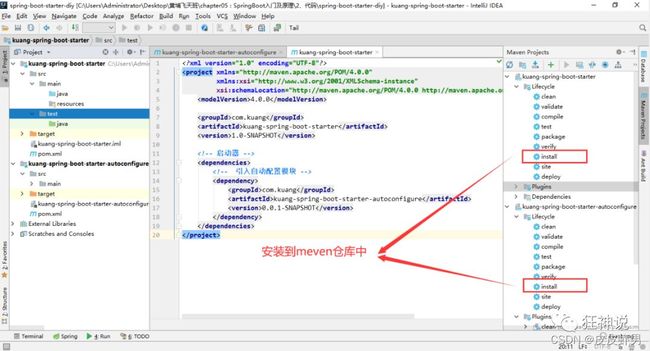
- 在IDEA中新建一个空项目(Empty Project): spring-boot-starter-diy。
- 新建一个普通Maven模块:kuang-spring-boot-starter。
- 新建一个SpringBoot模块:kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure。
- 基本结构如下:

- 在我们普通maven模块即kuang-spring-boot-starter的
pom.xml文件中导入我们自定义的SpringBoot模块即kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure的依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kuanggroupId>
<artifactId>kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigureartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 将Springboot模块即kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure除pom.xml文件外多余文件删除,且pom.xml文件中的依赖只留下
spring-boot-starter,注:spring-boot-starter是官方starter启动器依赖,是所有的启动器基本配置。
- 编写个人服务
package com.kuang;
public class HelloService {
HelloProperties helloProperties;
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
public String sayHello(String name){
return helloProperties.getPrefix() + name + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
}
- 编写HelloProperties 配置类
package com.kuang;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
// 前缀 kuang.hello
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "kuang.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
public String getPrefix() {
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}
- 编写我们的自动配置类并注入bean
package com.kuang;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication //web应用生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
HelloService service = new HelloService();
service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return service;
}
}
- 在resources编写一个自己的 META-INF\spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.kuang.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
7.3、新建项目测试测试上述自定义启动器
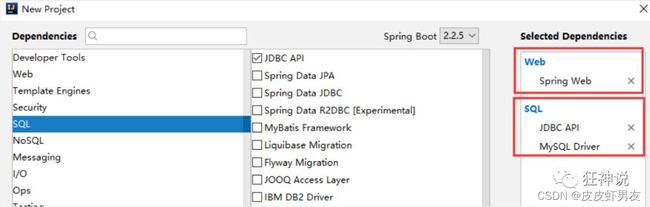
- 新建一个SpringBoot 项目
- 导入我们自己写的启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kuanggroupId>
<artifactId>kuang-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
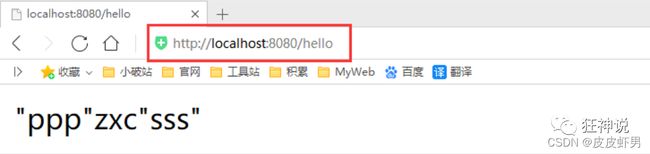
- 编写一个 HelloController 进行测试我们自己的写的接口!
package com.kuang.controller;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return helloService.sayHello("zxc");
}
}
- 编写配置文件 application.properties
kuang.hello.prefix="ppp"
kuang.hello.suffix="sss"
八、整合JDBC
8.1、SpringData简介
对于数据访问层,无论是 SQL(关系型数据库) 还是 NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot 底层都是采用 SpringData 的方式进行统一处理,
即Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data的方式进行统一处理各种数据库,
Spring Data 也是 Spring 中与 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud等齐名的知名项目。
- SpringData官网
- SpringBoot启动器
8.2、整合JDBC
8.2.1、创建测试项目并链接数据源
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
- 编写yaml配置文件连接数据库;
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- 由于SpringBoot已经默认帮我们进行了自动配置,我们在配置完这些东西后可以直接链接数据库。
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootDataJdbcApplicationTests {
//DI注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
- 结果:我们可以看到他默认给我们配置的数据源为 : class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource , 但我们并没有手动配置。
全局搜索一下该数据源,发现该数据源的所有自动配置都在 DataSourceAutoConfiguration文件:
@Import(
{Hikari.class, Tomcat.class, Dbcp2.class, Generic.class, DataSourceJmxConfiguration.class}
)
protected static class PooledDataSourceConfiguration {
protected PooledDataSourceConfiguration() {
}
}
这里导入的类都在 DataSourceConfiguration 配置类下,可以看出 Spring Boot 2.2.5 默认使用HikariDataSource 数据源,而以前版本,如 Spring Boot 1.5 默认使用 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource 作为数据源。
HikariDataSource 号称 Java WEB 当前速度最快的数据源,相比于传统的 C3P0 、DBCP、Tomcat jdbc 等连接池更加优秀。
NOTE:可以使用 spring.datasource.type 指定自定义的数据源类型,其值为要使用的连接池实现的完全限定名。
8.2.2、JDBCTemplate
- 有了数据源(com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource),然后可以拿到数据库连接(java.sql.Connection),有了连接,就可以使用原生的 JDBC 语句来操作数据库。
- 即使不使用第三方第数据库操作框架,如 MyBatis等,Spring 本身也对原生的JDBC 做了轻量级的封装,即JdbcTemplate。
- 数据库操作的所有 CRUD 方法都在 JdbcTemplate 中。
- Spring Boot 不仅提供了默认的数据源,同时默认已经配置好了 JdbcTemplate 放在了容器中,程序员只需自己注入即可使用。
- JdbcTemplate 的自动配置是依赖
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc包下的JdbcTemplateConfiguration类
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下几类方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句。
- update方法及batchUpdate方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;batchUpdate方法用于执行批处理相关语句。
- query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句。
- call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
8.2.3、测试
编写一个Controller,注入 jdbcTemplate,编写测试方法进行访问测试,如下:
