Webx学习笔记(二)SpringExt
1 SpringExt装配服务
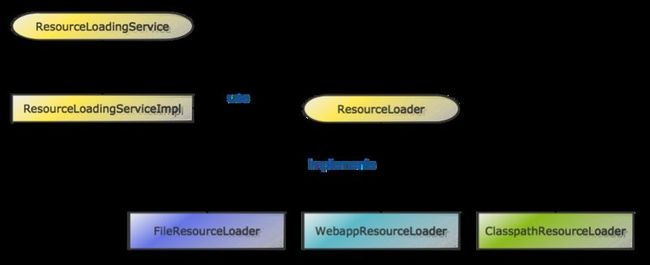
在Webx中有一个非常有用的ResourceLoadingService,ResourceLoadingService是一个可以从各种输入源中(如从File System、Classpath、Webapp中)查找和读取资源文件的服务。
ResourceLoadingService的结构如图所示。这是一个既简单又典型的面向对象的设计。
1.1Spring Beans
举例:用Spring Beans装配Resource Loading服务
<bean id="resourceLoadingService" class="com.alibaba...ResourceLoadingServiceImpl">
<property name="mappings">
<map>
<entry key="/file" value-ref="fileLoader" />
<entry key="/webroot" value-ref="webappLoader" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="fileLoader" class="com.alibaba...FileResourceLoader">
<property name="basedir" value="${user.home}" />
</bean>
<bean id="webappLoader" class=" com.alibaba...WebappResourceLoader" />
上述Spring beans的配置很好地体现了Spring的基础理念:IoC(Inversion of Control,依赖反转)。ResourceLoadingServiceImpl并不依赖FileResourceLoader和WebappResourceLoader,它只依赖它们的接口ResourceLoader。至于如何创建FileResourceLoader、WebappResourceLoader、需要提供哪些参数,这种琐事全由spring包办。
spring本身并不了解如何创建ResourceLoader的对象、需要用哪些参数、如何装配和注入等知识。这些知识全靠应用程序的装配者(assembler)通过上述spring的配置文件来告诉spring的。
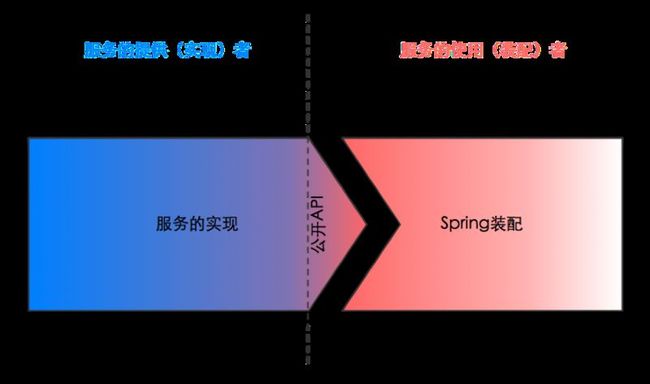
“服务提供者”和“服务使用者”(即“装配者”)。在上面的例子中,ResourceLoadingService的作者就是服务的提供者,使用ResourceLoadingService的人,当然就是服务使用者。服务使用者利用spring把ResourceLoadingService和ResourceLoader等其它服务装配在一起,使它们可以协同工作。
Spring的配置文件会依赖于服务实现类的公开API。装配者除非查看源代码(如ResourceLoadingServiceImpl的源码)或者API文档才能精确地获知这些API的细节。这可能带来如下问题:
-
没有检验机制,错误必须等到运行时才会被发现。
-
无法了解更多约束条件。
-
当服务的实现被改变时,Spring配置文件可能会失败。
1.2Spring Schema
用Spring Schema装配Resource Loading服务
<resource-loading id="resourceLoadingService"
xmlns="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services/resource-loading">
<resource pattern="/file">
<file-loader basedir="${user.home}" />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/webroot">
<webapp-loader />
</resource>
</resource-loading>
-
很明显,这个配置文件比起前面的Spring Beans风格的配置文件简单易读得多。因为在这个spring配置文件里,它所用的“语言”是“领域相关”的,和ResourceLoadingService 所提供的服务内容相关,而不是使用像bean、property这样的编程术语。这样自然易读得多。
-
它是可验证的。你不需要等到运行时就能验证其正确性。任何一个支持XML Schema的标准XML编辑器,包括Eclipse自带的XML编辑器,都可以告诉你配置的对错。
-
包含更多约束条件。例如,XML Schema可以告诉你,哪些参数是可选的,哪些是必须填的;参数的类型是什么等等。
-
最重要优点:服务的实现细节对装配者隐藏。当服务实现改变时,只要XML Schema是不变的,那么Spring的配置就不会受到影响。
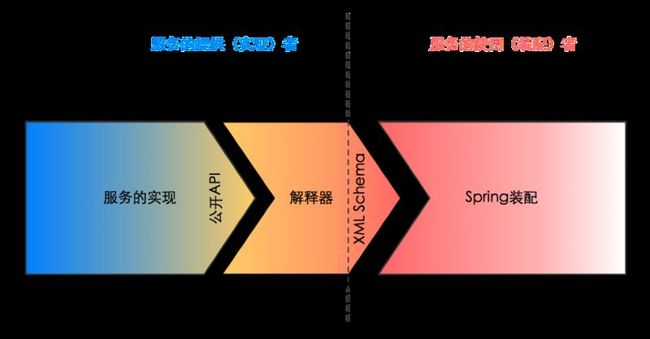
通过Spring Schema来定义配置文件,装配者无须再了解诸如“ResourceLoadingService的实现类是什么”、“需要什么参数”等细节。那么Spring是如何得知这些内容呢?
