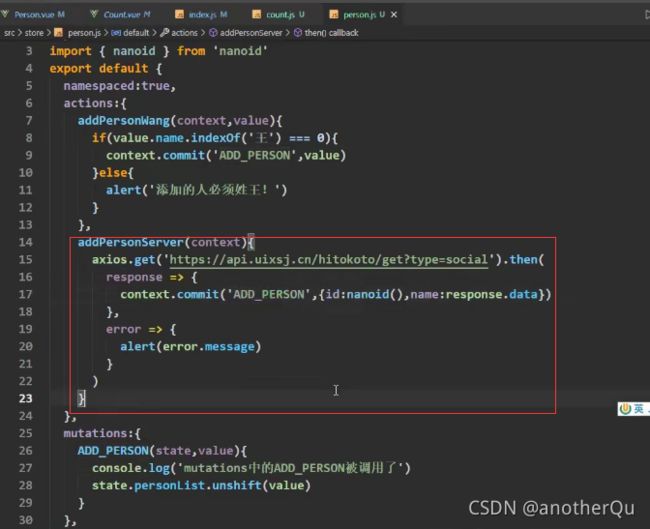
尚硅谷Vue技术全家桶(3)
4 vue中的Ajax
4.1 vue中解决ajax跨域问题
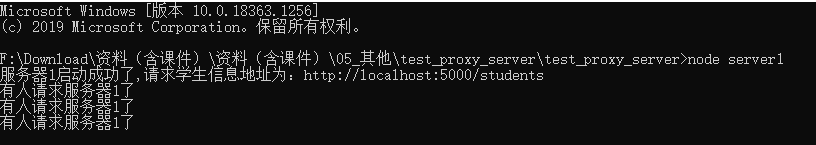
首先运行课件中的server1和server2:

运行后有请求地址,且每次请求有响应:
请求页面:

App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息button>
div>
template>
<script>
// 需要安装:npm i axios
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
},
data(){
return{
}
},
methods:{
getStudents(){
axios.get('http://localhost:5000/students').then(
response=>{
console.log(response.data);
},
error=>{
console.log(error.message);
}
)
}
}
}
script>
<style>
style>
以上在运行的时候出现了跨域问题:
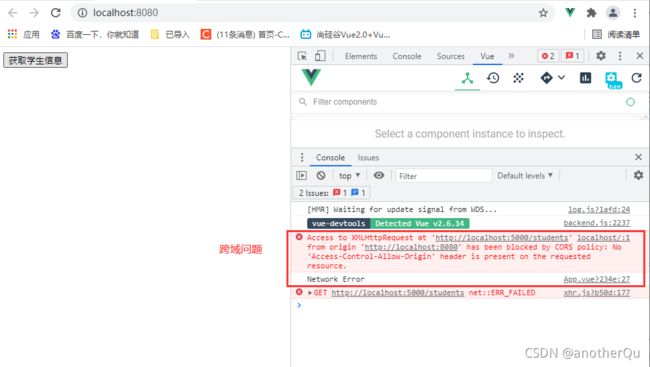
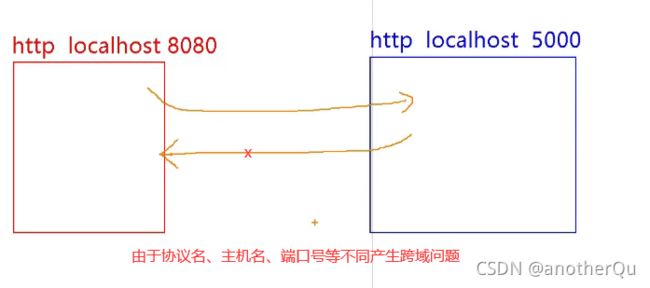
解决跨域三种方式:
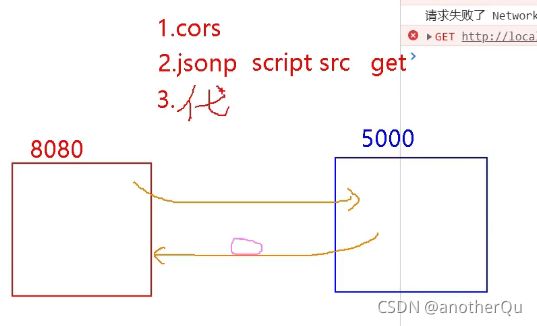
cors:最根本,后端请求头带信息直接允许跨域,但不常用,危险
jsonp:通过js的src标签的特性绕过跨域,但需要前后端都做处理,不常用
代理服务器:常用
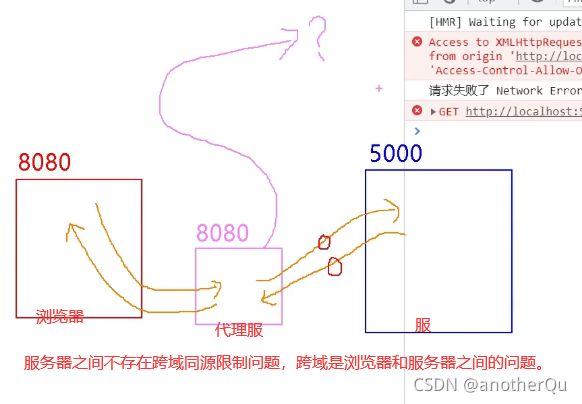
那么代理怎么实现:
1.nginx反向代理
2.vue-cli
这里讲解vue-cli对跨域问题的解决。
4.1.1 vue-cli解决跨域
1.vue.config.js:
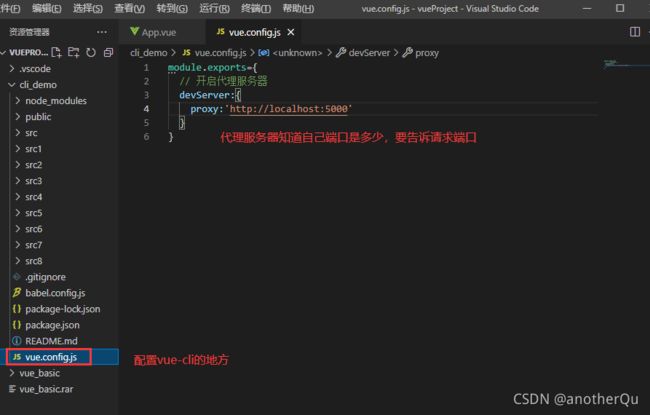
2.App.vue:

以上方式有两个问题:
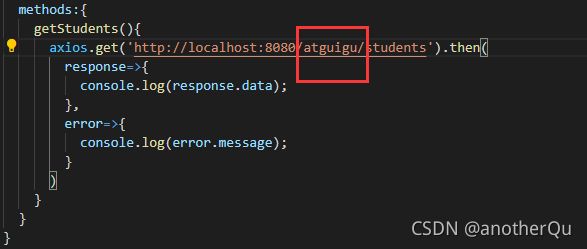
1.如果8080端口本地有个名叫student的文件,由于不需要跨域就能得到这个地址,所以就把本地的文件请求过来了。
2.请求端口5000写死了
4.1.2 对上节问题的改良
vue.config.js:
module.exports = {
devServer: {
proxy: {
// 请求前缀是atguigu,就走设置的target
// 'http://localhost:8080/atguigu/students
// 前缀是指除协议名、主机名、端口号以外的最前面
'/atguigu': {
target: 'http://localhost:5000',
// 路径重写,把/atguigu开头的重写成空的
// 不然请求路径里带着/atguigu,路径变成localhost:5000/atguigu/students,请求路径不是原来的了
pathRewrite:{'^/atguigu':''},
// websocket的支持与否
ws: true,
// 改变旧址,服务器询问代理服务器来自哪里时说谎与否(伪装)
// 用于控制请求头中的host值
changeOrigin: true
},
'/foo': {
target: ''
}
}
}
}
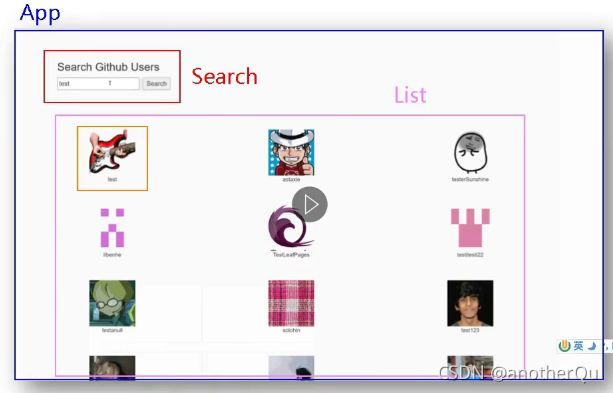
4.2 github用户搜索案例
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="keyWord" />
<button @click="searchUsers">searchUsersbutton>
div>
template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "Search",
data() {
return {
keyWord: "",
};
},
methods: {
searchUsers() {
// 这样不够语义化
// this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',[],false,true,'')
this.$bus.$emit("updateListData", {
users: [],
isFirst: false,
isLoading: true,
errorMsg: "",
});
axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${this.keyWord}`).then(
(response) => {
console.log("success!");
// 可以省略isFirst,上面已经改动过了,一次性的,不会再变化
this.$bus.$emit("updateListData", {
users: response.data.items,
isLoading: false,
errorMsg: "",
});
},
(error) => {