package com.kuang.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbc")
public class JdbcController {
/**
* Spring Boot 默认提供了数据源,默认提供了 org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
* JdbcTemplate 中会自己注入数据源,用于简化 JDBC操作
* 还能避免一些常见的错误,使用起来也不用再自己来关闭数据库连接
*/
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//查询employee表中所有数据
//List 中的1个 Map 对应数据库的 1行数据
//Map 中的 key 对应数据库的字段名,value 对应数据库的字段值
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<Map<String, Object>> userList(){
String sql = "select * from employee";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return maps;
}
//新增一个用户
@GetMapping("/add")
public String addUser(){
//插入语句,注意时间问题
String sql = "insert into employee(last_name, email,gender,department,birth)" +
" values ('狂神说','[email protected]',1,101,'"+ new Date().toLocaleString() +"')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
//查询
return "addOk";
}
//修改用户信息
@GetMapping("/update/{id}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "update employee set last_name=?,email=? where id="+id;
//数据
Object[] objects = new Object[2];
objects[0] = "秦疆";
objects[1] = "[email protected]";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,objects);
//查询
return "updateOk";
}
//删除用户
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "delete from employee where id=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
//查询
return "deleteOk";
}
}
九、整合Druid
9.1、Druid简介
- Java程序很大一部分要操作数据库,为了提高性能操作数据库的时候,又不得不使用数据库连接池。
- Druid 是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,结合了 C3P0、DBCP 等 DB 池的优点,同时加入了日志监控。
- Druid 可以很好的监控 DB 池连接和 SQL 的执行情况,天生就是针对监控而生的 DB 连接池。
- Druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。
- Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 Hikari 数据源,可以说 Hikari 与 Driud 都是当前 Java Web上最优秀的数据源,我们来重点介绍 Spring Boot 如何集成 Druid 数据源,如何实现数据库监控。
Github地址——Druid
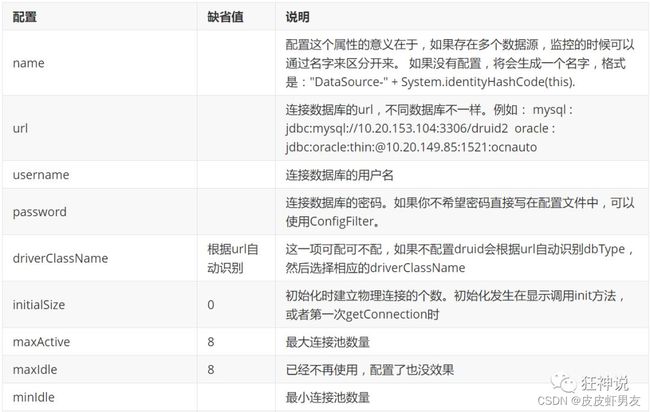
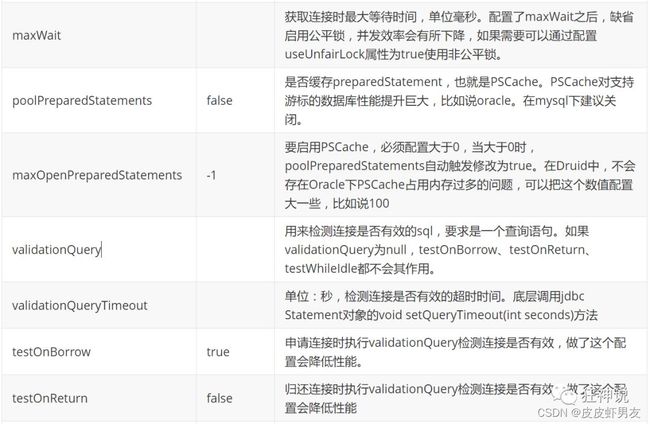
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource (Druid 数据源)基本配置参数如下:

9.2、配置Druid数据源
- 添加上 Druid 数据源依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.21version>
dependency>
- 切换数据源;之前已经说过 Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource 数据源,但可以 通过 spring.datasource.type 指定数据源。
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 自定义数据源
- 数据源切换之后,在测试类中注入 DataSource,然后获取到它,输出一看便知是否成功切换

- 切换成功!既然切换成功,就可以设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数 等设置项;可以查看源码
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
- 导入Log4j 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
- 现在需要程序员自己为 DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;我们需要 自己添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性;
package com.kuang.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
- 测试
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootDataJdbcApplicationTests {
//DI注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
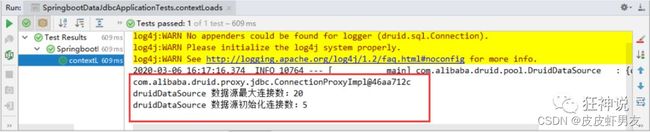
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = (DruidDataSource) dataSource;
System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源最大连接数:" + druidDataSource.getMaxActive());
System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源初始化连接数:" + druidDataSource.getInitialSize());
//关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
9.3、配置Druid数据源监控
9.3.1、配置 Druid 的后台管理
Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看。
所以第一步需要设置 Druid 的后台管理页面,比如 登录账号、密码 等;配置后台管理;
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
// 这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet
// 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号
initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//后台允许谁可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
initParams.put("allow", "");
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
配置完毕后,我们可以选择访问 :http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html

进入之后
9.3.2、配置 Druid web 监控 filter 过滤器
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter
//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
//exclusions:设置哪些请求进行过滤排除掉,从而不进行统计
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*,/jdbc/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
//"/*" 表示过滤所有请求
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
十、整合MyBatis
整合测试:
- 导入 MyBatis 所需要的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.1version>
dependency>
- 配置数据库连接信息(不变)
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
-
测试数据库是否连接成功!