奥秘在于所有的schema都会有一个“解释器”和它对应(即BeanDefinitionParser)。这个解释器负责将符合schema定义的XML配置,转换成Spring能解读的beans定义。解释器是由服务的开发者来提供的 ,ResourceLoadingService的开发者会提供这个解释器。
装配者,不再需要了解服务具体实现类的API,它只要遵循标准的XML Schema定义来书写spring配置文件,就可以得到正确的配置。这样一来,虚线左侧的服务提供者就有自由可以改变服务的实现类,他相信只要服务的接口和XML Schema不改变,服务的使用者就不会受影响。
将和具体实现相关的工作,例如提供类名、property名称和类型等工作,交还给服务的提供者,使服务的使用者(即装配者)可以用它所能理解的语言来装配服务,这是Spring Schema所带来的核心价值。
然而Spring Schema有一个问题 —— 它是不可扩展的。
在Spring配置文件上,你却无法自由地添加新的元素。比如:尝试在Spring Schema所装配的Resource Loading服务中,添加新的装载器。
<resource-loading id="resourceLoadingService"
xmlns="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services/resource-loading">
<resource pattern="/file">
<file-loader basedir="${user.home}" />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/webroot">
<webapp-loader />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/db">
<database-loader connection="jdbc:mysql:mydb" />
</resource>
</resource-loading>
装配者希望在这里添加一种新的装载器:database-loader。然而,如果在设计<resource-loading>的schema时,并没有预先考虑到database-loader这种情况,那么这段配置就会报错。无法做到不修改老的schema,就添加新的元素 —— 这导致Spring Schema的作用被大大削弱。
1.3. SpringExt Schema
SpringExt改进了Spring,使得Spring Schema可以被扩展。用SpringExt Schema装配Resource Loading服务
<resource-loading id="resourceLoadingService"
xmlns="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services"
xmlns:loaders="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services/resource-loading/loaders">
<resource pattern="/file">
<loaders:file-loader basedir="${user.home}" />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/webroot">
<loaders:webapp-loader />
</resource>
</resource-loading>
重新定义namespaces —— 将ResourceLoader和<resource-loading>所属的namespace分离。将file-loader和webapp-loader放在loaders名字空间中,表示它们是Resource Loaders的扩展。
要添加一种新的ResourceLoader扩展 —— DatabaseResourceLoader,只需要做以下两件事:
-
将包含
DatabaseResourceLoader所在的jar包添加到项目的依赖中。如果你是用maven来管理项目,那么意味着你需要修改一下项目的pom.xml。 -
在spring配置文件中添加如下行:
在SpringExt Schema所装配的Resource Loading服务中,添加新的装载器
<resource-loading id="resourceLoadingService"
xmlns="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services"
xmlns:loaders="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/services/resource-loading/loaders">
<resource pattern="/file">
<loaders:file-loader basedir="${user.home}" />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/webroot">
<loaders:webapp-loader />
</resource>
<resource pattern="/db">
<loaders:database-loader connection="jdbc:mysql:mydb" />
</resource>
</resource-loading>
添加一个新的loader,而无须改变<resource-loading>的schema。
2. SpringExt原理