ELK日志分析系统(ELasticsearch+Logstash+Kibana)——超详细实验+理论!!!
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、ELK日志分析系统简介
-
- 1.ELK日志分析解析图
- 二、ELK日志分析系统解析
-
- 2.1 Elasticsearch介绍
- 2.2 Logstash介绍
- 2.3 Kibana介绍
- 三、部署ELK日志分析系统
-
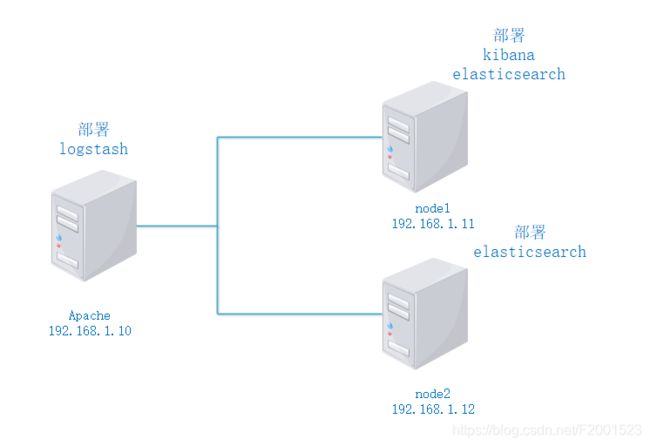
- 3.1 拓扑图
- 3.2 需求
- 3.3 流程
-
- 3.3.1 配置elasticsearch环境
-
- 3.3.1.1 本机网页上测试
- 3.3.1.2 查看集群健康检查和状态
- 3.3.1.3 查看集群属性
- 3.3.2 安装elasticsearch-head插件
- 3.3.3 安装logstash
- 3.3.4 安装Kibana
- 3.3.5 对接Apache
前言
在平常系统中会产生一些系统日志、应用程序日志和安全日志,如出现了错误可以通过日志去查看错误产生的原因,正因如此日志对于运维工程师处理问题的重要手段,但是日志是一个非常庞大的数据,它在分析的时候很困难,较复杂,所以,这章我们需要借助一个专门处理日志的系统就非常必要,这章介绍的是ELK日志分析系统(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)。
一、ELK日志分析系统简介
日志服务器
- 提高安全性
- 集中存放日志
缺陷:
- 对日志的分析困难
1.ELK日志分析解析图
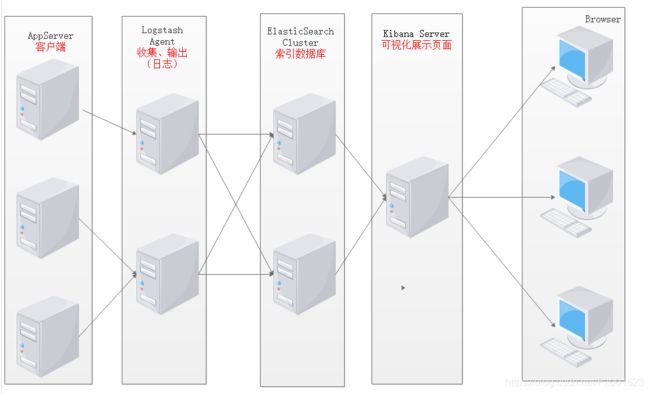
1.将日志进行集中化管理
2.将日志格式化(Logstash)
3.对格式化后的数据进行索引和存储(Elasticsearch)
4.前端数据的展示(Kibana)
5.用户通过的自已的浏览器访问Kibana页面查看
二、ELK日志分析系统解析
ELK日志分析系统
- ELK是由这个三种(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)工具组成
2.1 Elasticsearch介绍
Elasticsearch的概述
- 提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎
Elasticsearch核心概念
- 接近实时
- 集群
- 节点
- 索引
- 索引(库)> 类型(表)> 文档(记录)
- 分片和副本
2.2 Logstash介绍
Logstash概述
- 一款强大的数据处理工具
- 可实现数据传输、格式处理、格式化输出
- 数据输入、数据加工(如过滤,改写等)以及数据输出
LogStash主要组件·
- Shipper
- lndexer
- Broker
- Search and Storage
- Web Interface
2.3 Kibana介绍
Kibana概述
- 一个针对Elasticsearch的开源分析及可视化平台
- 搜索、查看存储在Elasticsearch索引中的数据
- 通过各种图表进行高级数据分析及展示
Kibana主要功能
- Elasticsearch无缝之集成
- 整合数据,复杂数据分析
- 让更多团队成员受益
- 接口灵活,分享更容易
- 配置简单,可视化多数据源
- 简单数据导出
三、部署ELK日志分析系统
3.1 拓扑图
3.2 需求
- 配置ELK日志分析群集
- 使用logstash收集Apache日志信息
- 由elasticsearch存储和建立索引
- 使用Kibana查看分析日志
3.3 流程
3.3.1 配置elasticsearch环境
node1与node2除了节点名和主机名分别为node1和node2,其他配置都一样