-
创建实体类,导入 Lombok!
Department.java
package com.kuang.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
}
- 创建mapper目录以及对应的 Mapper 接口
DepartmentMapper.java
//@Mapper : 表示本类是一个 MyBatis 的 Mapper
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface DepartmentMapper {
// 获取所有部门信息
List<Department> getDepartments();
// 通过id获得部门
Department getDepartment(Integer id);
}
- 对应的Mapper映射文件
DepartmentMapper.xml
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.mapper.DepartmentMapper">
<select id="getDepartments" resultType="Department">
select * from department;
select>
<select id="getDepartment" resultType="Department" parameterType="int">
select * from department where id = #{id};
select>
mapper>
- maven配置资源过滤问题
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>truefiltering>
resource>
resources>
- 编写部门的 DepartmentController 进行测试!
@RestController
public class DepartmentController {
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
// 查询全部部门
@GetMapping("/getDepartments")
public List<Department> getDepartments(){
return departmentMapper.getDepartments();
}
// 查询全部部门
@GetMapping("/getDepartment/{id}")
public Department getDepartment(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return departmentMapper.getDepartment(id);
}
}
十一、Web开发——静态资源处理和首页处理
11.1、静态资源处理
11.1.1、第一种静态资源映射规则
在SpringBoot中,SpringMVC的web配置都在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 这个配置类里面。
查看源码可发现在WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter存在一个方法:addResourceHandlers ,即添加资源处理。
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
// 已禁用默认资源处理
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
// 缓存控制
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
// webjars 配置
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
// 静态资源配置
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
通过源码可以发现所有的 /webjars/** , 都需要去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找对应的资源。
什么是webjars ?
webjars本质就是以jar包的方式引入我们的静态资源 ,我们需要导入一个静态资源文件,直接导入静态资源对应的jar包该即可。
若使用SpringBoot需要引入Webjars,仅需在webjars官网引入对应的pom依赖即可。
例如:要使用jquery,只需引入jquery对应版本的pom依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjarsgroupId>
<artifactId>jqueryartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
导入完毕,查看webjars目录结构,并访问Jquery.js文件。
只要是静态资源并引入对应的pom依赖后,SpringBoot就会去对应的路径寻找资源,这里访问:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.js。
11.1.2、第二种静态资源映射规则
Q:开发项目中要是需要使用自己的静态资源该怎么导入呢?
A:SpringBoot提供第二种静态资源映射规则(/**)。
我们去找staticPathPattern发现第二种映射规则 :/** , 访问当前的项目任意资源,它会去找 resourceProperties 这个类,我们可以点进去看一下分析:
// 进入方法
public String[] getStaticLocations() {
return this.staticLocations;
}
// 找到对应的值
private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
// 找到路径
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/"
};
ResourceProperties 可以设置和我们静态资源有关的参数;这里面指向了它会去寻找资源的文件夹,即上面数组的内容。
所以得出结论,以下四个目录存放的静态资源可以被我们识别:
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/"
"classpath:/resources/"
"classpath:/static/"
"classpath:/public/"
即我们可以在resources根目录下新建对应的文件夹来存放静态资源文件。
比如我们访问 http://localhost:8080/1.js , 他就会去这些文件夹中寻找对应的静态资源文件。
11.1.3、自定义静态资源路径
我们也可以自己通过配置文件来指定文件夹用来放静态资源文件,需要在application.properties中配置:
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/coding/,classpath:/file/
11.2、首页处理
源码中有一个欢迎页的映射,这就是我们的首页,如下:
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService,
ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(), // getWelcomePage 获得欢迎页
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
点进去getWelcomePage()继续看
private Optional<Resource> getWelcomePage() {
String[] locations = getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
// ::是java8 中新引入的运算符
// Class::function的时候function是属于Class的,应该是静态方法。
// this::function的funtion是属于这个对象的。
// 简而言之,就是一种语法糖而已,是一种简写
return Arrays.stream(locations).map(this::getIndexHtml).filter(this::isReadable).findFirst();
}
// 欢迎页就是一个location下的的 index.html 而已
private Resource getIndexHtml(String location) {
return this.resourceLoader.getResource(location + "index.html");
}
可以发现SpringBoot会寻找静态资源文件夹下的所有 index.html 页面来构建首页,被 /** 映射。比如:访问 http://localhost:8080/ ,SpringBoot直接会寻找静态资源文件夹下的 index.html。
补充、关于web网站图标说明
与其他静态资源一样,Spring Boot在配置的静态内容位置中查找图标文件,如果存在这样的文件,它将自动用作应用程序的图标。
自定义图标:
- 关闭SpringBoot默认图标
#关闭默认图标
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=false
十二、Web开发——Thymeleaf模板引擎
12.1、何为模板引擎?
