C++ | 12天学好C++ (Day7)->结构图可视化、代码加通俗理解
看了这篇博客,将会学到C++的基本操作!(如果不敲代码,可能会一知半解)
12天学好C++ 系列(Day7)| 继承inheritance
第七天 - 221005
目录
第七天 - 221005
chapter 8 继承类
8.1.C++ 受保护的成员
8.2.C++ 继承中的访问模式
8.3.继承中的成员函数覆盖
8.4.继承中的成员访问可视化
8.5.继承中的类型关系可视化编辑
8.6.多类继承
总结
参考文献
chapter 8 继承类
继承是 C++ 中面向对象编程的关键特性之一。它允许我们从现有类(基类)创建一个新类(派生类)。
派生类继承了基类的特性,并且可以有自己的附加特性。例如,
class Animal {
// eat() function
// sleep() function
};
class Dog : public Animal {
// bark() function
}; 在这里,Dog类是从Animal类派生的。由于Dog是从 派生的Animal,因此 的成员Animal可以访问Dog。
示例 1:C++ 继承的简单示例
// C++ program to demonstrate inheritance
#include
using namespace std;
// base class
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout << "I can eat!" << endl;
}
void sleep() {
cout << "I can sleep!" << endl;
}
};
// derived class
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void bark() {
cout << "I can bark! Woof woof!!" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
// Create object of the Dog class
Dog dog1;
// Calling members of the base class
dog1.eat();
dog1.sleep();
// Calling member of the derived class
dog1.bark();
return 0;
} 结果
狗1(派生类的对象Dog)可以访问基类的成员Animal。这是因为Dog继承自Animal.
8.1.C++ 受保护的成员
当涉及到 C++ 继承时,访问修饰符protected尤其重要。
与private成员一样,protected成员在类之外是不可访问的。但是,它们可以被派生类和友元类/函数访问。
protected如果我们想隐藏一个类的数据,但仍希望该数据被其派生类继承,则需要number。
示例 2:受 C++ 保护的成员
// C++ program to demonstrate protected members
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// base class
class Animal {
private:
string color;
protected:
string type;
public:
void eat() {
cout << "I can eat!" << endl;
}
void sleep() {
cout << "I can sleep!" << endl;
}
void setColor(string clr) {
color = clr;
}
string getColor() {
return color;
}
};
// derived class
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void setType(string tp) {
type = tp;
}
void displayInfo(string c) {
cout << "I am a " << type << endl;
