前端中的图形库
图形库
SVG
SVG的概念和引入方式
1.SVG 指的是可伸缩矢量图形(Scalable Vector Graphics),用来定义用于网络的基于矢量的图形,使用 XML 格式定义图形。SVG 图像在放大或改变尺寸的情况下其图形质量不会有所损失,是万维网联盟的标准。
2.SVG 与诸如 DOM 和 XSL 之类的 W3C 标准是一个整体。 2003 年一月,SVG 1.1 被确立为 W3C 标准。与其他图像格式相比,使用 SVG 的优势有以下几点:
- 可被非常多的工具创建、读取和修改
- 与JPEG和GIF图像比起来尺寸更小,压缩性更强
- 可在任何的分辨率下被高质量地打印,并可在图像质量不下降的情况下被放大
- 图像中的文本是可选的,还可被搜索(很适合制作地图)、索引、脚本化
- 可以与Java技术一起运行,有开放的标准,并且是纯粹的 XML
3.SVG文件,用.svg后缀来保存:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
// standalone="no"意味着SVG文档会引用一个外部文件——这里是DTD文件
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
//该DTD位于W3C,含有所有允许的SVG元素。
<svg width="100%" height="100%" version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
//根元素,width 和 height 属性可设置此 SVG 文档的宽度和高度,version定义所使用的SVG版本,xmlns定义SVG命名空间
<circle cx="200" cy="100" r="50" stroke="red" stroke-width="2" fill="green"/>
</svg>
4.SVG引用方式
方式一:用img引入SVG文件
<img src="1svg.svg"/>
方式二:用样式将SVG做背景
<div style="height:200px; width:200px; background:url(1svg.svg) no-repeat"></div>
方式三:用框架将SVG引入
<iframe src="1svg.svg"></iframe>
方式四:在html页面中书写svg(HTML5技术,命名空间必须有)
<div id="div1">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="100%" height="100%">
<circle cx="100" cy="100" r="40" fill="red" />
</svg>
</div>
img在你设置边框的时候,边框是和模型的一部分,设置边框后,盒子的宽度会增加2倍的边框宽。
svg在设置边框时,图形的大小只会增加边框宽度的一半。也就是说设置了边框宽度为10px,但事实上5px的边框向外扩张,5px的边框向内容区扩展。
5.SVG绘制的设置,可以用属性或css样式设置:
- fill填充色:fill=“white”/fill:white;
- fill-opacity填充透明度:fill-opacity=“0.5”/fill-opacity:0.5;
- stroke边框色:stroke=“black”/stroke:black;
- stroke-width边框宽:stroke-width=“5”/stroke-width:5;
- stroke-opacity边框透明度:stroke-opacity=“0.5”/stroke-opacity:0.5;
- opacity整个元素的透明值:opacity=“0.5”/opacity:0.5;
SVG绘制样式
SVG图形绘制
1.SVG图形绘制语法:
- circle(绘制圆形)——属性参数:cx(圆心X轴坐标)、cy(圆心Y轴坐标)、r(半径)
<circle cx="" cy="" r="" fill="" />
//cx和cy默认值为0
- ellipse(椭圆)——属性参数:cx(圆心X轴坐标)、cy(圆心Y轴坐标)、rx(X轴半径)、ry(Y轴半径)
<ellipse cx="" cy="" rx="" ry="" fill="" />
//rx和ry的值相等时即是圆形
-
rect(圆角矩形)——属性参数:width(宽度)、height(高度)、x(左上角X轴坐标)、y(左上角Y轴坐标)、rx(圆角X轴半径)、ry(圆角Y轴半径,省略时为半径为rx的正圆圆角)
<rect x="" y="" width="" height="" rx="" ry="" stroke="" stroke-width="" /> //注意:边框的宽度同时向内外延伸 -
line(画线,线是边框不能用fill填充色)——属性参数:x1(起点X轴坐标)、y1(起点Y轴坐标)、x2(终点X轴坐标)、y2(终点Y轴坐标)
<line x1="" y1="" x2="" y2="" stroke="" stroke-width="" /> //stroke默认白色 -
polyline(折线)——属性参数:points(折点设置)、必须设置fill='transparent’去掉填充
<polyline points="" fill="transparent" stroke="" /> //points的值为坐标对,如:10,10 10,50 50,50 50,100 100,100 100,150polygon(多边形)——属性参数:同上,不去掉填充
<polyline points="" fill="red"/>
SVG文字
text(文字)——属性参数:x(文字X轴坐标)、y(文字Y轴坐标)、font-size(字体大小)、font-family(文字样式)、text-anchor(对齐点,坐标在文字middle/start/end哪个位置)
<text x="" y="" text-anchor="" fill="" >文字内容</text>
//文字用填充色
SVG图片
image(图片)——属性参数:x(图片X轴坐标)、y(图片Y轴坐标)、width(图片宽)、height(图片高)、xlink:href(图片地址)
<image x="" y="" width="" height="" xlink:href=""/>
//这里图片不会变形,会按照width和height最小比例进行缩放
SVG路径
path(路径,单标签):path是SVG基本形状中最强大的一个,它能创建包括其他基本形状在内的所有形状。如矩形、圆形、椭圆、折线形、多边形,以及贝塞尔曲线、2次曲线等曲线。用属性d来定义路径点,它是一个命令+参数的序列。命令包括:
- M(moveto)/L(lineto):画笔移至某点/画笔从上个点绘制到当前点位
- H(horizontal lineto)/V(vertical lineto):绘制水平线/绘制垂直线
- C(curveto)/S(smooth curveto):三次贝塞尔曲线/简写的三次贝塞尔曲线命令
- Q(quadratic Bézier curve)/T(smooth quadratic Bézier curveto):二次贝塞尔曲线/简写的二次贝塞尔曲线命令
- A(elliptical Arc):绘制弧形
- Z(closepath):闭合路径(从当前位置绘制到起点)
<path d="M50 50 L150 150 L50 150" fill="red"/>
//大写的命令代表绝对位置(参照左上0,0点的位置),填充时无需设置Z闭合
<path d="M50 150 h100 v-50 Z" stroke="red" stroke-width="2" fill="transparent"/>
//小写的命令代表相对位置(相对于上个点增加或减少多少)
过于复杂的图往往是通过图像转换成path代码的:转换网址
SVG滤镜
SVG模糊和阴影滤镜
1.之前我们学习了css的滤镜,通过filter的值修改元素的效果,SVG也可以设置滤镜,不但可以在SVG中使用,部分甚至可以配合css的filter在HTML中使用。SVG中的滤镜在filter元素中定义,filter元素具有必需的id属性,用于标识滤镜,然后指向要使用的滤镜。SVG的滤镜有很多,用一些常用的举例说明。
2.feGaussianBlur:用于创建模糊效果
<filter id="f1" x="0" y="0">
//定义滤镜,获得f1标识,在SVG的filter属性或元素css的filter样式中使用
<feGaussianBlur in="SourceGraphic" stdDeviation="15" />
//in属性决定创建效果;stdDeviation决定了模糊量
</filter>
<rect width="90" height="90" stroke="green" stroke-width="3" fill="yellow" filter="url(#f1)" />
3.eOffset:用于创建阴影效果,拍摄SVG图形(图像或元素)并将其在xy平面中偏移,再用feBlend叠加到原图中,如果需要模糊阴影则将feGaussianBlur也设置上,用feColorMatrix将影子的颜色向黑色变化
<filter id="f1" x="0" y="0" width="200%" height="200%">
<feOffset result="offOut" in="SourceGraphic" dx="20" dy="20" />
//dx和dy,x轴和y轴偏移距离,将in的值改成SourceAlpha可以变成黑色影子(无论图形什么颜色),如果设置feColorMatrix可以让颜色向接近黑色变化
<feColorMatrix result="matrixOut" in="offOut" type="matrix" values="0.2 0 0 0 0 0 0.2 0 0 0 0 0 0.2 0 0 0 0 0 1 0" />