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,SpringBoot现在默认是不支持jsp的。
SpringBoot推荐使用模板引擎
模板引擎有非常多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,此外如还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf。但模板引擎的思想都是统一的,如下图:
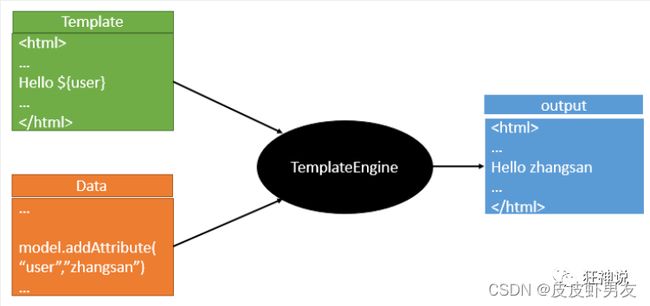
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。其他的我就不介绍了,我主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,他的这个语法更简单。而且呢,功能更强大。
12.2、引入Thymeleaf
对于springboot来说,引入其他的模块仅需引入该模块对应的start启动器(pom依赖)。 我们可以在以下三个网址找到Thymeleaf对应的pom依赖。
- Thymeleaf官方网站
- Github——Thymeleaf
- SpringBoot启动器官网
Thymeleaf对应的pom依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
12.3、Thymeleaf分析
SpringBoot中Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties,如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding;
}
在配置类可以在发现默认的前缀(classpath:/templates/)和后缀(.html),我们仅需把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染。使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将我们的html页面放在指定的文件夹下即可。
测试:
- 编写一个TestController
@Controller
public class TestController {
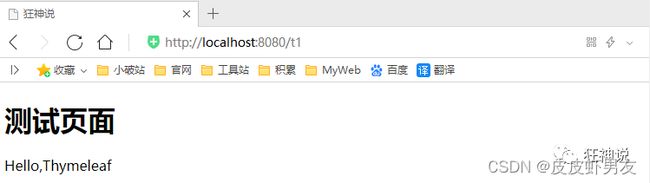
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(){
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
}
- 编写一个测试页面 test.html,并将其放在 templates 目录下
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面h1>
body>
html>
- 启动项目请求测试
12.4、Thymeleaf 语法学习
学习语法,还是参考官网文档最为准确! 在Thymeleaf 官网下载Thymeleaf的官方文档。
简单练习:查询数据并在页面中展示
- 修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(Model model){
//存入数据
model.addAttribute("msg","Hello,Thymeleaf");
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
- 我们要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。我们可以去官方文档的#3中看一下命名空间拿来过来:
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
- 编写前端页面test.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>狂神说title>
head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面h1>
<div th:text="${msg}">div>
body>
html>
2. 我们能写哪些表达式呢?
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:#18
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
==================================================================================
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _
测试:
- 我们编写一个Controller,放一些数据
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String test2(Map<String,Object> map){
//存入数据
map.put("msg","Hello
");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("qinjiang","kuangshen"));
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
- 在测试页面test.html取出数据
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>狂神说title>
head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面h1>
<div th:text="${msg}">div>
<div th:utext="${msg}">div>
<h4 th:each="user :${users}" th:text="${user}">h4>
<h4>
<span th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]span>
h4>
body>
html>
- 启动项目测试!
十三、MVC自动配置原理
13.1、官方文档阅读
Q:SpringBoot对SpringMVC到底做了哪些配置,包括如何扩展,如何定制?
A:途径一:源码分析;途径二:官方文档。
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
// 首页定制
Static index.html support.
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmvcconfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
13.2、ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver即内容协商视图解析器在上述官方文档中位列第一个功能,可见其重要性,其实它就是SpringMVC中的视图解析器,即根据方法的返回值取得视图对象(View),然后由视图对象决定如何渲染(转发,重定向)。
在配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration中ContentNegotiatingViewResolver源码如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver使用所有其他视图解析器来定位视图,因此它应该具有较高的优先级
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}
点击进入ContentNegotiatingViewResolver类,查看其源码:
@Nullable // 注解说明:@Nullable 即参数可为null
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = this.getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes)attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
// 获取候选的视图对象
List<View> candidateViews = this.getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
// 选择一个最适合的视图对象,然后把这个对象返回
View bestView = this.getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
// .....
}
Q:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver是怎样获得候选的视图的呢?
A:点击进入getCandidateViews,查看如何获得候选的视图。Iterator var5 = this.viewResolvers.iterator();可得出ContentNegotiatingViewResolver是把所有的视图解析器拿来,进行while循环,挨个解析!
结论:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 这个视图解析器就是用来组合所有的视图解析器的 。
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver类中存在一个属性为viewResolvers,查看它是在哪里进行赋值的。
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) { // 这里它是从beanFactory工具中获取容器中的所有视图解析器 // ViewRescolver.class 把所有的视图解析器来组合的 Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values(); ViewResolver viewResolver; if (this.viewResolvers == null) { this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.size()); } // ............... } ```
实现视图解析器:
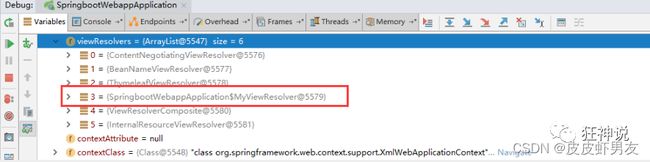
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver是在容器中去找视图解析器,那么我们可以自己给容器中去添加一个视图解析器,ContentNegotiatingViewResolver就会帮我们自动的将它组合进来。
- 我们在我们的主程序中去写一个视图解析器来试试;
@Bean //放到bean中
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//我们写一个静态内部类,视图解析器就需要实现ViewResolver接口
private static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
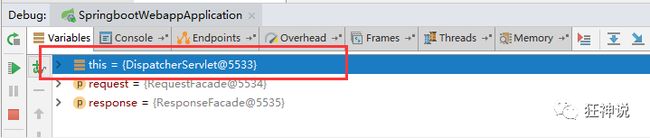
- 如何我们自己写的视图解析器有没有起作用呢?
