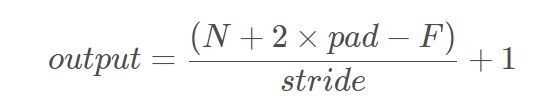深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码3(图像分类LeNet5模型)—利用Tensorflow和mnist数据集训练LeNet5-CNN模型实现手写数字识别
系列文章:
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码0.8—基于最小均方误差的线性判别函数参数拟合训练
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码0.9—MNIST数据集介绍、下载及基本操作
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码1(入门)—利用Tensorflow和mnist数据集训练单层前馈神经网络/感知机实现手写数字识别
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码2(初级)—利用Tensorflow和mnist数据集训练简单的深度网络模型实现手写数字识别
论文Lecun-1998和其中提出的LeNet5模型是深度卷积网络CNN模型的开山之作,其计算机视觉-图像分类领域的重要性不言而喻。
在本文实例中,我们利用Tensorflow和mnist数据集学习LeNet5模型的实现与训练,对手写数字图片实现更加准确的分类识别。
英文原始论文下载:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98.pdf,建议大家能够读一下原作中的原理描述部分,网上转述的往往会有一些理解上的偏差,原文阅读对于模型原理的体会能够更加深刻。
1、基础知识准备
(1)深度学习-卷积神经网络的基本原理
卷积层:卷积操作的目的是提取输入的不同特征,第一层卷积层可能只能提取一些低级的特征如边缘、线条和角等层级,更多层的网路能从低级特征中迭代提取更复杂的特征
Relu层:也叫激活函数层,激活函数是用来加入非线性因素的,因为线性模型的表达能力不够
池化层:也叫下采样层,池化层主要用于压缩数据特征,减少参数的计算量,减小过拟合
全连接层:在整个卷积神经网络中起到“分类器”的作用。如果说卷积层、池化层和激活函数层等操作是将原始数据映射到隐层特征空间的话,全连接层则起到将学到的“分布式特征表示”映射到样本标记空间的作用。在实际使用中,全连接层可由卷积操作实现
(2)Tensorflow基础知识
Tensorflow中的计算图、张量、Session的运行等基本概念
Tensorflow中和卷积、Relu、池化、全连接、梯度下降等操作相关的函数使用
(3)利用Tensorflow进行训练的相关操作方法
Tensorflow的基本使用方法和卷积神经网络CNN模型训练的基本过程,可参考文章:
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码2(初级)—利用Tensorflow和mnist数据集训练简单的深度网络模型实现手写数字识别
2、实例及网络模型主要原理
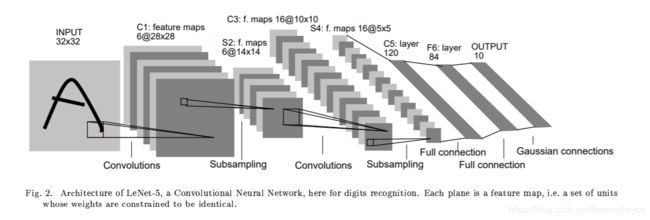
(1)网络模型的输入
输入采用mnist手写数字识别数据集,图片在数据集中的数据大小为1*784,通过reshape转换为28*28大小的矩阵
需要将输入图片大小从28*28转换为32*32
(2)建立网络模型
网络的第一层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,通道数/深度为6,不适用全0补充,步长为1
尺寸变化:32*32*2 to 28*28*6
网络的第二层:池化层,下采样为2*2,使用全0补充,步长为2
尺寸变化:28*28*6 to 14*14*6
网络的第三层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,通道数/深度为16,不使用全0补充,步长为1
尺寸变化:14*14*6 to 10*10*6
网络的第四层:池化层,下采样为2*2,使用全0补充,步长为2
尺寸变化:10*10*6 to 5*5*16
网络的第五层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,因为输入为5*5*16的map,所以也可视为全连接层
尺寸变化:5*5*16=1*400 to 1*120
网络的第六层:全连接层
尺寸变化:1*120 to 1*84
网络的第七层:输出层,基于径向基,近似为全连接层,经过softmax得到分类结果
尺寸变化:1*84 to 1*10
计算卷积操作输出维度的公式为:
其中N-输入维度、F-卷积核大小、stride-卷积步长、pad-0填充边缘
(3)准则函数
为了减少过拟合,引入了dropout机制和正则化项L2
损失函数使用目标类别和预测类别之间的交叉熵,通过损失函数最小化达到最小化误差的目的
(4)优化算法
训练优化器采用Adam梯度下降方法以最小化损失函数
(5)评估模型
利用tf.equal检测预测类别标签与真实类别标签是否一致,从而计算在测试数据集上的准确率
3、实例实现的主要步骤
(1)下载数据集,mnist数据集,可以直接去Lecun官网下载
Lecun MNIST数据集网址:
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
mnist数据集介绍可以参考这篇文章:
深度学习-卷积神经网络-实例及代码0.9—MNIST数据集介绍、下载及基本操作
(2)获取mnist数据集操作的python包,官方github上有(可能迁移了)
也可参考我项目中的mnist文件夹
https://github.com/firemonkeygit/DeepLearningTensorflowMNIST
(3)编写代码
包括建立模型、训练模型和评估模型
利用MNIST训练集mnist.image训练网络模型
利用MNIST测试集mnist.test测试结果进行模型评估
4、实例代码分析
本实例项目Github地址(如果对你有所帮助,欢迎关注点赞~):
https://github.com/firemonkeygit/DeepLearningTensorflowMNIST
参考MnistDLTrainLeNet5.py文件,经过调试可用
注意导入操作mnist数据集的python包和配置正确的数据集路径
代码执行结果:
step 0,train_accuracy 0.11999999731779099
step 0,test_accuracy 0.11749999970197678
step 100,train_accuracy 0.3799999952316284
step 100,test_accuracy 0.3871000111103058
step 200,train_accuracy 0.6899999976158142
step 200,test_accuracy 0.6510000228881836
step 300,train_accuracy 0.8299999833106995
step 300,test_accuracy 0.8349000215530396
step 400,train_accuracy 0.9100000262260437
step 400,test_accuracy 0.8770999908447266
step 500,train_accuracy 0.8799999952316284
step 500,test_accuracy 0.8921999931335449
step 600,train_accuracy 0.9399999976158142
step 600,test_accuracy 0.909500002861023
