- C++11堆操作深度解析:std::is_heap与std::is_heap_until原理解析与实践
文章目录堆结构基础与函数接口堆的核心性质函数签名与核心接口std::is_heapstd::is_heap_until实现原理深度剖析std::is_heap的验证逻辑std::is_heap_until的定位策略算法优化细节代码实践与案例分析基础用法演示自定义比较器实现最小堆检查边缘情况处理性能分析与实际应用时间复杂度对比典型应用场景与手动实现的对比注意事项与最佳实践迭代器要求比较器设计C++标
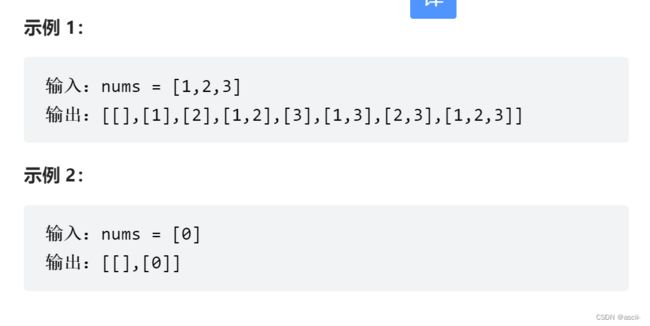
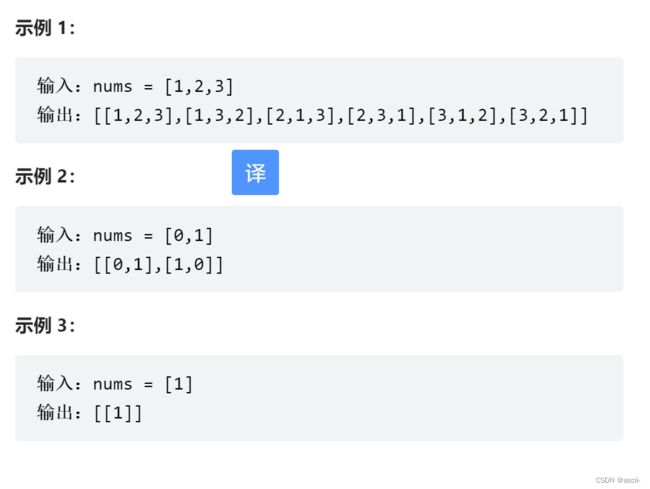
- C++ 11 Lambda表达式和min_element()与max_element()的使用_c++ lamda函数 min_element((1)
2401_84976182
程序员c语言c++学习
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上CC++开发知识点,真正体系化!由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新如果你需要这些资料,可以戳这里获取#include#include#includeusingnamespacestd;boolcmp(int
- C++ 11 Lambda表达式和min_element()与max_element()的使用_c++ lamda函数 min_element(
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加戳这里获取一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!intmain(){vectormyvec{3,
- 【LeetCode 热题 100】24. 两两交换链表中的节点——(解法一)迭代+哨兵
xumistore
LeetCodeleetcode链表算法java
Problem:24.两两交换链表中的节点题目:给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。文章目录整体思路完整代码时空复杂度时间复杂度:O(N)空间复杂度:O(1)整体思路这段代码旨在解决一个经典的链表操作问题:两两交换链表中的节点(SwapNodesinPairs)。问题要求将链表中每两个相邻的节点进行交换
- 冒泡、选择、插入排序:三大基础排序算法深度解析(C语言实现)
xienda
算法排序算法数据结构
在算法学习道路上,排序算法是每位程序员必须掌握的基石。本文将深入解析冒泡排序、选择排序和插入排序这三种基础排序算法,通过C语言代码实现和对比分析,帮助读者彻底理解它们的差异与应用场景。算法原理与代码实现1.冒泡排序(BubbleSort)工作原理:通过重复比较相邻元素,将较大元素逐步"冒泡"到数组末尾。voidbubbleSort(intarr[],intn){ for(inti=0;iarr[
- Leetcode 148. 排序链表
文章目录前引题目代码(首刷看题解)代码(8.9二刷部分看解析)代码(9.15三刷部分看解析)前引综合性比较强的一道题,要求时间复杂度必须O(logn)才能通过,最适合链表的排序算法就是归并。这里采用自顶向下的方法步骤:找到链表中点(双指针)对两个子链表排序(递归,直到只有一个结点,记得将子链表最后指向nullptr)归并(引入dummy结点)题目Leetcode148.排序链表代码(首刷看题解)c
- 全面触摸屏输入法设计与实现
长野君
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:触摸屏输入法是针对触摸设备优化的文字输入方案,包括虚拟键盘、手写、语音识别和手势等多种输入方式。本方案通过提供主程序文件、用户手册、界面截图、示例图、说明文本和音效文件,旨在为用户提供一个完整的、多样的文字输入体验。开发者通过持续优化算法和用户界面,使用户在无物理键盘环境下也能高效准确地进行文字输入。1.触摸屏输入法概述简介在现代信息技术飞速发展的今天,触摸屏
- LeetCode 148. 排序链表:归并排序的细节解析
进击的小白菜
2025Top100详解leetcode链表算法
