【andriod】设备APP开发之各种细节部署和操作
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、开发工具
-
- 1、软件介绍
- 2、Android JDK配置
- 3、Android Gradle配置
- 4、Android API配置
- 5、项目依赖配置
- 二、项目细节详情
-
- 1、andriodmanifest.xml配置详情
- 2、ExampleInstrumentedTest配置详情
- 3、ExampleUnitTest配置详情
- 4、Utils配置详情
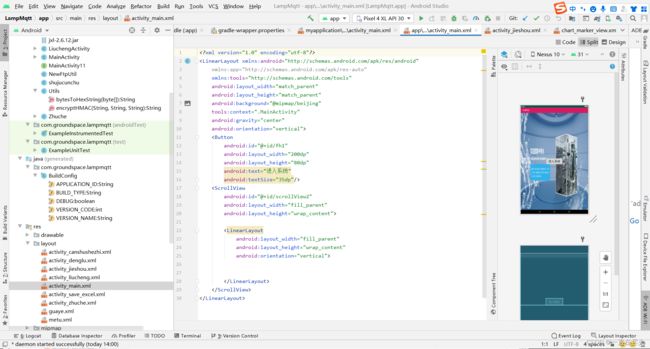
- 5、activity_main.xml配置详情
- 6、Gradle Scripts配置详情
- build.gradle(Project)
- build.gradle(Module)
- 总结
前言
随着工业自动化的不断发展,设备APP也越来越重要,本文就设备APP开发软件配置细节做一个深入详解。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、开发工具
1、软件介绍
Android Studio 是基于 IntelliJ IDEA 的官方 Android 应用开发集成开发环境 (IDE)。除了 IntelliJ 强大的代码编辑器和开发者工具,Android Studio 提供了更多可提高 Android 应用构建效率的功能,例如:
基于 Gradle 的灵活构建系统
快速且功能丰富的模拟器
可针对所有 Android 设备进行开发的统一环境
Instant Run,可将变更推送到正在运行的应用,无需构建新的 APK
可帮助您构建常用应用功能和导入示例代码的代码模板和 GitHub 集成
丰富的测试工具和框架
可捕捉性能、易用性、版本兼容性以及其他问题的 Lint 工具
C++ 和 NDK 支持
内置对 Google 云端平台的支持,可轻松集成 Google Cloud Messaging 和 App 引擎
2、Android JDK配置
3、Android Gradle配置
4、Android API配置
5、项目依赖配置
二、项目细节详情
1、andriodmanifest.xml配置详情
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.groundspace.lampmqtt">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:requestLegacyExternalStorage="true"
android:screenOrientation="sensor"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name="com.groundspace.lampmqtt.MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<receiver
android:name=".BootBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:permission="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
intent-filter>
receiver>
<activity android:name=".Jieshou"/>
<service android:name="org.eclipse.paho.android.service.MqttService">
service>
application>
manifest>
2、ExampleInstrumentedTest配置详情
package com.groundspace.lampmqtt;
import android.content.Context;
import androidx.test.InstrumentationRegistry;
import androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnit4;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
/**
* Instrumented test, which will execute on an Android device.
*
* @see Testing documentation
*/
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class ExampleInstrumentedTest {
@Test
public void useAppContext() {
// Context of the app under test.
Context appContext = InstrumentationRegistry.getTargetContext();
assertEquals("com.groundspace.lampmqtt", appContext.getPackageName());
}
}
3、ExampleUnitTest配置详情
package com.groundspace.lampmqtt;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* Example local unit test, which will execute on the development machine (host).
*
* @see Testing documentation
*/
class ExampleUnitTest {
@Test
public void addition_isCorrect() {
assertEquals(4, 2 + 2);
}
}
4、Utils配置详情
package com.groundspace.lampmqtt;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class Utils {
public static final String bytesToHexString(byte[] bArray) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(bArray.length);
String sTemp;
for (int i = 0; i < bArray.length; i++) {
sTemp = Integer.toHexString(0xFF & bArray[i]);
if (sTemp.length() < 2) {
sb.append(0);
}
sb.append(sTemp.toUpperCase());
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static String encryptHMAC(String signMethod, String content, String key) throws Exception {
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes("utf-8"), signMethod);
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm());
mac.init(secretKey);
byte[] data = mac.doFinal(content.getBytes("utf-8"));
return bytesToHexString(data);
}
}
5、activity_main.xml配置详情
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/beijing"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:singleLine="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingLeft="120dp"
android:paddingTop="85dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:src="@drawable/yaoquan"
android:gravity="left"
/>
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:singleLine="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingLeft="380dp"
android:paddingTop="200dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/fh1"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="进入系统"
android:textSize="35dp"/>
LinearLayout>
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
LinearLayout>
ScrollView>
LinearLayout>
6、Gradle Scripts配置详情
build.gradle(Project)
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.1.0'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
maven {
url "https://repo.eclipse.org/content/repositories/paho-snapshots/"
}
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}
build.gradle(Module)
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 31
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.groundspace.lampmqtt"
minSdkVersion 14
targetSdkVersion 31
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
buildToolsVersion '30.0.0'
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3:1.2.0'
implementation group: 'commons-codec', name: 'commons-codec', version: '1.11'
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
//noinspection GradleCompatible
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:31.0.0'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3'
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.android.service:1.1.1'
implementation files('..\\jxl-2.6.12.jar')
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.13.2'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.2'
implementation files('../.idea/libraries/gson-2.7.jar')
implementation files('../.idea/libraries/json.jar')
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了Android Studio 4.1写设备APP的配置,而Android Studio 4.1提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地开发客户端的具体部署和方法。