【数据库】MySQL表的增删改查(进阶)
MySQL表的增删改查(进阶)
文章目录
- MySQL表的增删改查(进阶)
-
- 关键字执行顺序
- 数据库约束
-
- NULL约束
- unique : 唯一约束
- default 默认值约束
- primary key 主键约束
- foreign key 外键约束
-
- 延伸问题:
- 表的设计
-
- 一对一
- 一对多
- 多对多
- 新增
- 查询
-
- 聚合查询
-
- 聚合函数
-
- count
- sum
- avg
- max
- min
- group by 子句
- having(先聚合再筛选)
- 联合查询
-
- 笛卡尔积
- 内连接
- 外连接
- 自连接
- 子查询
- 合并查询
关键字执行顺序
SQL查询中各个关键字的执行先后顺序: from > on> join > where > group by > with > having >select > distinct > order by > limit
数据库约束
约束其实就是数据库可以让程序员定义一些数据的校验规则,当插入数据/修改数据时,对数据进行校验,如果不符合校验规则,就会报错。
约束的本质就是及时发现数据中的错误,保证数据的准确性。
NULL约束
create table student (id int not null,name varchar(20));
- 在创建表时指定约束,id 这一列不能有null
unique : 唯一约束
create table student (id int unique,name varchar(20));
- id这一列不能有相同的数据
default 默认值约束
create table student (id int default 0 , name varchar(20));
- id这一列的某一行如果没有插入数据,默认为0
primary key 主键约束
create table student(id int primary key ,name varchar(20));
- 把某一列设为主键,说明这是在设计表时非常重要的一列,主键表示一条记录的身份标识,用于区分这条记录和别的记录的。
- 不能为空,相当于 not null
- 不能重复,相当于unique
- 一个表里只能有一个主键
由于主键必须要填,还不能重复,MySQL为了方便填写主键,对于整型类型的主键,就内置了自增主键这个功能。帮我们自动生成主键的值
create table student(id int primary key auto_increment , name varchar(20));
insert into student values(null,“hao”);
- 插入数据id为null,就代表按自增主键方式插入数据,如果当前表为空,则插入的第一条记录的id为1,如果表中有数据,则插入的记录的id为表中最大id+1。这样就能保证插入的每一条记录的id都是不一样的。
自增主键帮我们生成唯一的值,但是如果数据库是分布式部署(数据量太大,一台机器存不下,多台机器来存),自增主键就会出现问题,因为插入数据时,数据可能分布在不同机器上,一台机器你只知道本机的id最大值,不知道其他机器的啊,就有可能导致id不唯一。
这三个节点构成了整个数据集合
一种解决思路:让着几个节点联通起来,这样就能知道最大id,但是这样费时,不高效
第二种思路:唯一id = 时间戳(ms) + 机房编号/主机编号+随机因子
- 时间戳:插入数据时的时间戳,随机因子:随机数
通过这种方式构成唯一id ,虽然也有可能id一样,但是概率极低,所以工程上一般不忽略。
foreign key 外键约束
外键描述了两张表之间的关联关系。一个表中可以有多个外键
A表中的一个字段,是B表的主键,那他就可以是A表的外键。(一个表中的字段要想设为外键,则这个字段在另一个表中必须得是主键)
B表称为父表,A表称为字表
create table class(classId int primary key,classNmae varchar(20));
create table student(studentId int primary key ,name varchar(20),classId int,foreign key(classId) references class(classId));
父表对字表的约束:子表外键中只能插入父表中对应的主键中以及存在的值。
字表对父表的限制:子表外键中如果已经有父表中对应主键的值,则父表中不能删除或更新父表中对应的值。
- 有了外键的约束,再插入数据时,都要先触发在主表当中的查询,父表中存在才能插入/修改成功,这样就会相对耗时
- 如果查询时遍历表就相对慢,如果查询时依赖索引,就相对还可以,所以建立外键约束时,要求父表的列必须为主键或unique(主键和unique自带索引)。
延伸问题:
商品表(goodsId,name,price) 订单表(orderId,time,goodsId)
订单表中的goodsId和商品表中的goodsId建立外键约束,此时订单表中有某一商品,但是商品因为换季需要下架,而这条商品记录又不能删除,怎么办?
