Python——类的继承和单例模式 singleton、运算符重载
目录
一、设计模式
二、单例模式
三、类的继承
四、super()方法
五、运算符重载 operator overload
六、类的专有方法
一、设计模式
开闭模式 open close principle
对扩展开放,对修改关闭
里氏代换原则 liskov substitution principle
任何基类可以出现的地方,派生类一定可以出现– 即基类可被派生类替换
依赖倒转原则 Dependence Inversion Principle
针对接口编程,依赖抽象而不依赖具体
接口隔离原则(Interface Segregation Principle)
使用多个隔离的接口,比使用单个接口要好,降低类之间的耦合度
最小知道原则(Demeter Principle)
一个实体应当尽量少地与其他实体发生作用系统功能模块应相对独立
合成复用原则(Composite Reuse Principle)
尽量使用合成/聚合的方式,而不是使用继承
二、单例模式
全局只有一个实例
- 应用场景
输入法和全局配置参数
该实现方式在多线程场景下不安全
class Singleton:
_instance=None
def __init__(self, name, volume):
self.name=name
self.volume=volume
def __new__(cls,name,volume):
if not Singleton._instance:
#if not hasattr(Singleton,'_instance'):
Singleton._instance=object.__new__(cls)
Singleton.__init__(Singleton._instance,name,volume)
return Singleton._instance
slist=[Singleton('z',100) for i in range(10)]
for s in slist:
print(hex(id(s)),end='\t')
print(f"{s.name}\t{s.volume}")
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
0x1ca17bce310 z 100
三、类的继承
继承其他类的类称为派生类(derived class)
被其他类继承的类称为这些类的基类(base
class)
class DerivedClassName(BaseClassName):
……
- 作用域
基类必须与派生类定义在一个作用域内
可以用表达式指定模块
-
class DerivedClassName(modname.BaseClassName): pass - 派生类
派生类定义的执行过程与基类类似
如果在类中找不到请求调用的属性会搜索基类
如果基类由别的类派生而来,则会递归式搜索 - 继承的检查
isinstance()用于检查实例类型issubclass()用于检查类继承 - 多继承
python支持多继承
派生类可以同时继承多个基类
class People:
"""
人的类,定义人相关的一些基本信息如姓名,身高,年龄等。
"""
def __init__(self,name,height,age):
self.__name=name
self.__height=height
self.__age=age
def get_name(self):
return self.__name
def set_name(self,name):
self.__name=name
def get_height(self):
return self.__height
def set_height(self,height):
self.__height=height
def get_age(self):
return self.__age
def set_age(self,age):
self.__age=age
def print_info(self):
print('in People')
print('Name:{},Age:{},Height:{}'.\
format(self.get_name(),self.get_age(),self.get_height()))
def __add__(self,other):
return self.get_height()+other.get_height()
class Speaker():
"""
演讲家类
"""
def __init__(self,topic):
self.__topic=topic
def get_topic(self):
return self.__topic
def set_topic(self,topic):
self.__topic=topic
def speak(self):
print('in Speaker')
print("speak topic is {}".format(self.get_topic()))
class Student(People,Speaker):
"""
学生类,继承人的类,同时添加一些新的属性,并覆盖方法
"""
def __init__(self,name,height,age,topic,ID,major):
People.__init__(self,name,height,age)
Speaker.__init__(self,topic)
self.__ID=ID
self.__major=major
def get_ID(self):
return self.__ID
def set_ID(self,ID):
self.__ID=ID
def get_major(self):
return self.__major;
def set_major(self,major):
self.__major=major
def print_info(self):
print('ID:{}, Name:{}, Major:{}, Age:{}, Height:{}'.\
format(self.get_ID(),self.get_name(),self.get_major(), self.get_age(),self.get_height()))
def speak(self):
#super(Student,self).print_info()
#super(Student,self).speak()
super().print_info()
super().speak()
p1=People('z',175,40)
s1=Student('zjc',175,35,'python',33060828,'cs')
print(p1+s1)
#s1.print_info()
s1.speak()
People.print_info(s1)
350
in People
Name:zjc,Age:35,Height:175
in Speaker
speak topic is python
in People
Name:zjc,Age:35,Height:175
class DerivedClassName(Base1,Base2,Base3):
……
需要注意圆括号中基类的顺序:从左到右搜索
多继承会导致菱形 diamond关系:有至少一个基类可以从子类经由多个继承路径到达
基类方法可能被多次调用
四、super()方法
防止重复访问,每个基类只调用一次
通过子类实例对象课调用父类已被覆盖
慎用多继承(二义性)
class BaseClass:
num_base_calls=0
def call_me(self):
print("calling method on Base Class")
BaseClass.num_base_calls+=1
class LeftSubclass(BaseClass):
num_left_calls=0
def call_me(self):
BaseClass.call_me(self)
#super().call_me()
print("calling method on Left Subclass")
LeftSubclass.num_left_calls+=1
class RightSubclass(BaseClass):
num_right_calls=0
def call_me(self):
BaseClass.call_me(self)
#super().call_me()
print("calling method on Right Subclass")
RightSubclass.num_right_calls+=1
class Subclass(LeftSubclass,RightSubclass):
num_sub_calls=0
def call_me(self):
LeftSubclass.call_me(self)
RightSubclass.call_me(self)
#super().call_me()
print("print calling method on Subclass")
Subclass.num_sub_calls+=1
s=Subclass()
s.call_me()
#print(s)
print("\tsub_call:{}\n\
left_call:{}\n\
right_call:{}\n\
base_call:{}".format(Subclass.num_sub_calls,LeftSubclass.num_left_calls,RightSubclass.num_right_calls,BaseClass.num_base_calls))
calling method on Base Class
calling method on Left Subclass
calling method on Base Class
calling method on Right Subclass
print calling method on Subclass
sub_call:1
left_call:1
right_call:1
base_call:2
五、运算符重载 operator overload
– 对已有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型
– 运算符重载不能改变其本来寓意
– 运算符重载只是一种 “语法上的方便” (sugar)
– 是一种函数调用的方式
class Point:
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __add__(self,other):
return Point(self.x+other.x,self.y+other.y)
def __sub__(self,other):
return Point(self.x-other.x,self.y-other.y)
def __str__(self):
return "({},{})".format(self.x,self.y)
def __lt__(self,other):
return self.xother.x
def __le__(self,other):
return self.x<=other.x
def __ge__(self,other):
return self.x>=other.x
def __eq__(self,other):
return self.x==other.x
def __ne__(self,other):
return self.x!=other.x
def __call__(self):
'''
Point类的实例可调用,也称可调用对象
'''
print('我不是函数,别调了')
p1=Point(1,2)
p2=Point(3,4)
print(p1+p2)
p3=p2-p1
print(p3)
print(p1
(4,6)
(2,2)
True
(3,4)
(2,2)
(1,2)
我不是函数,别调了
我不是函数,别调了
我不是函数,别调了
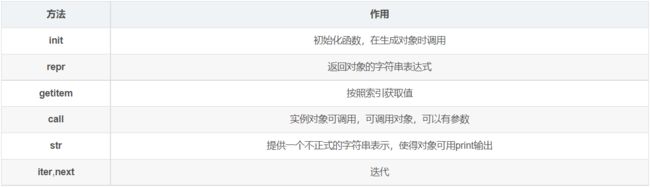
六、类的专有方法