<feGaussianBlur result="blurOut" in="matrixOut" stdDeviation="10" />
<feBlend in="SourceGraphic" in2="blurOut" mode="normal" />
</filter>
<rect width="90" height="90" stroke="green" stroke-width="3" fill="yellow" filter="url(#f1)" />
SVG渐变滤镜
1.linearGradient:用于定义线性渐变,用stop定义线性渐变的颜色点。线性渐变可以定义为水平,垂直或角度渐变:当y1和y2相等且x1和x2不同时,将创建水平渐变;当x1和x2相等且y1和y2不同时,将创建垂直渐变;当x1和x2不同且y1和y2不同时,将创建角度渐变。
<linearGradient id="grad1" x1="0%" y1="0%" x2="100%" y2="0%">
// x1,x2,y1,y2 属性定义渐变的开始和结束位置
<stop offset="0%" style="stop-color:rgb(255,255,0);stop-opacity:1" />
//offset为该颜色点在开始到结束的位置
<stop offset="100%" style="stop-color:rgb(255,0,0);stop-opacity:1" />
//style的stop-color和stop-opacity用于设置颜色和透明度
</linearGradient>
<ellipse cx="200" cy="70" rx="85" ry="55" fill="url(#grad1)" />
<text fill="#ffffff" font-size="45" font-family="Verdana" x="150" y="86">SVG</text>
2.radialGradient:用于定义径向渐变,用stop定义线性渐变的颜色点。cx,cy为最外层中心(决定形状,一般为50%,50%即中心点),fx,fy为最内层中心(渐变中心点,要设置在图形内)
<radialGradient id="grad1" cx="50%" cy="50%" r="50%" fx="50%" fy="90%">
<stop offset="0%" style="stop-color:red;stop-opacity:1" />
//offset的值决定了梯度,0%即最内层
<stop offset="50%" style="stop-color:green;stop-opacity:0.5" />
<stop offset="100%" style="stop-color:blue;stop-opacity:1" />
//100%即最外层
</radialGradient>
<ellipse cx="200" cy="70" rx="85" ry="55" fill="yellow" />
<text fill="url(#grad1)" font-size="55" font-family="Verdana" x="140" y="90" >SVG</text>
SVG变形和分组
1.SVG变形与css3的变形相似,只不过是写在SVG标记的transform属性上,但是相对于SVG根元素的0,0点,且不能加单位。
- translate:位移
<rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" transform="translate(30,40)" />
-
rotate:旋转
<rect x="-50" y="-50" width="100" height="100" transform="translate(100 100) rotate(45)" /> //为了让其以中心点旋转,我们需要把0,0点设置在其中心点上,然后位移到需要的位置,再旋转 -
skewX()和skewY():斜切
<rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" transform="skewX(30) skewY(30)" /> -
scale:缩放和翻转
<rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" transform="translate(100 100) scale(-0.5)" /> //负值也是翻转,但是由于中心点在0,0点,一样需要设置中心点防止位移
2.g(分组标签):是一个容器标签,用来组合元素,这样可以同时控制一组元素,比如执行变形的时候:
<g style="cursor:pointer" transform="translate(100 100) rotate(45) scale(-1,1)">
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="40" fill="yellow" stroke="red" stroke-width="3" />
<text x="0" y="8" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle"> 新卓越</text>
</g>
SVG动画
SVG基础动画
1.SVG元素不同于HTML的元素,没有办法用定位或边距来改变位置,但可以使用css3的animation样式来执行动画,除此以外SVG还提供了animate标记来设置动画,注意这是需要将SVG编辑设置成双标记,将animate变成它的子元素
2.animate的重要属性:
-
attributeName——需要动画的属性名称;
-
from/to——属性的初始值/终止值;values——动画每个设置点,两个值时与from和to的写法效果一致;
-
dur——动画时长;repeatCount——重复次数,默认一次,indefinite为无限循环
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="10"> <animate attributeName="x" values="10;150;10" dur="4s" repeatCount="indefinite"/> //values设置3个值且最后一个值等于第一个值比较适合循环 </rect> <rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="120"> <animate attributeName="width" from="100" to="240" dur="4s" repeatCount="3"/> </rect>
3.如果想让元素的更多属性具有动画效果,只要添加更多的animate元素到该元素内部即可。
<rect width="100" height="100" x="10" y="10" fill="red">
<animate attributeName="rx" values="0;25;0" dur="4s" repeatCount="indefinite" />
<animate attributeName="fill" values="red;blue;green;red" dur="4s" repeatCount="indefinite" />
</rect>
SVG变形动画
1.当我们的动画需要做旋转之类的效果时,animate标记明显满足不了,这时就是animateTransform登场的时候了。
2.animateTransform的重要属性:
- attributeName——需要动画的属性名称,只有"transform";type——变形动画类型,rotate(旋转)、scale(缩放)、translate(位移)、skewX(X轴方向偏移)、skewY(Y轴方向偏移);
- from/to——各有三个参数,分别为开始/结束角度,X轴开始/结束坐标,Y轴开始/结束坐标;
- dur——动画时长;repeatCount——重复次数,默认一次,indefinite为无限循环
3.将animateTransform设置在要执行变形动画的标记里:
<rect x="50" y="50" width="30" height="40" fill="blue" stroke="black" stroke-width="1" transform="rotation">
<animateTransform attributeName="transform" begin="0s" dur="5s" type="rotate" from="0 65 70" to="360 65 70" repeatCount="indefinite" />
//form和to的第二个第三个值起始就是旋转的中心点
</rect>
4.如果想让文字标记也有动画效果,可以用g标记将所有想执行动画的标记包装起来
<g>
<rect x="50" y="50" width="30" height="40" fill="blue" stroke="black" stroke-width="1" transform="rotation"/>
<text x="50" y="70" text-anchor="center" fill="white">文字</text>
<animateTransform attributeName="transform" begin="0s" dur="5s" type="rotate" from="0 65 70" to="360 65 70" repeatCount="indefinite" />
</g>
SVG路径动画
1.如果我们希望元素按照我们设计的路线执行动画就要用到animateMotion标记了,路径类似path的方式定义
2.animateMotion的重要属性:
- path——同path标记的d属性,设置一个动画的路径;
- dur——动画时长;repeatCount——重复次数,默认一次,indefinite为无限循环
