初阶数据结构之【队列】
✨hello,愿意点进来的小伙伴们,你们好呐!
✨ 系列专栏:【数据结构】
本篇内容:浅解数据结构队列
作者简介:一名现大二的三非编程小白
- 前言
-
- 队列的概念
- 队列常用方法
-
- 创建MyQueue类
- 判断队列是否为null
- 入队列 offer
- 出队列
- 获取队列头元素 peek
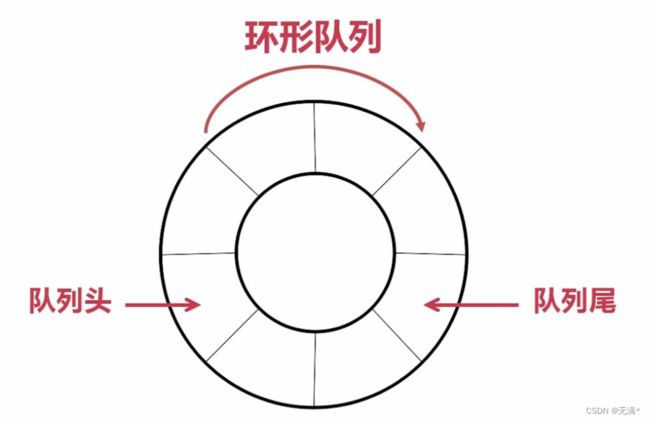
- 循环队列
- 队列转栈
- 栈转队列
前言
我们在上一篇文中认识了先进后出的栈,现在我们再来见识一下数据结构中先进先出的队列吧。与队列与栈相互之间可以怎么转换呢?
队列的概念
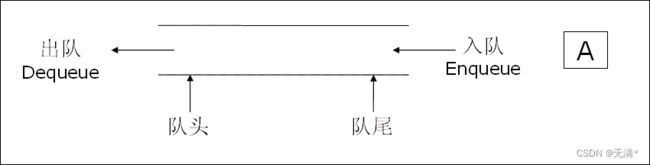
队列:是只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Rear)
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头 (Tail)
就好比如核酸排队,先排队的人就先核酸一样。
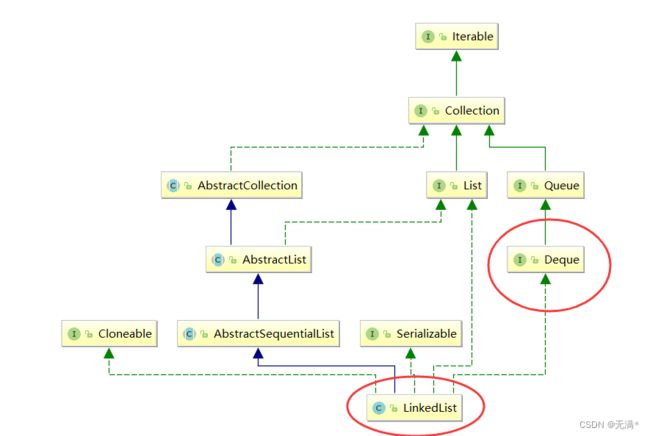
在Java中 队列(Queue)是一个接口,底层其实是通过链表来实现的。
接下来让我们来了解一下队列中的常用方法吧
队列常用方法
队列中的常用方法是很容易使用的,为了更深刻地理解这些方法的底层,我来简单实现一下这些方法。
创建MyQueue类
public class MyQueue2 {
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode tail;
public int usedSize;
}
判断队列是否为null
public boolean isEmpty(){
return usedSize == 0;
}
入队列 offer
public void offer(int val){
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
if(isEmpty()){
head = node;
tail = head;
}else{
tail.next = node;
tail = tail.next;
}
usedSize++;
}
出队列
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(head.next == null){
tail = null;
}
int ret = head.val;
head = head.next;
usedSize--;
return ret;
}
获取队列头元素 peek
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return head.val;
}
这样子我们将队列的常用方法以底层为单向链表简单地实现了一遍
接下来我们来用顺序表来实现一下队列,这种通过数组实现的队列,通常情况下叫做循环队列
循环队列
class MyCircularQueue {
private int front;
private int rear;
private int capacity;
private int[] elements;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
capacity = k + 1;
elements = new int[capacity];
rear = front = 0;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elements[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return ((rear + 1) % capacity) == front;
}
}
队列转栈
==1.先将要入栈的元素存入一个空队列中,出栈的时候便将非空队列中的元素,入size - 1 个元素给空队列中,再将出队列的队列最后一个元素弹出
2. ==
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> queue1;
public Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(x);
}else if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size - 1;i++){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
return queue1.poll();
}else{
int size = queue2.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size - 1;i++){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
return queue2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size();
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
ret = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(ret);
}
return ret;
}else{
int size = queue2.size();
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
ret = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(ret);
}
return ret;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
栈转队列
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> s1;
private Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack();
s2 = new Stack();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.empty()){
while(!s1.empty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.empty()){
while(!s1.empty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
}