step 700,train_accuracy 0.949999988079071
step 700,test_accuracy 0.9081000089645386
step 800,train_accuracy 0.949999988079071
step 800,test_accuracy 0.9251999855041504
step 900,train_accuracy 0.8999999761581421
step 900,test_accuracy 0.9323999881744385
final_accuracy 0.9399999976158142
详细代码贴出来如下:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from TensorflowTest.mnist import input_data
#1.transform mnist from 28*28 to 32*32
def mnist_reshape_32(_batch):
batch=np.reshape(_batch,[-1,28,28])
num=batch.shape[0]
batch_32=np.array(np.random.rand(num,32,32),dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(num):
batch_32[i]=np.pad(batch[i],2,'constant',constant_values=0)
return batch_32
# def weight_variable(shape,name):
# return tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1),nam=name)
# def bias_variable(shape,name):
# return tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape),name=name)
# def conv2d(x,w,padding):
# return tf.nn.conv2d(x,w,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding=padding)
# def relu_bias(x,bias,name):
# return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(x,bias),name=name)
# def max_pool_2x2(x):
# return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
keep_prob=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
def LeNetModel(x,regular):
x_data=tf.reshape(x,[-1,32,32,1])
#C1层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,通道数/深度为6,不适用全0补充,步长为1
#尺寸变化:32*32*2 to 28*28*6
with tf.variable_scope('LayerC1'):
c1weight=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,1,6],stddev=0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('c1/weight',c1weight)
c1bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[6]))
tf.summary.histogram('c1/bias',c1bias)
c1conv=tf.nn.conv2d(x_data,c1weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID')
c1relu=tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(c1conv,c1bias))
tf.summary.histogram('c1/output',c1relu)
#S2层:池化层,下采样为2*2,使用全0补充,步长为2
#尺寸变化:28*28*6 to 14*14*6
with tf.name_scope('LayerS2'):
s2pool=tf.nn.max_pool(c1relu,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('s2/output',s2pool)
#C3层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,通道数/深度为16,不使用全0补充,步长为1
#尺寸变化:14*14*6 to 10*10*6
with tf.variable_scope('LayerC3'):
c3weight=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,6,16],stddev=0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('c3/weight',c3weight)
c3bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[16]))
tf.summary.histogram('c3/bias',c3bias)
c3conv=tf.nn.conv2d(s2pool,c3weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID')
c3relu=tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(c3conv,c3bias))
tf.summary.histogram('c3/output',c3relu)
#S4层:池化层,下采样为2*2,使用全0补充,步长为2
#尺寸变化:10*10*6 to 5*5*16
with tf.variable_scope('LayerS4'):
s4pool=tf.nn.max_pool(c3relu,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('s4/output',s4pool)
#C5层:卷积层,卷积核为5*5,因为输入为5*5*16的map,所以也可视为全连接层
#尺寸变化:5*5*16=1*400 to 1*120
#训练时引入dropout随机将部分节点输出改为0,dropout可以避免过拟合,模型越简单越不容易过拟合
#训练时引入正则化限制权重的大小,使得模型不能任意拟合训练数据中的随机早上,从而避免过拟合
s4pool_shape=s4pool.get_shape().as_list()
size=s4pool_shape[1]*s4pool_shape[2]*s4pool_shape[3]
s4pool_reshape=tf.reshape(s4pool,[-1,size])
with tf.variable_scope('LayerC5'):
c5weight=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([size,120],stddev=0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('c5/weight',c5weight)