- rotate——旋转方式,默认值不旋转,auto沿着内圈旋转,auto-reverse沿着外圈旋转
3.用animateMotion设置动画,为了方便看我们将对应的路径一起画了出来:
<path d="M 250,80 H 50 Q 30,80 30,50 Q 30,20 50,20 H 250 Q 280,20,280,50 Q 280,80,250,80ZM 250,80 H 50 Q 30,80 30,50 Q 30,20 50,20 H 250 Q 280,20,280,50 Q 280,80,250,80Z" stroke="red" fill="transparent"/>
<rect x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" fill="blue" stroke="black" stroke-width="1">
<animateMotion path="M 250,80 H 50 Q 30,80 30,50 Q 30,20 50,20 H 250 Q 280,20,280,50 Q 280,80,250,80Z" dur="3s" repeatCount="indefinite" rotate="auto">
</rect>
4.甚至我们可以用mpath直接把某个path图形当成路径
<path id="path1" d="M100,250 C 100,50 400,50 400,250" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2"/>
<path d="M-25,-12.5 L25,-12.5 L 0,-87.5 z" fill="yellow" stroke="red" stroke-width="7.06">
<animateMotion dur="6s" repeatCount="indefinite" rotate="auto">
<mpath xlink:href="#path1"/>
</animateMotion>
</path>
SVG的JS操作
<div style="width:500px;height:500px">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="100%" height="100%">
</svg>
</div>
<script>
var oSVG=document.getElementsByTagName('svg')[0];
var oCircle=createSVG('circle',{
"cx":"120",
"cy":"120",
"r":"50",
"fill":"blue"
});
oCircle.onclick=function(){
console.log('yes');
}
oSVG.appendChild(oCircle);
function createSVG(tagName,option){
var sXmls="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg";
var obj=document.createElementNS(sXmls,tagName);
for(var attr in option){
obj.setAttribute(attr,option[attr]);
}
return obj;
}
</script>
练习
//绘制六边形
<div class="div1">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="100%" height="100%">
<path d="M100 30 L140 60 L140 100 L100 130 L60 100 L60 60 Z" stroke="black" stroke-width="3px" fill="transparent"></path>
</svg>
</div>
//屏幕解锁静态效果
<div class="div1">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="100%" height="100%">
<circle cx="40" cy="40" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="120" cy="40" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="200" cy="40" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="40" cy="120" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="120" cy="120" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="200" cy="120" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="40" cy="200" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="120" cy="200" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
<circle cx="200" cy="200" r="25" fill="transparent" stroke="black" stroke-width="4px"/>
</svg>
</div>
//靶子效果
<div class="div1">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="100%" height="100%">
<g transform="translate(160 160)">
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="140" fill="red"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="120" fill="#fee4d3"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="100" fill="red"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="80" fill="#fee4d3"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="60" fill="red"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="40" fill="#fee4d3"/>
<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="20" fill="red"/>
//方式一
<path d="M0 -160 L0 160 Z" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="transparent"></path>
<path d="M-160 0 L160 0 Z" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="transparent"></path>
//方式二
<!-- <line x1="0" y1="-180" x2="0" y2="180" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" />
<line x1="-180" y1="0" x2="180" y2="0" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" /> -->
</g>
</svg>
</div>
Canvas
Canvas的概念
1.canvas是 HTML5 提供的一种新标签,它本身并不具备绘画能力,只是一个画布,一个容器。绘图能力是基于html5的getContext(“2d”)返回的CanvasRenderingContext2D对象(3d需要用到webgl)来完成的。
2.什么时候会用到canvas
- 游戏:canvas 在基于 Web 的图像显示方面比 Flash 更加立体、更加精巧,在流畅度和跨平台方面更强大。
- 可视化数据.数据图表化:比如:百度的 echart
- banner 广告:之前也是由 Flash 完成。而智能机时代,HTML5 技术能够在 banner 广告上发挥更巨大的作用。
- 模拟器/远程计算机控制/图形编辑器:用canvas可以实现这些原本不能在 Web 上控制的功能。
- 其他可嵌入网站的内容(活动页面、特效):图表、音频、视频,还有许多元素能够更好地与 Web 融合,且不需要任何插件。
- 完整的 canvas 移动化应用
3.与SVG的区别
- svg不依赖分辨率,支持事件处理器,最适合带有大型渲染区域的应用程序(比如谷歌地图),复杂度高会减慢渲染速度(任何过度使用 DOM 的应用都不快),不适合游戏应用;
- canvas依赖分辨率,不支持事件处理器,弱的文本渲染能力,能够以 .png 或 .jpg 格式保存结果图像,最适合图像密集型的游戏,其中的许多对象会被频繁重绘
4.创建一个canvas标记,看起来和img标签差不多,只是它只有两个可选的属性 width、heigth 属性,没有 src、alt 属性。不设置widht、height属性时,则默认 width为300、height为150,单位都是px。
也可以使用css属性来设置宽高,但是如宽高属性和初始比例不一致,他会出现缩放。
