SpringBoot_开发常用篇_测试
测试
1.测试环境临时属性设置
怎么给测试类添加临时属性?
之前学习的在yml配置属性
yml:
test:
prop: testValue
测试
@SpringBootTest
public class PropertiesAndArgs {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testPro(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
数据读取成功!,将yml的数据注释掉,在@SpringBootTest注解上配置临时属性
1.1(通过properties属性配置)临时属性
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
public class PropertiesAndArgs {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testPro(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
注意:临时属性和yml中属性都存在的画,临时属性起作用。
1.2(通过args属性配置)临时命令行参数
@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue1"})
public class PropertiesAndArgs {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testPro(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
注意,二者同时出现,命令行高于properties
2.测试环境临时添加bean
比如在测试环境中添加分页插件的bean辅助测试。
这里为了方便 瞎几把写了一个bean
@Configuration
public class StrConfig{
@Bean
public String dosome(){
return "test bean";
}
}
使用注解@Import导入测试环境中的配置类
@SpringBootTest
@Import(StrConfig.class)
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Autowired
private StrConfig strConfig;
@Test
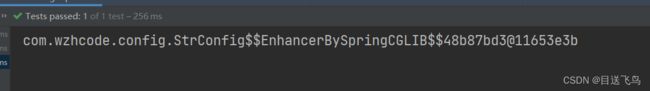
void testConfigImport(){
System.out.println(strConfig);
}
}
3.测试类中启动web
3.1端口问题(默认为NONE)
@SpringBoot的webEnvironment属性
SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.None是不启动(默认)
SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT是按照定义的端口启动
SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT按照随机端口启动
3.2虚拟请求
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc//开启mvc虚拟调用
public class WebTest {
@Test
void testWeb2(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
//模拟请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
//执行请求
mvc.perform(builder);
}
}
MockMvcRequestBuilders的get/post…等方法写uri
通过mvc的perform执行请求
3.3验证虚拟请求
- 匹配相应状态
使用结果校验器MockMvcResultMatchers,,
@Test
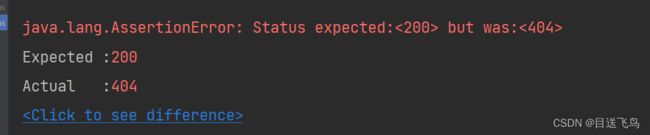
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books1");
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
//设置预期值 与真实值比较 成功-通过测试 失败-测试失败
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();//可以通过status()拿到调用的预期值
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();//通过status.isOk();可以得到本次调用成功的预期---200
//添加预期值到本次调用过程进行匹配
actions.andExpect(ok);
}
- 匹配响应体
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
//设置预期值 与真实值比较 成功-通过测试 失败-测试失败
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();//拿到测试状态
ResultMatcher res = content.json("{\"name\":\"水浒传\",\"price\":1000,\"description\":\"中国古代农民起义小说\"}");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程进行匹配
actions.andExpect(res);
}
- 匹配响应体(jason)
调整Controller
@GetMapping
public Book getById(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("水浒传");
book.setPrice(1000);
book.setDescription("中国古代农民起义小说");
return book;
}
测试
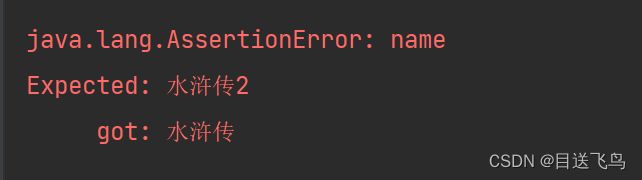
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
//设置预期值 与真实值比较 成功-通过测试 失败-测试失败
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();//拿到测试状态
ResultMatcher res = content.json("{\"name\":\"水浒传2\",\"price\":1000,\"description\":\"中国古代农民起义小说\"}");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程进行匹配
actions.andExpect(res);
}
- 匹配响应头
@Test
void testContentType(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
//设置预期值 与真实值比较 成功-通过测试 失败-测试失败
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type","application/jason");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程进行匹配
actions.andExpect(contentType);
}
3.4测试数据事务回滚
不想将测试数据留在表中。如何呢?
使用MP快速生成dao和service。
使用注解@Transactional开启事务,加了该注解实际上默认添加了@Rollback(true),就是默认回滚。,如果添加@Rollback(false),那么就不会回滚。

3.5测试数据随机值
测试数据写死不好,最好写成随机值。springboot提供了处理随机值的方法,当然不仅仅只在测试中可以写!
- 在yml文件中
testcase:
book:
id: ${random.int(5,10)}#这里表示5~10内的整数
name: ${random.value}
uuid: ${random.uuid}
publishTime: ${random.long}
- 用实体类封装
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "testcase.book")
public class BookCase {
private int id;
private String name;
private String uuid;
private long publishTime;
}
使用@Componet将交由容器管理,使用@Data简化代码,使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix=“testcase.book”)用来将yml的数据封装到对应属性中。测试结果如下:
![]()
在测试类中拿到Spring容器
实现ApplicationContextAware接口及setApplicationContext方法即可
@SpringBootTest
public class BeanTest implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Test
void beanTest(){
SimpleDateFormat sim = applicationContext.getBean(SimpleDateFormat.class);
System.out.println(sim.format(new Date()));
}
}