console.log("error:", error.message);
this.$bus.$emit("updateListData", {
users: [],
isLoading: false,
errorMsg: error.message,
});
}
);
},
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
List.vue:
<template>
<div>
<div v-show="info.users.length">
<ul>
<li v-for="user in this.info.users" :key="user.node_id">
{{ user.login }}---{{ user.node_id }}---{{ user.id }}<br />
<a :href="user.html_url">
<img :src="user.avatar_url" />
a>
li>
ul>
div>
<div v-show="info.isFirst">
<h2>welcome to use!h2>
div>
<div v-show="info.isLoading">
<h2>loading......h2>
div>
<div v-show="info.errorMsg">
<h2>{{ info.errorMsg }}h2>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "List",
data() {
return {
info: {
users: [],
isFirst: true,
isLoading: false,
errorMsg: "",
},
};
},
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on("updateListData", (info) => {
// es6语法,合并对象
this.info = { ...this.info, ...info };
});
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.$bus.$off("updateListData");
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
4.3 vue项目常用的2个ajax库
4.3.1 axios
前文有使用,这里不解释。
4.3.2 vue-resource
在vue1.x的时候使用广泛,现在不用,不解释。
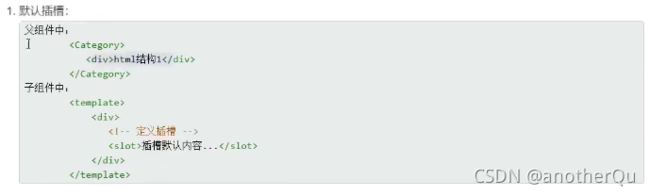
4.4 slot插槽
组件标签里面东西不确定,可以用插槽
4.4.1 默认插槽、具名插槽
App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<Category title="foods">
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidua>
Category>
<Category title="games">
<img slot="slotOne" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<img slot="slotOne" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<template v-slot:slotTwo>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}li>
ul>
template>
Category>
<Category title="films">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in films" :key="index">{{ item }}li>
ul>
<video
controls
src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"
>video>
Category>
div>
template>
<script>
import Category from "./components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Category,
},
data() {
return {
foods: ["火锅", "烧烤", "牛排"],
games: ["红警", "cf"],
films: ["教父", "atguigu"],
};
},
};
script>
<style>
/* 样式可以放这里,也可以放Category.vue里面 */
video {
width: 100%;
}
style>
Category.vue:
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}h3>
<slot>我是默认值,当没有传递填充插槽的内容时显示slot>
<slot name="slotOne">slot>
<slot name="slotTwo">slot>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Category",