我们给 DispatcherServlet 中的 doDispatch方法加个断点进行调试一下,因为所有的请求都会走到这个方法中。
13.3、转换器和格式化器
找到格式化转换器:
@Bean
@Override
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
// 拿到配置文件中的格式化规则
WebConversionService conversionService =
new WebConversionService(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());
addFormatters(conversionService);
return conversionService;
}
点击去:
public String getDateFormat() {
return this.dateFormat;
}
/**
* Date format to use. For instance, `dd/MM/yyyy`. 默认的
*/
private String dateFormat;
可以看到在我们的Properties文件中,我们可以进行自动配置它!
如果配置了自己的格式化方式,就会注册到Bean中生效,我们可以在配置文件中配置日期格式化的规则:

13.3、修改SpringBoot的默认配置
- SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的,即用户自定义组件比自动配置组件优先级高。
- 如果某些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,. SpringBoot就将用户配置的组件和自己默认的组件组合起来。
扩展使用SpringMVC 官方文档如下:
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, viewcontrollers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
即我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解。
自定义MyMvcConfig
//应为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口
//可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
}
页面结果如下:

确实也跳转过来了,若当我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方就推荐我们这么去使用,既保SpringBoot留所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置。
原理分析:
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 SpringMVC的自动配置类,里面有一个类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
-
这个类上有一个注解,在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
-
我们点进EnableWebMvcConfiguration这个类看一下,它继承了一个父类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个父类中有这样一段代码:
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 从容器中获取所有的webmvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
- 我们可以在这个类中去寻找一个我们刚才设置的viewController当做参考,发现它调用了一个
protected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}
- 我们点进去看一下
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
Iterator var2 = this.delegates.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
// 将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置来一起调用!包括我们自己配置的和Spring给我们配置的
WebMvcConfigurer delegate = (WebMvcConfigurer)var2.next();
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}
所以得出结论:所有的WebMvcConfiguration都会被作用,不止Spring自己的配置类,我们自己的配置类当然也会被调用。
13.4、全面接管SpringMVC
官方文档描述如下:
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC ,
you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置,只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc。
注意:若全面接管了SpringMVC,则所有的SpringMVC自动配置都失效,包括且不限于静态资源映射,开发中开发中不推荐使用全面接管SpringMVC。
Q:为什么加了一个注解,自动配置就失效了?
- 点击进入@EnableWebMvc这个注解。
- 发现它导入了一个类。
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
- 点击进入DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration这个类,发现它继承了一个父类 WebMvcConfigurationSupport。
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
// ......
}
- 回顾Webmvc自动配置类。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
// 这个注解的意思就是:容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
总结一句话:@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了;而导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能。
补充:多多留心WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件。
十四、集成Swagger
14.1、Swagger简介
由前后端分离产生的问题:
- 前端 -> 前端控制层、视图层
- 后端 -> 后端控制层、服务层、数据访问层
- 前后端通过API进行交互
- 前后端相对独立且松耦合
因此前后端集成,前端或者后端无法做到“及时协商,尽早解决”,最终导致问题集中爆发。
解决方案:
首先定义schema [ 计划的提纲 ],并实时跟踪最新的API,降低集成风险。
Swagger优势:
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架。
- Restful Api 文档在线自动生成器 ,可使 API 文档 与API 定义同步更新
- 直接运行,在线测试API。
- 支持多种语言 (如:Java,PHP等)。
14.2、SpringBoot集成Swagger
SpringBoot集成Swagger即springfox,需要两个jar包:
- Springfox-swagger2
- swagger-springmvc
使用Swagger
注意:使用Swagger2需要jdk1.8及以上版本
- 新建一个SpringBoot-web项目
- 添加Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
- 编写HelloController,测试确保运行成功
- 要使用Swagger,我们需要编写一个配置类-SwaggerConfig来配置 Swagger,如下:
@Configuration //配置类
@EnableSwagger2// 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
14.3、配置Swagger
- Swagger实例Bean是Docket,所以通过配置Docket实例来配置Swaggger。
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
- 可以通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
//配置文档信息
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
Contact contact = new Contact("联系人名字", "http://xxx.xxx.com/联系人访问链接", "联系人邮箱");
return new ApiInfo(
"Swagger学习", // 标题
"学习演示如何配置Swagger", // 描述
"v1.0", // 版本
"http://terms.service.url/组织链接", // 组织链接
contact, // 联系人信息
"Apach 2.0 许可", // 许可
"许可链接", // 许可连接
new ArrayList<>()// 扩展
);
}
- Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
- 重启项目,访问测试 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
14.4、配置扫描接口
- 构建Docket时通过select()方法配置怎么扫描接口。
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
- 重启项目测试,由于我们配置根据包的路径扫描接口,所以我们只能看到一个类
- 除了通过包路径配置扫描接口外,还可以通过配置其他方式扫描接口,这里注释一下所有的配置方式:
any() // 扫描所有,项目中的所有接口都会被扫描到
none() // 不扫描接口
// 通过方法上的注解扫描,如withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class)只扫描get请求
withMethodAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
// 通过类上的注解扫描,如.withClassAnnotation(Controller.class)只扫描有controller注解的类中的接口
withClassAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
basePackage(final String basePackage) // 根据包路径扫描接口
- 除此之外,我们还可以配置接口扫描过滤:
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
- 这里的可选值还有
any() // 任何请求都扫描
none() // 任何请求都不扫描
regex(final String pathRegex) // 通过正则表达式控制
ant(final String antPattern) // 通过ant()控制
14.5、配置Swagger开关
- 通过enable()方法配置是否启用swagger,如果是false,swagger将不能在浏览器中访问了
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
- 如何动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示?
