http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/22107553
array对象属性及内建方法
数组属性
The following attributes contain information about the memory layoutof the array:
| ndarray.flags | Information about the memory layout of the array.查看数据存储区域的属性。C_CONTIGUOUS : True F_CONTIGUOUS : False OWNDATA : True WRITEABLE : True ALIGNED : True UPDATEIFCOPY : False |
| ndarray.shape | Tuple of array dimensions. 代表一个array的形态,是一个向量还是一个矩阵,抑或是一个更复杂的向量组。数组的大小可以通过其shape属性获得.数组的维度。这是一个指示数组在每个维度上大小的整数元组。例如一个n排m列的矩阵,它的shape属性将是(2,3),这个元组的长度显然是秩,即维度或者ndim属性。 |
| ndarray.strides | Tuple of bytes to step in each dimension when traversing an array. |
| ndarray.ndim | Number of array dimensions.代表这个array的维度,数组轴的个数,结果是一个数,在python的世界中,轴的个数被称作秩。 |
| ndarray.data | Python buffer object pointing to the start of the array’s data.包含实际数组元素的缓冲区,通常我们不需要使用这个属性,因为我们总是通过索引来使用数组中的元素。 |
| ndarray.size | Number of elements in the array.在array中拥有的元素数量。数组元素的总个数,等于shape属性中元组元素的乘积。 |
| ndarray.itemsize | Length of one array element in bytes.这个array数组中每一个元素所占的字节数、字节大小(数组中的数据项的所占内存空间大小)。例如,一个元素类型为float64的数组itemsiz属性值为8(=64/8),又如,一个元素类型为complex32的数组item属性为4(=32/8). |
| ndarray.nbytes | Total bytes consumed by the elements of the array.这个array的总字节数(=itemsize*size) |
| ndarray.base | Base object if memory is from some other object. |
The data type object associated with the array can be found in thedtype attribute:
| ndarray.dtype | Data-type of the array’s elements.一个用来描述数组中元素类型的对象,可以通过创造或指定dtype使用标准Python类型。另外NumPy提供它自己的数据类型。 |
| ndarray.T | Same as self.transpose(), except that self is returned if self.ndim < 2.矩阵转置,同transpose()方法。 |
| ndarray.real | The real part of the array.代表一个array中所有元素的实数部分 |
| ndarray.imag | The imaginary part of the array.代表一个array中所有元素的虚数部分 |
| ndarray.flat | A 1-D iterator over the array.将这个array整理成一维的,可以索引的一系列的元素组合。它实际上是通过iterator实现的,我们可以通过for x in array.flat来取得到所有的元素。 |
| ndarray.ctypes | An object to simplify the interaction of the array with the ctypes module. |
Note:
1 与matrix不同,没有.I。
2 .reshape函数改变参数形状并返回它,而resize函数改变数组自身。
3 .ndim: 在NumPy中维度(dimensions)叫做轴(axes),轴的个数叫做秩(rank)。例如,以下例子中,数组的秩为2(它有两个维度).第0维度长度为2,第1维度长度为3.
[[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 2.]]