[root@server2 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node1 #切换主机名为node1
[root@server2 ~]# bash #刷新
[root@node1 ~]# vi /etc/hosts #映射一下主机名和ip地址
添加:
192.168.1.11 node1
192.168.1.12 node2
elk是用java写的,需要查看支不支持java环境
[root@node1 ~]# java -version #查看java版本
openjdk version "1.8.0_131"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode)
[root@node1 ~]# cd elk/
[root@node1 elk]# ll
[root@node1 elk]# rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm 安装rpm包
[root@node1 elk]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@node1 elk]# systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
#给原配置文件做一下备份,在修改配置
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# cp -p elasticsearch.yml elasticsearch.yml.bak
更改配置文件,:set nu显示行号,以下为对应行号修改的内容
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# vim elasticsearch.yml
17: cluster.name: my-elk-cluster # 集群名称
23: node.name: node1 # 当前节点名
33: path.data: /data/elk_data # 数据存储的位置(目录不存在,需要创建)
37: path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/ # 日志文件存放的位置(软件自带,不需要创建)
43: bootstrap.memory_lock: false
# true:允许内存中的数据交还给SWAP,flase:不允许内存中的数据交还给SWAP。
选择false,因为swap分区实在硬盘上建立的,如果内存不够,数据溢出,分到硬盘上的话,会影响速度
55: network.host: 0.0.0.0 # 监听地址,0.0.0.0表示所有网段
59: http.port: 9200 # ES端口号,外部通信的端口号 PS:9300是集群内部通信端口
68: discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"] # 群集中包含的节点名
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# mkdir -p /data/elk_data ## 创建数据存放目录
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# id elasticsearch ## ES的程序用户,安装的时候自动创建的用户
uid=990(elasticsearch) gid=985(elasticsearch) 组=985(elasticsearch)
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data/elk_data/ ## 授权,交给用户 elasticsearch去管理
