翻译:Contoso 大学 - 7 – 处理并发
By Tom Dykstra, Tom Dykstra is a Senior Programming Writer on Microsoft's Web Platform & Tools Content Team.
原文地址:http://www.asp.net/mvc/tutorials/getting-started-with-ef-using-mvc/handling-concurrency-with-the-entity-framework-in-an-asp-net-mvc-application
全文目录:Contoso 大学 - 使用 EF Code First 创建 MVC 应用
在上一次的教程中我们处理了关联数据问题。这个教程演示如何处理并发问题。你将使用 Department 实体创建一个页面,这个页面在支持编辑和删除的同时,还可以处理并发错误。下面的截图演示了 Index 页面和 Delete 页面,包括在出现并发冲突的时候提示的一些信息。
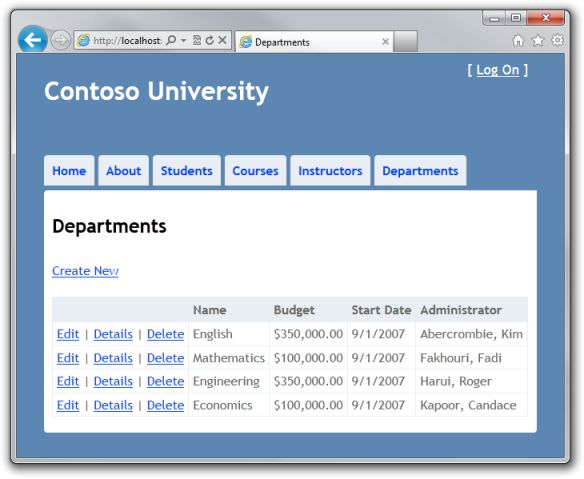
7-1 并发冲突
并发冲突出现在这样的时候,一个用户正在显示并编辑一个实体,但是在这个用户将修改保存到数据库之前,另外的一个用户却更新了同样的实体。如果你没有通过 EF 检测类似的冲突,最后一个更新数据的用户将会覆盖其他用户的修改。在一些程序中,这样的风险是可以接受的,如果只有很少的用户,或者很少的更新,甚至对数据的覆盖不是真的很关键,或者解决并发的代价超过了支持并发所带来的优势。在这种情况下,你就不需要让你的程序支持并发冲突的处理。
7-1-1 悲观并发 ( 锁定 )
如果你的应用需要在并发环境下防止偶然的数据丢失,一种方式是通过数据库的锁来实现。这种方式被称为悲观并发。例如,在从数据库中读取一行数据之前,可以申请一个只读锁,或者一个更新访问锁。如果你对数据行使用了更新访问锁,就没有其他的用户可以获取不管是只读锁还是更新访问锁,因为他们可能获取正在被修改中的数据。如果你使用只读锁来锁定一行,其他用户也可以使用只读访问,但是不能进行更新。
管理锁有一些缺点,对程序来说可能很复杂。它需要重要的数据库管理资源,对于大量用户的时候可能导致性能问题 ( 扩展性不好 ),由于这些原因,不是所有的数据库管理系统都支持悲观锁。EF 对悲观锁没有提供内建的支持,这个教程也不会演示如何实现它。
7-1-2 乐观并发
除了悲观并发之外的另一方案是乐观并发。乐观并发意味着允许并发冲突发生,如果出现了就做出适当的反应。例如,John 执行 Department 的编辑页面,将 English 系的 Budget 从 $350,000.00 修改为 $100,000.00 ( John 管理与 English 有竞争的系,希望将一些资金转移到他自己的系使用 )。
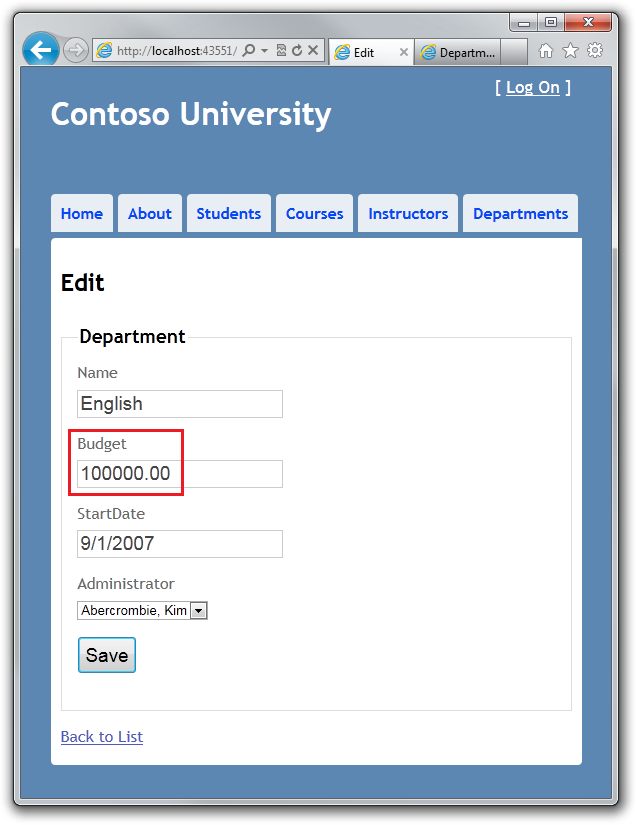
在 John 点击保存 Save 之前,Jane 运行同样的页面,将开始时间 Start Date 字段从 9/1/2007 修改为 1/1/1999 ( Jane 管理历史系,希望它的历史更加悠久 )
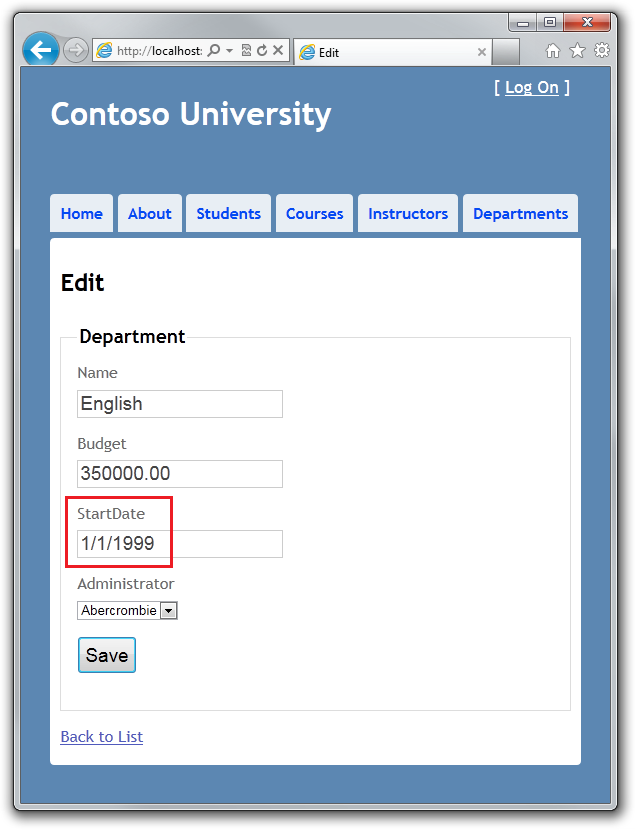
John 先点击保存 Save,然后在回到 Index 页面的时候看到自己的修改。然后 Jane 点击保存 Save。下一步发生什么取决于如何处理并发冲突。可能的情况如下:
- 你可以追踪用户修改和更新了哪些数据库中的列。在这个例子的场景下,不会丢失数据,因为两个用户更新了不同的属性。下一次其他人在浏览英语系的时候,他们会发现 John 和 Jane 所做的所有修改:开始时间成为 1/1/1999,预算成为 $100,000.00。
这种方法可以减少可能造成数据丢失的冲突次数,但是如果用户修改同一个实体的相同属性的话,会丢失数据, EF 具体依赖于你如何实现你的更新代码。这种方式不适合 Web 应用程序,因为需要你维护大量的状态,以便追踪所有新值的原始状态。维护大量的状态会影响到程序的性能,因为既需要服务器的资源,又需要将状态保存在页面中 ( 例如,使用隐藏域 )。
- 你可以允许 Jane 的修改覆盖 John 的修改。下一次用户浏览英语系的时候,将会看到 1/1/1999 和恢复的 $350,000.00 值。这被称为 Client Wins 或者 Last in Wins 场景 ( 客户端的值优先于保存的值 )。像在这节开始介绍的,如果你没有使用任何代码处理并发,这将会自动发生。
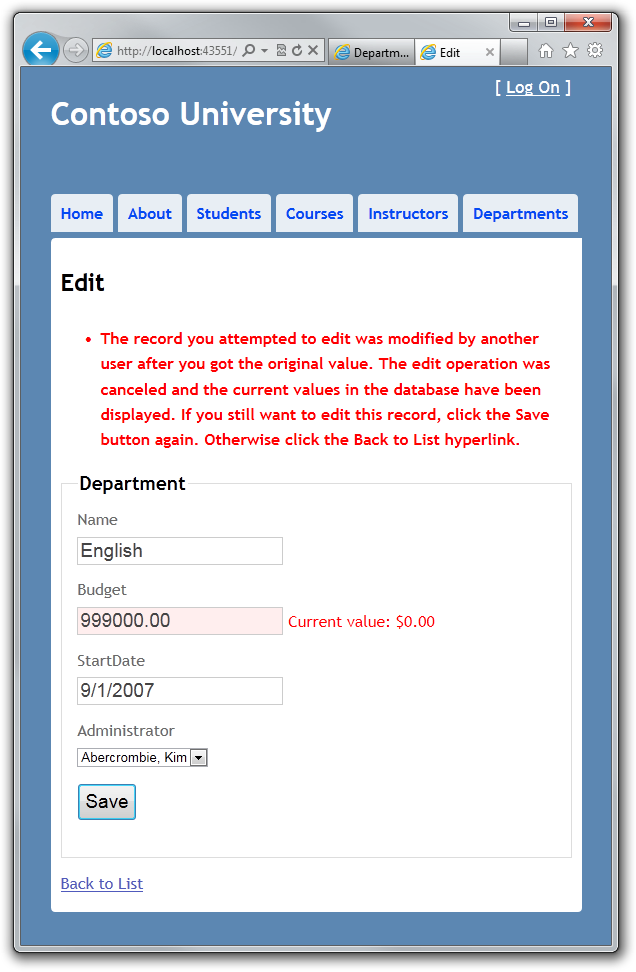
- 你可以阻止 Jane 的修改更新到数据库中。通常情况下,我们希望显式一个错误信息。展示数据当前的状态,如果她仍然希望做出这样修改的话,允许她重做修改。这被称为 Store Wins 场景。( 保存的值优先于客户提交的值 ) 在这个教程中,你将要实现 Store Wins 场景。这种方法在提示用户发生什么之前,不会覆盖其他用户的修改。
7-1-3 检测并发冲突
你可以通过处理 EF 抛出的 OptimisticConcurrencyException 异常来处理冲突。为了知道什么时候 EF 抛出了这种异常,EF 必须能够检测冲突。因此,你必须合理配置数据库和数据模型。启用冲突检测的一些选项如下:
- 在数据库的表中,包含用于追踪修改的列,在行被修改的时候可以用来进行检测。然后配置 EF 在更新 Update 或者删除 Delete 的 Where 子句中包含检测列。用于追踪的列的数据类型通常是 timestamp,但是其中并不真的包含实际的日期或者时间值。相反,值是在行每次更新的时候的一个递增值( 因此,在最近的 SQL Server 中,同样的类型被称为行版本 rowversion ) 。在更新 Update 或者 Delete 命令中,Where 子句中包含跟踪列的原始值。如果行被其他用户更新了,那么,此时跟踪列中的值就会与原始值不同,由于 Where 子句的作用,Update 或者 Delete 语句就不会取得需要更新的行。当 EF 发现没有行被 Update 或者 Delete 命令更新的时候 ( 就是说,影响的行数为 0 ),就理解为发生了并发冲突。
- 配置 EF 在 Update 或者 Delete 语句的 Where 中包含所有的原始列。如同第一个方式,如果在数据行被读取之后,行发生了任何修改,Where 将不能取得需要更新的行,这样 EF 就理解为发生了并发冲突。这种方式像使用跟踪列一样有效。但是,如果数据库中的表有很多列,就会导致巨大的 Where 子句,你也必须维护大量的状态。如前所述,维护大量的状态会影响程序的性能,因为既需要消耗服务器资源,也需要在页面中包含状态。因此,不建议使用这种方式,在这个教程中也不使用这种方法。
在本教程剩下的部分,你需要在 Department 实体上增加一个追踪列,创建控制器和视图,然后检查一切是否工作正常。
