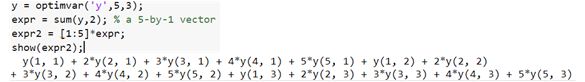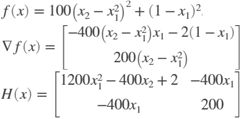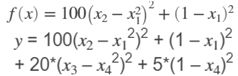matlab optimization toolbox 笔记
1 Introduction
matlab optimization 工具箱功能十分强大,这一章节梳理problem based optimization 和solver based optimization的问题。
Optimization Toolbox™ provides functions for finding parameters that minimize or maximize objectives while satisfying constraints. The toolbox includes solvers for linear programming (LP), mixed-integer linear programming (MILP), quadratic programming (QP), nonlinear programming (NLP), constrained linear least squares, nonlinear least squares, and nonlinear equations.
2 problem based optimization
2.1 workflow
prob = optimproblem('ObjectiveSense','maximize'); % 1.定义最大值问题
x = optimvar('x',15,3,'Type','integer','LowerBound',0,'UpperBound',1); % 2.定义状态变量
prob.Objective = sum(sum(f.*x)); % 3.定义目标函数
% 4.定义约束条件
onesum = sum(x,2) == 1;
vertsum = sum(x,1) <= 1;
prob.Constraints.onesum = onesum;
prob.Constraints.vertsum = vertsum;
% 5.变量初始化
x0.x = randn(size(x));
x0.y = eye(4); % Assumes y is a 4-by-4 variable
% 6.求解器
sol = solve(prob);
% Or, for nonlinear problems,
sol = solve(prob,x0)
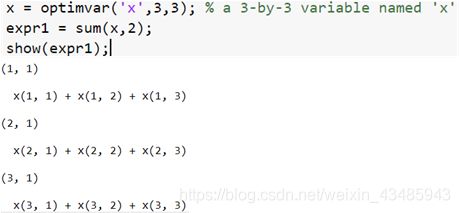
2.2 表达式
expr = optimexpr; % 空表达式
expr = fcn2optimexpr(@parameterfun,x,a,b,c);
2.3 变量设置
- 定义变量
x = optimvar('x',["United","Lufthansa","Virgin Air"]);
x("Lufthansa").LowerBound = 0;
x(1).LowerBound = -2;
showbounds(x)
show(x)
x
通过show(x)显示变量,通过showbounds(x)显示限制,还可以通过optimvar(‘x’,[“United”,“Lufthansa”,“Virgin Air”])对变量添加name indices。

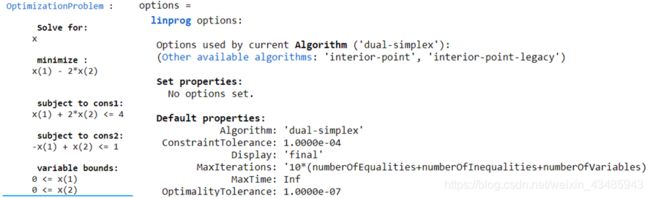
2.4 求解器设置
- 查看构建的optimization 问题和求解器
prob = optimproblem;
x = optimvar('x',2,'LowerBound',0);
prob.Objective = x(1) - 2*x(2);
prob.Constraints.cons1 = x(1) + 2*x(2) <= 4;
prob.Constraints.cons2 = -x(1) + x(2) <= 1;
show(prob) %查看构建的optimization问题
options = optimoptions(prob) % 查看使用的求解器
- optimoptions 设置
prob = optimproblem;
x = optimvar('x',2,'LowerBound',0);
prob.Objective = x(1) - 2*x(2);
prob.Constraints.cons1 = x(1) + 2*x(2) <= 4;
prob.Constraints.cons2 = -x(1) + x(2) <= 1;
show(prob) %查看构建的optimization问题
options = optimoptions(prob) % 查看使用的求解器
options.Display = 'iter';
sol = solve(prob,'Options',options,'Solver','quadprog');
2.5 查看计算结果的精度
通过fval误差的衡量指标,例如最小二乘问题,就是预测和实际的偏差平方。
exitflag 是一个字符,会提示求解情况
[sol,fval,exitflag,output,lambda] = solve(prob); % or
fval = evaluate(prob.Objective,sol)
3 solver based optimization
因为对主要的优化问题的算法并不是很熟悉,先关注workflow。
3.1 目标函数
% 在rosentwo.m中定义函数rosentwo
function [f,g,H] = rosentwo(x)
% Calculate objective f
f = 100*(x(2) - x(1)^2)^2 + (1-x(1))^2;
if nargout > 1 % gradient required
g = [-400*(x(2)-x(1)^2)*x(1)-2*(1-x(1));
200*(x(2)-x(1)^2)];
if nargout > 2 % Hessian required
H = [1200*x(1)^2-400*x(2)+2, -400*x(1);
-400*x(1), 200];
end
end
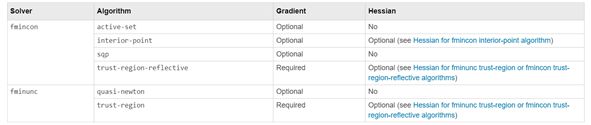
如果要使用gradient,需要进行在options中进行设置
options = optimoptions(@fminunc,'Algorithm','trust-region',...
'SpecifyObjectiveGradient',true);
[x fval] = fminunc(@rosentwo,[-1;2],options)
如果objective 比较复杂,需要使用hessian,需要在option中进行设置
options = optimoptions('fminunc','Algorithm','trust-region',...
'SpecifyObjectiveGradient',true,'HessianFcn','objective');
- 匿名函数(Anonymous Function),适合函数非常简单的情况
anonrosen = @(x)(100*(x(2) - x(1)^2)^2 + (1-x(1))^2);
3.2 constraints
在matlab的几个主要的solver,使用非线性约束,用函数引用;使用线性约束,用线性矩阵Ax-b;使用变量bound,bl,bu;
x = fmincon(fun,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nonlcon)
% Step 1. 将约束函数和目标函数计算重复的内容单独提取出来
function [f1,c1,ceq1] = computeall(x)
ceq1 = [];
c1 = norm(x)^2 - 1;
f1 = 100*(x(2) - x(1)^2)^2 + (1-x(1))^2;
pause(1) % simulate expensive computation
end
% Step 2. 通过内嵌函数保留历史数值
function [x,f,eflag,outpt] = runobjconstr(x0,opts)
if nargin == 1 % No options supplied
opts = [];
end
xLast = []; % Last place computeall was called
myf = []; % Use for objective at xLast
myc = []; % Use for nonlinear inequality constraint
myceq = []; % Use for nonlinear equality constraint
fun = @objfun; % the objective function, nested below
cfun = @constr; % the constraint function, nested below
% Call fmincon
[x,f,eflag,outpt] = fmincon(fun,x0,[],[],[],[],[],[],cfun,opts); % fmincon(fun,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nonlcon)
function y = objfun(x)
if ~isequal(x,xLast) % Check if computation is necessary
[myf,myc,myceq] = computeall(x);
xLast = x;
end
% Now compute objective function
y = myf + 20*(x(3) - x(4)^2)^2 + 5*(1 - x(4))^2;
end
function [c,ceq] = constr(x)
if ~isequal(x,xLast) % Check if computation is necessary
[myf,myc,myceq] = computeall(x);
xLast = x;
end
% Now compute constraint functions
c = myc; % In this case, the computation is trivial
ceq = myceq;
end
end
% step3: 统计算法所需要消耗的时间
opts = optimoptions(@fmincon,'Algorithm','interior-point','Display','off');
x0 = [-1,1,1,2];
tic
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = runobjconstr(x0,opts);
toc
% step4: 对比没有优化的方式
function y = myrosen2(x)
f1 = computeall(x); % get first part of objective
y = f1 + 20*(x(3) - x(4)^2)^2 + 5*(1 - x(4))^2;
end
function [c,ceq] = constr(x)
[~,c,ceq] = computeall(x);
end
tic
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = fmincon(@myrosen2,x0,...
[],[],[],[],[],[],@constr,opts);
toc
3.3 设置options
- 如何设置
options = optimoptions(options,'StepTolerance',1e-10);
options.StepTolerance = 1e-10;
options = resetoptions(options,'StepTolerance');
options = optimoptions(@fminunc,'Algorithm','trust-region',...
'SpecifyObjectiveGradient',true); % 设置是否使用gradient
- 通过output函数,获取优化过程中的中间变量
function [history,searchdir] = runfmincon
% Set up shared variables with OUTFUN
history.x = [];
history.fval = [];
searchdir = [];
% call optimization
x0 = [-1 1];
options = optimoptions(@fmincon,'OutputFcn',@outfun,...
'Display','iter','Algorithm','active-set');
xsol = fmincon(@objfun,x0,[],[],[],[],[],[],@confun,options);
function stop = outfun(x,optimValues,state)
stop = false;
switch state
case 'init'
hold on
case 'iter'
% Concatenate current point and objective function
% value with history. x must be a row vector.
history.fval = [history.fval; optimValues.fval];
history.x = [history.x; x];
% Concatenate current search direction with
% searchdir.
searchdir = [searchdir;...
optimValues.searchdirection'];
plot(x(1),x(2),'o');
% Label points with iteration number and add title.
% Add .15 to x(1) to separate label from plotted 'o'
text(x(1)+.15,x(2),...
num2str(optimValues.iteration));
title('Sequence of Points Computed by fmincon');
case 'done'
hold off
otherwise
end
end
function f = objfun(x)
f = exp(x(1))*(4*x(1)^2 + 2*x(2)^2 + 4*x(1)*x(2) +...
2*x(2) + 1);
end
function [c, ceq] = confun(x)
% Nonlinear inequality constraints
c = [1.5 + x(1)*x(2) - x(1) - x(2);
-x(1)*x(2) - 10];
% Nonlinear equality constraints
ceq = [];
end
end