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
// 设置要显示swagger的环境
Profiles of = Profiles.of("dev", "test");
// 判断当前是否处于该环境
// 通过 enable() 接收此参数判断是否要显示
boolean b = environment.acceptsProfiles(of);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(b) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
14.6、配置API分组
- 如果没有配置分组,默认是default。通过groupName()方法即可配置分组:
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("hello") // 配置分组
// 省略配置....
}
-
重启项目查看分组
-
如何配置多个分组?配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket即可:
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
- 重启项目查看即可
14.7、实体配置
- 新建一个实体类
@ApiModel("用户实体")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
- 只要这个实体在请求接口的返回值上(即使是泛型),都能映射到实体项中
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
注:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
14.8、常用注解
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下
下述是经常用到的注解:
| Swagger注解 | 简单说明 |
|---|---|
| @Api(tags = “xxx模块说明”) | 作用在模块类上 |
| @ApiOperation(“xxx接口说明”) | 作用在接口方法上 |
| @ApiModel(“xxxPOJO说明”) | 作用在模型类上:如VO、BO |
| @ApiModelProperty(value = “xxx属性说明”,hidden = true) | 作用在类方法和属性上,hidden设置为true可以隐藏该属性 |
| @ApiParam(“xxx参数说明”) | 作用在参数、方法和字段上,类似@ApiModelProperty |
给请求的接口配置一些注释
@ApiOperation("狂神的接口")
@PostMapping("/kuang")
@ResponseBody
public String kuang(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String username){
return username;
}
这样的话,可以给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加一些配置信息,让人更容易阅读!
相较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档(写得好本身就是文档)而且更不容易出错,只需要录入数据然后点击Execute,如果再配合自动化框架,可以说基本就不需要人为操作了。
Swagger是个优秀的工具,现在国内已经有很多的中小型互联网公司都在使用它,相较于传统的要先出Word接口文档再测试的方式,显然这样也更符合现在的快速迭代开发行情。当然了,提醒下大家在正式环境要记得关闭Swagger,一来出于安全考虑二来也可以节省运行时内存。
十五、Dubbo和Zookeeper集成
15.1、分布式理论
15.1.1、什么是分布式系统?
在《分布式系统原理与范型》一书中有如下定义:“分布式系统是若干独立计算机的集合,这些计算机对于用户来说就像单个相关系统”;
分布式系统是由一组通过网络进行通信、为了完成共同的任务而协调工作的计算机节点组成的系统。分布式系统的出现是为了用廉价的、普通的机器完成单个计算机无法完成的计算、存储任务。其目的是利用更多的机器,处理更多的数据。
分布式系统(distributed system)是建立在网络之上的软件系统。
首先需要明确的是,只有当单个节点的处理能力无法满足日益增长的计算、存储任务的时候,且硬件的提升(加内存、加磁盘、使用更好的CPU)高昂到得不偿失的时候,应用程序也不能进一步优化的时候,我们才需要考虑分布式系统。因为,分布式系统要解决的问题本身就是和单机系统一样的,而由于分布式系统多节点、通过网络通信的拓扑结构,会引入很多单机系统没有的问题,为了解决这些问题又会引入更多的机制、协议,带来更多的问题。
15.1.2、架构随流量演变
随着互联网的发展,网站应用的规模不断扩大,常规的垂直应用架构已无法应对,分布式服务架构以及流动计算架构势在必行,急需一个治理系统确保架构有条不紊的演进。
在Dubbo的官网文档有这样一张图:

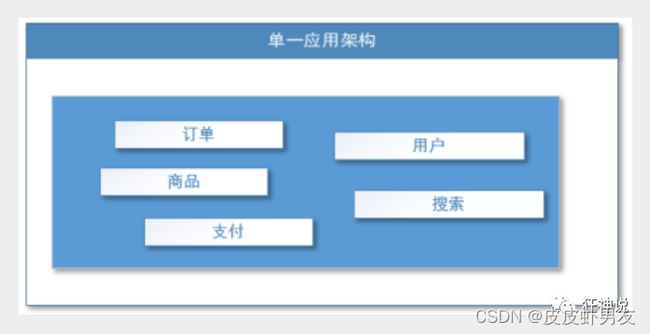
(1)单一应用架构
当网站流量很小时,只需一个应用,将所有功能都部署在一起,以减少部署节点和成本。此时,用于简化增删改查工作量的数据访问框架(ORM)是关键。
适用于小型网站,小型管理系统,将所有功能都部署到一个功能里,简单易用。
缺点:
- 性能扩展比较难
- 协同开发问题
- 不利于升级维护
(2)垂直应用架构
当访问量逐渐增大,单一应用增加机器带来的加速度越来越小,将应用拆成互不相干的几个应用,以提升效率。此时,用于加速前端页面开发的Web框架(MVC)是关键。

通过切分业务来实现各个模块独立部署,降低了维护和部署的难度,团队各司其职更易管理,性能扩展也更方便,更有针对性。
缺点:公用模块无法重复利用,开发性的浪费
(3)分布式服务架构
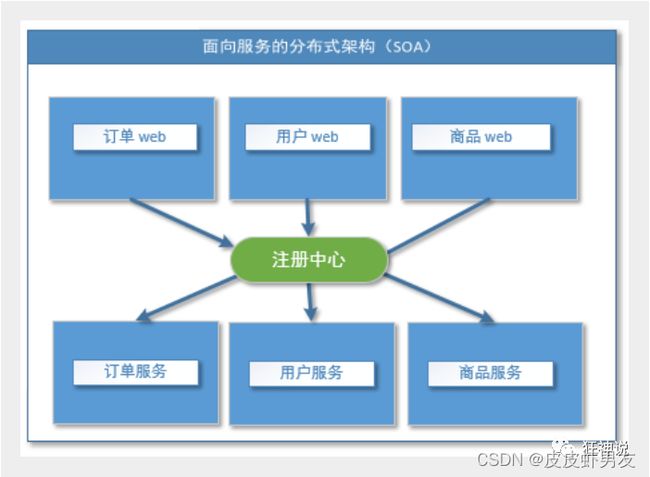
当垂直应用越来越多,应用之间交互不可避免,将核心业务抽取出来,作为独立的服务,逐渐形成稳定的服务中心,使前端应用能更快速的响应多变的市场需求。此时,用于提高业务复用及整合的分布式服务框架(RPC)是关键。

(4)流动计算架构
当服务越来越多,容量的评估,小服务资源的浪费等问题逐渐显现,此时需增加一个调度中心基于访问压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。此时,用于提高机器利用率的资源调度和治理中心(SOA)[ Service Oriented Architecture]是关键。
15.2、什么是RPC
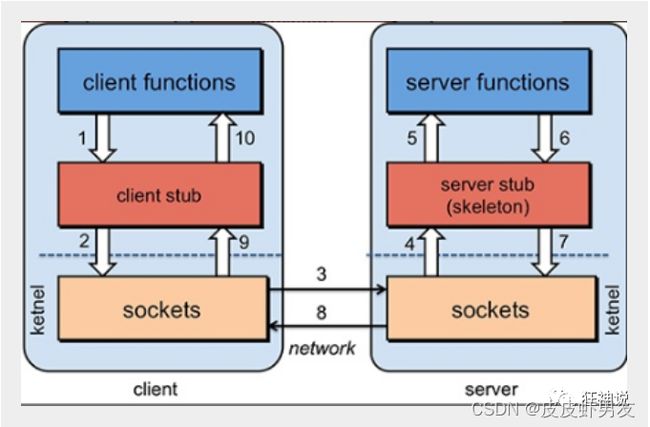