注意:如果你没有使用追踪列来实现并发,你就必须通过使用 ConcurrencyCheck 特性标记所有的非主属性用在并发跟踪中。这将会使 EF 将所有的列包含在 Update 语句的 Where 子句中。
7-2 对 Department 实体增加跟踪属性
在 Models\Departments.cs 文件中,增加跟踪属性。
[Timestamp] public Byte[] Timestamp { get; set; }
Timestamp 特性指定随后的列将会被包含在 Update 或者 Delete 语句的 Where 子句中。
7-3 创建 Department 控制器
如同创建其他的控制器一样,创建 Department 控制器和视图,使用如下的设置。
在 Controllers\DepartmentController.cs 中,增加一个 using 语句。
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
将文件中所有的 “LastName” 修改为 “FullName” ( 共有 4 处 ),使得系控制器中的下拉列表使用教师的全名而不是名字。
将 HttpPost Edit 方法使用下面的代码替换掉。
[HttpPost] public ActionResult Edit(Department department) { try { if (ModelState.IsValid) { db.Entry(department).State = EntityState.Modified; db.SaveChanges(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } } catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException ex) { var entry = ex.Entries.Single(); var databaseValues = (Department)entry.GetDatabaseValues().ToObject(); var clientValues = (Department)entry.Entity; if (databaseValues.Name != clientValues.Name) ModelState.AddModelError("Name", "Current value: " + databaseValues.Name); if (databaseValues.Budget != clientValues.Budget) ModelState.AddModelError("Budget", "Current value: " + String.Format("{0:c}", databaseValues.Budget)); if (databaseValues.StartDate != clientValues.StartDate) ModelState.AddModelError("StartDate", "Current value: " + String.Format("{0:d}", databaseValues.StartDate)); if (databaseValues.InstructorID != clientValues.InstructorID) ModelState.AddModelError("InstructorID", "Current value: " + db.Instructors.Find(databaseValues.InstructorID).FullName); ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "The record you attempted to edit " + "was modified by another user after you got the original value. The " + "edit operation was canceled and the current values in the database " + "have been displayed. If you still want to edit this record, click " + "the Save button again. Otherwise click the Back to List hyperlink."); department.Timestamp = databaseValues.Timestamp; } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after Exception) ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists contact your system administrator."); } ViewBag.InstructorID = new SelectList(db.Instructors, "InstructorID", "FullName", department.InstructorID); return View(department); }
视图通过页面中的隐藏域保存原始的时间戳。当编辑页面提交到服务器的时候,通过模型绑定创建 Department 实例的时候,实例将会拥有原始的 Timestamp 属性值,其他的属性获取新值。然后,当 EF 创建 Update 命令时,命令中将包含查询包含原始 Timestamp 值的 Where 子句。
在执行 Update 语句之后,如果没有行被更新,EF 将会抛出 DbUpdateConcurrencyException 异常,代码中的 catch 块从异常对象中获取受影响的 Department 实体对象,实体中既有从数据库中读取的值,也有用户新输入的值。
var entry = ex.Entries.Single(); var databaseValues = (Department)entry.GetDatabaseValues().ToObject(); var clientValues = (Department)entry.Entity;
然后,代码为用户在编辑页面上每一个输入的值与数据库中的值不同的列添加自定义的错误信息。
if (databaseValues.Name != currentValues.Name) ModelState.AddModelError("Name", "Current value: " + databaseValues.Name); // ...
长的错误信息解释了发生的状况以及如何解决的方式。