除非确实需要缩放,否则建议永远不要使用css属性来设置canvas的宽高。
<canvas id="c1" width="400" height="400"></canvas>
//设置绘图环境
var oC = document.getElementById('c1'); //获得画布
var oCG = oC.getContext('2d'); //注意:2d小写
Canvas绘制样式
canvas基本方法
canvas元素起点为左上角(0,0),x 向右增大,y 向下增大。所有元素的位置都相对于原点来定位。绘制canvas需要在2d对象上绘制路径(不会画出来),然后调用描边或填充才会画出来
oCG.fillStyle = color;
//设置填充颜色
oCG.strokeStyle = color;
//设置描边颜色
oCG.lineCap = "round";
//端点样式:butt(方形,默认)、round(圆角)、square(多出宽的一半)
oCG.lineJoin = "round";
//边界连接点样式:miter(直角,默认)、round(圆角)、bevel(斜角)
oCG.moveTo(x,y);
//移动画笔到x,y点
oCG.lineTo(x,y);
//绘制直线路径(从画笔上一个的位置绘制到x,y点)
oCG.beginPath();
//开始绘制新路径(以区分与之前的路径)
oCG.closePath();
//闭合该次绘制的最后位置和初始位置
oCG.stroke();
//描边,以线的方式画出绘制的路径
oCG.fill();
//填充,将闭合的路径内填充颜色
注意:
oCG.lineWidth="1"的线的宽度和oCG.lineWidth="2"的线的宽度相同,但是前者的线浅后者的线宽。这是因为:oCG.lineWidth=“1”;oCG.lineTo(20,20);oCG.stroke();的时候就会从(20,20)处向左延伸0.5px并且向右延伸0.5px按理说线的左右像素为19.5px和20.5px但是由于像素点为1px的整数所以实际上会将(20,20)处向左拉伸1px并且向右拉伸1px此时颜色变浅。左右像素为19px和21px,线宽为2px。
oCG.lineWidth="2"则是正常结果。
oCG.beginPath()是指从这里开始重新绘制另外一个路径,不会再重绘前面的路径,而OCG.closePath()则是指闭合路径。两个方法看上去是反义词,事实上只是两个不同的用途并非相反用途。
canvas图形绘制
//绘制矩形:x,y是矩形左上角坐标,width和height是尺寸
oCG.rect(x, y, width, height);
oCG.strokeRect(x, y, width, height);
//直接用描边画出来
oCG.fillRect(x, y, width, height);
//直接用填充画出来
oCG.clearRect(x, y, width, height);
//清除该矩形内的绘制的内容,相当于橡皮擦
//绘制圆弧:圆心到最右边点是 0 度,顺时针方向弧度增大,弧度和角度的转换公式:rad = deg*Math.PI/180
oCG.arc(x, y, r, sAngle, eAngel, anticlockwise);
//x,y是圆心坐标,r是半径,sAngle是起始弧度,eAngel是结束弧度,注意是弧度,anticlockwise是否是逆时针(true 是逆时针,false:顺时针)
oCG.arcTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, r);
//用起始点到x1,y1和x1,y1到x2,y2作为切线,用r作为半径画弧
canvas文字
绘制文字,填充字体用fillStyle设置fillText绘制;描边字体用strokeStyle设置strokeText绘制:
oCG.font = "18px bold 黑体";
// 设置字体
oCG.fillStyle = "#ff0";
// 设置颜色
oCG.textAlign = "center";
// 设置水平对齐方式
oCG.textBaseline = "middle";
// 设置垂直对齐方式
oCG.fillText("要写的文字", 100, 100);
// 绘制文字(参数:内容,指定位置x,y坐标)
textAlign:start(默认): 文本在指定的位置开始;end: 文本在指定的位置结束;center: 文本的中心被放置在指定的位置;left: 文本左对齐;right: 文本右对齐。
textBaseline:alphabetic(默认):文本基线是字母基线;top:文本基线是四线格的顶端;hanging:文本基线是悬挂基线;middle:文本基线是四线格的正中;ideographic:文本基线是表意字基线;bottom:文本基线是四线格的底端。
canvas图片
绘制图片:该方法也可以绘制视频或另一个画布,将图片对象换成视频/画布对象即可
var img = new Image(); //如图片未在dom中需先创建img对象
img.src = '图片路径';
img.onload = function (){ //图片加载成功后绘制图片
oCG.drawImage(img,sx,sy,swidth,sheight,x,y,width,height);
}
img是绘制的图片对象,sx,sy,swidth,sheight是原图切片,如果不设置就是用整张图片绘制,x和y是距离0,0点的距离,width和height是绘制大小(如果缺省就是等于原图大小)
//举个例子
oCG.drawImage(img,300,100,550,220,50,50,400,120);
//从原图(300,100)位置开始,截取宽550高220的尺寸。在canvas里(50,50)开始绘制图,大小为400*120
canvas绘制背景
设置背景图:同图片一样,不在dom中的图需要先加载
var img = new Image();
img.src = '图片路径';
img.onload = function (){ //图片加载成功后绘制背景图
oCG.fillStyle = oCG.createPattern(this,'repeat');
//用图片来绘制填充图像,平铺方式(repeat、repeat-x、repeat-y、no-repeat)
oCG.fillRect(0,0,300,300); //设置完成后可以用此填充图来绘制任何形状
}
保存设置
配置状态的保存和恢复(save和restore):是绘制复杂图形时必不可少的操作,类似js的函数作用域,在一个save和restore范围内的设置只对其内部生效:
oCG.save(); // 保存默认状态
oCG.fillStyle = 'red'
oCG.fillRect(15, 15, 120, 120);
oCG.save(); // 再次保存当前状态
oCG.fillStyle = '#FFF'
oCG.fillRect(30, 30, 90, 90);
oCG.restore(); // 重新加载之前的颜色状态,退出这次的save()操作
oCG.fillRect(45, 45, 60, 60);
oCG.restore(); // 加载默认颜色配置,退出这次的save()操作
oCG.fillRect(60, 60, 30, 30); // 使用加载的配置绘制一个矩形
变形和合成
1.和css一样,画布变形也是将要绘制的图形缩放、位移和旋转,但是画布变形的是整个画布,一旦设置所有后续绘制的新元素都被影响。让变形只对需要变形的绘制起效,就要用到save和restore方法。
- translate位移:移动canvas的原点到指定的位置
oCG.translate(x, y); //x轴和y轴的偏移值
- scale缩放:缩放canvas中要绘制的图形
oCG.scale(x, y); //x轴和y轴的缩放因子
- rotate旋转:旋转坐标轴
oCG.rotate(angle); //正值为顺时针,参数值为弧度
2.我们画多个图形时,肯定会出现重叠的情况,默认是后绘制的会覆盖原绘制的,我们可以通过设置合成(globalCompositeOperation)的值改变合成后的样子
oCG.globalCompositeOperation = type;
type的值:source-over(默认,新图覆盖原图)、source-in(仅显示重叠部分的新图)、source-out(仅显示未重叠部分的新图)、source-atop(显示重叠部分的新图和所有原图)、destination-over(原图覆盖新图)、destination-in(仅显示重叠部分的原图)、destination-out(仅显示未重叠部分的原图)、destination-atop(显示重叠部分的原图和所有新图)、lighter(同默认,重叠部分颜色叠加)、darken(同默认,重叠部分高亮)、lighten(同默认,重叠部分变暗)、xor(同默认,重叠部分透明)、copy(仅保留新图)
小例子
//绘制一个正方形
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByTagName('canvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
oCG.fillRect(100,100,150,150);
</script>
//绘制一个旋转45度的正方形
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByTagName('canvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
oCG.translate(175,175);
//将画布的原点移动到(175,175)的位置也就是原本正方形的中心点
oCG.rotate(45*Math.PI/180);
//将所作图形按照原点顺时针旋转45度
oCG.fillRect(-75,-75,150,150);