props: ["title"],
};
script>
<style>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
}
style>
4.4.2 作用域插槽
App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<Category title="games">
<template scope="atguigu">
<ul>
<li v-for="(g, index) in atguigu.games" :key="index">{{ g }}li>
ul>
<h4>{{ atguigu.x }}h4>
template>
Category>
<Category title="games">
<template slot-scope="{ games }">
<ol>
<li v-for="(g, index) in games" :key="index">{{ g }}li>
ol>
template>
Category>
div>
template>
<script>
import Category from "./components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Category,
},
data() {
return {};
},
};
script>
<style>
/* 样式可以放这里,也可以放Category.vue里面 */
video {
width: 100%;
}
style>
Category.vue:
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}h3>
<slot :games="games" x="hello">slot>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Category",
data() {
return {
games: ["红警", "cf"],
};
},
};
script>
<style>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
}
style>
4.4.3总结
5 vuex
5.1 理解vuex
5.1.1 vuex是什么
5.1.2 什么时候使用
1.多个组件依赖于同一数据(多读一)
2.不同组件的行为变更同一数据(多写一)
5.1.3 案例
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ sum }}h2>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increament">+button>
<button @click="decreament">-button>
<button @click="increamentOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="increamentWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
sum: 0, //当前和
n: 1, //用户选择的数据
};
},
methods: {
increament() {
this.sum += this.n;
},
decreament() {
this.sum -= this.n;
},
increamentOdd() {
if (this.sum % 2) {
this.sum += this.n;
}
},
increamentWait() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.sum += this.n;
}, 500);
},
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
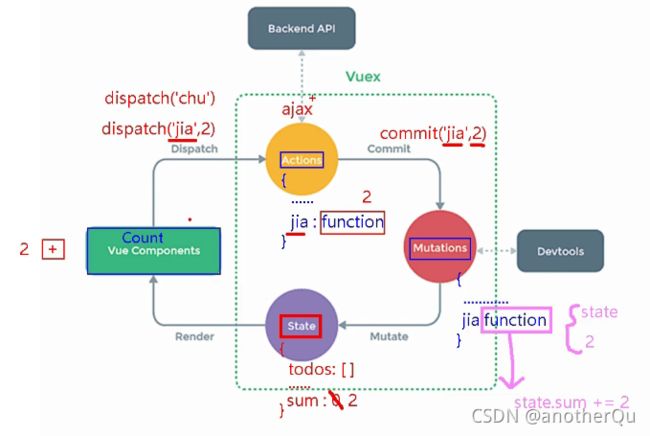
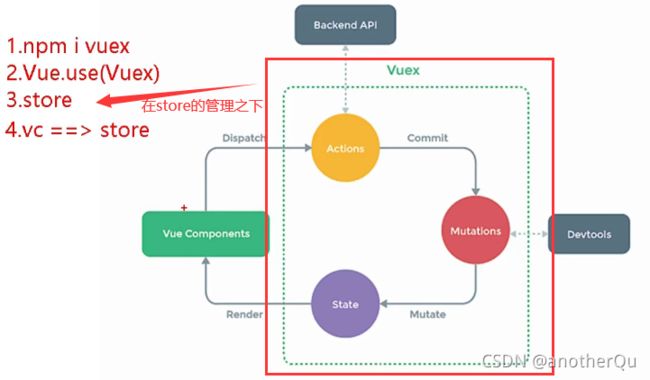
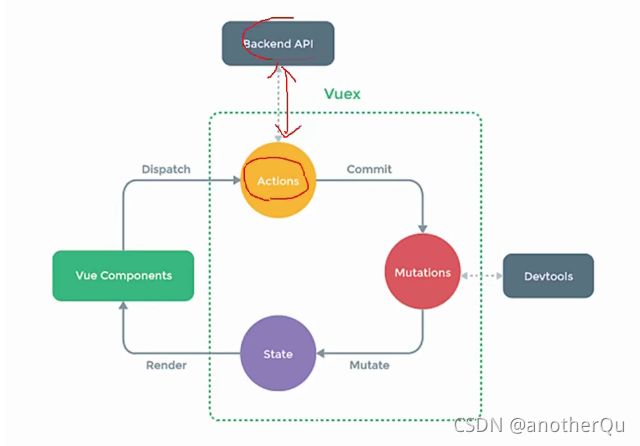
5.1.4 vuex原理图
npm i vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 所有import会优先运行,所以达不到在引入store之前use(Vuex)的效果,所以Vue.use(Vuex)要放到index.js里
import store from './store'//下面路径文件名是index,可以省略
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// es6简写
// 在vm,vc上放上$store
store,
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
}
}).$mount('#app')
App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<Count>Count>
div>
template>