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service ## 开启服务
[root@node1 elasticsearch]# netstat -anpt | grep 9200 ## 过滤9200端口(外部访问集群端口)
tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 59536/java
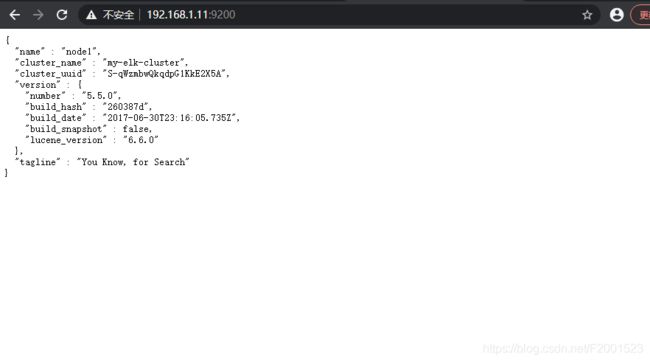
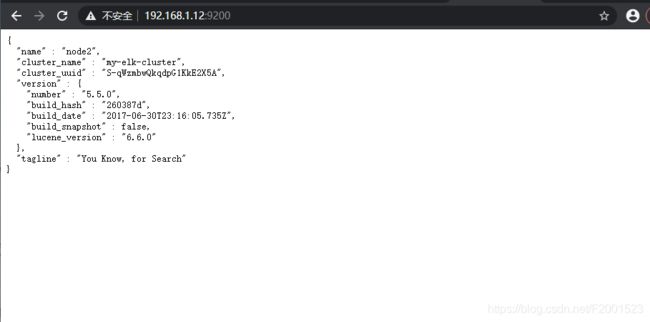
3.3.1.1 本机网页上测试
查看节点1的相关信息
{
"name" : "node1", ## 节点名称
"cluster_name" : "my-elk-cluster", ## 集群名称
"cluster_uuid" : "", ## 集群id
"version" : {
"number" : "5.5.0", ## ES版本
"build_hash" : "260387d",
"build_date" : "2017-06-30T23:16:05.735Z", ## 这个日期是ES版本诞生的日期,也就是5.5版本的诞生日期
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "6.6.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
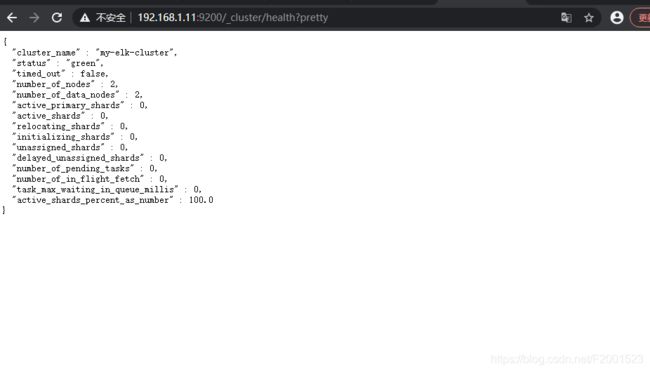
3.3.1.2 查看集群健康检查和状态
在浏览器输入 http://192.168.1.11:9200/_cluster/health?pretty ## 这里用11或12测试都可以
{
"cluster_name" : "my-elk-cluster", ## 集群名称
"status" : "green", ## 健康值,green就是ok的
"timed_out" : false,
"number_of_nodes" : 2,
"number_of_data_nodes" : 2,
"active_primary_shards" : 0,
"active_shards" : 0,
"relocating_shards" : 0,
"initializing_shards" : 0,
"unassigned_shards" : 0,
"delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks" : 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0,
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0,
"active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0
}
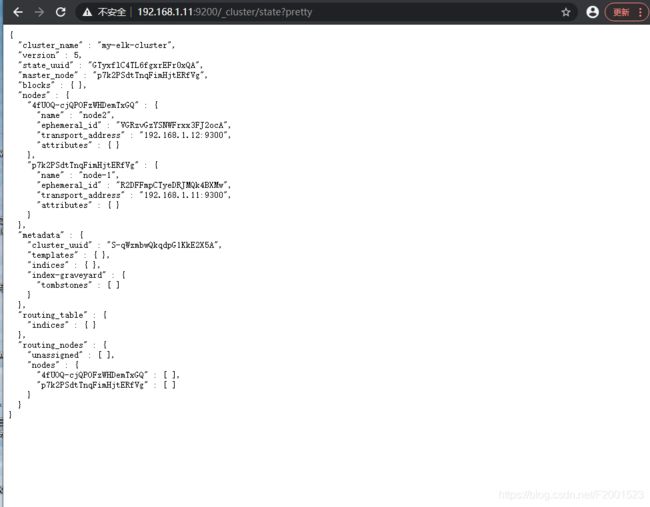
3.3.1.3 查看集群属性
群集属性状态 ,可以看到群集内部通信端口9300
输入网址 http://192.168.1.11:9200/_cluster/state?pretty
{
"cluster_name" : "my-elk-cluster",
"version" : 5,
"state_uuid" : "GTyxflC4TL6fgxrEFr0xQA",
"master_node" : "p7k2PSdtTnqFimHjtERfVg",
"blocks" : { },
"nodes" : {
"4fUOQ-cjQPOFzWHDemTxGQ" : {
"name" : "node2",
"ephemeral_id" : "VGRzvGzYSNWFrxx3FJ2ocA",
"transport_address" : "192.168.1.12:9300",