文章目录题目描述一、方法思路:归并排序的核心步骤二、关键实现细节:快慢指针分割链表1.快慢指针的初始化问题2.为什么选择`fast=head.next`?示例1:链表长度为偶数(`1->2->3->4`)三、完整代码实现四、复杂度分析五、总结题目描述LeetCode148题要求对链表进行排序,时间复杂度需为O(nlogn),且空间复杂度为O(logn)。由于链表的特殊结构(无法随机访问),归并排序
- 嵌入式系统LCD显示模块编程实践
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本文档提供了一个具有800x480分辨率的3.5英寸液晶显示模块LW350AC9001的驱动程序代码,以及嵌入式系统中使用C/C++语言进行硬件编程的实践指南。该模块的2mm厚度使其适用于空间受限的便携式设备。内容包括驱动程序源代码、硬件控制接口使用方法,以及如何在嵌入式系统中进行图形处理、电源管理与性能优化。1.嵌入式系统原理1.1嵌入式系统概念嵌入式系统是
- FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署fpga开发verilog
FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)引言:为什么这个FPGA入门路线能帮你快速上岗?本文设计了一条**"Verilog语法→工具链操作→光学项目实战→岗位技能对标"的阶梯式学习路径。不同于泛泛而谈的FPGA教程,我们聚焦光学类产品开发**核心能力(时序接口设计、图像处理算法移植、高速接口应用),通过3个递进式项目(从LED闪烁到图像边缘检测),
- PyTorch & TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署pytorchtensorflowfpga开发
PyTorch&TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)引言:为什么算法移植工程师必须掌握框架基础?针对光学类产品算法FPGA移植岗位需求(如可见光/红外图像处理),深度学习框架是算法落地的"桥梁"——既要用PyTorch/TensorFlow验证算法可行性,又要将训练好的模型(如CNN、目标检测)转换为FPGA可部署的格式(ONNX、TFLite)。本文采用"
- 【超硬核】JVM源码解读:Java方法main在虚拟机上解释执行
HeapDump性能社区
java开发语言后端jvm
本文由HeapDump性能社区首席讲师鸠摩(马智)授权整理发布第1篇-关于Java虚拟机HotSpot,开篇说的简单点开讲Java运行时,这一篇讲一些简单的内容。我们写的主类中的main()方法是如何被Java虚拟机调用到的?在Java类中的一些方法会被由C/C++编写的HotSpot虚拟机的C/C++函数调用,不过由于Java方法与C/C++函数的调用约定不同,所以并不能直接调用,需要JavaC
- 算法学习笔记:17.蒙特卡洛算法 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
在计算机科学和数学领域,蒙特卡洛算法(MonteCarloAlgorithm)以其独特的随机抽样思想,成为解决复杂问题的有力工具。从圆周率的计算到金融风险评估,从物理模拟到人工智能,蒙特卡洛算法都发挥着不可替代的作用。本文将深入剖析蒙特卡洛算法的思想、解题思路,结合实际应用场景与Java代码实现,并融入考研408的相关考点,穿插图片辅助理解,帮助你全面掌握这一重要算法。蒙特卡洛算法的基本概念蒙特卡
- 算法学习笔记:15.二分查找 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
呆呆企鹅仔
算法学习算法学习笔记考研二分查找
在计算机科学的查找算法中,二分查找以其高效性占据着重要地位。它利用数据的有序性,通过不断缩小查找范围,将原本需要线性时间的查找过程优化为对数时间,成为处理大规模有序数据查找问题的首选算法。二分查找的基本概念二分查找(BinarySearch),又称折半查找,是一种在有序数据集合中查找特定元素的高效算法。其核心原理是:通过不断将查找范围减半,快速定位目标元素。与线性查找逐个遍历元素不同,二分查找依赖
- Python 脚本最佳实践2025版