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "The record you attempted to edit " + "was modified by another user after you got the original value. The" + "edit operation was canceled and the current values in the database " + "have been displayed. If you still want to edit this record, click " + "the Save button again. Otherwise click the Back to List hyperlink.");
最后,代码将 Department 的 Timestamp 属性值设置为数据库中新获取的值。新的 Timestamp 值被保存在重新显示页面的隐藏域中,下一次用户点击保存的时候,当前显示的编辑页面值会被重新获取,这样就可以处理新的并发错误。
在 Views\Department\Edit.cshtml 中,增加一个隐藏域来保存 Timestamp 属性值,紧跟在 DepartmentID 属性之后。
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Timestamp)
在 Views\Department\Index.cshtml 中,使用下面的代码替换原有的代码,将链接移到左边,更新页面标题和列标题,在 Administrator 列中,使用 FullName 代替 LastName
@model IEnumerable<ContosoUniversity.Models.Department> @{ ViewBag.Title = "Departments"; } <h2>Departments</h2> <p> @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create") </p> <table> <tr> <th></th> <th>Name</th> <th>Budget</th> <th>Start Date</th> <th>Administrator</th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.DepartmentID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.DepartmentID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id=item.DepartmentID }) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Budget) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.StartDate) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Administrator.FullName) </td> </tr> } </table>
7-4 测试乐观并发处理
运行程序,点击 Departments.
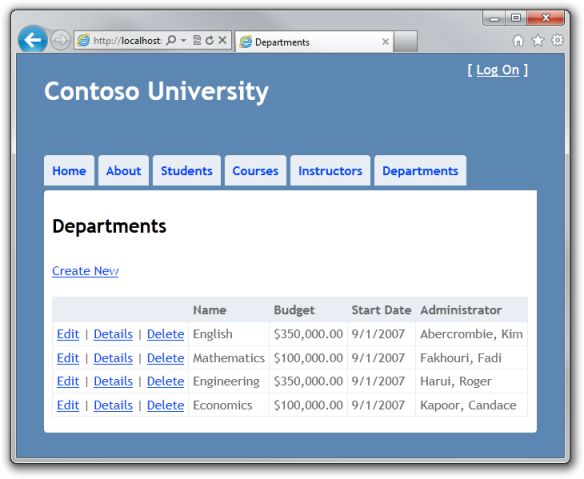
点击 Edit 超级链接,然后再打开一个新的浏览器窗口,窗口中使用相同的地址显示相同的信息。
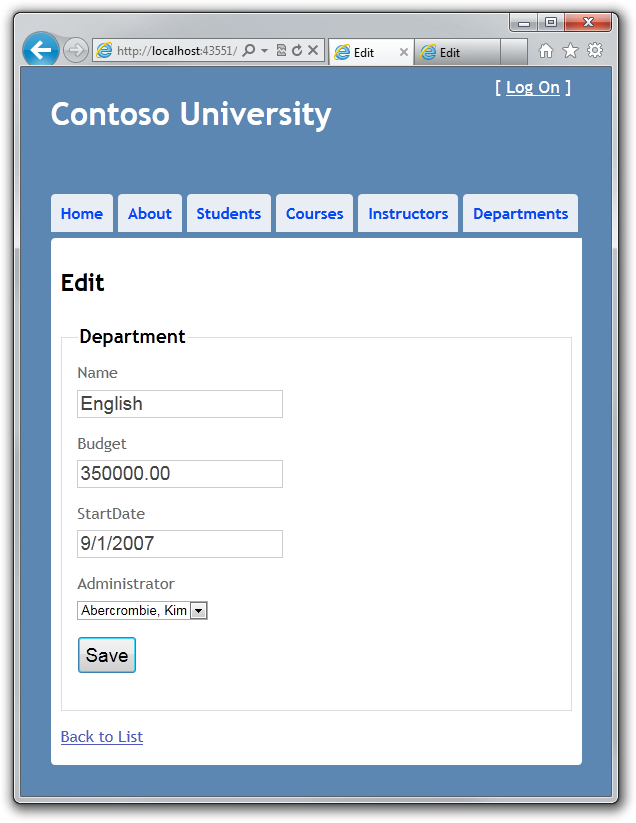
