强引用
- 强引用:Object o = new Object()
- 软引用:new SoftReference(o);
- 弱引用:new WeakReference(o);
- 虚引用:new PhantomReference(o,Queue);
本次会用到命令-XX:+PrintGCDetails
会打印
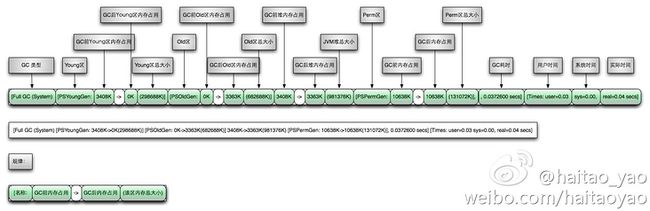
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 29680K->4080K(29696K)] 73163K->72619K(98304K), 0.0245660 secs] [Times: user=0.15 sys=0.02, real=0.03 secs]
[Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 4080K->3557K(29696K)] [ParOldGen: 68539K->68498K(68608K)] 72619K->72055K(98304K), [Metaspace: 8977K->8977K(1056768K)], 0.1491246 secs] [Times: user=1.02 sys=0.01, real=0.15 secs] | 引用类型 | 什么时候回收 | |
|---|---|---|
| 强引用 | 强引用的对象,只要 GC root 可达,不会被回收,内存不够用了,会抛出 oom | |
| 软引用:SoftReference | 软引用对象,GC root 中,只有软引用可以到达某个对象 a,在 oom 之前,垃圾回收会回收对象 a | |
| 弱引用:WeakReference | 弱引用,GC root 中,youngGC 就回回收c | |
| 虚引用:PhantomReference | 虚引用,必须配合 ReferenceQueue 使用,代替finalize |
强引用
强引用就是我们最常用的创建对象的方式Object o = new Object(),只要引用还在,就不会被回收,堆内存占满就直接抛出OOM。但是当指向null后,在gc时就回回收对应内存
// Thread.sleep(10000);
// strongReference();
// -XX:+PrintGCDetails -Xms100m -Xmx100m
private static void strongReference() throws InterruptedException {
int size=100000;
Element[] arr= new Element[size];
try{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i]=new Element(i);
Thread.sleep(1);
//arr[i]=null;
}
}catch (Throwable e){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(arr[i]==null){
System.out.println("null number:"+i);//null number:84318
break;
}
}
}
}如果执显式设置为null后
软引用
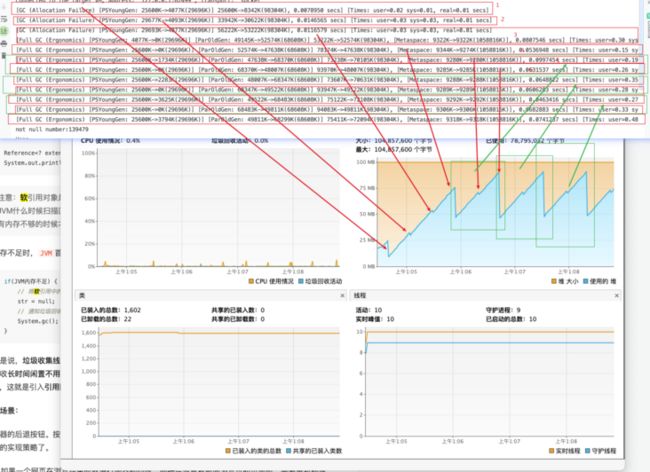
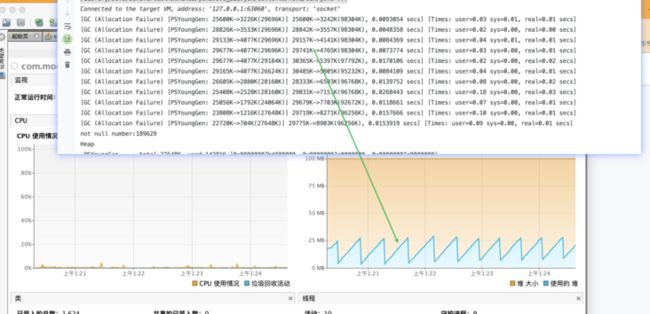
软引用,使用SoftReference创建,但是,当内存不够的时候,回把对象回收,not null number:139479,整个程序执行,并无发生oom。
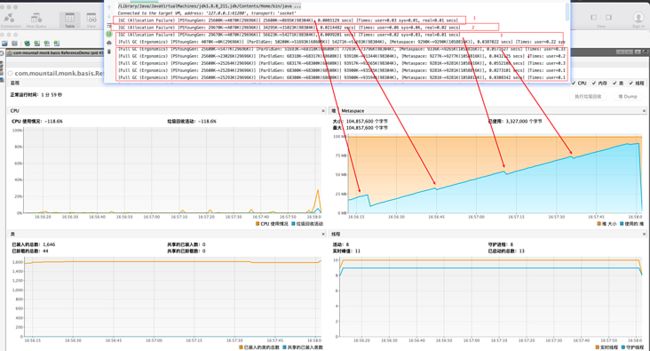
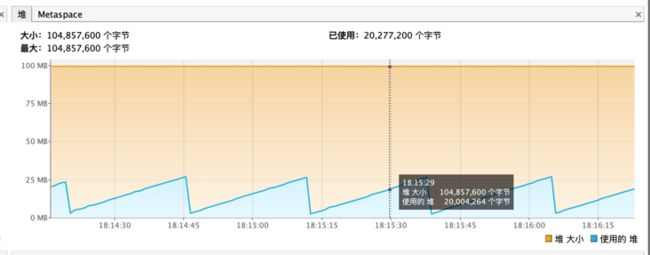
源代码注释中写了在抛出oom之前清除,通过PrintGCDetails也可以看到,基本都是在FullGC中处理,结合visualVM可以看到,并不是所有FullGC都会处理,一半都是堆内存占用快满了,才会触发
All soft references to softly-reachable objects are guaranteed to have
* been cleared before the virtual machine throws an
* OutOfMemoryError
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
// strongReference();
softReference();
}
private static void softReference() throws InterruptedException {
int size=200000;