前文可以直接把这篇文章喂给AI,可以放到AI角色设定里,也可以直接作为提示词.这样,你只管提需求,写脚本就让AI来.概述追求简洁和清晰:脚本应简单明了。使用函数(functions)、常量(constants)和适当的导入(import)实践来有逻辑地组织你的Python脚本。使用枚举(enumerations)和数据类(dataclasses)等数据结构高效管理脚本状态。通过命令行参数增强交互性
- (Python基础篇)字典的操作
EternityArt
基础篇python开发语言
一、引言在Python编程中,字典(Dictionary)是一种极具灵活性的数据结构,它通过“键-值对”(key-valuepair)的形式存储数据,如同现实生活中的字典——通过“词语(键)”快速查找“释义(值)”。相较于列表和元组的有序索引访问,字典的优势在于基于键的快速查找,这使得它在处理需要频繁通过唯一标识获取数据的场景中极为高效。掌握字典的操作,能让我们更高效地组织和管理复杂数据,是Pyt
- LeetCode算法题:电话号码的字母组合
吱屋猪_
算法leetcodejava
题目描述:给定一个仅包含数字2-9的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按任意顺序返回。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意1不对应任何字母。2->"abc"3->"def"4->"ghi"5->"jkl"6->"mno"7->"pqrs"8->"tuv"9->"wxyz"例如,给定digits="23",返回["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd
- Leetcode 3604. Minimum Time to Reach Destination in Directed Graph
Espresso Macchiato
leetcode笔记leetcode3604leetcodemediumleetcode双周赛160BFS广度优先遍历最优路径
Leetcode3604.MinimumTimetoReachDestinationinDirectedGraph1.解题思路2.代码实现题目链接:3604.MinimumTimetoReachDestinationinDirectedGraph1.解题思路这一题思路上就是一个广度优先遍历,我们不断考察当前时间点以及位置的情况下,下一个点可行的位置,然后考察最近的时间点能够到达的位置,遍历全部可能
- C++ 设计模式:抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
冀晓武
C++设计模式c++设计模式抽象工厂模式
链接:C++设计模式链接:C++设计模式-工厂方法链接:C++设计模式-原型模式链接:C++设计模式-建造者模式抽象工厂(AbstractFactory)是一种创建型设计模式,它提供一个接口,用于创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象,而无需指定它们的具体类。抽象工厂模式通常用于创建一组相关的产品对象,例如不同类型的机器人和它们的配件。1.问题分析在某些情况下,我们需要创建一组相关或相互依赖的对象,但我们
- 霍夫变换(Hough Transform)算法原来详解和纯C++代码实现以及OpenCV中的使用示例
点云SLAM
算法图形图像处理算法opencv图像处理与计算机视觉算法直线提取检测目标检测霍夫变换算法
霍夫变换(HoughTransform)是一种经典的图像处理与计算机视觉算法,广泛用于检测图像中的几何形状,例如直线、圆、椭圆等。其核心思想是将图像空间中的“点”映射到参数空间中的“曲线”,从而将形状检测问题转化为参数空间中的峰值检测问题。一、霍夫变换基本思想输入:边缘图像(如经过Canny边缘检测)输出:一组满足几何模型的形状(如直线、圆)关键思想:图像空间中的一个点→参数空间中的一个曲线参数空
- 用OpenCV标定相机内参应用示例(C++和Python)
下面是一个完整的使用OpenCV进行相机内参标定(CameraCalibration)的示例,包括C++和Python两个版本,基于棋盘格图案标定。一、目标:相机标定通过拍摄多张带有棋盘格图案的图像,估计相机的内参:相机矩阵(内参)K畸变系数distCoeffs可选外参(R,T)标定精度指标(如重投影误差)二、棋盘格参数设置(根据自己的棋盘格设置):棋盘格角点数:9x6(内角点,9列×6行);每个