在第一个浏览器的窗口中修改一个字段的内容,然后点击 Save。
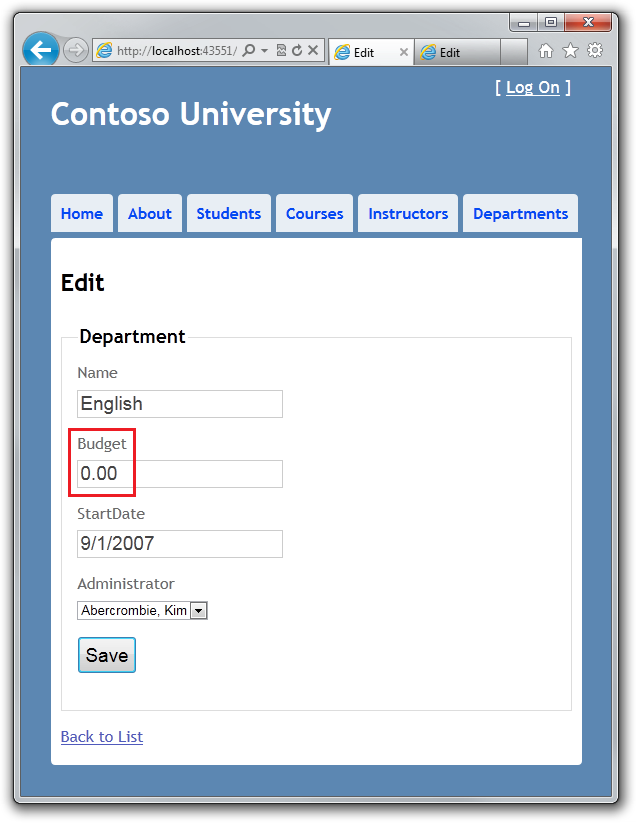
浏览器回到 Index 页面显示修改之后的值。
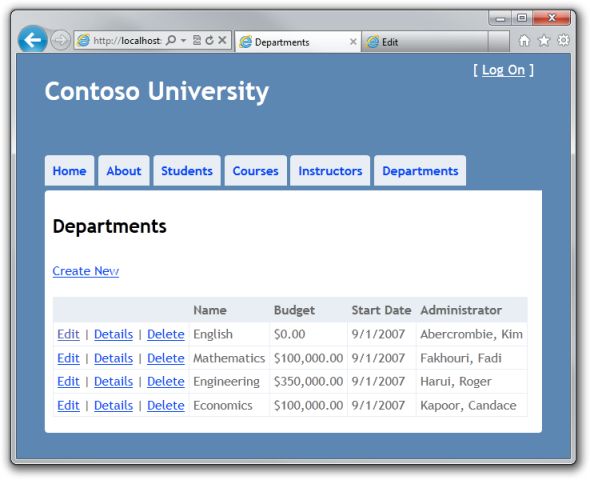
在第二个浏览器窗口中将同样的字段修改为不同的值,
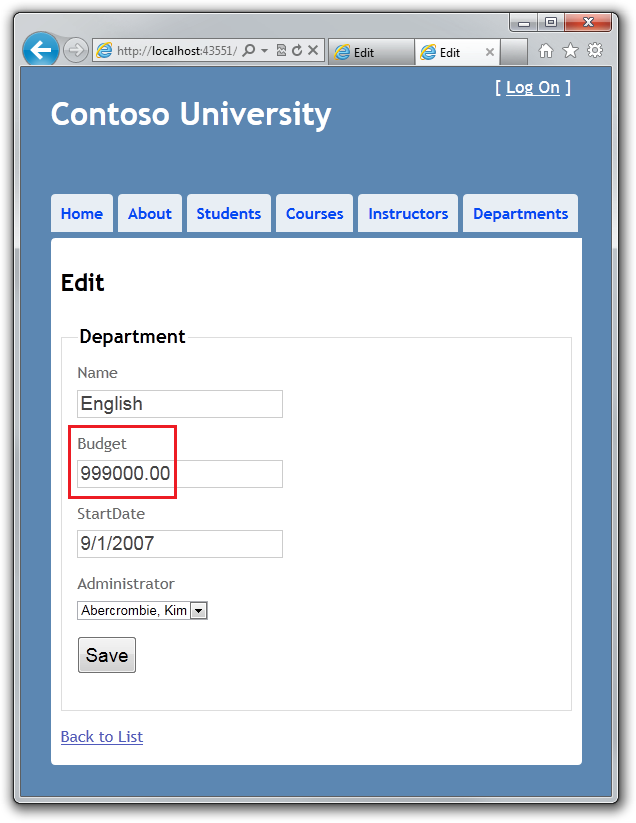
在第二个浏览器窗口中,点击 Save,将会看到如下错误信息。
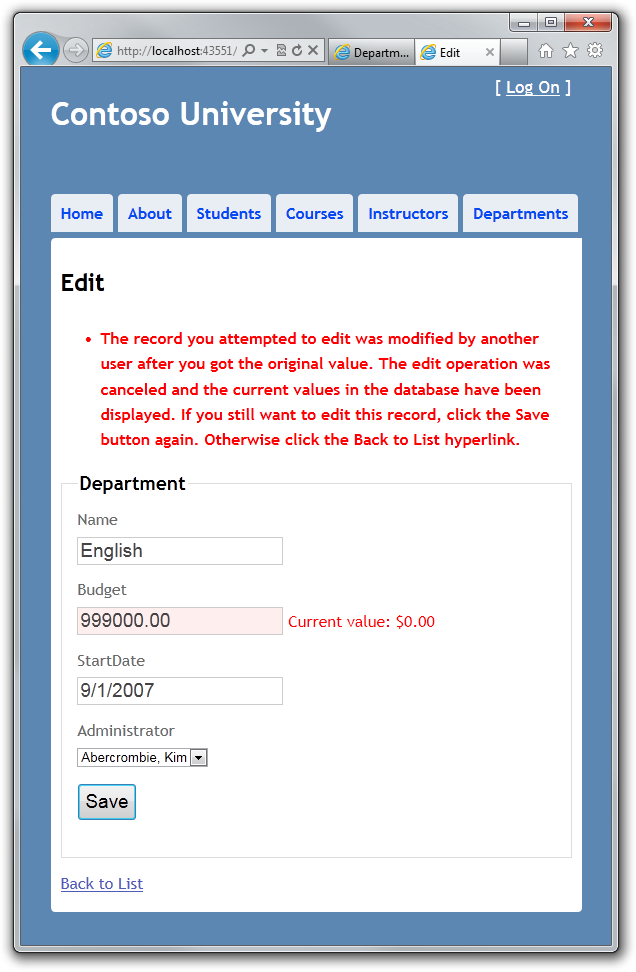
再次点击 Save。在第二个浏览器窗口中输入的值被保存到数据库中,在 Index 页面显示的时候出现在页面上。
7-5 增加删除页面
对于删除页面,EF 使用类似的方式检测并发冲突。当 HttpGet Delete 方法显示确认页面的时候,视图在隐藏域中包含原始的 Timestamp 值,当用户确认删除的时候,这个值被传递给 HttpPost Delete 方法,当 EF 创建 Delete 命令的时候,在 Where 子句中包含使用原始 Timestamp 值的条件,如果命令影响了 0 行 ( 意味着在显示删除确认页面之后被修改了 ),并发异常被抛出,通过传递错误标志为 true ,HttpGet Delete 方法被调用,带有错误提示信息的删除确认页面被显示出来。
在 DepartmentController.cs 中,使用如下代码替换 HttpGet Delete 方法。
public ActionResult Delete(int id, bool? concurrencyError) { if (concurrencyError.GetValueOrDefault()) { ViewBag.ConcurrencyErrorMessage = "The record you attempted to delete " + "was modified by another user after you got the original values. " + "The delete operation was canceled and the current values in the " + "database have been displayed. If you still want to delete this " + "record, click the Delete button again. Otherwise " + "click the Back to List hyperlink."; } Department department = db.Departments.Find(id); return View(department); }
方法接收一个可选的表示是否是在并发冲突之后重新显示页面的参数,如果这个标志为 true,错误信息通过 ViewBag 传递到视图中。
使用下面的代码替换 HttpPost Delete 方法中的代码 ( 方法名为 DeleteConfirmed )