//既然原本的(175,175)充当了画布原点,那么原本的正方形的左上角点(100,100)就变成了(-75,-75)
</script>
//要求:绘制一个红色小方块,不断旋转的同时由小变大再由大变小
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByTagName('canvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
var scal=1;
var rota=1;
var flag=true;
//var change=0.01;
//oCG.globalCompositeOperation = "copy";
//有了这句可以代替oCG.clearRect()
setInterval(function(){
oCG.clearRect(0,0,oC.width,oC.height);
oCG.save();
oCG.translate(250,250);
//方法一
if(scal<2&&flag){
scal+=0.01;
}else{
scal-=0.01;
flag=false;
if(scal<=0.1){
scal+=0.01;
flag=true;
}
}
//方法二
// if(scal>2){
// change=-0.01;
//}else if(scal<=0){
// change=0.01;
//}
//scal+=change;
oCG.scale(scal,scal);
oCG.rotate((rota++)*Math.PI/180);
oCG.fillStyle="#f40";
oCG.fillRect(-75,-75,150,150);
oCG.restore();
},17)
</script>
canvas保存图片
1.我们可以将绘制好的canvas生成图片或保存下来,需要将生成的base64放在img的src属性或a的href属性中
2.toDataURL:把 canvas 绘制的内容输出成base64内容,参数为图片格式(image/png、image/jpeg)
方法一
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<a href="">aa</a>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByTagName('canvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
oCG.fillStyle="red";
oCG.arc(150,150,100,0,360);
oCG.fill();
var oA = document.querySelector("a");
oA.href = oC.toDataURL("image/png");
oA.download = "p.png"; //download为下载图片的名字
</script>
方式二
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<img src="" />
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByTagName('canvas')[0];
var img = document.querySelector("img");
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
oCG.fillStyle="red";
oCG.arc(150,150,100,0,360);
oCG.fill();
img.src = oC.toDataURL("image/png"); //注意toDataURL是画布方法,不是2d绘图环境的方法
</script>
3.配合html2canvas.js库,我们设置可以将一个html的部分转换成canvas,然后再生成图片或者下载
<style>
table,td{
border: 1px #000 solid;
background-color: orange;
}
td{
width: 120px;
height: 60px;
}
</style>
<table cellspacing="0">
<tbody>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<a href="">aa</a>
</tbody>
</table>
<script src="../canvastoimg.js"></script>
<script>
var oTable=document.getElementsByTagName('table')[0];
var oA=document.getElementsByTagName('a')[0];
new html2canvas(oTable).then(canvas=>{
let oImg=new Image();
oImg.src=canvas.toDataURL('image/png');
document.body.appendChild(oImg);
oA.href=canvas.toDataURL('image/png');
oA.download="my.png";
})
</script>
Canvas动画
1.canvas的动画并不是绘制的图形动起来了,而是通过不停的绘制清空来实现动画的。
2.实现动画帧的步骤:
- 清空canvas:在绘制每一帧动画之前,需要用clearRect()清空画布
- 保存canvas状态:如果在绘制的过程中会更改canvas的状态(颜色、移动了坐标原点等),又在绘制每一帧时都是原始状态的话,则需要保存canvas的状态
- 绘制动画图形:绘制你需要的动画帧
- 恢复canvas状态:绘制完成一帧之后恢复前面保存了的canvas状态
3.下面我们就画出了一帧,接着使用计时器重复上面过程:如setInterval()/setTimeout()/requestAnimationFrame()等方法,setTimeout()和requestAnimationFrame()需要递归,接着让每一帧画面都出现一些变化就实现了动画效果,如:
var x = 0,y = 0;
var timer = setInterval(function (){
oCG.clearRect(0,0,oC.offsetWidth,oC.offsetHeight);
oCG.fillRect(x++,y++,100,100);
if(x>oC.offsetWidth-100){
clearInterval(timer);
}
},50)
练习
电子时钟效果
几个注意点:
-
对于时来说:(走一圈360度24小时)
1小时时针走30度
对于分针来说1小时走了360度走了60分钟,对于时针来说1小时走了30度也走了60分钟,那么走1分钟时针走了(30/60)度。
-
对于分来说:(走一圈360度60分钟)
分针走了一分钟秒针就走了60秒。60分钟为一整圈,那么1分钟就走了6度。也就是说60秒走了6度。进而可以得出1分钟是6度;1秒钟是0.1度。
对于秒针来说1分钟走了360度走了60秒,对于分针来说1分钟走了6度也走了60秒,那么走1秒分针走了(6/60)度。
-
那么每分钟时针的角度(Hours30+Minutes/2-90)而不是(Hours30+Minutes/2)的原因是按照钟表来说将12点方向看成0度位置,可以写成(Hours30+Minutes/2);但是由于canvas画布12点方向是-90度,因此实际的计算公式为(Hours30+Minutes/2-90)。
-
oCG.arc(200,200,50,(Hours*30+Minutes/2-90)Math.PI/180,(Hours30+Minutes/2-90)*Math.PI/180,false);这种开始角度和终止角度绘制出来的图形是一个有偏向角度的直线。
//电子时钟效果
<canvas width="400" height="400" class="myCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByClassName('myCanvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
oCG.strokeStyle="black";
var Hours=0;
var Minutes=0;
var Seconds=0;
for(var i=0;i<60;++i){
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.moveTo(200,200);
oCG.arc(200,200,150,(i*6)*Math.PI/180,((i+1)*6)*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.stroke();
}
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.fillStyle="white";
oCG.arc(200,200,140,0,360*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.fill();
oCG.strokeStyle="orange";
for(var i=0;i<12;++i){
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.moveTo(200,200);
oCG.arc(200,200,150,(i*30)*Math.PI/180,(i*30)*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.stroke();
}
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.fillStyle="white";