cout << "My color is " << c << endl;
}
void bark() {
cout << "I can bark! Woof woof!!" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
// Create object of the Dog class
Dog dog1;
// Calling members of the base class
dog1.eat();
dog1.sleep();
dog1.setColor("black");
// Calling member of the derived class
dog1.bark();
dog1.setType("mammal");
// Using getColor() of dog1 as argument
// getColor() returns string data
dog1.displayInfo(dog1.getColor());
return 0;
} 结果
变量类型是protected并且因此可以从派生类访问Dog。我们可以看到这一点,因为我们已经使用函数type在Dog类中进行了初始化setType()。
另一方面,private变量颜色无法在 中初始化Dog。
8.2.C++ 继承中的访问模式
使用public关键字从先前存在的基类继承类,也可以使用privateandprotected关键字来继承类。例如,
class Animal {
// code
};
class Dog : private Animal {
// code
};
class Cat : protected Animal {
// code
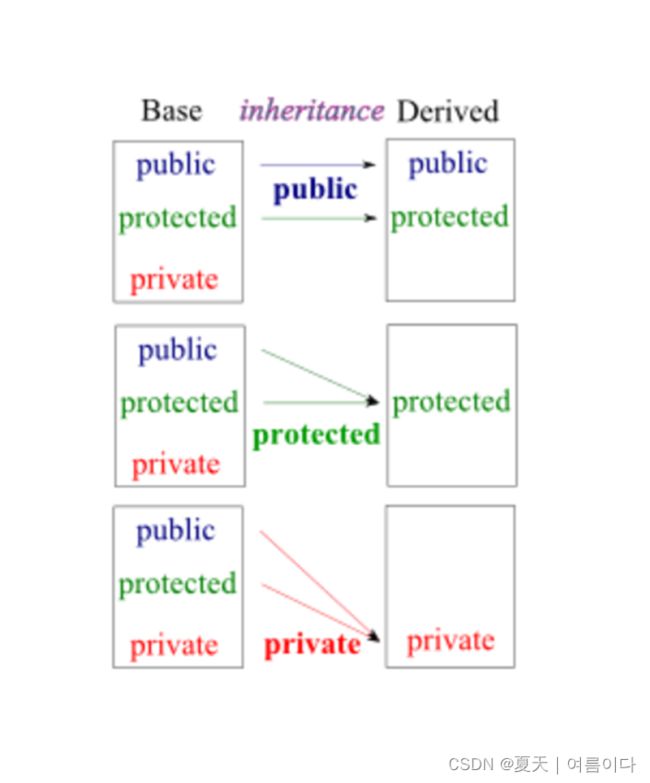
};可以派生类的各种方式称为访问模式。这些访问模式具有以下效果:
- public:如果派生类在
public模式下声明,则基类的成员会被派生类继承。 - private:在这种情况下,基类的所有成员都成为
private派生类的成员。 - protected:
public基类的protected成员成为派生类的成员。
基类的private成员总是private在派生类中。
8.3.继承中的成员函数覆盖
假设基类和派生类具有相同名称和参数的成员函数。
如果我们创建派生类的对象并尝试访问该成员函数,则调用派生类中的成员函数而不是基类中的成员函数。
派生类的成员函数覆盖基类的成员函数。
8.4.继承中的成员访问可视化
8.5.继承中的类型关系可视化
8.6.多类继承
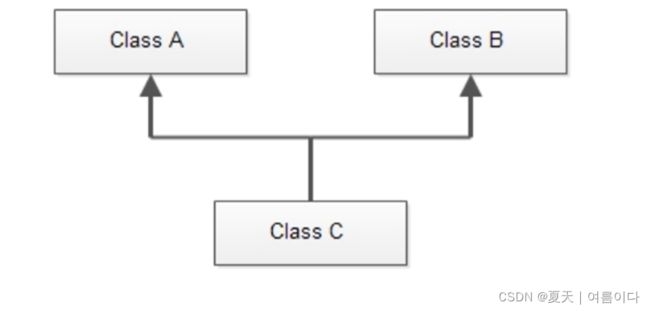
图显示了多个继承,其中类 C 派生自类 A 和类 B,彼此独立。
类 C 继承了它的基类 A 和 B 的所有成员。下面的程序段显示了类 C 如何从两个基类 A 和 B 公开派生。
class C : public A,public B {
//Implementation
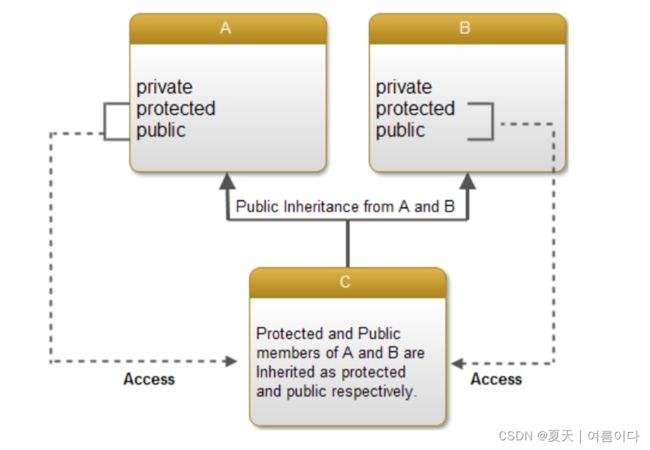
};每个基类成员的继承规则和访问说明符的用法与单继承相同。对每个基类成员的访问独立于对派生类所使用的其他基类成员的访问。例如:在上述派生中,基类 A 和 B 的公共成员作为公共成员继承,而受保护成员在派生类 C 中作为受保护成员继承。
因此,派生类的对象可以访问所有类的公共成员。可表示为:
总结
1.Private 不能从外部访问,protected 不能从外部访问,但可以从派生类访问,而 public 可以从任何地方访问。
2.在需要调试基类中的代码而不是在不使用继承的情况下到处进行时,测试和调试要容易得多。
参考文献
【1】C++ Inheritance
【2】https://cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/inheritance/
【3】C++ Tutorial: Private Inheritance - 2020
【4】Multiple Inheritance in C++ - Computer Notes
【5】Inheritance in c++ And It's types [Explained] with example program