- C++设计模式:简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂
起个别名
C++算法c++
1.工厂模式的特点在我们现实生活中,买馒头和自己蒸馒头、去饭店点一份大盘鸡和自己养鸡,杀鸡,做大盘鸡,这是全然不同的两种体验:自己做麻烦,而且有失败的风险,需要自己承担后果。买现成的,可以忽略制作细节,方便快捷并且无风险,得到的肯定是美味的食物。对于后者,就相当于是一个加工厂,通过这个工厂我们就可以得到想要的东西,在程序设计中,这种模式就叫做工厂模式,工厂生成出的产品就是某个类的实例,也就是对象。
- Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求
可曾去过倒悬山
java前端架构
Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求三年经验是Java程序员的分水岭,技术栈深度决定你成为“业务码农”还是“架构师候选人”。本文整合阿里、美团、滴滴等大厂招聘要求,为你绘制可落地的进阶路线。一、Java核心:从语法糖到JVM底层三年经验与初级的核心差异在于系统级理解,大厂面试常考以下能力:JVM与性能调优内存模型(堆外内存、元空间)、GC算法(G1/ZGC适用场
- 被动降噪的概念及编程实现
CodeByte
人工智能算法javascript编程
被动降噪是指通过编程技术和算法,对输入的数据进行处理,以减少或消除其中的噪声。噪声可以是各种形式的干扰,例如来自传感器、通信信号或其他外部源的干扰。在本文中,我们将探讨被动降噪的意义以及如何使用编程来实现这一目标。被动降噪的意义:噪声对数据的准确性和可靠性产生负面影响。在许多应用领域,例如图像处理、音频处理和信号处理中,噪声的存在可能导致数据质量下降,使得后续的分析和处理变得困难。因此,被动降噪技
- 传统检测响应慢?陌讯多模态引擎提速90+FPS实战
2501_92473147
算法计算机视觉目标检测
开篇痛点:实时目标检测在安防监控中的核心挑战在安防监控领域,实时目标检测是保障公共安全的关键技术。然而,传统算法如YOLOv5或开源框架MMDetection常面临两大痛点:误报率高(复杂光照或遮挡场景下检测不稳定)和响应延迟(高分辨率视频流处理FPS低于30)。实测数据显示,城市交通监控系统误报率达15%,导致安保资源浪费;客户反馈表明,延迟超100ms时,目标跟踪可能失效。这些问题源于算法泛化
- 反光衣识别漏检率 30%?陌讯多尺度模型实测优化
在建筑工地、交通指挥等场景中,反光衣是保障作业人员安全的重要装备,对其进行精准识别是智能监控系统的核心功能之一。但传统视觉算法在实际应用中却屡屡碰壁:强光下反光衣易与背景混淆、远距离小目标漏检率高达30%、复杂场景下模型泛化能力不足[实测数据来源:某智慧工地项目2024年Q1日志]。这些问题直接导致安全监控系统预警滞后,给安全生产埋下隐患。一、技术解析:反光衣识别的核心难点与陌讯算法创新反光衣识别
- 【GESP】C++三级真题 luogu-B4359 [GESP202506 三级] 分糖果
CoderCodingNo
GESPc++java开发语言
GESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较简单。题目题解详见:【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoder【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoderGESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较
- LeetCode Hot 100 回文链表
源
leetcode链表算法
给你一个单链表的头节点head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。示例1:输入:head=[1,2,2,1]输出:true示例2:输入:head=[1,2]输出:false提示:链表中节点数目在范围[1,105]内0vals;while(head!=nullptr){vals.emplace_back(head->val);head=head->next;}
- C++设计秘籍:为什么所有参数都需类型转换时,非成员函数才是王道?