oCG.arc(200,200,130,0,360*Math.PI/180,false);
//少写oCG.fill()就会有一些不同之处
oCG.fill();
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.fillStyle="black";
oCG.arc(200,200,5,0,360*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.fill();
setInterval(function(){
init();
},1000);
function init(){
oCG.clearRect(100,100,200,200);
//不加这里的oCG.beginPath()会出现问题。
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.fillStyle="black";
oCG.arc(200,200,5,0,360*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.fill();
var time=new Date();
Hours=time.getHours();
Minutes=time.getMinutes();
Seconds=time.getSeconds();
//下面的这三个oCG.beginPath()也很重要。如果不写可能会出现时针中有一根红色的细线,分针中也有根红色的细线。
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.strokeStyle="gray";
oCG.lineWidth="5";
oCG.moveTo(200,200);
oCG.arc(200,200,50,(Hours*30+Minutes/2-90)*Math.PI/180,(Hours*30+Minutes/2-90)*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.stroke();
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.strokeStyle="black";
oCG.lineWidth="3";
oCG.moveTo(200,200);
oCG.arc(200,200,80,(Minutes*6+Seconds/10-90)*Math.PI/180,(Minutes*6+Seconds/10-90)*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.stroke();
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.strokeStyle="#f40";
oCG.lineWidth="2";
oCG.moveTo(200,200);
oCG.arc(200,200,100,(Seconds*6-90)*Math.PI/180,(Seconds*6-90)*Math.PI/180,false);
oCG.stroke();
}
init();
</script>
//绘制视频
<video src="./Intermission-Walk-in_512kb.mp4" id="video" controls></video>
<canvas class="myCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByClassName('myCanvas')[0];
var oCG=oC.getContext('2d');
var video=document.getElementsByTagName('video')[0];
//必须是window.onload,此外video.onloadedmetadata也是可以的
window.onload = function (){ //图片加载成功后绘制图片
oC.width=video.videoWidth;
oC.height=video.videoHeight;
setInterval(function(){
oCG.clearRect(0,0,oC.offsetWidth,oC.offsetHeight);
oCG.drawImage(video,0,0);
},16.67);
}
</script>
//自制画笔功能
<canvas width="400" height="300" class="myCanvas"></canvas>
<br/>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入画笔的宽度" value="3"/>
<span>画笔的颜色:</span><input type="color" />
<script>
var oC=document.getElementsByClassName('myCanvas')[0];
var oCG = oC.getContext('2d');
var oWidth=document.getElementsByTagName('input')[0];
var oColor=document.getElementsByTagName('input')[1];
oCG.lineWidth=oWidth.value;
oCG.strokeStyle=oColor.value;
oC.onmousedown=function(e){
oCG.beginPath();
oCG.moveTo(e.pageX-oC.offsetLeft,e.pageY-oC.offsetTop);
document.onmousemove=function(ev){
oCG.lineTo(ev.pageX-oC.offsetLeft,ev.pageY-oC.offsetTop);
oCG.stroke();
}
document.onmouseup=function(){
oCG.closePath();
document.onmouseup=document.onmousemove=null;
}
}
oWidth.onchange=function(){
oCG.lineWidth=oWidth.value;
}
oColor.onchange=function(){
oCG.strokeStyle=oColor.value;
}
</script>
jCanvas
jCanvas的概念
1.js有jQuery库,canvas如果不做封装写起来也是很麻烦,且不能像对象一样操作。jCanvas就是一个基于jQuery的免费且开源的 HTML5的Canvas API。它能让你用原生的Canvas API来实现,并可以做更多的事情。你也可以将原生的Canvas API方法和jCanvas一起使用,draw()方法就可以这样使用。你还可以用自己的方法结合 extend()函数来扩展jCanvas的功能。
2.jCanvas需要依赖 jQuery才能正常工作,所以还要确保引入了 jQuery文件:
<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="js/jcanvas.js"></script>
jCanvas绘制样式
绘制矩形
drawRect()方法
$("canvas").drawRect({
fillStyle: 'steelblue', //设置填充色
strokeStyle: 'blue', //设置边框色
strokeWidth: 4, //设置边框宽
x: 150, //设置基点x轴位置
y: 100, //设置基点y轴位置
fromCenter: false, //基点是否为中心点(false为矩形左上角)
width: 200, //设置矩形宽
height: 100 //设置矩形高
});
绘制圆弧和圆
drawArc() 方法
$("canvas").drawArc({
fillStyle: 'steelblue',
strokeStyle: 'blue',
strokeWidth: 4,
x: 300, y: 100, //设置圆心x/y轴位置
radius: 50, //设置半径
ccw:true, //是否逆时针(false默认值为顺时针)
start: 0, end: 200 //设置起点/终点角度(0为12点位置)
});
链式操作
由于绘制对象是jQ对象,因此可以像jQ一样进行链式操作,绘制一个笑脸:
$("canvas").drawArc({ // draw the face
fillStyle: 'yellow',
strokeStyle: '#333',
strokeWidth: 4,
x: 300,
y: 100,
radius: 80
}).drawArc({ // draw the left eye
fillStyle: '#333',
strokeStyle: '#333',
x: 265,
y: 85,
radius: 5
}).drawArc({ // draw the right eye
fillStyle: '#333',
strokeStyle: '#333',
x: 335,
y: 85,
radius: 5
}).drawArc({ // draw the smile
strokeStyle: '#333',
strokeWidth: 4,
x: 300, y: 120,
radius: 30,
start: 110,
end: 250
});
绘制线条
drawLine()
$("canvas").drawLine({
strokeStyle: 'steelblue',
strokeWidth: 10,
rounded: true, //设置边界连接点是否为圆角
closed: true, //设置是否闭合路径
x1: 100, y1: 28, //设置第一个点坐标......