"attributes" : { }
},
"p7k2PSdtTnqFimHjtERfVg" : {
"name" : "node-1",
"ephemeral_id" : "R2DFFmpCTyeDRJMQk4BXMw",
"transport_address" : "192.168.1.11:9300",
"attributes" : { }
}
},
。。。。。
3.3.2 安装elasticsearch-head插件
2台节点服务器都需要做
1.安装elasticsearch-head插件,上述查看集群的方式极其不方便,我们可以通过安装elasticsearch-head插件来管理集群
节点1服务器 192.168.1.11
上传node-v8.2.1.tar.gz 到 /opt
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
## 编译安装node
[root@node1 ~]# cd /opt
[root@node1 /opt]# tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
[root@node1 /opt]# cd node-v8.2.1/
[root@node1 /node-v8.2.1]# ./configure
[root@node1 /node-v8.2.1]# make -j3 && make install ## 这里编译安装时间会有点长
2.安装phyantomjs前端框架
上传phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@node1 ~]# tar jxvf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@node1 ~]# cd phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/
[root@node1 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64 ]# cd bin/
[root@node1 bin ]# cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin/
3.安装elasticsearch-head 可视化工具
上传elasticsearch-head.tar.gz
[root@node1 ~]# tar zxvf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz
[root@node1 ~]# cd elasticsearch-head/
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm install ## 安装
4.修改主配置文件
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml ## 这里的配置文件插在末尾
http.cors.enabled: true ## 开启跨域访问支持,默认为false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" ## 跨域访问允许的域名地址
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
## 启动服务器 ##
[root@node1 ~]# cd elasticsearch-head/
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm run start & #切到后台运行
[1] 108188
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]#
> elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 start /root/elasticsearch-head
> grunt server
Running "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# netstat -anpt | grep 9100
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9100 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 108198/grunt
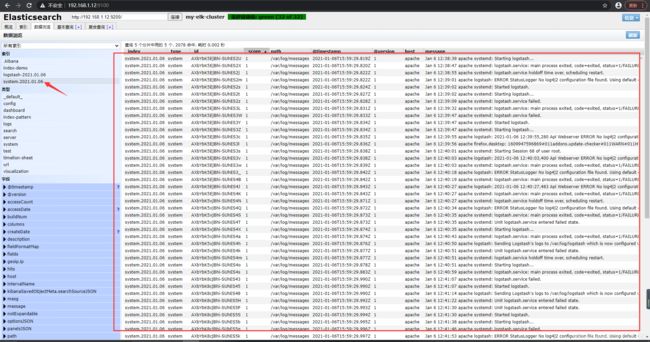
在浏览器输入 192.168.1.11:9100(12也可以) 测试一下
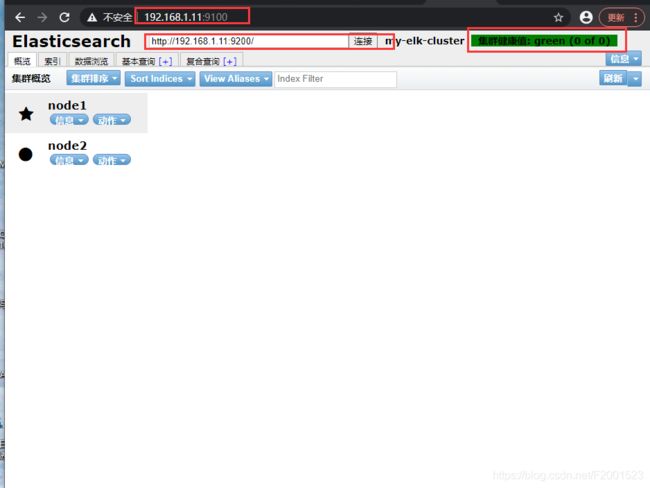
查看他们的节点信息,可以看到两个都是主节点,不存在主从关系
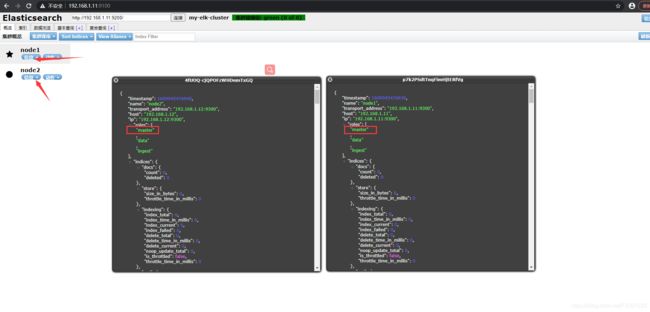
创建一个索引信息,创建索引为index-demo,类型为test,可以看到成功创建
这里的数据会被存储到ES集群中
[root@node1 ~]# curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -tent-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"created" : true
}
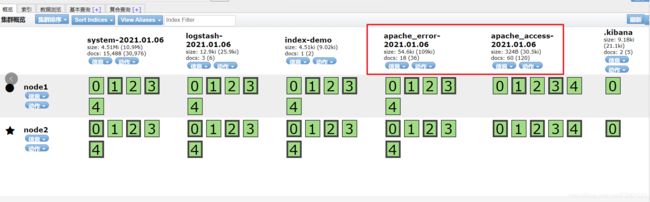
刷新一下,可以看到存储的分片处理与备份。加粗的是分片(主文件),细框的是备份文件,不论哪个节点宕机,存储都不会丢失,可以确保文件中数据的安全性
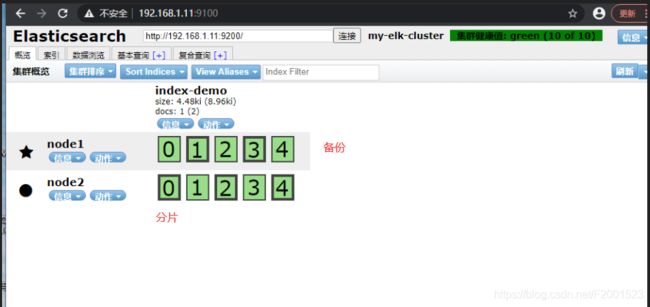
3.3.3 安装logstash
安装logstash并做一些日志搜集输出到elasticsearch中,登陆主机192.168.1.10,关闭防火墙和核心防护
1.安装apache服务(httpd)
[root@apache ~]# yum -y install httpd
[root@apache ~]# java -version #查看是否java环境,如没有安装就yum -y install java
openjdk version "1.8.0_131"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode)
[root@apache ~]# cd /var/log/httpd/
[root@apache httpd]# ll #apache服务还未开启,可以看到是查不到日志的产生的
总用量 0
[root@apache httpd]# systemctl start httpd
[root@apache httpd]# ll #开启apache服务后,是可以查看到日志文件的
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 6 12:23 access_log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 941 1月 6 12:23 error_log
2.安装logstash
上传logstash-5.5.1.rpm
[root@apache httpd]# rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm
[root@apache httpd]# rpm -qc logstash ## rpm -qc 查看配置文件位置
/etc/logstash/jvm.options
/etc/logstash/logstash.yml