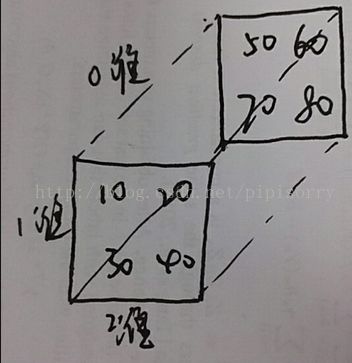
三维数组的维度
如x = [[[10, 20], [30, 40]], [[50, 60], [70, 80]]]
[[[10 20]
[30 40]]
[[50 60]
[70 80]]]
4 .T: 一维列向量的转置还是本身。如(3,)的向量[1,2,3]其转置还是[1,2,3]。
5 .base. Slicing creates a view, whose memory is shared with x:
>>> y = x[2:]
>>> y.base is x
TrueThe byte offset of element (i[0],i[1],...,i[n]) in an arrayais:
offset = sum(np.array(i) * a.strides)>>> y = np.reshape(np.arange(2*3*4), (2,3,4))
>>> y
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
>>> y.strides
(48, 16, 4)[Other attributes¶]
皮皮Blog
ndarray数组内建方法
Array conversion
| ndarray.item(*args) | Copy an element of an array to a standard Python scalar and return it.取得某一位置的元素 |
| ndarray.tolist() | Return the array as a (possibly nested) list.将array转化成一个Python中的list对象,ndarray转换成python list |
| ndarray.itemset(*args) | Insert scalar into an array (scalar is cast to array’s dtype, if possible) |
| ndarray.tostring([order]) | Construct Python bytes containing the raw data bytes in the array.返回的是bytes。 |
| ndarray.tobytes([order]) | Construct Python bytes containing the raw data bytes in the array. |
| ndarray.tofile(fid[, sep, format]) | Write array to a file as text or binary (default). |
| ndarray.dump(file) | Dump a pickle of the array to the specified file.将这个对象序列化至文件。同cPickle中的dump作用 |
| ndarray.dumps() | Returns the pickle of the array as a string.将序列化的结果通过字符串加以输出 |
| ndarray.astype(dtype[, order, casting, ...]) | Copy of the array, cast to a specified type. |
| ndarray.byteswap(inplace) | Swap the bytes of the array elements |
| ndarray.copy([order]) | Return a copy of the array. |
| ndarray.view([dtype, type]) | New view of array with the same data. |
| ndarray.getfield(dtype[, offset]) | Returns a field of the given array as a certain type. |
| ndarray.setflags([write, align, uic]) | Set array flags WRITEABLE, ALIGNED, and UPDATEIFCOPY, respectively. |
| ndarray.fill(value) | Fill the array with a scalar value. |
numpy类型及数据类型转换
numpy函数返回标准Python数值类型
通过下标所获取的数组元素的类型为NumPy中所定义的类型。将其转换为Python的标准类型还需要花费额外的时间。为了解决这个问题,数组提供了item()方法,它用来获取数组中的单个元素,并且直接返回标准的Python数值类型:
>>> a = np.arange(6.0).reshape(2,3)
>>> a.item(1,2) # 和a[1,2]类似
5.0
>>> type(a.item(1,2)) # item()所返回的是Python的标准float类型
>>> type(a[1,2]) # 下标方式获得的是NumPy的float64类型
NumPy和SciPy多维数组相互转化
import numpy
import scipy
a1 = zeros((4,6))
type(a1)
a2 = numpy.asarray(a1)
type(a2)
a3 = numpy.zeros((3,5))
type(a3)
a4 = scipy.asarray(a3)
type(a4)
ndarray中的list转换为tuple
data = np.array(
[[ 0.22403094, 0.08515318],
[ 0.7529882 , -0.65134297],
[ 1.41298052, 0.94194292],
[-0.45589253, -1.00021018]] )
data = data.T
data = zip(data[0], data[1])
print(data)
[(0.22403094000000001, 0.085153179999999995),
(0.7529882, -0.65134296999999997),
(1.4129805200000001, 0.94194292000000002),
(-0.45589253000000002, -1.0002101800000001)]a = np.array([True, False, True, False, False, True]).astype(int)
print(a) #[1 0 1 0 0 1]a = np.array(['-0.99', '', '0.56', '0.56', '-2.02', '-0.96'])
a[a == ''] = 0.0
a = a.astype(float)
print(a) #[-0.99 0. 0.56 0.56 -2.02 -0.96]Note: 也可以这样转换a = list(map(float, a))
将int数组转换成bool数组
a.astype('bool')
Note: 负数如-1转换成bool是True!
将numpy类型转换为datetime
a.astype(np.datetime64)
类型转换时的出错
ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence
出错原因:
1 trying to create an array from a list that isn't shaped like a multi-dimensional array. For examplenumpy.array([[1,2], [2, 3, 4]]) or numpy.array([[1,2], [2, [3, 4]]])
还有个类似的原因就是将array中的元素如['1', '2']当成一个列表元素,而不是当作二维的。这在pandas数据转换时可能发生的,至今lz不明原因:
l_array = df['VenueLocation'].map(lambda s: np.array(s.split(','))).values2 Another possible cause for this error message is trying to use a string as an element in an array of type float: numpy.array([1.2, "abc"], dtype=float)
[ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence]
Shape manipulation
For reshape, resize, and transpose, the single tuple argument may bereplaced with n integers which will be interpreted as an n-tuple.
