labelme生成的标注数据转换成yolov5格式
本文中的代码旨在一键生成yolov5数据集的格式
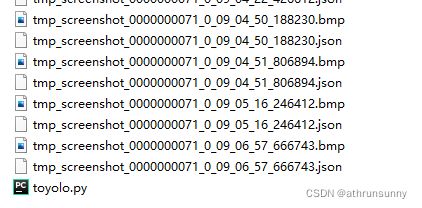
使用labelme标注的json数据会生成在标注时图像文件所在的路径下,数据形式大概是这样的:
json文件和图像数据同名。
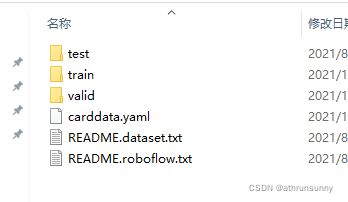
而yolov5实际训练时使用的数据格式是这样的:
网上大部分代码都是将yolov5标注格式的txt生成在根目录下,这样在生成txt文件后还需要手动整理成yolov5可训练的文件形式,下面的代码旨在减少人工处理的时间,一键生成可直接训练的文件形式。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Time: 2021.10.26
Author: Athrunsunny
Version: V 0.1
File: toyolo.py
Describe: Functions in this file is change the dataset format to yolov5
"""
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
import shutil
import yaml
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd()
def change_image_format(label_path=ROOT_DIR, suffix='.jpg'):
"""
统一当前文件夹下所有图像的格式,如'.jpg'
:param suffix: 图像文件后缀
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:return:
"""
externs = ['png', 'jpg', 'JPEG', 'BMP', 'bmp']
files = list()
for extern in externs:
files.extend(glob(label_path + "\\*." + extern))
for file in files:
name = ''.join(file.split('.')[:-1])
file_suffix = file.split('.')[-1]
if file_suffix != suffix.split('.')[-1]:
new_name = name + suffix
image = cv2.imread(file)
cv2.imwrite(new_name, image)
os.remove(file)
def get_all_class(file_list, label_path=ROOT_DIR):
"""
从json文件中获取当前数据的所有类别
:param file_list:当前路径下的所有文件名
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:return:
"""
classes = list()
for filename in file_list:
json_path = os.path.join(label_path, filename + '.json')
json_file = json.load(open(json_path, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
for item in json_file["shapes"]:
label_class = item['label']
if label_class not in classes:
classes.append(label_class)
return classes
def split_dataset(label_path, test_size=0.3, isUseTest=False, useNumpyShuffle=False):
"""
将文件分为训练集,测试集和验证集
:param useNumpyShuffle: 使用numpy方法分割数据集
:param test_size: 分割测试集或验证集的比例
:param isUseTest: 是否使用测试集,默认为False
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:return:
"""
files = glob(label_path + "\\*.json")
files = [i.replace("\\", "/").split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files]
if useNumpyShuffle:
file_length = len(files)
index = np.arange(file_length)
np.random.seed(32)
np.random.shuffle(index)
test_files = None
if isUseTest:
trainval_files, test_files = np.array(files)[index[:int(file_length * (1 - test_size))]], np.array(files)[
index[int(file_length * (1 - test_size)):]]
else:
trainval_files = files
train_files, val_files = np.array(trainval_files)[index[:int(len(trainval_files) * (1 - test_size))]], \
np.array(trainval_files)[index[int(len(trainval_files) * (1 - test_size)):]]
else:
test_files = None
if isUseTest:
trainval_files, test_files = train_test_split(files, test_size=test_size, random_state=55)
else:
trainval_files = files
train_files, val_files = train_test_split(trainval_files, test_size=test_size, random_state=55)
return train_files, val_files, test_files, files
def create_save_file(label_path=ROOT_DIR):
"""
按照训练时的图像和标注路径创建文件夹
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:return:
"""
# 生成训练集
train_image = os.path.join(label_path, 'train', 'images')
if not os.path.exists(train_image):
os.makedirs(train_image)
train_label = os.path.join(label_path, 'train', 'labels')
if not os.path.exists(train_label):
os.makedirs(train_label)
# 生成验证集
val_image = os.path.join(label_path, 'valid', 'images')
if not os.path.exists(val_image):
os.makedirs(val_image)
val_label = os.path.join(label_path, 'valid', 'labels')
if not os.path.exists(val_label):
os.makedirs(val_label)
# 生成测试集
test_image = os.path.join(label_path, 'test', 'images')
if not os.path.exists(test_image):
os.makedirs(test_image)
test_label = os.path.join(label_path, 'test', 'labels')
if not os.path.exists(test_label):
os.makedirs(test_label)
return train_image, train_label, val_image, val_label, test_image, test_label
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def push_into_file(file, images, labels, label_path=ROOT_DIR, suffix='.jpg'):
"""
最终生成在当前文件夹下的所有文件按image和label分别存在到训练集/验证集/测试集路径的文件夹下
:param file: 文件名列表
:param images: 存放images的路径