<script>
import Count from "./components/Count.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Count,
},
data() {
return {};
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
Count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ $store.state.sum }}h2>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increament">+button>
<button @click="decreament">-button>
<button @click="increamentOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="increamentWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
n: 1, //用户选择的数据
};
},
methods: {
// 这里可以看作vuex操作中类似于后端controller层的位置,service层和dao层在index.js里
increament() {
// this.sum += this.n;
// 写数据操作
// 通过this.$store.dispatch来传输要执行的动作给index.js中的actions
// 两个参数:动作名,参数
this.$store.dispatch("jia", this.n);
},
decreament() {
// this.sum -= this.n;
// 如果没有什么逻辑处理,可以直接越过actions,直接进行this.$store.commit和mutations对话
// this.$store.dispatch("jian", this.n);
this.$store.commit("JIAN", this.n);
},
increamentOdd() {
// if (this.sum % 2) {
// this.sum += this.n;
// }
this.$store.dispatch("increamentOdd", this.n);
},
increamentWait() {
this.$store.dispatch("increamentWait", this.n);
},
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
index.js:
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最核心的store
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// actions:响应组件动作,类似于后端的service层
const actions = {
// 动作名,小写
// 两个参数:上下文,参数
jia(context, value) {
// console.log('action:jia',context,value);
// context.commit操作mutations中相应方法,操作数据
context.commit('JIA', value)
},
// 由于jian操作直接对话mutations,所以可注掉这里的jian函数
// jian(context, value) {
// context.commit('JIAN', value)
// },
increamentOdd(context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}
},
increamentWait(context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
// this.sum += this.n;
context.commit('JIA', value)
}, 500);
},
}
// mutations:操作数据,类似于后端的dao层
const mutations = {
// 动作名,推荐使用大写,用来区分actions和mutations的操作
// 两个参数:存数据的state,参数
JIA(state, value) {
// console.log('mutation:JIA',state,value);
// 实际的对数据的操作
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
}
// state:存储数据,类似于后端的database
const state = {
sum: 0
}
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
// es6简写
state
})
注:
1.逻辑一般写在actions(类似于后端的service)里,methods里只做个调用(类似于controller层)。
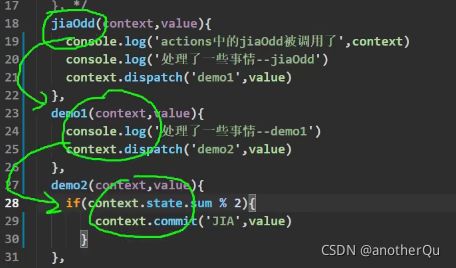
2.actions里逻辑复杂,进行功能拆分,互相调:
5.2 vuex核心概念和api
5.2.1 state里面的getters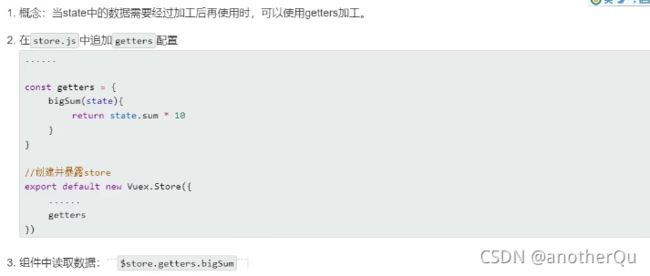
5.2.2 mapState和mapGetters
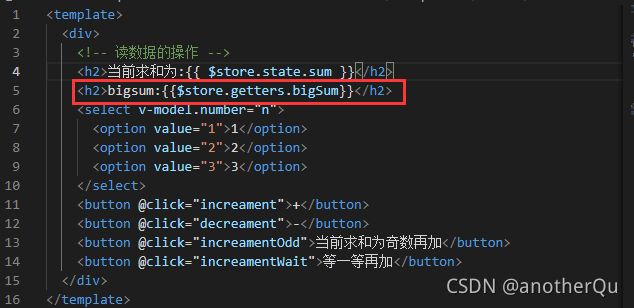
上节中Count.vue写 s t o r e . g e t t e r s . x x x 和 store.getters.xxx和 store.getters.xxx和store.state这种前缀太麻烦,可以写成计算属性:

上面也很麻烦,写成官方形式:

Count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ he }}h2>
<h2>bigsum:{{ bigSum }}h2>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increament">+button>
<button @click="decreament">-button>
<button @click="increamentOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="increamentWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
n: 1, //用户选择的数据
};
},
methods: {
// 这里可以看作vuex操作中类似于后端controller层的位置,service层和dao层在index.js里
increament() {
// this.sum += this.n;
// 写数据操作
// 通过this.$store.dispatch来传输要执行的动作给index.js中的actions
// 两个参数:动作名,参数
this.$store.dispatch("jia", this.n);
},
decreament() {
// this.sum -= this.n;
// 如果没有什么逻辑处理,可以直接越过actions,直接进行this.$store.commit和mutations对话
// this.$store.dispatch("jian", this.n);
this.$store.commit("JIAN", this.n);
},
increamentOdd() {
// if (this.sum % 2) {
// this.sum += this.n;
// }
this.$store.dispatch("increamentOdd", this.n);
},
increamentWait() {
this.$store.dispatch("increamentWait", this.n);
},
},
computed: {
// 不需要自己写
// sum(){
// return this.$store.state.sum
// },
// bigSum(){
// return this.$store.getters.bigSum
// }
// 传递字符串参数都是要带引号的,只是key值省略了引号,value值的引号是不能省的
// ...{object}:意思是把object展开,放到这里,es6语法
// 对象写法
...mapState({ he: "sum" }),
// getters中的数据和state中的数据分开
// 数组写法,k和v相同可用
// 这里不是对象的简写形式,对象简写应该是bigSum:bigSum,这里bigSum:'bigSum'
...mapGetters(["bigSum"]),
},
mounted() {
// 传递字符串参数都是要带引号的,只是key值省略了引号,value值的引号是不能省的
const x = mapState({ he: "sum", dahe: "bigSum" });
console.log(x); //{he: ƒ, dahe: ƒ}
},
};
script>
<style>
style>
5.2.3 mapActions和mapMutations
上节简化了vuex读数据的方式,这节简化vuex写数据的方式。
Count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ he }}h2>
<h2>bigsum:{{ bigSum }}h2>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increament(n)">+button>
<button @click="decreament(n)">-button>
<button @click="increamentOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="increamentWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
n: 1, //用户选择的数据
};
},
methods: {
//对象写法
...mapMutations({ increament: "JIA", decreament: "JIAN" }),
// 数组写法,当然上面调用的方法也要改成JIA/JIAN