讳疾忌医丶
c++前端开发语言
当所有参数都需要类型转换时,为什么要选择非成员函数?在C++的世界里,有一个看似简单却蕴含深意的设计原则:当所有参数(包括被this指针所指的那个隐式参数)皆须进行类型转换时,请为此采用非成员函数实现。这个原则背后隐藏着C++类型系统的精妙设计,也揭示了成员函数与非成员函数在处理隐式类型转换时的本质差异。想象一下,你正在设计一个数学计算库,需要支持整数与有理数的混合运算。如果你天真地将所有操作都实
- 【华为机试】HJ61 放苹果
不爱熬夜的Coder
算法华为机试golang华为golang算法面试
文章目录HJ61放苹果描述输入描述输出描述示例1示例2解题思路算法分析问题本质分析状态定义与转移递推关系详解动态规划表构建算法流程图示例推导过程代码实现思路时间复杂度分析关键优化点边界情况处理递归解法对比实际应用场景测试用例分析算法特点数学原理完整题解代码HJ61放苹果描述我们需要将m个相同的苹果放入n个相同的盘子中,允许有的盘子空着不放。求解有多少种不同的分法。输入描述输入两个整数m,n(0B[
- PHP,安卓,UI,java,linux视频教程合集
cocos2d-x小菜
javaUIPHPandroidlinux
╔-----------------------------------╗┆
- 各表中的列名必须唯一。在表 'dbo.XXX' 中多次指定了列名 'XXX'。
bozch
.net.net mvc
在.net mvc5中,在执行某一操作的时候,出现了如下错误:
各表中的列名必须唯一。在表 'dbo.XXX' 中多次指定了列名 'XXX'。
经查询当前的操作与错误内容无关,经过对错误信息的排查发现,事故出现在数据库迁移上。
回想过去: 在迁移之前已经对数据库进行了添加字段操作,再次进行迁移插入XXX字段的时候,就会提示如上错误。
&
- Java 对象大小的计算
e200702084
java
Java对象的大小
如何计算一个对象的大小呢?