/etc/logstash/startup.options
[root@apache httpd]# systemctl start logstash.service
[root@apache httpd]# systemctl enable logstash.service
[root@apache httpd]# ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/ # 建立软链接,便于被系统所识别
3、logstash(Apache)与elasticsearch (node)功能是否正常,做对接测试
logstash字段描述解释:
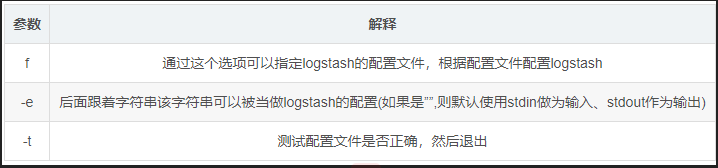
4、输入采用标准输入,输出采用标准输出----登录 192.168.1.10 在apache服务器上
[root@apache httpd]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }' # 测试
www.baidu.com # 输入www.baidu.com
2021-01-06T15:40:04.913Z apache www.baidu.comwww.baidu.com
5、使用 rubydebug 显示详细信息输出,code为一种编解码器
[root@apache httpd]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
www.baidu.com ## 输入www.baidu.com
{
"@timestamp" => 2021-01-06T15:32:59.945Z,
"@version" => "1",
"host" => "apache",
"message" => "www.baidu.com"
}
6.使用logstash将信息写入elasticsearch输入 输出 对接
[root@apache httpd]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.1.11:9200"] } }'
直到出现Successfullys
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
12:46:06.728 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
www.baidu.com
www.taobao.com
可以看到网页中的数据,可以成功查看记录
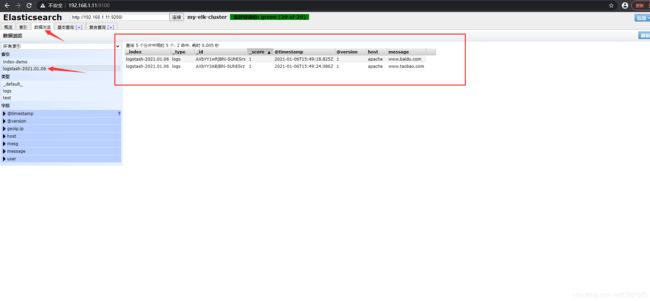
7.测试系统日志能否被采集
[root@apache httpd]# chmod o+r /var/log/messages //对系统日志加other读权限
[root@apache httpd]# ll /var/log/messages #查看权限
-rw----r--. 1 root root 180190 1月 6 12:57 /var/log/messages
[root@apache httpd]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf //写入配置文件
input {
file{
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.1.12:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
F5刷新一下,就可以查看到192.168.1.12上的日志数据
3.3.4 安装Kibana
在node2节点上
#将kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm 放在/usr/local/src