RPC【Remote Procedure Call】是指远程过程调用,是一种进程间通信方式,他是一种技术的思想,而不是规范。它允许程序调用另一个地址空间(通常是共享网络的另一台机器上)的过程或函数,而不用程序员显式编码这个远程调用的细节。即程序员无论是调用本地的还是远程的函数,本质上编写的调用代码基本相同。
也就是说两台服务器A,B,一个应用部署在A服务器上,想要调用B服务器上应用提供的函数/方法,由于不在一个内存空间,不能直接调用,需要通过网络来表达调用的语义和传达调用的数据。为什么要用RPC呢?就是无法在一个进程内,甚至一个计算机内通过本地调用的方式完成的需求,比如不同的系统间的通讯,甚至不同的组织间的通讯,由于计算能力需要横向扩展,需要在多台机器组成的集群上部署应用。RPC就是要像调用本地的函数一样去调远程函数;
推荐阅读文章:https://www.jianshu.com/p/2accc2840a1b
RPC基本原理
步骤解析:
![]()
Note:RPC两个核心模块:通讯,序列化。
15.3、测试环境搭建
15.3.1、Dubbo
Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。
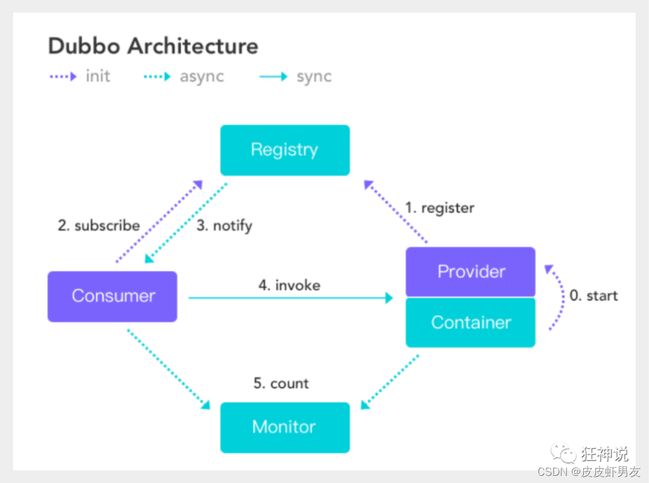
- dubbo官网
- 服务提供者(Provider):暴露服务的服务提供方,服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
- 服务消费者(Consumer):调用远程服务的服务消费方,服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务,服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
- 注册中心(Registry):注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者
- 监控中心(Monitor):服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心
调用关系说明
- 服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
- 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
- 服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
- 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。
- 服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
- 服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
15.3.2、Dubbo环境搭建
Dubbo官方文档推荐我们使用zookeeper注册中心
Window下安装zookeeper
- 下载并解压zookeeper
- 运行/bin/zkServer.cmd
注意:初次运行会报错,没有zoo.cfg配置文件导致闪退。
解决方案:编辑zkServer.cmd文件末尾添加pause ;这样运行出错就不会退出,会提示错误信息,方便找到原因。
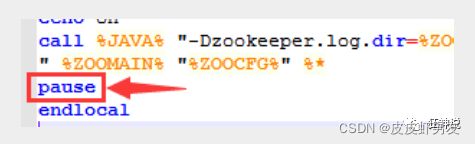

- 修改zoo.cfg配置文件
将conf文件夹下面的zoo_sample.cfg复制一份改名为zoo.cfg即可。
注意几个重要位置:
- dataDir=./ 临时数据存储的目录(可写相对路径)
- clientPort=2181 zookeeper的端口号
- 使用zkCli.cmd测试
ls /:列出zookeeper根下保存的所有节点
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 4] ls /
[zookeeper]
create –e /kuangshen 123:创建一个kuangshen节点,值为123

get /kuangshen:获取/kuangshen节点的值
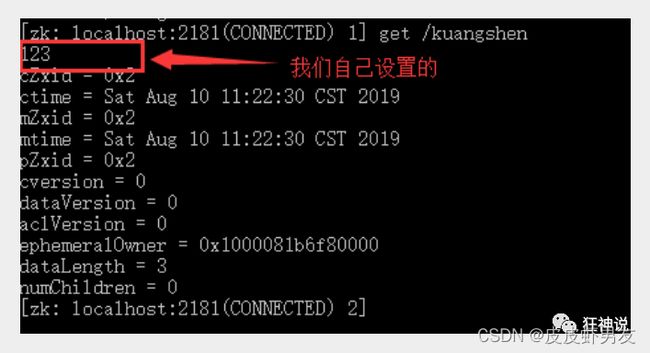
查看一下节点
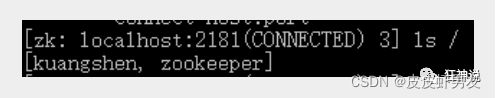
window下安装dubbo-admin
- dubbo本身并不是一个服务软件。它其实就是一个jar包,能够帮你的java程序连接到zookeeper,并利用zookeeper消费、提供服务。
- 但是为了让用户更好的管理监控众多的dubbo服务,官方提供了一个可视化的监控程序dubbo-admin,不过这个监控即使不装也不影响使用。
安装流程:
- 下载dubbo-admin
地址 :https://github.com/apache/dubbo-admin/tree/master
- 解压进入目录
修改 dubbo-admin\src\main\resources \application.properties指定zookeeper地址
server.port=7001
spring.velocity.cache=false
spring.velocity.charset=UTF-8
spring.velocity.layout-url=/templates/default.vm
spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=false
spring.messages.basename=i18n/message
spring.root.password=root
spring.guest.password=guest
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
- 在项目目录下打包dubbo-admin
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
- 执行 dubbo-admin\target 下的dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
java -jar dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
注意:zookeeper的服务一定要打开。
执行完毕,我们去访问一下 http://localhost:7001/ , 这时候我们需要输入登录账户和密码,我们都是默认的root-root。
登录成功后,查看界面,如下:
15.4、SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper
15.4.1、框架搭建
- 启动zookeeper。
- IDEA创建一个空项目。
- 创建一个模块,实现服务提供者:provider-server , 选择web依赖即可
- 项目创建完毕。
我们实现测试服务,比如卖票的服务:
编写接口