x2: 50, y2: 200,
x3: 300, y3: 200,
x4: 200, y4: 109
});
绘制文字
drawText()
$("canvas").drawText({
text: 'Canvas is fun', //文字内容
fontFamily: 'cursive', //字体
fontSize: 40, //字体大小
x: 290, y: 150,
fillStyle: 'lightblue',
strokeStyle: 'blue',
strokeWidth: 1
});
绘制路径
drawPath()方法。你可以用画线条和曲线同样的方式画箭头,但你必须提供一些箭头专有的属性
$("canvas").drawPath({
strokeStyle: '#000',
strokeWidth: 4,
x: 10,
y: 10,
//以(10,10)为canvas画布的原点
p1: { //当type="line"时其实就相当于绘制线条
type: 'line', //路径类型(常用的line-线、arc-圆弧、quadratic-二次曲线、vector-矢量)
x1: 100, y1: 100, x2: 200, y2: 100
},
});
//绘制箭头
$("canvas").drawPath({
strokeStyle: '#000',
strokeWidth: 4,
x: 10,
y: 10,
p1: { //第二部分
type: 'line',
startArrow: false, //是否有一个箭头画在路径的开始点。
endArrow: true, //是否有一个箭头画在路径的结束点
arrowRadius: 25, //箭头的每个尖端的长度
arrowAngle: 90, //箭头两个尖端的夹角
x1: 100,
y1: 100,
x2: 290,
y2: 100
},
p2: { //第三部分
type: 'line',
startArrow: false,
endArrow: true,
arrowRadius: 25,
arrowAngle: 90,
x1: 100,
y1: 100,
x2: 100,
y2: 250
}
});
绘制图片
drawImage()方法
$('canvas').drawImage({
source: $('#fish')[0], //绘制DOM已经存在的图片,或用'imgs/cat.jpg'绘制未加载的图片
x: 50,
y: 50,
fromCenter: false,
width: 100,
height: 100, //图片大小
shadowColor: '#222', //阴影颜色
shadowBlur: 3, //模糊距离
rotate: 40, //旋转角度
load (){ //未加载的图片可以设置
//加载图片后的代码,
}
});
该方法本来就是在图片加载成功之后才绘制的。
创建图层
addLayer()方法或layer属性,向画布添加了一个图层。
$('canvas').drawRect({
layer: true, //创建一个图层后绘制图形
name: 'myBox', //用来检索图层、删除图层或变动图层
fillStyle: '#585',
x: 100,
y: 100,
width: 100,
height: 50
});
jCanvas事件和动画
1.可以在任何jCanvas图层上绑定任意数量的jCanvas事件。jCanvas支持鼠标事件和触摸事件事件会和 图层API结合使用。
2.支持事件的方法:drawRect()、drawArc()、drawEllipse()、drawLine()、drawQuadratic()、drawBezier()、drawVector()、drawGraph()、drawPolygon()、、drawImage()、drawText()
3.支持的事件:click、dblclick、mousedown、mouseup、mousemove、mouseover、mouseout、dragstart、drag、dragstop、touchstart、touchend、touchmove
4.配合animateLayer执行动画效果
$('canvas').drawRect({
layer: true,
//绘制图层
fillStyle: '#6c0',
x: 100,
y: 100,
width: 100,
height: 80,
click (layer) {
//layer为图层对象
$(this).animateLayer(layer,{
rotate : layer.rotate+144
},400)
}, //参数:执行动画的图层对象、变化样式和动画时间
animatestart (layer){},
//动画开始时,要运行的代码
animate (layer, fx){},
//动画相关属性的动画fx(prop属性为执行动画的样式、start为初始值、now为当前值、end为结束值)的每个帧上运行这些代码
animateend (layer){}
//动画结束时,要运行的代码
});
jCanvas拖拽图层
1.利用属性draggable设置为true可以把一个图层变成可拖曳。
$('canvas').drawArc({
layer: true,
draggable: true,
fillStyle: '#36c',
x: 150,
y: 150,
radius: 50
}).drawRect({
layer: true,
draggable: true,
fillStyle: '#6c1',
x: 100,
y: 100,
width: 100,
height: 100
});
2.拖曳事件:通过定义dragstart、drag、dragstop和dragcancel为各种拖曳事件提供回调函数。
$('canvas').drawArc({
layer: true,
draggable: true,
fillStyle: '#36c',
x: 150,
y: 150,
radius: 50,
groups: ['shapes'],
//设置图层组,设置该值的图层即为同一组
dragGroups: ['shapes'],
//拖曳编组,当图层被拖曳时,同一编组中所有其它图层都会被拖动。
dragstart (layer) { },
// 在拖曳开始时要运行的代码
drag (layer) { },
// 当正在拖曳时要运行的代码
dragstop (layer) { },
// 在停止拖曳时要运行的代码
dragcancel (layer) { }
// 在把一个图层拖出画布时要运行的代码(拖拽过程中鼠标离开画布)
}).drawRect({
layer: true,
draggable: true,
fillStyle: '#6c1',
x: 100,
y: 100,
width: 100, h
eight: 100,
groups: ['shapes'],
dragGroups: ['shapes'] //设置与上面相同的组和拖拽编组
});
练习
//制作一个不断有不同颜色的圆圈有不透明变为透明的效果
<canvas width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script src="../jquery.js"></script>
