Kaggle-海底海星目标检测Baseline
Kaggle-海底海星目标检测Baseline
Frankie : 目前本科在读,师从深度之眼比赛班导师-Taylor老师,刚接触图像算法竞赛半年,已经获得 IFLYTEK 1024 Challenge - X光目标检测第二名,华为云-重庆语义分割算法大赛二等奖等。
1、赛题链接
https://www.kaggle.com/c/tensorflow-great-barrier-reef
2、赛题描述
本次竞赛的目标是通过建立一个在珊瑚礁水下视频中训练的物体检测模型,实时准确地识别海星。
商业价值:帮助研究人员识别威胁澳大利亚大堡礁的物种,并采取明智的行动,为子孙后代保护珊瑚礁。
※ 比赛时间线
2021 11 月 22 日 年 - 开始日期。
2022 2 月 7 日 年 - 报名截止日期。 您必须在此日期之前接受比赛规则才能参加比赛。
2022 2 月 7 日 年 - 团队合并截止日期。 这是参与者可以加入或合并团队的最后一天。
2022 2 月 14 日 年 - 最终提交截止日期。
※ 丰厚的奖金
一等奖:30,000美元
二等奖:25,000美元
三等奖:20,000美元
四等奖:15,000美元
五等奖:10,000美元
3、数据描述
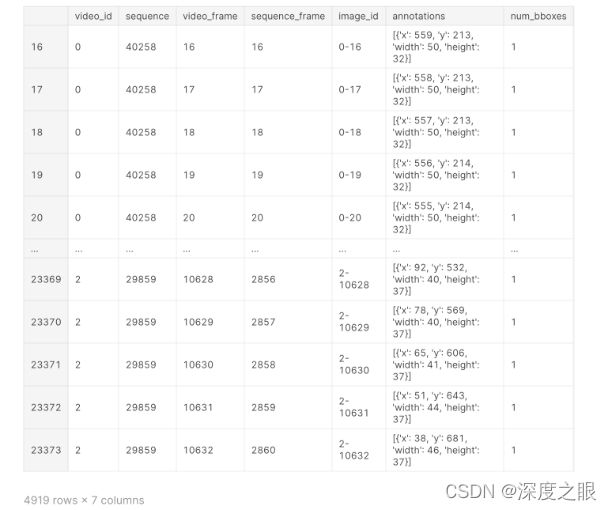
train.csv中包含了三个视频抽帧后的图片信息标注,其中几个重要参数:
video_id- 图像所属视频的 ID 号。视频 ID 没有有意义的排序。
video_frame- 视频中图像的帧数。当潜水员浮出水面时,预计会偶尔看到帧数的差距。
sequence- 给定视频的无间隙子集的 ID。序列 id 没有有意义的排序。
sequence_frame - 给定序列中的帧号。
image_id - 图像的 ID 代码,格式为“{video_id}-{video_frame}”
annotations- 边界框由其在图像内左上角的像素坐标 (x_min, y_min) 及其宽度和高度(以像素为单位)描述。
import pandas as pd
train_df = pd.read_csv('../input/tensorflow-great-barrier-reef/train.csv')
train_df = train_df[train_df['annotations'] != "[]"]
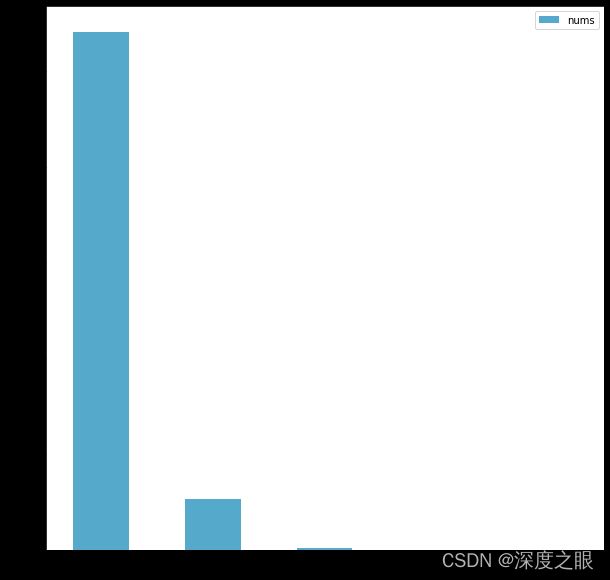
sum(train_df['video_id'] == 0), sum(train_df['video_id'] == 1), sum(train_df['video_id'] == 2)
视频0: 2143张有目标
视频1: 2099张有目标
视频2: 677张有目标
4、评价指标
F2-Score
选择F2指标目的是为了尽量不漏检允许一些FP. 因此处理FN比处理FP要重要.
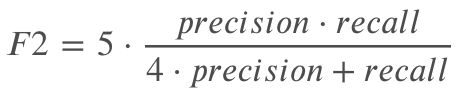
5、对赛题标签的理解
划分数据集时,为了避免数据泄露,可以对0,1视频进行训练。2视频进行线下验证
5.1、筛选出有标注的数据
import pandas as pd
import sklearn
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
import glob
import pycocotools
from pycocotools import mask
import random
import cv2
import re
import ast
train_df = pd.read_csv('../input/tensorflow-great-barrier-reef/train.csv')
train_df = train_df[train_df['annotations'] != "[]"]
5.2、生成bbox函数
def get_boxes(row):
"""Return the bboxes for a given row as a 3D matrix """
return pd.DataFrame(row['annotations'], columns=['x', 'y', 'width', 'height']).astype(float).values
5.3、生成标注文件
output_train_json_dict = {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": []
}
output_test_json_dict = {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": []
}
category_dict = {"id": 1, "name": "starfish", "supercategory": "none"}
output_train_json_dict["categories"].append(category_dict)
output_test_json_dict["categories"].append(category_dict)
annot_train_id = 0
annot_test_id = 0
annot_id = 0
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
for f in tqdm(df_train.itertuples()):
img_path = '../input/tensorflow-great-barrier-reef/train_images/video_' + str(f[1]) + '/' + f[5].split('-')[1] + '.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
height, width, channels = img.shape
img_info = {
"id": f[0],
"width": width,
"height": height,
"file_name": img_path
}
if f[1] != 2:
output_train_json_dict["images"].append(img_info)
else:
output_test_json_dict["images"].append(img_info)
if f[6] != '[]':
bbox_list = ast.literal_eval(f[6])
for bbox in bbox_list:
if bbox['height'] + bbox['y'] > 720:
bbox['height'] = 720 - bbox['y']
annot = {
"category_id": 1,
"bbox": [bbox['x'], bbox['y'], bbox['width'], bbox['height']],
"id": annot_id,
"image_id": f[0],
"area": bbox['width'] * bbox['height'],
"segmentation": [],
"iscrowd": 0
}
if f[1] != 2:
output_train_json_dict["annotations"].append(annot)
annot_train_id += 1
annot_id = annot_train_id
else:
output_test_json_dict["annotations"].append(annot)
annot_test_id += 1
annot_id = annot_test_id
with open('train_starfish.json', 'w') as f:
output_json = json.dumps(output_train_json_dict)
f.write(output_json)
with open('test_starfish.json', 'w') as f:
output_json = json.dumps(output_test_json_dict)
f.write(output_json)
6、Baseline流程
Baseline以简单的Faster-RCNN入手 (详细见baseline README文件)
安装编译mmdet
定义数据
修改配置文件
添加测试脚本
调参提交
7、赛题难点思考
1、如何利用无目标图片
2、如何有效利用连续帧中目标处理(如下两图为连续帧)