// ...mapMutations(['JIA','JIAN']),
// 对象写法
// ...mapActions({increamentOdd:'increamentOdd',increamentWait:'increamentWait'}),
// 数组写法
...mapActions(["increamentOdd", "increamentWait"]),
},
computed: {
// 不需要自己写
// sum(){
// return this.$store.state.sum
// },
// bigSum(){
// return this.$store.getters.bigSum
// }
// 传递字符串参数都是要带引号的,只是key值省略了引号,value值的引号是不能省的
// ...{object}:意思是把object展开,放到这里,es6语法
// 对象写法
...mapState({ he: "sum" }),
// getters中的数据和state中的数据分开
// 数组写法,k和v相同可用
// 这里不是对象的简写形式,对象简写应该是bigSum:bigSum,这里bigSum:'bigSum'
...mapGetters(["bigSum"]),
},
mounted() {},
};
script>
<style>
style>
![]()
5.2.4 兄弟组件共用vuex的数据案例
添加新组件Show.vue
Show.vue:
<template>
<div class="two">
<h2>sum:{{ sum }}h2>
<h2>bigSum:{{ bigSum }}h2>
sum:<input type="number" v-model.number="sum" /><br />
bigSum:<input type="number" v-model.number="bigSum" /><br />
<button @click="JIA(1)">sum++button>
<button @click="increamentWait(1)">sum++(wait)button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Show",
data() {
return {};
},
computed: {
...mapState(["sum"]),
...mapGetters(["bigSum"]),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(["JIA"]),
...mapActions(["increamentWait"]),
},
};
script>
<style>
.two {
background-color: aqua;
}
style>
5.2.5 vuex的index.js中对actions,mutations等的功能拆分解耦
防止index.js中actions,mutations等里面功能很多,很复杂,使用模块化的方式对功能进行拆分。
index,js:
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最核心的store
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 模块整体,这里叫moduleOne
const moduleOne = {
// 使用命名空间
namespaced: true,
// 注意,这里都由之前的()变为了:
actions: {
jia(context, value) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
},
increamentOdd(context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}
},
increamentWait(context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}, 500);
},
},
mutations: {
JIA(state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
sum: 0
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
// 创建并暴露特定store模块
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
// a:moduleOne,
// es6简写
// moduleOne:moduleOne
moduleOne,
}
})
Count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ he }}h2>
<h2>bigsum:{{ bigSum }}h2>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increament(n)">+button>
<button @click="decreament(n)">-button>