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")] public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(Department department) { try { db.Entry(department).State = EntityState.Deleted; db.SaveChanges(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException) { return RedirectToAction("Delete", new System.Web.Routing.RouteValueDictionary { { "concurrencyError", true } }); } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after Exception) ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists contact your system administrator."); return View(department); } }
你刚刚替换的脚手架代码方法仅仅接收一个记录的 Id
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
将这个参数替换为通过模型绑定创建的 Department 实体实例。这使得可以访问额外的 Timestamp 属性。
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(Department department)
如果发生了并发冲突,代码将会传递表示应该显示错误的标志给确认页面,然后重新显示确认页面。
在 Views\Department\Delete.cshtml 文件中,使用如下代码替换脚手架生成的代码,做一些格式化,增加一个错误信息字段。
@model ContosoUniversity.Models.Department @{ ViewBag.Title = "Delete"; } <h2>Delete</h2> <p class="error">@ViewBag.ConcurrencyErrorMessage</p> <h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3> <fieldset> <legend>Department</legend> <div class="display-label"> @Html.LabelFor(model => model.Name) </div> <div class="display-field"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Name) </div> <div class="display-label"> @Html.LabelFor(model => model.Budget) </div> <div class="display-field"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Budget) </div> <div class="display-label"> @Html.LabelFor(model => model.StartDate) </div> <div class="display-field"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.StartDate) </div> <div class="display-label"> @Html.LabelFor(model => model.InstructorID) </div> <div class="display-field"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Administrator.FullName) </div> </fieldset> @using (Html.BeginForm()) { @Html.HiddenFor(model => model.DepartmentID) @Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Timestamp) <p> <input type="submit" value="Delete" /> | @Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index") </p> }
代码中在 h2 和 h3 之间增加了错误信息。
<p class="error">@ViewBag.ConcurrencyErrorMessage</p>
在 Administrator 区域将 LastName 替换为 FullName。
<div class="display-label"> @Html.LabelFor(model => model.InstructorID) </div> <div class="display-field"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Administrator.FullName) </div>
最后,增加了用于 DepartmentId 和 Timestamp 属性的隐藏域,在 Html.BeginForm 语句之后。
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.DepartmentID)
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Timestamp)
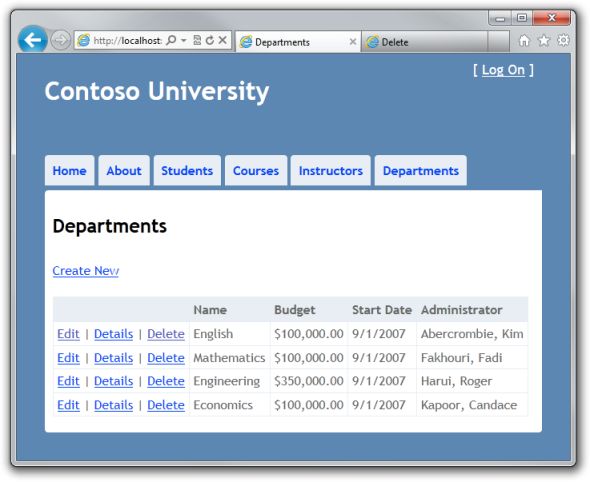
运行 Departments 的 Index 页面,使用同样的 URL 打开第二个浏览器窗口。
在第一个窗口中,在某个系上点击 Edit ,然后修改一个值,先不要点击 Save。
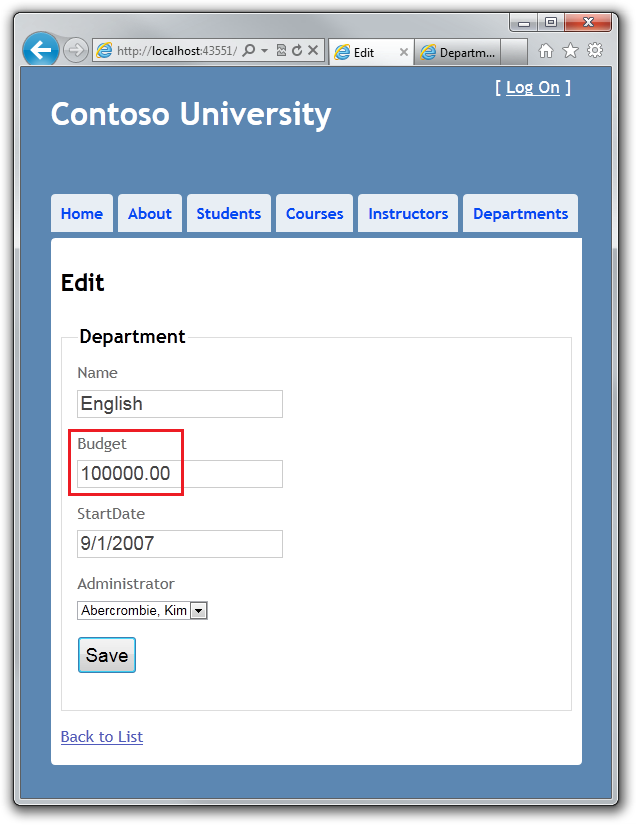
在第二个窗口中,在同样的系上,选择 Delete ,删除确认窗口出现了。
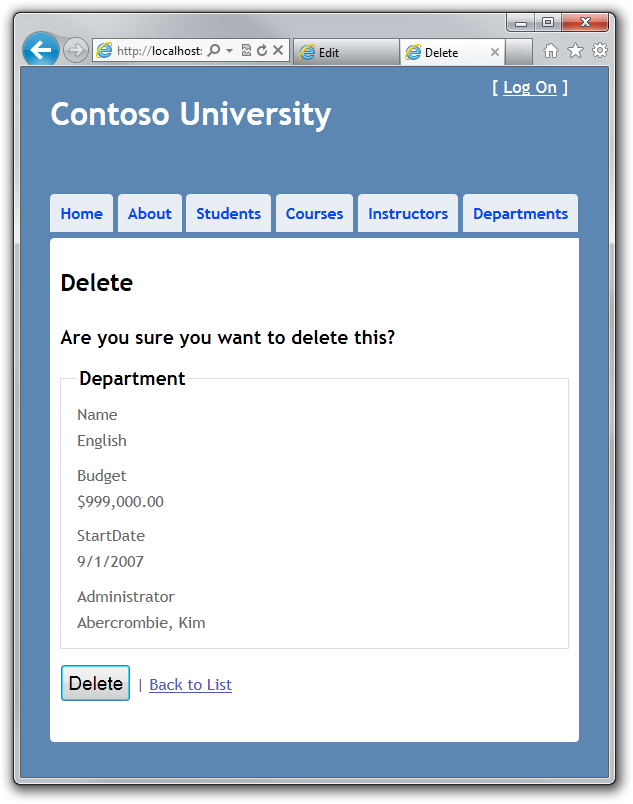
在第一个窗口中,点击 Save,在 Index 页面中确认修改信息。
现在,在第二个浏览器窗口中点击 Delete,你将会看到并发错误信息,其中 Department的名称已经使用当前数据库中的值刷新了。
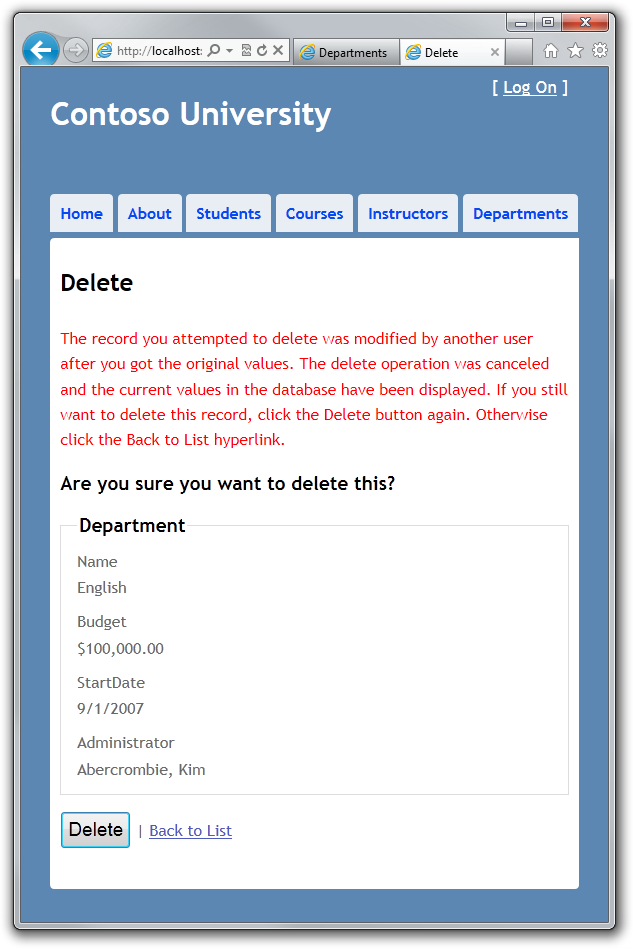
如果再次点击 Delete,你将会被重定向到 Index 页面,在显示中 Department 已经被删除了。
这里完整地介绍了处理并发冲突。对于处理并发冲突的其他场景,可以在 EF 团队的博客上查阅Optimistic Concurrency Patterns和Working with Property Values。下一次教程将会演示针对教师 Instructor 和学生 Student 实体的表层次的继承。