方案:逻辑上删除,物理上不删除(假删),相当于操作系统删除数据,只是把盘块标记为无效。可以把商品表设计为 (goodsId,name,price,ok)
ok为1说明商品在架上,ok为0说明商品下架,根据ok的值筛选商品展出。
表的设计
面试官问:你的项目数据库是如何设计的,其实就是问你的数据库中每个表是干啥的,每个表中有啥字段。
表的设计我们应该根据场景,找出"实体",一般每个实体分配一个表,然后梳理实体之间的关系:一对一,一对多,多对多,没关系,根据关系设计表。
一对一
案例:学生 账号 (一个学生一个账户,一个账户只能一个学生使用)
(1)把学生和账号放到一个表里
student(id,name,account,password)
(2) student(studentId,name,accountId) account(accountId,password)
student(studentId,name) account(accountId,password,studentId)
- 可以通过一个额外的Id把两张表中对应的数据关联起来
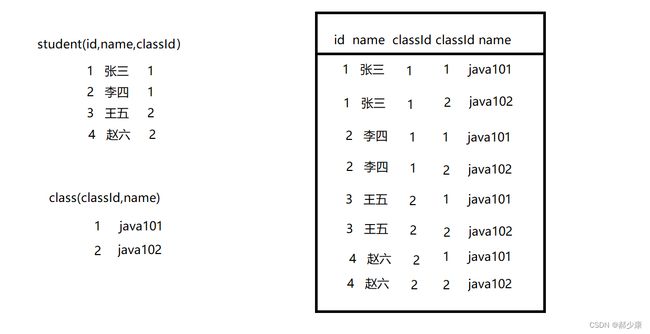
一对多
案例 :学生 班级(一个学生只能在一个班级,一个班级可以有多个学生)
(1)student(studentId,name,classId) class(classsId,className)
(2) student(studentId,name) class(classId,className,studentList)
- 第二种在MySQL中不支持,因为studentList得是一个数组,MySQL中没有数组类型
多对多
案例 :学生 课程(一个学生可以选多个课程,一个课程可以有多少学生选)
student(studentId,name) course(courseId,courseName) student_course(studentId,courseId)
- 通过一个中间表连接另外两个表,中间表就反映了学生与课程之间这种多对多的关系
新增
insert into test1 select * from test2;
insert into test1(id) select id from test2;
- 把在test2表中查询到的数据插入到test1表中,前提是对应列的数据类型必须一致,也可以查询自己表中的数据插入到自己表中。
查询
聚合查询
聚合函数
- 聚合函数计算时对于算数运算是不包含NULL的,因为NULL和任何值算数运算结果都是NULL
count
select count(*) from exam_result; select count(0) from exam_result;
- 这两个都是查询表中有几条记录
select count(id) from exam_result;
- 查询id这一列数据个数,NULL不包含在内
sum
select sum(math) from exam_result; (查询数学总成绩)(不包含NULL)
select sum(math) from exam_result where math > 80;(查询数学大于80的成绩总和)
avg
select avg(math) from exam_result;(查询数学平均分)(不包含NULL)
select avg(chinese+math+english) from exam_result;(查询总成绩平均分)
max
select max(math) from exam_result;(查询数学最高分)
min
select min(math) from exam_result;(查询数学最低分)
- 对于既有聚合函数,又有where条件的,先根据where筛选,除去不符合条件的记录,再对筛选结果使用聚合函数
group by 子句
分组查询
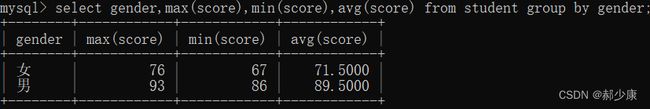
group by 指定列分组,select指定的字段必须是分组依据字段,其他字段若想出现在select中,则必须包含在聚合函数中。
select gender,max(score),min(score),avg(score) from student group by gender;
select gender,max(score),min(score),avg(score) from student where name!=“李四” group by gender;

- 先根据where筛选,再对筛选后的数据分组,再聚合查询
having(先聚合再筛选)
若想先聚合查询再筛选,需要用having 代替where
select gender,max(score),min(score),avg(score) from student group by gender having min(score) > 70;
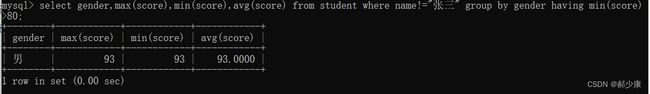
也可以先where筛选再聚合再having筛选(having对聚合结果筛选)
select gender,max(score),min(score),avg(score) from student where name!=“张三” group by gender having min(score) >80;
- 先把张三筛除,再分组聚合,再筛除min(score)<80的
联合查询
笛卡尔积
联合查询也叫多表查询,先把多张表的数据笛卡尔积,然后再进行查询。下面就演示一下如何笛卡尔积。
- 将两张表中数据排列组合得到一个新表,新表列数是原两张表列数之和,行数是原两张表行数之积。(这个就叫笛卡尔积)