| ndarray.reshape(shape[, order]) | Returns an array containing the same data with a new shape. |
| ndarray.resize(new_shape[, refcheck]) | Change shape and size of array in-place. |
| ndarray.transpose(*axes) | Returns a view of the array with axes transposed. |
| ndarray.swapaxes(axis1, axis2) | Return a view of the array with axis1 and axis2 interchanged. |
| ndarray.flatten([order]) | Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension. |
| ndarray.ravel([order]) | Return a flattened array. |
| ndarray.squeeze([axis]) | Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of a. |
ravel(): flatten the array.由ravel()展平的数组元素的顺序通常是“C风格”的,就是说,最右边的索引变化得最快,所以元素a[0,0]之后是a[0,1]。如果数组被改变形状(reshape)成其它形状,数组仍然是“C风格”的。NumPy通常创建一个以这个顺 序保存数据的数组,所以ravel()将总是不需要复制它的参数3。但是如果数组是通过切片其它数组或有不同寻常的选项时,它可能需要被复制。函数reshape()和ravel()还可以被同过一些可选参数构建成FORTRAN风格的数组,即最左边的索引变化最快。
Item selection and manipulation
For array methods that take an axis keyword, it defaults toNone. If axis is None, then the array is treated as a 1-Darray. Any other value for axis represents the dimension along whichthe operation should proceed.
| ndarray.take(indices[, axis, out, mode]) | Return an array formed from the elements of a at the given indices. |
| ndarray.put(indices, values[, mode]) | Set a.flat[n] = values[n] for all n in indices. |
| ndarray.repeat(repeats[, axis]) | Repeat elements of an array. |
| ndarray.choose(choices[, out, mode]) | Use an index array to construct a new array from a set of choices. |
| ndarray.sort([axis, kind, order]) | Sort an array, in-place. |
| ndarray.argsort([axis, kind, order]) | Returns the indices that would sort this array. |
| ndarray.partition(kth[, axis, kind, order]) | Rearranges the elements in the array in such a way that value of the element in kth position is in the position it would be in a sorted array. |
| ndarray.argpartition(kth[, axis, kind, order]) | Returns the indices that would partition this array. |
| ndarray.searchsorted(v[, side, sorter]) | Find indices where elements of v should be inserted in a to maintain order. |
| ndarray.nonzero() | Return the indices of the elements that are non-zero. |
| ndarray.compress(condition[, axis, out]) | Return selected slices of this array along given axis. |
| ndarray.diagonal([offset, axis1, axis2]) | Return specified diagonals. |
Calculation
| ndarray.argmax([axis, out]) | Return indices of the maximum values along the given axis. |
| ndarray.min([axis, out, keepdims]) | Return the minimum along a given axis.取得最小值。还有一点值得说,就是max、min这些函数都可以针对某一坐标轴(具体维度)进行运算,例如array.max(axis=0),就在0坐标上求最大值{0-按列求值,返回一行, 1-按行求值,返回一列} |
| ndarray.argmin([axis, out]) | Return indices of the minimum values along the given axis of a. |
| ndarray.ptp([axis, out]) | Peak to peak (maximum - minimum) value along a given axis. |
| ndarray.clip([min, max, out]) | Return an array whose values are limited to [min, max]. |
| ndarray.conj() | Complex-conjugate all elements. |
| ndarray.round([decimals, out]) | Return a with each element rounded to the given number of decimals. |
| ndarray.trace([offset, axis1, axis2, dtype, out]) | Return the sum along diagonals of the array. |
| ndarray.sum([axis, dtype, out, keepdims]) | Return the sum of the array elements over the given axis. |
| ndarray.cumsum([axis, dtype, out]) | Return the cumulative sum of the elements along the given axis.求累计和 |
| ndarray.mean([axis, dtype, out, keepdims]) | Returns the average of the array elements along given axis. |
| ndarray.var([axis, dtype, out, ddof, keepdims]) | Returns the variance of the array elements, along given axis. e.g. np.var(a,axis=0) |
| ndarray.std([axis, dtype, out, ddof, keepdims]) | Returns the standard deviation of the array elements along given axis. |
| ndarray.prod([axis, dtype, out, keepdims]) | Return the product of the array elements over the given axis求所有元素之积 |
| ndarray.cumprod([axis, dtype, out]) | Return the cumulative product of the elements along the given axis.求累计积 |
| ndarray.all([axis, out, keepdims]) | Returns True if all elements evaluate to True.如果所有元素都为真,那么返回真;否则返回假。 e.g. 判断ndarray中的元素是否都>0:if (b > 0).all() |
| ndarray.any([axis, out, keepdims]) | Returns True if any of the elements of a evaluate to True.只要有一个元素为真则返回真 |
Arithmetic, matrix multiplication, and comparison operations¶
Comparison operators:Unary operations:Arithmetic:Arithmetic, in-place:
Special methods¶
For standard library functions:Basic customization:Container customization: (see Indexing)
Conversion; the operations complex, int,long, float, oct, andhex. They work only on arrays that have one element in themand return the appropriate scalar.
