3.rsync远程同步+inotify监控实时同步概述,部署
文章目录
- 一,rsync 概述
-
-
- 1.rsync服务器
- 2.rsync同步方式
- 3.rsync特性
-
- 二、rsync与cp、scp对比
- 三,rsync命令
- 四,rsync 本地复制实例
- 五,rsync同步源
-
-
- 1.配置源的两种表示方法
- 2.配置 Rsync 下行同步
-
- 1.配置环境
- 2.将 Master 服务器数据备份到 Slave 服务器
- 3.slave配置
-
- 六,inotify简介
- 七,配置Rsync+Inotify 实时同步
-
-
- 1.Master 关闭只读模式并为共享目录赋权(配制上行同步)
- 2.优化 Slave 内核参数
- 3.客户端(192.168.113.127):编译安装 inotify-tools
- 4.客户端启动监听
- 5、编写触发同步脚本使 rsync+inotify 两个服务结合在一起
-
一,rsync 概述
1.rsync服务器
- rsync是一款开源的、快速的、多功能的、可实现全量及增量的本地或远程数据同步备份的优秀工具。并且可以不改变原有数据的属性信息,实现数据的备份迁移特性
- rsync软件支持跨平台,适用于 unix/linux/windows 等多种操作系统平台
- rsync是一个快速和非常方便的文件复制工具。它能本地复制,远程复制,或者远程守护进程方式复制,它提供了大量的参数来控制其行为的各个方面,并且允许非常灵活的方式来实现文件的传输复制
- 传输前执行压缩,因此非常适合用于架构集中式备份或异地备份等应用
- 同时Rsync支持本地复制,或者与其他SSH、rsync主机同步
- Rsync是Linux系统下的数据镜像备份工具,使用快速增量备份工具Remote
Sync可以远程同步 - 可以在不同主机之间进行同步,可实现全量备份与增量备份,保持链接和权限,且
采用优化的同步算法,以其 delta-transfer 算法闻名 - rsync监听端口:873
- rsync运行模式:C/S
- 官方网站:https://rsync.samba.org
2.rsync同步方式
- 全量备份:
1.原有的数据全部传送
2.把原来的文件和新的文件一起统一传送
3.全量复制,效率低
- 差量备份:
1.备份上次完全备份以后有变化的数据
2.针对的上次的完全备份
3.备份过程中不清除存档属性
- 增量备份:
1.在传输数据之前通过一些算法通过你有的数据和我有的数据进行对比,把不一样的数据通过网络传输
2.增量复制,效率高
3.备份上次备份以后有变化的数据
4.不管是那种类型的备份,有变化的数据就备份,
5.他会清除存档属性
3.rsync特性
- 可以镜像保存整个目录和文件系统
- 可以很容易做到保持原文件的权限、时间、软硬连接等
- 无须特殊权限即可安装
快速
第一次同步时rsync会复制全部内容,但在下一次只传输修改过的文件
rsync在传输数据的过程中可以实行压缩及解压缩操作,因此可以使用更少的宽带
安全
可以使用scp、ssh等方式来传输文件
也可通过直接socket连接
支持匿名传输,以方便进行网站镜像
二、rsync与cp、scp对比
- cp命令是一种典型的将文件完整的拷贝到一个位置。而rsync是,第一次拷贝,在目标位置没有的时候,rsync是全量拷贝过去,但是第二次拷贝的时候,只会对差异项进行同步拷贝。所有如果对同一个文件进行二次备份的话,rsync速度会相较于cp而言更快
- cp只支持本地,而rsync支持远程
- scp是基于cp原理,也是属于完整性拷贝文件。假设rsync和scp拷贝的文件都是第一,目标地址都没有要同步的文件,此时,这两者的差异在于,第一个,这个要传输的文件大不大,第二个要看在传输的过程中,用的带宽大不大。如果文件不大的情况下,scp是把数据从磁盘中的块存储提取出来,封装一下,网络传过去,此时scp更快,如果是更大的文件,比如说40G,带宽只支持100M的带宽,scp想要传输,需要拆分数据,一段一段传输。而rsync会根据一个逻辑意义上的空间,把数据划分出来,把数据先压缩再传输,所以这种方式而言,带宽校,文件大,这个时候先压缩再传输会比较快。此时适合用rsync远程同步
三,rsync命令
命令使用语法格式:
rsync 【选项】原始位置 目标位置
##常用的是-avz
| 常用选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -v,–verbose | 详细模式输出 |
| -q,–quiet | 精简输出模式 |
| -c,–checksum | 打开校验开关,强制对文件传输进行校验 |
| -a,–archive | 归档模式,表示以递归方式传输文件,并保持所有文件树形 |
| -z | 在传输文件时进行压缩 |
| -r,–recursive | 对子目录以递归模式处理,包含目录及子目录中的所有文件 |
| -H,–hard-links | 保留硬链接 |
| -l, --links | 保留软链接 |
| -A | 保留ACL属性信息 |
| -g | 保留文件的属组标记(仅超级用户使用) |
| -D | 保留设备文件及其他特殊文件 |
| -t | 保留文件的时间标记 |
| -p | 保留文件的权限标记 |
| -o | 保留文件的属主标记(仅超级用户使用) |
| –delete | 删除目标位置有而原始位置没有的文件(一致性) |
| –delete-after | 传输结束以后再删除 |
四,rsync 本地复制实例
带/ 与 不带的区别
例如:
- rsync -avz dxj/ /opt/ :只会拷贝abc目录下面的文件,而不会拷贝dxj这个目录
- rsync -avz /dxj /opt/:会连着目录一起拷贝到/opt下
#rsync -avz dxj/ /opt/ :只会拷贝abc目录下面的文件,而不会拷贝dxj这个目录
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
[root@localhost opt]# mkdir /dxj
[root@localhost opt]# cd /dxj
[root@localhost dxj]# touch 1.txt 2.txt
[root@localhost dxj]# cd /
[root@localhost /]# rsync -avz dxj/ /opt