SoftReference[] list=new SoftReference[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list[i]=new SoftReference(new Element(i));
Thread.sleep(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(list[i].get()!=null){
System.out.println("not null number:"+i);
break;
}
}
} 弱引用
弱引用,调用方式和上面差不多,就是类换成了WeakReference,其他一概没有变,功过图可以看到它是在YoungGC的时候就清除了
private static void weakReference() throws InterruptedException {
int size=200000;
WeakReference[] list=new WeakReference[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list[i]=new WeakReference(new Element(i));
Thread.sleep(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(list[i].get()!=null){
System.out.println("not null number:"+i);
break;
}
}
} 虚引用
PhantomReference和上面三个不大一样,我一开时以为也是方便清理,可是看了注释不大一样。
PhantomReference最常用于以一种比Java finalization更灵活的方式来调度预分析清理操作。
Phantom
* references are most often used for scheduling pre-mortem cleanup actions in
* a more flexible way than is possible with the Java finalization mechanism.也就是说它设计的目的就是为了替代finalize
private static void phantomReference() throws InterruptedException {
Element e=new Element(1);
ReferenceQueue referenceQueue=new ReferenceQueue();
PhantomReference reference=new PhantomReference(e,referenceQueue){
@Override
public void clear() {
System.out.println(1111111);
super.clear();
}
};
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
PhantomReference reference1= (PhantomReference) referenceQueue.remove();
reference1.clear();
} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {
interruptedException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
e=null;
System.out.println("element is null");
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
/*
element is null
[GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 3083K->567K(29696K)] 3083K->567K(98304K), 0.0014892 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[Full GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 567K->0K(29696K)] [ParOldGen: 0K->456K(68608K)] 567K->456K(98304K), [Metaspace: 2955K->2955K(1056768K)], 0.0046349 secs] [Times: user=0.02 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]
1111111
*/ 本来茶队晋级已经够高兴了,后来TA打李逵,带来了3场精彩对决,看的热血沸腾的,加油茶队
本文由mdnice多平台发布