String representations:
怎么没有ndarray.dot(b[, out])了?相当于matlab中的*。dot product of two arrays.参考下面基本运算部分。
np.vdot(a,b)专门计算矢量的点积,和dot()的区别在于对complex数据类型的处理不一样;inner(a,b)用来计算内积;outer(a,b)计算外积。
[Array methods¶]
[numpy-ref-1.8.1: page14]
皮皮Blog
numpy数组操作
[numpy教程:数组操作]
[numpy教程:数学函数和基本统计函数 ]
皮皮Blog
二维数组(矩阵)基本运算
要注意的是,这里的矩阵在严格意义上不是矩阵(本质上是二维数组),而是二维数组,不支持求逆操作,numpy中的矩阵对象参考[numpy教程 - 矩阵及其运算]
+ , - , *(元素乘法), dot(矩阵乘法), *= , += , -= , **(元素乘方),<, >, ...sin,exp, ...
Note:与MATLAB不同,MATLAB中*是矩阵乘法;*是元素乘法(点乘)。
NumPy中乘法运算符*是元素乘法(点乘,元素逐个相乘),相当于np.multiply(A, B);矩阵乘法是使用dot函数或创建矩阵对象实现。
另外,dot函数相乘时数值越界可能导致正数变负数的错误,如矩阵中元素的类型为int8时,>127的都变负数!
矩阵乘法和点乘运算
数组的算术运算是按元素逐个运算。数组运算后将创建包含运算结果的新数组。NumPy中的乘法运算符*按元素逐个计算,矩阵乘法可以使用dot函数或创建矩阵对象实现。
>>> A= np.array([[1,1],
...[0,1]])
>>> B= np.array([[2,0],
...[3,4]])
>>> A*B # 逐个元素相乘
array([[2, 0],
[0, 4]])
>>> np.dot(A,B) # 矩阵相乘
array([[5, 4],
[3, 4]])[NumPy简明教程]
element-wise相乘: 多维数组 * 一个数 ndarray * num
ll = ones([2,3])*2
print(ll)
[[ 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2.]]a_fore = l[l != '*']皮皮Blog
多维数组的迭代
是就第一个轴而言的
>>> for row in b: ... print row数组元素的迭代器
对每个数组中元素进行运算,我们可以使用flat属性,该属性是数组元素的一个迭代器:
>>> for element in b.flat: ... print element,特别的例子
a=np.arange(0,60,10).reshape(-1,1)+np.arange(0,6)
np.arange(0,60,10).reshape(-1,1) =
[[ 0]
[10]
[20]
[30]
[40]
[50]]
>>> a
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55]])
其中 a[3,3:6]表示第4行的第4到6列,结果是array([33, 34, 35]);
a[:2] 表示前两行:array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]])
注意区分:
a[:2] 和a[[0,1]] a[[0,1],:]都可以表示上面的结果。但是第一个切片是按顺序的,第二个可以随意。比如说:
>>> a[[1,2,0,2]]
array([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25]])
a[:,2] 表示第3列,array([ 2, 12, 22, 32, 42, 52])
a[1::,::2]表示的是(行从1~5,步长默认1;列从0~5,步长2)
array([[10, 12, 14],
[20, 22, 24],
[30, 32, 34],
[40, 42, 44],
[50, 52, 54]])
皮皮blog
from:http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/22107553
ref: [The N-dimensional array (ndarray)¶]*
numpy - 介绍、基本数据类型、多维数组ndarray及其内建函数
NumPy Reference*
Python For Data Analysis’s documentation
Theano学习二----numpy
python学习笔记1
Numpy教程
python快速处理数据