Spring IOC核心知识
控制反转(IOC: Inversion Of Control),把对象的创建和对象之间的调用过程都交给Spring管理,从而降低耦合度。
IOC底层原理
三大技术:XML解析、工厂模式、反射
IOC创建对象的过程:

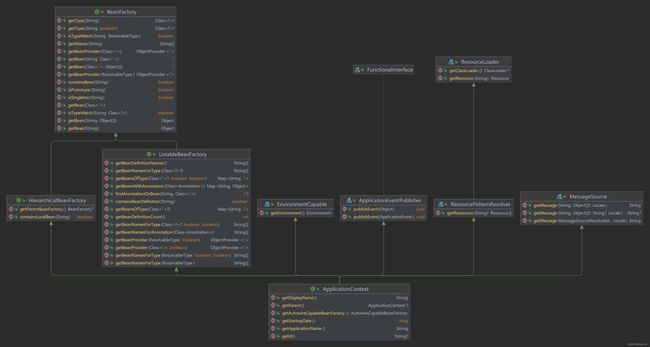
IOC重要接口
IOC容器底层是对象工厂
两种方式实现IOC:BeanFactory、ApplicationContext
-
BeanFactory:IOC基本实现,Spring内部使用,不提供给开发使用;加载配置文件的时候不会创建对象,在获取对象(使用)的时候才会创建对象;
-
ApplicationContext:BeanFactory接口的子接口,面向开发人员使用,提供的功能更大;加载配置文件的时候就会把在配置文件中的对象创建出来
ApplicationContext的实现类:FileSystemXmlApplicationContext和ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载文件系统的配置
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径的配置
IOC操作Bean管理
Bean管理主要是:Spring创建对象和注入属性
基于XML创建对象
public class Student{
}
<bean id="student" class="com.xxx.Student">bean>
(1)在Spring配置文件中,使用bean标签,标签里面添加对应的属性,就可以实现对象的创建
(2)在bean标签里面有很多的属性,如:id、class、name
(3)创建对象的时候,默认执行无参构造方法
基于XML注入属性
DI:Dependency Injection 依赖注入,就是注入属性
两种注入方式
- set方法注入属性
声明对象
public class Student{
// 属性
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
// set方法注入
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
// set方法注入
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
// set方法注入
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
xml配置bean
<bean id="student" class="com.xxx.Student">
<property name="name" value="张三">property>
<property name="age">
<null/>
property>
<property name="address" value="张三">
<value>
>]]>
value>
property>
bean>
- 有参构造器注入属性
声明对象
public class Student{
// 属性
private String name;
private Integer age;
// 有参构造器注入
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name=name;
this.age = age;
}
}
xml配置bean
<bean id="student" class="com.xxx.Student">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="15">constructor-arg>
bean>
普通Bean和FactoryBean
Spring中有两种Bean:普通Bean和FactoryBean
- 普通Bean:在配置文件中定义的bean类型就是返回的类型
- FactoryBean:在配置文件中定义的bean类型可以和返回类型不一样
通过FactoryBean创建Bean
public class Student {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<Student> {
// 通过此方法返回对象实例
@Override
public Student getObject() throws Exception {
return new Student();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}
BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别
- BeanFactory:负责生产和管理Bean的一个工厂接口,提供一个Spring Ioc容器规范,
- FactoryBean: 一种Bean创建的一种方式,对Bean的一种扩展。对于复杂的Bean对象初始化创建使用其可封装对象的创建细节
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/196688174
Bean的生命周期
(1)通过构造器创建bean实例(无参构造)
(2)为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean引用
(3)调用bean的初始化方法
(4)使用bean
(5)当容器关闭的时候,调用bean的销毁方法
Bean的自动装配
根据指定的装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型),Spring进行自动装配
public class Dept {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Emp {
private Dept dept;
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
}
将上面的Emp和Dept通过xml配置bean,实现自动装配
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dept" class="com.xlt.study.Dept">
<property name="name" value="市场部">property>
bean>
<bean id="emp" class="com.xlt.study.Emp" autowire="byName">bean>
beans>
外部属性文件
以引入Druid数据库配置为例
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="application.yml">context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${spring.datasource.driver-class-name}">property>
<property name="url" value="${spring.datasource.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${spring.datasource.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${spring.datasource.password}">property>
bean>
beans>