c5bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[120]))
tf.summary.histogram('c5/bias',c5bias)
if regular!=None:
tf.add_to_collection('loss',regular(c5weight))
c5=tf.matmul(s4pool_reshape,c5weight)
c5relu=tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(c5,c5bias))
c5relu=tf.nn.dropout(c5relu,keep_prob)
tf.summary.histogram('c5/output',c5relu)
#F6层:全连接层
#尺寸变化:1*120 to 1*84
with tf.variable_scope('LayerF6'):
f6weight=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([120,84],stddev=0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('f6/weight',f6weight)
f6bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[84]))
tf.summary.histogram('f6/bias',f6bias)
if regular!=None:
tf.add_to_collection('loss',regular(f6weight))
f6=tf.matmul(c5relu,f6weight)
f6relu=tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(f6,f6bias))
f6relu=tf.nn.dropout(f6relu,keep_prob)
tf.summary.histogram('f6/output',f6relu)
#OUTPUT层:输出层,基于径向基,近似为全连接层,经过softmax得到分类结果
#尺寸变化:1*84 to 1*10
with tf.variable_scope('LayerF7'):
f7weight=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([84,10],stddev=0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('f7/weight',f7weight)
f7bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[10]))
tf.summary.histogram('f7/bias',f7bias)
if regular!=None:
tf.add_to_collection('loss',regular(f7weight))
f7=tf.matmul(f6relu,f7weight)+f7bias
tf.summary.histogram('f7/output',f7)
return f7
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('../../MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
xs=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,32,32])
yLabels=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.001)
ys=LeNetModel(xs,regularizer)
cross_entropy=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=ys,labels=tf.argmax(yLabels,1))
with tf.name_scope('lossValue'):
loss=tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)+tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('loss'))
tf.summary.scalar('lossValue',loss)
#with tf.name_scope('lossValue'):
train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss)
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(ys,1),tf.argmax(yLabels,1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
xs_test32=mnist_reshape_32(mnist.test.images)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
merged=tf.summary.merge_all()
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(100)
batch_xs32=mnist_reshape_32(batch_xs)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs32,yLabels:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
if i%100==0:
train_accuracy=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs32,yLabels:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
print("step {0},train_accuracy {1}".format(i,train_accuracy))
rs=sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs32,yLabels:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
writer.add_summary(rs,i)
if i%100==0:
test_accuracy=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={xs:xs_test32,yLabels:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
print("step {0},test_accuracy {1}".format(i,test_accuracy))
final_accuracy=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs32,yLabels:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
print("final_accuracy {0}".format(final_accuracy))