【Matlab】基于特征的全景图像拼接(计算机视觉工具箱)
基于特征的全景图像拼接属于计算机视觉工具箱中的特征检测和提取部分。
文章目录
-
- 示例运行
-
- 1.加载图像
- 2.注册图像对
- 3.初始化全景图
- 4.创建全景图
- 自定义拼接
示例运行
该示例是基于特征的图像配准技术自动创建全景图(图像拼接)。
1.加载图像
此示例中使用的图像集包含建筑物的图片。这些都是用未经校准的智能手机相机拍摄的,方法是沿着地平线从左到右扫描相机,捕获建筑物的所有部分。
% Load images. 加载示例图像
buildingDir = fullfile(toolboxdir('vision'),'visiondata','building');
buildingScene = imageDatastore(buildingDir);
% Display images to be stitched. 图片组合在一起显示
montage(buildingScene.Files)
展示图像如下:
2.注册图像对
要创建全景图,请首先使用以下步骤注册连续的图像对:
- 检测和匹配I(n)和I(n−1)之间的特征;
- 估计几何变换T(n),即图像I(n)到I(n−1);
- 计算映射的转换I(n)进入全景图像作为T(n)*T(n-1)……*T(1)。
% Read the first image from the image set. 读取第一张图片
I = readimage(buildingScene,1);
% Initialize features for I(1) 初始化特征
grayImage = im2gray(I);
points = detectSURFFeatures(grayImage);
[features, points] = extractFeatures(grayImage,points);
% Initialize all the transformations to the identity matrix. Note that the
% projective transformation is used here because the building images are fairly
% close to the camera. For scenes captured from a further distance, you can use
% affine transformations. 初始化所有单位矩阵的变换。
numImages = numel(buildingScene.Files);
tforms(numImages) = projtform2d;
% Initialize variable to hold image sizes. 初始化变量以保存图像大小
imageSize = zeros(numImages,2);
% Iterate over remaining image pairs 迭代剩余的图像对
for n = 2:numImages
% Store points and features for I(n-1).
pointsPrevious = points;
featuresPrevious = features;
% Read I(n).
I = readimage(buildingScene, n);
% Convert image to grayscale.
grayImage = im2gray(I);
% Save image size.
imageSize(n,:) = size(grayImage);
% Detect and extract SURF features for I(n).
points = detectSURFFeatures(grayImage);
[features, points] = extractFeatures(grayImage, points);
% Find correspondences between I(n) and I(n-1).
indexPairs = matchFeatures(features, featuresPrevious, 'Unique', true);
matchedPoints = points(indexPairs(:,1), :);
matchedPointsPrev = pointsPrevious(indexPairs(:,2), :);
% Estimate the transformation between I(n) and I(n-1).
tforms(n) = estgeotform2d(matchedPoints, matchedPointsPrev,...
'projective', 'Confidence', 99.9, 'MaxNumTrials', 2000);
% Compute T(1) * T(2) * ... * T(n-1) * T(n).
tforms(n).A = tforms(n-1).A * tforms(n).A;
end
此时,所有转换都相对于第一个图像。这是一种对图像配准过程进行编码的便捷方法,因为它允许对所有图像进行顺序处理。但是,使用第一个图像作为全景图的开始并不能产生最美观的全景图,因为它往往会扭曲构成全景图的大多数图像。通过修改变换,使场景中心失真最小,可以创建更好的全景图。
首先使用 projtform2d 方法来查找每个转换的输出限制。然后,输出限制用于自动查找大致位于场景中心的图像。
% Compute the output limits for each transformation.
for i = 1:numel(tforms)
[xlim(i,:), ylim(i,:)] = outputLimits(tforms(i), [1 imageSize(i,2)], [1 imageSize(i,1)]);
end
接下来,计算每次变换的平均 X 限制,并找到位于中心的图像。此处仅使用 X 限制,因为已知场景是水平的。如果使用另一组图像,则可能需要同时使用 X 和 Y 限制来查找中心图像。
avgXLim = mean(xlim, 2);
[~,idx] = sort(avgXLim);
centerIdx = floor((numel(tforms)+1)/2);
centerImageIdx = idx(centerIdx);
最后,将中心图像的反变换应用于所有其他图像。
Tinv = invert(tforms(centerImageIdx));
for i = 1:numel(tforms)
tforms(i).A = Tinv.A * tforms(i).A;
end
3.初始化全景图
现在,创建一个初始的空全景图,所有图像都映射到其中。
使用该方法计算所有转换的最小和最大输出限制。这些值用于自动计算全景图的大小。outputLimits
for i = 1:numel(tforms)
[xlim(i,:), ylim(i,:)] = outputLimits(tforms(i), [1 imageSize(i,2)], [1 imageSize(i,1)]);
end
maxImageSize = max(imageSize);
% Find the minimum and maximum output limits.
xMin = min([1; xlim(:)]);
xMax = max([maxImageSize(2); xlim(:)]);
yMin = min([1; ylim(:)]);
yMax = max([maxImageSize(1); ylim(:)]);
% Width and height of panorama.
width = round(xMax - xMin);
height = round(yMax - yMin);
% Initialize the "empty" panorama.
panorama = zeros([height width 3], 'like', I);
4.创建全景图
使用 imwarp 将图像映射到全景图并使用vision、AlphaBlender将图像叠加在一起。
blender = vision.AlphaBlender('Operation', 'Binary mask', ...
'MaskSource', 'Input port');
% Create a 2-D spatial reference object defining the size of the panorama.
xLimits = [xMin xMax];
yLimits = [yMin yMax];
panoramaView = imref2d([height width], xLimits, yLimits);
% Create the panorama.
for i = 1:numImages
I = readimage(buildingScene, i);
% Transform I into the panorama.
warpedImage = imwarp(I, tforms(i), 'OutputView', panoramaView);
% Generate a binary mask.
mask = imwarp(true(size(I,1),size(I,2)), tforms(i), 'OutputView', panoramaView);
% Overlay the warpedImage onto the panorama.
panorama = step(blender, panorama, warpedImage, mask);
end
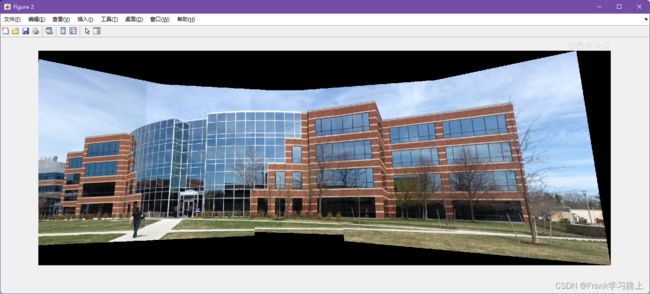
figure
imshow(panorama)
运行后全景图如下:
自定义拼接
了解了示例后,我自己用摄像头拍了3张照片,并改变文件读取路径(了解fullfile使用):
buildingDir = fullfile('C:\Users\admin\Documents\MATLAB\Examples\vision\FeatureBasedPanoramicImageStitchingExample');
3张照片读取如下:
其他地方都不用改动,运行后出现全景图如下:
以上。