[root@localhost /]# cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
1.txt 2.txt rh
#rsync -avz /dxj /opt/:会连着目录一起拷贝到/opt下
[root@localhost opt]# cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# rm -rf *
[root@localhost opt]# ls
[root@localhost opt]# rsync -avz /dxj /opt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
dxj
[root@localhost opt]# cd /dxj
[root@localhost dxj]# ls
1.txt 2.txt
五,rsync同步源
- 指备份操作的远程服务器,也称为备份源
例:
A服务器同步B服务器的数据,B服务器就是备份源
反过来,B服务器同步A服务器的数据,那么A服务器就是备份源 - 在远程同步任务中,负责发起 rsync 同步操作的客户机称为客户端,而负责响应来自客户端的 rsync 同步操作的服务器称为备份源,也称之为同步源
- 在下行同步(下载)中,同步源负责提供文档的原始位置,发起端应对该位置有读取权限
- 在上行同步(上传)中,同步源负责提供文档的目标位置,发起端应对该位置具有写入权限

1.配置源的两种表示方法
格式一:
#用户名@主机地址: :共享模块名
rsync -avz backuper@192.168.113.127::wwwroot /root
#xiayan指的是我在同步的时候用的哪个用户身份
#wwwroot代表的是模块,模块下面会写同步的默认路径和一些特性,所以我们只需要写模块就好了
#/root指的是本地节点
格式二:
#rsync:/用户名@主机地址/共享模块名
rsync -avz rsync://backuper@192.168.113.127/wwwroot /root
#URL:具体的位置点,例如:http://www.baidu.com./class1/men/id01.html
#URI:标识的是拥有同一类特性或类型的一个集合 ,例如http://www.baidu.com./class1/men
2.配置 Rsync 下行同步
1.配置环境
| 主机 | 操作系统 | IP 地址 | 主要软件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Master(服务端) | CentOS7 | 192.168.113.127 | rsync |
| Slave(客户端 ) | CentOS7 | 192.168.113.128 | rsync / inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz |
2.将 Master 服务器数据备份到 Slave 服务器
( Master:192.168.113.127)
#关闭防火墙及安全机制
[root@rsync ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@rsync ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@rsync ~]# setenforce 0
#rsync系统一般已默认安装,安装httpd是为了生成/var/www/html目录(后续会用到作为共享目录)
[root@rsync ~]# yum install -y httpd rsunc
#编辑rsync配置文件,按照下面操作该删的删,该取消注释的取消注释,或直接复制
uid = root
gid = root
use chroot = yes
address = 192.168.113.127
port 873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
hosts allow = 192.168.113.0/24
[wwwroot]
path = /var/www/html
comment = Document Root of www.xtj.com
read only = yes
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db
####上述解释####
uid = root #用户id,表示共享权限能执行的身份
gid = root #组id
use chroot = yes #开启,禁锢在源目录,表示允许在访问我备份的目录或文件的时候,使用的角色是root,同时你访问本地目录时拥有的也是root权限
address = 192.168.113.127 #监听地址
port 873 #默认端口号为873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #日志文件存放位置
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid #存放进程id的文件位置
hosts allow = 192.168.113.0/24 #允许访问的主机网段,有点类似于黑白名单
[wwwroot] #共享模块的名称,rsync默认调用该模块,默认我调用的路径是该模块指定的路径
path = /var/www/html #源目录路径
comment = Document Root of www.yxp.com #
read only = yes #是否为只读
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z #同步时不再压缩的文件类型,因为同步时,-avz已经进行压缩
auth users = backuper #授权用户,使用wwwroot模块的用户是哪个用户,多个账户以空格隔开
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db #存放账号信息的数据文件,一行一个
#编辑用户账号文件,固定格式为[名称:密码],一行一个
[root@rsync ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd_users.db