package com.kuang.provider.service;
public interface TicketService {
public String getTicket();
}
编写实现类
package com.kuang.provider.service;
public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService {
@Override
public String getTicket() {
return "《狂神说Java》";
}
}
- 创建一个模块,实现服务消费者:consumer-server , 选择web依赖即可
- 项目创建完毕,我们写一个服务,比如用户的服务。
编写service
package com.kuang.consumer.service;
public class UserService {
//我们需要去拿去注册中心的服务
}
15.4.2、服务提供者
- 将服务提供者注册到注册中心,我们需要整合Dubbo和zookeeper,所以需要导包,我们可以在github搜索dubbo-springboot,得到其依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbogroupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.7.3version>
dependency>
zookeeper的包我们去maven仓库下载,zkclient;
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.sgroschupfgroupId>
<artifactId>zkclientartifactId>
<version>0.1version>
dependency>
注:新版zookeeper及其依赖包,解决日志冲突,还需要剔除日志依赖;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-frameworkartifactId>
<version>2.12.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipesartifactId>
<version>2.12.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeepergroupId>
<artifactId>zookeeperartifactId>
<version>3.4.14version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
- 在springboot配置文件中配置dubbo相关属性!
#当前应用名字
dubbo.application.name=provider-server
#注册中心地址
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
#扫描指定包下服务
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.kuang.provider.service
- 在service的实现类中配置服务注解,发布服务。注意导包问题
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Service //将服务发布出去
@Component //放在容器中
public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService {
@Override
public String getTicket() {
return "《狂神说Java》";
}
}
逻辑理解 :应用启动起来,dubbo就会扫描指定的包下带有@component注解的服务,将它发布在指定的注册中心中!
15.4.3、服务消费者
- 导入依赖,和之前的依赖一样;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbogroupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.7.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.sgroschupfgroupId>
<artifactId>zkclientartifactId>
<version>0.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-frameworkartifactId>
<version>2.12.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipesartifactId>
<version>2.12.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeepergroupId>
<artifactId>zookeeperartifactId>
<version>3.4.14version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
- 配置参数
#当前应用名字
dubbo.application.name=consumer-server
#注册中心地址
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
package com.kuang.consumer.service;
import com.kuang.provider.service.TicketService;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service //注入到容器中
public class UserService {
@Reference //远程引用指定的服务,他会按照全类名进行匹配,看谁给注册中心注册了这个全类名
TicketService ticketService;
public void bugTicket(){
String ticket = ticketService.getTicket();
System.out.println("在注册中心买到"+ticket);
}
}
- 测试类编写;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ConsumerServerApplicationTests {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
userService.bugTicket();
}
}
15.4.4、启动测试
NOTE:SpingBoot + dubbo + zookeeper思想在于服务拆分。