[root@node2 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@node2 src]# rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
[root@node2 src]# cd /etc/kibana/
[root@node2 kibana]# ll #可以看到有一个kibana的配置文件
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4649 7月 19 2017 kibana.yml
[root@node1 kibana]# vim kibana.yml
2 server.port: 5601 #Kibana端口号
7 server.host: "0.0.0.0" #监听所有网段
21 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.1.12:9200" #和 ES建立联系
30 kibana.index: ".kibana" #建立索引
[root@node2 kibana]# systemctl start kibana.service
[root@node2 kibana]# systemctl enable kibana.service
去页面看 192.168.1.12:5601
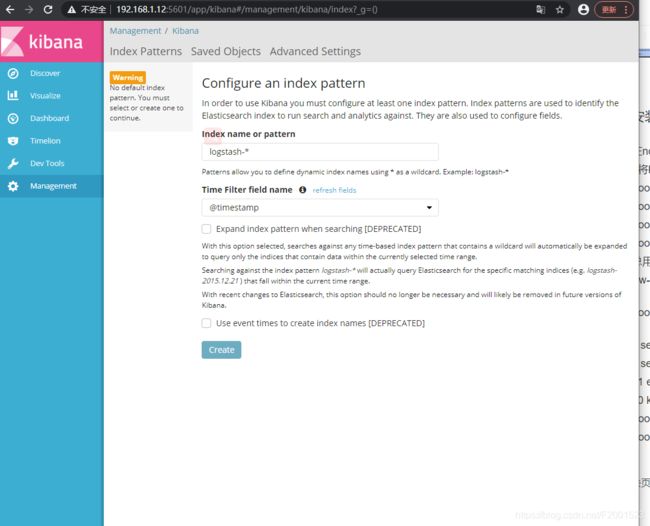
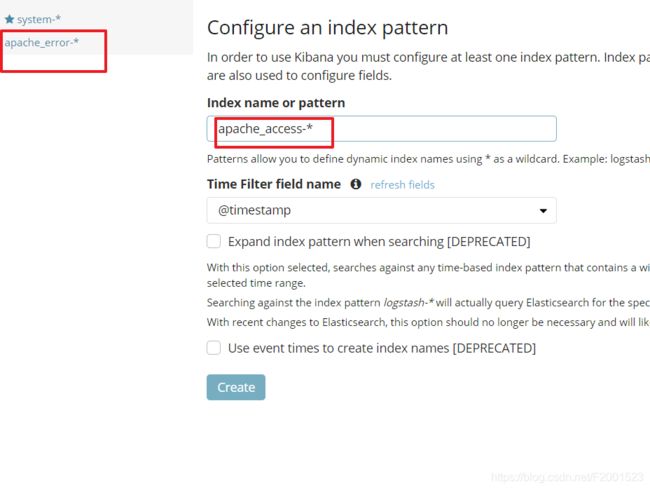
创建一个索引名字Index name pattern:system-* ## 这是对接系统的日志文件
然后点击 create 创建按钮
Discover里查看 ,非常清晰
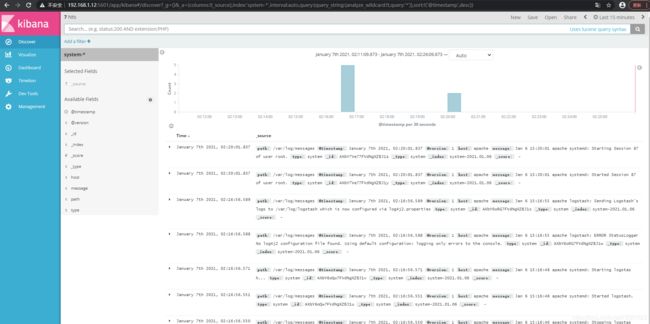
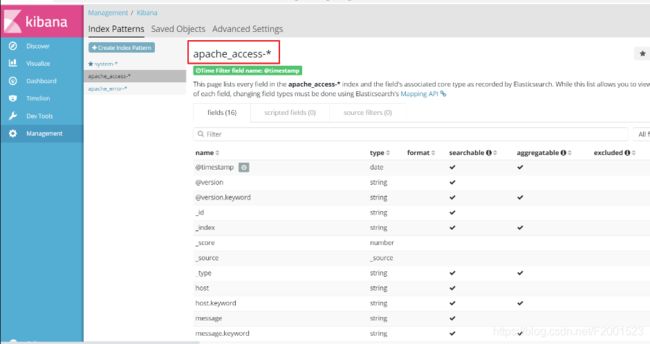
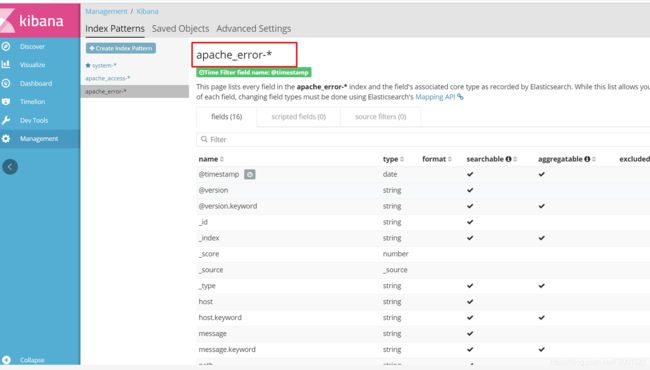
3.3.5 对接Apache
对接apache主机的apache的日志文件(访问的、错误的)
[root@apache ~]cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
[root@apache conf.d]# vim apache_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/var/log/httpd/access_log" ## apache 的 access日志位置
type => "access" ## 类型为 access,就是类似于索引,在kibana可以便于查看
start_position => "beginning" ## 从日志的开头开始
}
file{
path => "/var/log/httpd/error_log" ## apache 的 error日志位置
type => "error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "access" { ## 做一个判断,对应上面的索引名。如果匹配为access,则把内容导向节点,然后名称为apache_access.%{+YYYY.MM.dd}格式
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.1.12:9200"]
index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.1.12:9200"]
index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
[root@apache conf.d]# logstash -f apache_log.conf #启动指定