- Mybatis Spring
171815164
mybatis
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerService userService = (CustomerService) ac.getBean("customerService");
Customer cust
- JVM 不稳定参数
g21121
jvm
-XX 参数被称为不稳定参数,之所以这么叫是因为此类参数的设置很容易引起JVM 性能上的差异,使JVM 存在极大的不稳定性。当然这是在非合理设置的前提下,如果此类参数设置合理讲大大提高JVM 的性能及稳定性。 可以说“不稳定参数”
- 用户自动登录网站
永夜-极光
用户
1.目标:实现用户登录后,再次登录就自动登录,无需用户名和密码
2.思路:将用户的信息保存为cookie
每次用户访问网站,通过filter拦截所有请求,在filter中读取所有的cookie,如果找到了保存登录信息的cookie,那么在cookie中读取登录信息,然后直接
- centos7 安装后失去win7的引导记录
程序员是怎么炼成的
操作系统
1.使用root身份(必须)打开 /boot/grub2/grub.cfg 2.找到 ### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober ### 在后面添加 menuentry "Windows 7 (loader) (on /dev/sda1)" {
- Oracle 10g 官方中文安装帮助文档以及Oracle官方中文教程文档下载
aijuans
oracle
Oracle 10g 官方中文安装帮助文档下载:http://download.csdn.net/tag/Oracle%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87API%EF%BC%8COracle%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3%EF%BC%8Coracle%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3 Oracle 10g 官方中文教程
- JavaEE开源快速开发平台G4Studio_V3.2发布了
無為子
AOPoraclemysqljavaeeG4Studio
我非常高兴地宣布,今天我们最新的JavaEE开源快速开发平台G4Studio_V3.2版本已经正式发布。大家可以通过如下地址下载。
访问G4Studio网站
http://www.g4it.org
G4Studio_V3.2版本变更日志
功能新增
(1).新增了系统右下角滑出提示窗口功能。
(2).新增了文件资源的Zip压缩和解压缩
- Oracle常用的单行函数应用技巧总结
百合不是茶
日期函数转换函数(核心)数字函数通用函数(核心)字符函数
单行函数; 字符函数,数字函数,日期函数,转换函数(核心),通用函数(核心)
一:字符函数:
.UPPER(字符串) 将字符串转为大写
.LOWER (字符串) 将字符串转为小写
.INITCAP(字符串) 将首字母大写
.LENGTH (字符串) 字符串的长度
.REPLACE(字符串,'A','_') 将字符串字符A转换成_
- Mockito异常测试实例
bijian1013
java单元测试mockito
Mockito异常测试实例:
package com.bijian.study;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.
- GA与量子恒道统计
Bill_chen
JavaScript浏览器百度Google防火墙
前一阵子,统计**网址时,Google Analytics(GA) 和量子恒道统计(也称量子统计),数据有较大的偏差,仔细找相关资料研究了下,总结如下:
为何GA和量子网站统计(量子统计前身为雅虎统计)结果不同?
首先:没有一种网站统计工具能保证百分之百的准确出现该问题可能有以下几个原因:(1)不同的统计分析系统的算法机制不同;(2)统计代码放置的位置和前后
- 【Linux命令三】Top命令
bit1129
linux命令
Linux的Top命令类似于Windows的任务管理器,可以查看当前系统的运行情况,包括CPU、内存的使用情况等。如下是一个Top命令的执行结果:
top - 21:22:04 up 1 day, 23:49, 1 user, load average: 1.10, 1.66, 1.99
Tasks: 202 total, 4 running, 198 sl
- spring四种依赖注入方式
白糖_
spring
平常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程序员实例化,而是通过spring容器帮我们new指定实例并且将实例注入到需要该对象的类中。依赖注入的另一种说法是“控制反转”,通俗的理解是:平常我们new一个实例,这个实例的控制权是我
- angular.injector
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS API
angular.injector
描述: 创建一个injector对象, 调用injector对象的方法可以获得angular的service, 或者用来做依赖注入. 使用方法: angular.injector(modules, [strictDi]) 参数详解: Param Type Details mod
- java-同步访问一个数组Integer[10],生产者不断地往数组放入整数1000,数组满时等待;消费者不断地将数组里面的数置零,数组空时等待
bylijinnan
Integer
public class PC {
/**
* 题目:生产者-消费者。
* 同步访问一个数组Integer[10],生产者不断地往数组放入整数1000,数组满时等待;消费者不断地将数组里面的数置零,数组空时等待。
*/
private static final Integer[] val=new Integer[10];
private static
- 使用Struts2.2.1配置
Chen.H
apachespringWebxmlstruts
Struts2.2.1 需要如下 jar包: commons-fileupload-1.2.1.jar commons-io-1.3.2.jar commons-logging-1.0.4.jar freemarker-2.3.16.jar javassist-3.7.ga.jar ognl-3.0.jar spring.jar
struts2-core-2.2.1.jar struts2-sp
- [职业与教育]青春之歌
comsci
教育
每个人都有自己的青春之歌............但是我要说的却不是青春...
