MyBatis-Plus之注解
MyBatis-Plus之注解
- 1.0 MyBatis-Plus之注解 @TableName
-
- 1.1 扩展配置指定表名
- 2.0 注解 @TableId
-
- 2.1 @TableId 将属性对应的字段指定为主键
- 2.2 @TableId(value="uid")
- 2.2 @TableId(value="uid",type= IdType.AUTO)
- 2.3 通过全局配置实现自增ID(全局)
- 2.4 扩展:雪花算法
- 2.5 @TableField("user_name")
- 2.6 @TableLogic
-
- 2.6 实现逻辑删除 @TableLogic;
文章顺序及整体目录可查看(点我即可)
1.0 MyBatis-Plus之注解 @TableName
我们现在指定数据库表和mappr的关联在是在mapper接口中引入的user进行的绑定;

如果存在的实体和我们的表名不一样的话我们怎么设置呢?
今天我们来解决这个问题!
在实体类中通过@TableName设置指定的表名。这样就可以根据指定的表名去操作对应的数据库;
mapper依然指定的是user;

我们在实体类中指定表名@TableName("t_user")
1.1 扩展配置指定表名
当然我们在使用user实体类添加的话,可能也会遇到比较多的实体加起来会比较麻烦,这个时候我们可以去配置下;
我们这个时候把user中tableName删除;
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#加入mybatis 日志查看执行语句sql语句
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
#为用户所有的实体类配置 前缀 所有的表的都会加上 t_
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: t_
执行依旧是ok的;
2.0 注解 @TableId
2.1 @TableId 将属性对应的字段指定为主键
比如在mapper中,他只能识别id为主键,并设置为自增;这个时候我们的主键比如不叫id的时候就会导致,mapper报错;此时我们就会用到
@TableId 注解:将属性对应的字段指定为主键
2.2 @TableId(value=“uid”)
当我们实体的id为id的时候,数据库却为uid 我们可以指定@TableId(value="uid") ;来指定主键的字段;
@TableId(value="uid") 可缩写为: @TableId("uid")

2.2 @TableId(value=“uid”,type= IdType.AUTO)
@TableId(value="uid",type= IdType.AUTO)中的type是用来设置主键生成策略的;默认是雪花算法;
查看代码:TableId
/*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2020, baomidou ([email protected]).
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not
* use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of
* the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
* WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
* License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under
* the License.
*/
package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 表主键标识
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2016-01-23
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface TableId {
/**
* 字段值(驼峰命名方式,该值可无)
*/
String value() default "";
/**
* 主键ID
* {@link IdType}
*/
IdType type() default IdType.NONE;
}
/*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2020, baomidou ([email protected]).
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not
* use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of
* the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
* WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
* License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under
* the License.
*/
package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation;
import lombok.Getter;
/**
* 生成ID类型枚举类
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2015-11-10
*/
@Getter
public enum IdType {
/**
* 数据库ID自增
*/
AUTO(0),
/**
* 该类型为未设置主键类型(注解里等于跟随全局,全局里约等于 INPUT)
*/
NONE(1),
/**
* 用户输入ID
* 该类型可以通过自己注册自动填充插件进行填充
*/
INPUT(2),
/* 以下3种类型、只有当插入对象ID 为空,才自动填充。 */
/**
* 分配ID (主键类型为number或string),
* 默认实现类 {@link com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.incrementer.DefaultIdentifierGenerator}(雪花算法)
*
* @since 3.3.0
*/
ASSIGN_ID(3),
/**
* 分配UUID (主键类型为 string)
* 默认实现类 {@link com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.incrementer.DefaultIdentifierGenerator}(UUID.replace("-",""))
*/
ASSIGN_UUID(4),
/**
* @deprecated 3.3.0 please use {@link #ASSIGN_ID}
*/
@Deprecated
ID_WORKER(3),
/**
* @deprecated 3.3.0 please use {@link #ASSIGN_ID}
*/
@Deprecated
ID_WORKER_STR(3),
/**
* @deprecated 3.3.0 please use {@link #ASSIGN_UUID}
*/
@Deprecated
UUID(4);
private final int key;
IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
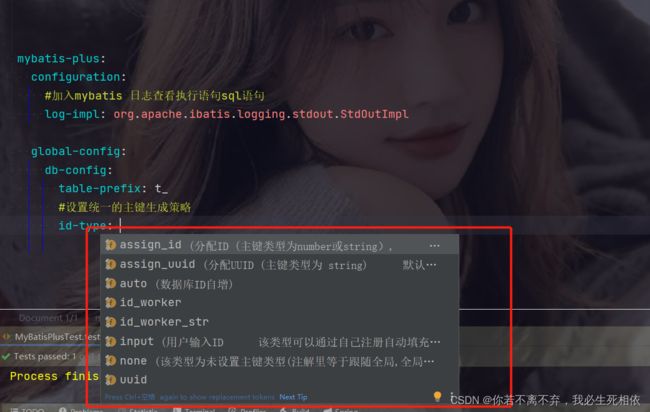
2.3 通过全局配置实现自增ID(全局)
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#加入mybatis 日志查看执行语句sql语句
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: t_
#设置统一的主键生成策略
id-type: auto
大家根据自己的要求去设置具体的生产策略;
#设置统一的主键生成策略
id-type: auto
2.4 扩展:雪花算法


分库分表实现可查看:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42055933/article/details/126375606?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
此处简单理解即可;
2.5 @TableField(“user_name”)
@TableField("user_name"):设置普通字段和数据库表之间的关;

2.6 @TableLogic
物理删除:真实删除,将对应数据从数据库中删除,之后查询不到此条被删除的数据
逻辑删除:假删除,将对应数据中代表是否被删除字段的状态修改为“被删除状态”,之后在数据库中仍旧能看到此条数据记录
使用场景:可以进行数据恢复
2.6 实现逻辑删除 @TableLogic;
@TableLogic 加在实体类上面就是逻辑删除,并非正在的删除功能;
@TableLogic
private int isDelect;
我们执行删除试下:
@Test
public void testDelectBatchIds(){
//通过id中批量删除
List<Long> longs = Arrays.asList(1L, 2L);
int deleteBatchIds = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(longs);
if (deleteBatchIds>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
System.out.println("deleteBatchIds"+deleteBatchIds);
}
他只是修改了我们的值,并没有真正的进行删除;
==> Preparing: UPDATE t_user SET is_delect=1 WHERE uid IN ( ? , ? ) AND is_delect=0
==> Parameters: 1(Long), 2(Long)
<== Updates: 2
我们来执行下查询全部看下:
/**
* 查询全部
*/
@Test
public void testSelectList(){
//通过条件构造器查询一个list集合,若没有条件则可设置null
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}