- sql语句 :select * from 表1,表2;
- 如果原来的表很大,再笛卡尔积,得到新表就更大,这个过程比较低效,可能会把服务器搞卡。所以要尽量避免大数据量的笛卡尔积
- 新表中,可以明显看出有些记录是无效的(两个classId不相等),所以应该过滤掉无效数据。(两张表中的classId相等就称为连接条件)
- 将两张或多张表笛卡尔积,然后过滤掉无效数据,得到有效数据表,这个过程就是联合查询。
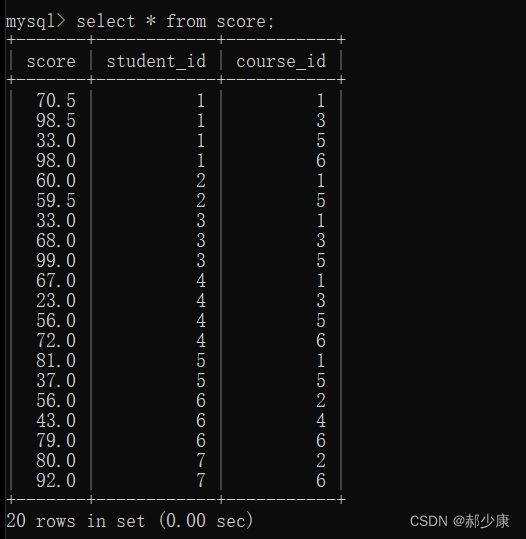
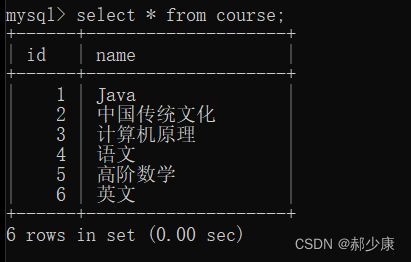
下面我们先构造几张表:
- 学生表
- 班级表
- 成绩表
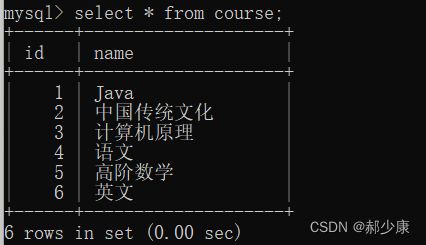
- 课程表
有了这几张表,下面进行多表查询
内连接
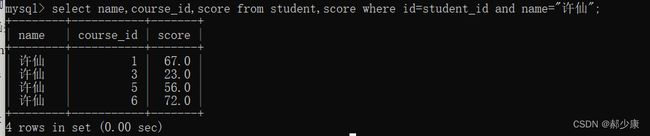
1.查询许仙同学成绩
(1)select * from student,score; (笛卡尔积后的表)
(2) select * from student,score where id=student_id;(筛选掉无效数据)
(3)select * from student,score where id=student_id and n查询ame=“许仙”;(只找许仙同学)
(4)select name,course_id,score from student,score where id=student_id and name=“许仙”;(只显示必要的字段)
- 根据这几步就可以找到许仙同学各科成绩
2.查询每个同学总成绩
select name,sum(score) from student,score where student.id=score.student_id group by name;
- 这里我们发现这个表里少了老外学中文(id=8),因为我们指定的两张表连接条件为(student.id=score.student_id),而student表中有id为8,而score表中没有student_id=8,所以这种情况,我们只找符合连接条件的筛选出来(这种情况叫做内连接)
3.查询每个同学的各科成绩
三张表联合查询
select student.name,course.name,score from student,score,course where student.id=score.student_id and score.course_id = course.id;
- 查询结果中依然没有我们的老外学中文这名同学,因为score中没有这名同学的id (内连接)
外连接
外连接分为左外连接和右外连接
左外连接
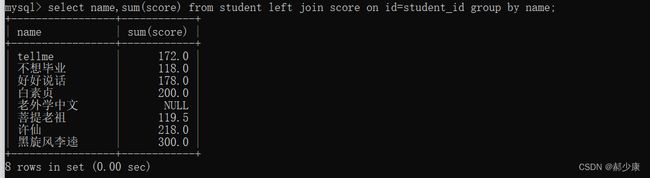
select name,sum(score) from student left join score on id=student_id group by name;
- 可以看到这里老外学中文出现了,但是由于score表中没有这个同学的id,所以他的总分是NULL。
- 左外连接:左表完全显示+显示重合部分
右外连接
select 列名 from 表1 right join 表2 on 条件;
- 对于右外连接,右表完全显示+显示重合部分
自连接
显示所有“计算机原理”成绩比“Java”成绩高的学生 :
计算机原理id:3 Java id:1
计算机原理成绩和Java成绩 都在同一列,是行与行之间的比较,所以可以使用自连接(一张表与自己进行笛卡尔积),将行与行之间的比较转换为列与列之间的比较。
select * from score as c1,score as c2 where c1.course_id=1 and c2.course_id=3 and c1.student_id=c2.student_id and c2.score>c1.score;
筛选条件为:对于一条记录:左右表学生id相同,课程id分别为1和3,id为3的表中score比id为1的表中score高
子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
单行子查询:返回一行记录的子查询
案例: 查询与“不想毕业” 同学的同班同学
select name from student where class_id=(select class_id from student where name=“不想毕业”);
多行子查询:返回多行记录的子查询
案例:查询“语文”或“英文”课程的成绩信息
select course_id, score from score where course_id in (select id from course where name=“语文” or name=“英文”);
- 注意:这里用的是in,并且子查询需要加括号
合并查询
在实际应用中,为了合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用集合操作符 union,union all。使用UNION和UNION ALL时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致
select * from course where id<3 union select * from course where name=‘英文’;
- 这种方式对于相同记录去重
select * from course where id<3 union all select * from course where name=‘英文’;
- 这种方式对于相同记录不去重