backuper:123123
#官方要求,最好只是赋权600
[root@rsync ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd_users.db
#开启服务
[root@rsync ~]# rsync --daemon
#检测端口号,确认服务是否成功开启
[root@rsync ~]# netstat -natp | grep rsync
#切换至共享目录下,创建要被备份的文件
[root@rsync ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@rsync html]# touch dog.html cat.html
[root@rsync html]# ls
cat.html dog.html
3.slave配置
(192.168.113.128)
#关闭防火墙及安全机制
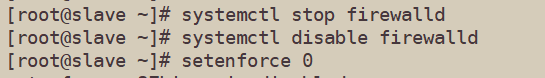
[root@slave ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@slave ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@slave ~]# setenforce 0
#安装rsync
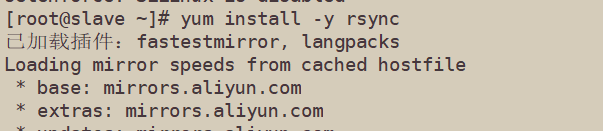
[root@slave ~]# yum install -y rsync
#创建一个目录/ABC,用来同步
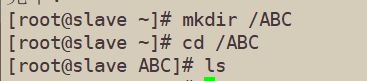
[root@slave ~]# mkdir /ABC
[root@slave ~]# cd /ABC
#使用rsync同步备份源的同步文件
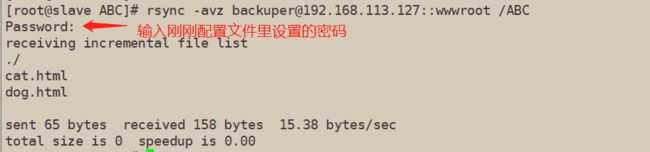
[root@slave ABC]# rsync -avz backuper@192.168.113.127::wwwroot /ABC
#查看同步是否成功
[root@slave ABC]# ls
cat.html dog.html
#编辑免交互密钥文件,第一行为密码
[root@slave ABC]# vim /etc/server.pass
123123
#给密钥文件赋权600
[root@slave ABC]# chmod 600 /etc/server.pass
#rsync,使用密钥文件/etc/server/pass对应backuper用户,IP地址为192.168.113.1127的共享模块文件进行压缩,并归档同步至当前服务器的/abc目录下,同时删除差异内容,如果原目标有的,会增加,原目标没有的,会删除。保持一致性
[root@slave ABC]# rsync -az --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.113.127::wwwroot /ABC
#查看下行同步是否成功
[root@slave /]# ls /ABC
![]()
![]()
六,inotify简介
- 可以监控文件系统的变动情况,并做出通知响应
#调整inotify内核参数(优化)
letc/ sysctl.conf(内核参数配置文件)
inotifywait: #用于持续监控,实时输出结果
inotifywatch: #用于短期监控,任务完成后再输出结果
max_queue_events #监控事件队列大小
max_user instances #最多监控实例数,可以看成最多可以监控多少个实例
max_user_watches #每个实例最多监控文件数
- inotifywait格式参数
| 常用参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -m | 持续进行监控 |
| -r | 递归监控所有子对象 |
| -q | 简化输出信息 |
| -e | 指定要监控哪些事件类型(*) |
七,配置Rsync+Inotify 实时同步
- 使用inotify通知接口,可以用来监控文件系统的各种变化情况,如文件存取、删除、移动、修改等。利用这一机制,可以非常方便地实现文件异动告警、增量备份,并针对目录或文件的变化及时作出响应
- 将inotify机制与rsync工具相结合,可以实现触发式备份(实时同步),即只要原始位置的文档发生变化,则立即启动增量备份操作;否则处于静默等待状态
- 因为 inotify 通知机制由 Linux 内核提供,因此主要做本机监控,在触发式备份中应用时更适合上行同步
1.Master 关闭只读模式并为共享目录赋权(配制上行同步)
(192.168.113.127)
#关闭只读模式,否则将不可写入
[root@rsync html]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
read only = no
#修改完配置文件需要重启服务,这里采用直接杀掉进程号的方式
[root@rsync html]# kill `cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid`
#检查一下服务是否已被终止
[root@rsync html]# netstat -natp | grep rsync
#再次开启服务并检查端口号确认
[root@rsync html]# rsync --daemon
[root@rsync html]# netstat -natp | grep rsync
tcp 0 0 192.168.113.127:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 69288/rsyn
2.优化 Slave 内核参数
(192.168.113.128)
[root@slave /]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events #监控事件队列
16384
[root@slave /]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances #最多监控实例数
128