:param labels: 存放labels的路径
:param label_path: 当前文件路径
:param suffix: 图像文件后缀
:return:
"""
for filename in file:
image_file = os.path.join(label_path, filename + suffix)
label_file = os.path.join(label_path, filename + '.txt')
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(images, filename + suffix)):
try:
shutil.move(image_file, images)
except OSError:
pass
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(labels, filename + suffix)):
try:
shutil.move(label_file, labels)
except OSError:
pass
def json2txt(classes, txt_Name='allfiles', label_path=ROOT_DIR, suffix='.jpg'):
"""
将json文件转化为txt文件,并将json文件存放到指定文件夹
:param classes: 类别名
:param txt_Name:txt文件,用来存放所有文件的路径
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:param suffix:图像文件后缀
:return:
"""
store_json = os.path.join(label_path, 'json')
if not os.path.exists(store_json):
os.makedirs(store_json)
_, _, _, files = split_dataset(label_path)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(label_path, 'tmp')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(label_path, 'tmp'))
list_file = open('tmp/%s.txt' % txt_Name, 'w')
for json_file_ in files:
json_filename = os.path.join(label_path, json_file_ + ".json")
imagePath = os.path.join(label_path, json_file_ + suffix)
list_file.write('%s\n' % imagePath)
out_file = open('%s/%s.txt' % (label_path, json_file_), 'w')
json_file = json.load(open(json_filename, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
if os.path.exists(imagePath):
height, width, channels = cv2.imread(imagePath).shape
for multi in json_file["shapes"]:
points = np.array(multi["points"])
xmin = min(points[:, 0]) if min(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
xmax = max(points[:, 0]) if max(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
ymin = min(points[:, 1]) if min(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
ymax = max(points[:, 1]) if max(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
label = multi["label"]
if xmax <= xmin:
pass
elif ymax <= ymin:
pass
else:
cls_id = classes.index(label)
b = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax))
bb = convert((width, height), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
# print(json_filename, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, cls_id)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(store_json, json_file_ + '.json')):
try:
shutil.move(json_filename, store_json)
except OSError:
pass
def create_yaml(classes, label_path, isUseTest=False):
nc = len(classes)
if not isUseTest:
desired_caps = {
'path': label_path,
'train': 'train/images',
'val': 'valid/images',
'nc': nc,
'names': classes
}
else:
desired_caps = {
'path': label_path,
'train': 'train/images',
'val': 'valid/images',
'test': 'test/images',
'nc': nc,
'names': classes
}
yamlpath = os.path.join(label_path, "data" + ".yaml")
# 写入到yaml文件
with open(yamlpath, "w+", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for key, val in desired_caps.items():
yaml.dump({key: val}, f, default_flow_style=False)
# 首先确保当前文件夹下的所有图片统一后缀,如.jpg,如果为其他后缀,将suffix改为对应的后缀,如.png
def ChangeToYolo5(label_path=ROOT_DIR, suffix='.jpg', test_size=0.3, isUseTest=False):
"""
生成最终标准格式的文件
:param test_size: 分割测试集或验证集的比例
:param label_path:当前文件路径
:param suffix: 文件后缀名
:param isUseTest: 是否使用测试集
:return:
"""
change_image_format(label_path)
train_files, val_files, test_file, files = split_dataset(label_path, test_size=test_size, isUseTest=isUseTest)
classes = get_all_class(files)
json2txt(classes)
create_yaml(classes, label_path, isUseTest=isUseTest)
train_image, train_label, val_image, val_label, test_image, test_label = create_save_file(label_path)
push_into_file(train_files, train_image, train_label, suffix=suffix)
push_into_file(val_files, val_image, val_label, suffix=suffix)
if test_file is not None:
push_into_file(test_file, test_image, test_label, suffix=suffix)
print('create dataset done')
if __name__ == "__main__":
ChangeToYolo5()
在保存图像的目录下,创建toyolo.py文件,将以上代码拷贝粘贴。
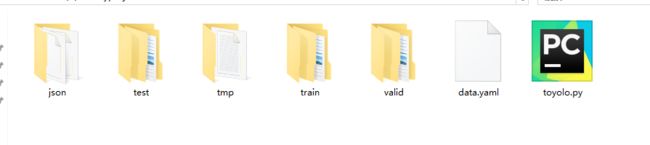
运行时先确保相应的库已经安装,运行后生成的文件目录如下:
生成的data.yaml可以直接复制到\yolov5\data目录下,tmp目录主要是处理的图像名,
json主要是原始标注生成的json