大家如果在自己的职业生涯没有给自己以后创业留一点点机会,仅仅凭学历和人脉关系,是难以在竞争激烈的市场中生存下去的....
&nbs
- oracle连接(join)中使用using关键字
daizj
JOINoraclesqlusing
在oracle连接(join)中使用using关键字
34. View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the ORDERS and ORDER_ITEMS tables.
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
SELECT oi.order_id, product_id, order_date
FRO
- NIO示例
daysinsun
nio
NIO服务端代码:
public class NIOServer {
private Selector selector;
public void startServer(int port) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(
- C语言学习homework1
dcj3sjt126com
chomework
0、 课堂练习做完
1、使用sizeof计算出你所知道的所有的类型占用的空间。
int x;
sizeof(x);
sizeof(int);
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int x1;
char x2;
double x3;
float x4;
printf(&quo
- select in order by , mysql排序
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
If i select like this:
SELECT id FROM users WHERE id IN(3,4,8,1);
This by default will select users in this order
1,3,4,8,
I would like to select them in the same order that i put IN() values so:
- 页面校验-新建项目
fanxiaolong
页面校验
$(document).ready(
function() {
var flag = true;
$('#changeform').submit(function() {
var projectScValNull = true;
var s ="";
var parent_id = $("#parent_id").v
- Ehcache(02)——ehcache.xml简介
234390216
ehcacheehcache.xml简介
ehcache.xml简介
ehcache.xml文件是用来定义Ehcache的配置信息的,更准确的来说它是定义CacheManager的配置信息的。根据之前我们在《Ehcache简介》一文中对CacheManager的介绍我们知道一切Ehcache的应用都是从CacheManager开始的。在不指定配置信
- junit 4.11中三个新功能
jackyrong
java
junit 4.11中两个新增的功能,首先是注解中可以参数化,比如
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runn
- 国外程序员爱用苹果Mac电脑的10大理由
php教程分享
windowsPHPunixMicrosoftperl
Mac 在国外很受欢迎,尤其是在 设计/web开发/IT 人员圈子里。普通用户喜欢 Mac 可以理解,毕竟 Mac 设计美观,简单好用,没有病毒。那么为什么专业人士也对 Mac 情有独钟呢?从个人使用经验来看我想有下面几个原因:
1、Mac OS X 是基于 Unix 的
这一点太重要了,尤其是对开发人员,至少对于我来说很重要,这意味着Unix 下一堆好用的工具都可以随手捡到。如果你是个 wi
- 位运算、异或的实际应用
wenjinglian
位运算
一. 位操作基础,用一张表描述位操作符的应用规则并详细解释。
二. 常用位操作小技巧,有判断奇偶、交换两数、变换符号、求绝对值。
三. 位操作与空间压缩,针对筛素数进行空间压缩。
&n
- weblogic部署项目出现的一些问题(持续补充中……)
Everyday都不同
weblogic部署失败
好吧,weblogic的问题确实……
问题一:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Failed to read candidate component class: URL [zip:E:/weblogic/user_projects/domains/base_domain/serve
- tomcat7性能调优(01)
toknowme
tomcat7
Tomcat优化: 1、最大连接数最大线程等设置
<Connector port="8082" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
useBodyEncodingForURI="t
- PO VO DAO DTO BO TO概念与区别
xp9802
javaDAO设计模式bean领域模型
O/R Mapping 是 Object Relational Mapping(对象关系映射)的缩写。通俗点讲,就是将对象与关系数据库绑定,用对象来表示关系数据。在O/R Mapping的世界里,有两个基本的也是重要的东东需要了解,即VO,PO。
它们的关系应该是相互独立的,一个VO可以只是PO的部分,也可以是多个PO构成,同样也可以等同于一个PO(指的是他们的属性)。这样,PO独立出来,数据持