<button @click="increamentOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="increamentWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
n: 1, //用户选择的数据
};
},
methods: {
// 读写都需要指定使用的哪个模块(这里是moduleOne)
// 使用不同的模块就再加一行对那个模块的相同操作就行了
...mapMutations("moduleOne", { increament: "JIA", decreament: "JIAN" }),
...mapActions("moduleOne", ["increamentOdd", "increamentWait"]),
},
computed: {
...mapState("moduleOne", { he: "sum" }),
...mapGetters("moduleOne", ["bigSum"]),
},
mounted() {},
};
script>
<style>
style>
Show.vue:
<template>
<div class="two">
<h2>sum:{{ sum }}h2>
<h2>bigSum:{{ bigSum }}h2>
sum:<input type="number" v-model.number="sum" /><br />
bigSum:<input type="number" v-model.number="bigSum" /><br />
<button @click="JIA(1)">sum++button>
<button @click="increamentWait(1)">sum++(wait)button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Show",
data() {
return {};
},
computed: {
...mapState("moduleOne", ["sum"]),
...mapGetters("moduleOne", ["bigSum"]),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations("moduleOne", ["JIA"]),
...mapActions("moduleOne", ["increamentWait"]),
},
};
script>
<style>
.two {
background-color: aqua;
}
style>
如果是自己读写的话:
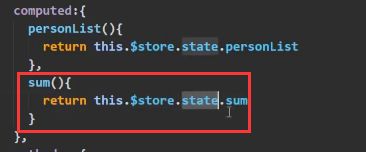
上面这种形式要做出修改,
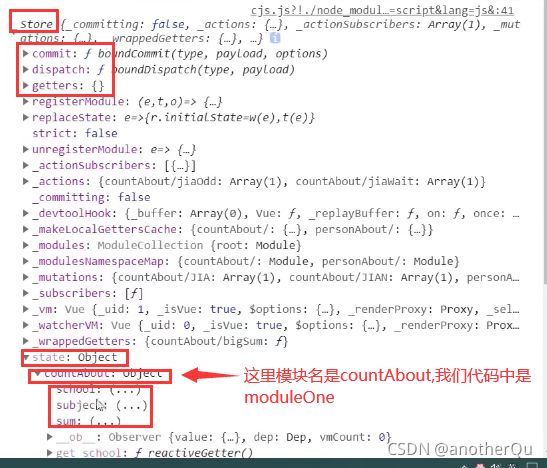
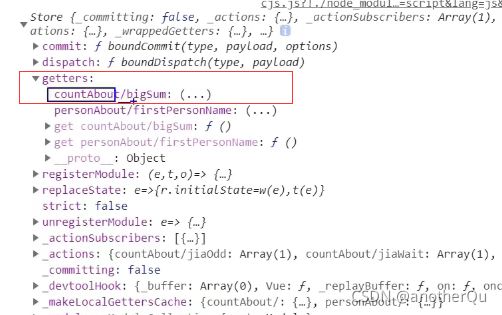
从store的结构中可以知道该怎么修改:
读数据就加个模块名
 写数据比较奇葩。。。:
写数据比较奇葩。。。:
加了个“模块名/”,
$store.dispatch同理
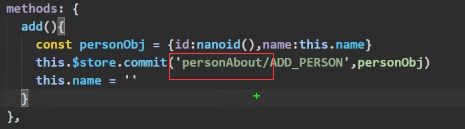
getters的数据也和写的格式类似:
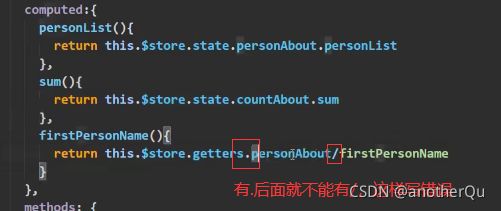
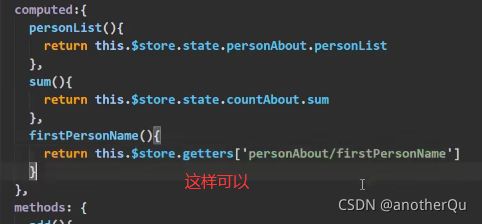
将moduleOne模块提取出来,分离更彻底:
index.js:
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最核心的store
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入store模块
import moduleOne from './moduleOne'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露特定store模块
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
// a:moduleOne,
// es6简写
// moduleOne:moduleOne
moduleOne,
}
})
moduleOne.js:
export default {
// 使用命名空间
namespaced: true,
// 注意,这里都由之前的()变为了:
actions: {
jia(context, value) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
},
increamentOdd(context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}
},
increamentWait(context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}, 500);
},
},
mutations: {
JIA(state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
sum: 0
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}