[root@slave /]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches #每个实例最多监控文件数
8192
#加大每个参数
[root@slave /]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
#当要监控的目录、文件数据量较多或者变化频繁时,建议加大参数值,最后一行插入
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 16384
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
#刷新
[root@slave /]# sysctl -p
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 16384
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
3.客户端(192.168.113.127):编译安装 inotify-tools
#安装gcc gcc-c++
[root@slave /]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++
#切换至/opt上传inotify-tools安装包,并解压
[root@slave /]# cd /opt
[root@slave opt]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@slave opt]# tar zxf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
#编译安装
[root@slave opt]# cd /opt/inotify-tools-3.14/
[root@slave inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure
[root@slave inotify-tools-3.14]# make -j 4 && make install
4.客户端启动监听
(192.168.113.128)
#持续监听对/ABC的modify,create,move,delete操作
#监控 /ABC 下,添加文件、移动文件等操作,并跟踪屏幕输出结果
[root@slave opt]# inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,delete,move /ABC
#然后另开一个终端,进行 创建、删除、重命名 等操作,查看变化
cd /ABC
touch 7.txt
touch 8.txt
rm -rf 8.txt
mv 8.txt 9.txt
5、编写触发同步脚本使 rsync+inotify 两个服务结合在一起
vim /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib /ABC"
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -azH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass /ABC backuper@192.168.113.127::wwwroot"
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
----详解----
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib /ABC"
#INOTIFY_CMD变量:持续监控 /opt/abc目录中的创建,删除,移动,修改,改变时间的操作
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -azH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass /ABC backuper@192.168.113.127::wwwroot"
#RSYNC_CMD变量:使 backuper 用户,/etc/server.pass 密钥文件,将 /ABC 目录下的文件进行压缩,归档,保留硬链接文件同步至 192.168.113.128 的共享模块定义的目录 /var/www/html 下,并删除差异性内容,保持一致性
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE #持续监控...
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then #如果服务并未启动,则执行同步
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
#给脚本赋权
[root@slave inotify-tools-3.14]# cd /opt
[root@slave opt]# chmod +x inotify.sh
#设置开机自启动
[root@slave opt]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@slave opt]# echo "/opt/inotify.sh" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
#执行脚本
[root@slave ABC]# sh -x /opt/inotify.sh
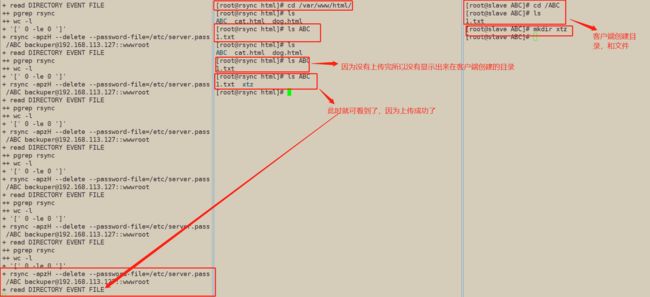
#在当前/ABC目录下进行增,删,改,然后去主服务器(192.168.113.127)/var/www/html下查看是否做到上行同步,同步会有点慢要等一小会
#例:在客户端创建
[root@slave ABC]# cd /ABC
[root@slave ABC]# touch 1.txt
#在服端查看(192.168.113.127),成功上传
[root@rsync ABC]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@rsync html]# ls
ABC cat.html dog.html
[root@rsync html]# ls ABC
1.txt