<script src="./jcanvas.js"></script>
<script>
var index=0;
setInterval(function(){
index++;
$('canvas').drawArc({
layer:true,
name:'circle'+index, fillStyle:`rgb(${Math.random()*255},${Math.random()*255},${Math.random()*255})`,
x: Math.random()*$('canvas')[0].offsetWidth,
y: Math.random()*$('canvas')[0].offsetHeight,
radius: 5,
ccw:true,
start: 0,
end:360,
anmateend(layer){
$('canvas').removeLayer(layer.name);
}
}).animateLayer('circle'+index,{
opacity:0,
radius:50
},900)
},90)
</script>
ECharts数据可视化
ECharts的概念
数据可视化的目的是借助图形化清晰有效的传达与沟通信息,把数据从数字转换成图形,更好的揭示数据规律。ECharts,一个使用 JavaScript 实现的开源可视化库,可以流畅的运行在 PC 和移动设备上,兼容当前绝大部分浏览器(IE8/9/10/11,Chrome,Firefox,Safari等),底层依赖矢量图形库 ZRender,提供直观,交互丰富,可高度个性化定制的数据可视化图表。
ECharts用法
- 下载并引入echarts.js文件
- 准备具备大小的DOM容器
- 初始化echarts实例对象
- 指定配置项和数据(option)
- 将设置好的配置项赋予echarts实例对象
<script src="echarts.min.js"></script>
<div class="box"></div>
//设置容器(必须有大小)
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector(".box"));
//得到echarts实例对象
var option = {
//指定配置项和数据
//配置code
};
myChart.setOption(option);
//将配置项赋予echarts实例对象
ECharts的配置
option配置对象中包含很多需要配置的属性:
- title:标题。通过text属性设置图标标题(字符串格式)
- tooltip:提示框组件。通过trigger属性设置触发方式:‘item’——数据项图形触发,主要在散点图,饼图等无类目轴的图表中使用;‘axis’——坐标轴触发,主要在柱状图,折线图等会使用类目轴的图表中使用;‘none’——不触发
- legend:图例组件。通过data属性设置所有图例的项(数组格式)
- toolbox:工具箱组件。feature属性用于定义工具箱功能(对象格式,如设置saveAsImage:{}用于保存图片)
- grid:网格——坐标系内部分。left/right/bottom属性决定坐标系到容器左右下的距离(百分比字符串)。containLabel属性决定是否显示刻度标记(布尔值格式)
- xAxis:横坐标。用type属性控制坐标轴类型:‘value’——数值轴;‘category’——类目轴,必须同时设置data设置类目数据;‘time’——时间轴;‘log’——对数轴。data属性设置类目轴的具体数据(数组格式)。bounderyGap属性设置数据是在点中(true)/点上(false)。
- yAxis:纵坐标。同上
- series:系列图表类型,值为数组。每项为一个对象对应每个图例的图表类型,该对象中的属性为:name——图例名称;type——图例类型(‘line’:折线图;‘bar’:柱状图;‘pie’:饼状图;‘scatter’:散点图;‘radar’:雷达图;‘tree’:树图;‘map’:地图;‘graph’:关系图);stack——若设置并赋予相同的值则数据会发生堆叠(不交叉);data:具体数据(数组)
- color:图形颜色,值为数组
ECharts引入官网实例
1.首先在官网查找我们需要的类似实例,将其引入到HTML页面中,并根据需求定制图标。由于每个实例都需要初始化echarts实例对象和设置,因此需要用到立即执行函数来防止变量污染。
2.定制图表效果:根据我们的需要修改图表内容和样式,找到该实例的设置内容,按照配置属性修改(更详细的设置请查看官网的配置项手册)
3.图表自适应浏览器大小
window.onresize = function (){
myChart.resize();
}
练习
chart.js和Echarts(百度)的区别
- charts.js灵活性更高,需要掌握的语法知识更多,入手慢
- Echarts灵活性不高,可以使用现成的demo然后修改样式使用。入手快。
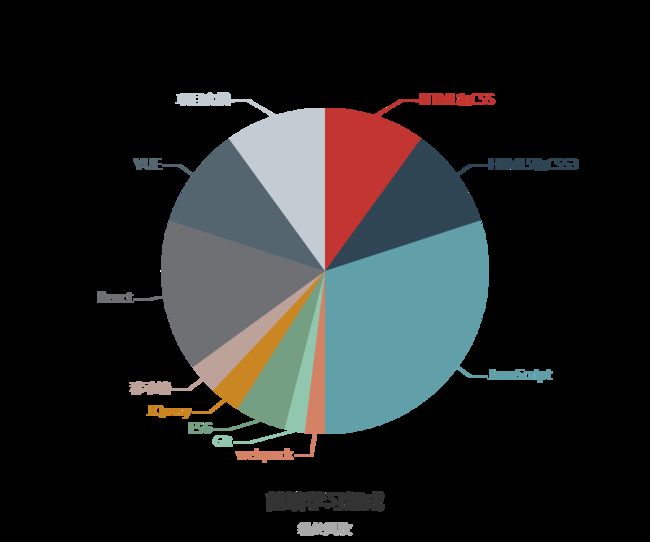
//做一个学习前端的Echarts图
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 500px;
}
</style>
<div class="box"></div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.6.2/echarts.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector(".box"));
var option={
title: {
text: '前端学习组成',
subtext: '纵使风吹',
left: 'center',
bottom:'0%'
},
tooltip: {
trigger: 'item'
},
legend: {
orient: 'vertical',
left: 'left',
},
series: [
{
name: '组成部分',
type: 'pie',
radius: '60%',
data: [
{value: 0.1, name: 'HTML和CSS'},
{value: 0.1, name: 'HTML5和CSS3'},
{value: 0.3, name: 'JavaScript'},
{value: 0.02, name: 'webpack'},
{value: 0.02, name: 'Git'},
{value: 0.05, name: 'ES6'},
{value: 0.03, name: 'JQuery'},
{value: 0.03, name: '移动端'},
{value: 0.15, name: 'React'},
{value: 0.1, name: 'VUE'},
{value: 0.1, name: '项目实战'},
],
emphasis: {
itemStyle: {
shadowBlur: 10,
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)'
}
}
}
]
}
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
如图所示: