构造函数作用
构造函数可以在创建对象的时候初始化成员数据,或者利用现有对象修改现有对象数据(赋值拷贝构造函数)。
构造函数特征
自动调用,在创建对象的时候编译器自动调用 - 构造函数名和类名相同 - 构造函数没有返回值 - 可以有多个构造函数(类似函数重载)
构造函数种类
- 默认构造函数
- 自定义构造函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值构造函数
默认构造函数
编译器合成的默认构造函数
没有手动创建默认构造函数的时候,编译器会去自动合成构造函数
- 合成默认构造函数使用类内初始化数据去初始化数据
- 如果没有类内初始化数据,那么合成构造函数内就是空的什么都不做
默认构造函数
程序:
Student.h
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Student { public: void describion(); private: // 类内初始化 // 创建对象的时候如果没有构造函数那边编译器会自己合成默认构造函数并且用这些数据来初始化对象 // 编译器和合成的默认构造函数和手动定义的默认构造函数区别是: // 编译器合成的只会拿这些类内初始化数据去初始化对象 // 手动定义的默认构造函数如果有初始化数据的时候也可以用其他数据去覆盖初始化数据,也就是说数据初始化的值以构造函数内为准 int age = 12; char name[20] = "bian"; string sex = "男"; };
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
void Student::describion() {
cout << this->name << " " << this->sex << " " << this->age << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student s1; // 创建对象调用默认构造函数
s1.describion();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
bian 男 12
请按任意键继续. . .
手动定义的默认构造函数
手动定义的默认构造函数特点:Student::Student()
手动定义的默认构造函数和编译器和成的默认构造函数没太大区别。
唯一的区别:手动默认构造函数可以使用类内初始化的值,也可以不使用类内初始化的值。
程序:
Student.h
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Student { public: Student(); void describion(); private: // 类内初始化 int age = 12; char name[20] = "bian"; string sex = "男"; };
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
// 自定义默认构造函数
Student::Student() {
// 使用类内初始化数据来初始化
// 其实这种就是编译器合成默认构造函数
this->age = age;
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, "bian");
this->sex = sex;
/*
// 使用其他数据来初始化对象,此做法会覆盖类内初始化的设置值
this->age = 14;
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, "wang");
this->sex = "女";
*/
}
void Student::describion() {
cout << this->name << " " << this->sex << " " << this->age << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student s1; // 创建对象调用默认构造函数
s1.describion();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
bian 男 12
请按任意键继续. . .
自定义带参数的构造函数
自定义带参数的构造函数特点:Student::Student(int age, const char name)*
带参数,可以重载。
代码:
Student.h
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Student { public: Student(); // 默认构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name); // 自定义带参构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name, string sex); // 自定义带参构造重载函数 void describion(); private: // 类内初始化 int age = 12; char name[20] = "bian"; string sex = "男"; };
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
// 自定义默认构造函数
Student::Student() {
// 使用类内初始化数据来初始化
// 其实这种就是编译器合成默认构造函数
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义默认构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, "bian");
this->sex = "未知";
}
// 自定义带参构造函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
}
// 自定义带参构造重载函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name, string sex) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造重载函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
this->sex = sex;
}
void Student::describion() {
cout << this->name << " " << this->sex << " " << this->age << endl;
cout << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student s1; // 调用自定义默认构造函数
s1.describion();
Student s2(13, "wang"); // 调用自定义带参构造函数
s2.describion();
Student s3(14, "gao", "女"); // 调用自定义带参构造函数(重载)
s3.describion();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
Student::Student
自定义默认构造函数
bian 未知 12Student::Student
自定义带参构造函数
wang 男 13Student::Student
自定义带参构造重载函数
gao 女 14请按任意键继续. . .
为什么会出现 wang 男 13,可以思考下这个男。答案在标题下方。
拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数特点:Student::Student(const Student& other)
深浅拷贝是针对在堆区开辟内存的数据,深拷贝重新开辟内存存数据,浅拷贝直接把原来的堆区拿过来用
合成拷贝构造函数
合成拷贝构造函数是编译器自动合成的属于浅拷贝
自定义拷贝构造函数
自定义拷贝构造函数可以实现深拷贝
Student.h
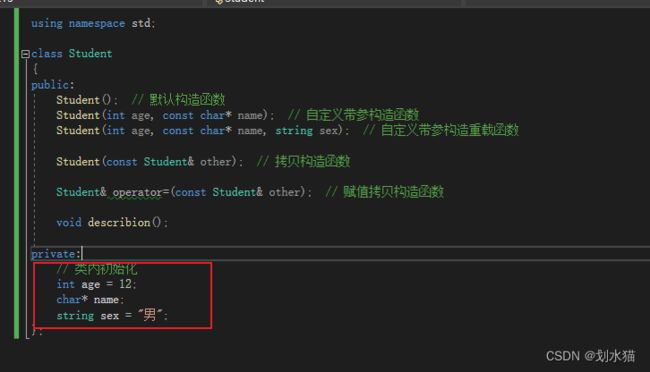
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Student { public: Student(); // 默认构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name); // 自定义带参构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name, string sex); // 自定义带参构造重载函数 Student(const Student& other); // 拷贝构造函数 void describion(); private: // 类内初始化 int age = 12; char* name; string sex = "男"; };
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
// 自定义默认构造函数
Student::Student() {
// 使用类内初始化数据来初始化
// 其实这种就是编译器合成默认构造函数
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义默认构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, "bian");
this->sex = "未知";
}
// 自定义带参构造函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
}
// 自定义带参构造重载函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name, string sex) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造重载函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
this->sex = sex;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Student::Student(const Student& other) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "拷贝构造函数" << endl;
// 浅拷贝,堆区地址还是以前的,其实编译器合成的拷贝构造函数就是这个
this->age = other.age;
this->name = other.name;
this->sex = other.sex;
// 深拷贝部分主要是堆区空间重新开辟
this->age = other.age;
// 重新开辟堆区
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, other.name);
this->sex = other.sex;
}
void Student::describion() {
cout << this->name << " " << this->sex << " " << this->age << endl;
cout << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
// 拷贝构造函数调用第二种时机函数形参是值传递而不是引用
void test1(Student other) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << endl;
}
// 拷贝构造函数调用第三种时机返回值是值传递
Student test2(const Student& other) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << endl;
return other;
}
int main() {
Student s1; // 调用自定义默认构造函数
s1.describion();
Student s2(13, "wang"); // 调用自定义带参构造函数
s2.describion();
Student s3(14, "gao", "女"); // 调用自定义带参构造函数(重载)
s3.describion();
// 拷贝构造函数:调用时机1、利用已有对象创建新对象
Student s4 = s2;
s4.describion();
Student s5(s3);
s5.describion();
// 拷贝构造函数:调用时机2、函数参数的值传递
test1(s5);
// 拷贝构造函数:调用时机3、函数返回值的值传递
test2(s5);
cout << endl;
// 拷贝构造函数:代用时机4、数组值时对象
Student s6[2] = { s1, s2 };
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
Student::Student
自定义默认构造函数
bian 未知 12Student::Student
自定义带参构造函数
wang 男 13Student::Student
自定义带参构造重载函数
gao 女 14Student::Student
拷贝构造函数
wang 男 13Student::Student
拷贝构造函数
gao 女 14Student::Student
拷贝构造函数
test1test2
Student::Student
拷贝构造函数Student::Student
拷贝构造函数
Student::Student
拷贝构造函数
请按任意键继续. . .
结果解析:
拷贝构造函数的调用时间
程序演示已经在自定义拷贝构造函数中写了。
- 使用已有对象创建新对象
- 函数参数是对象值传递
- 函数返回值是对象值传递
- 数组成员是对象
赋值构造函数(operator=)
赋值构造函数特点:Student& operator=(const Student& other)
利用已有对象修改已有对象(f2 = f1;)
重载=运算符
程序:
Student.h
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Student { public: Student(); // 默认构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name); // 自定义带参构造函数 Student(int age, const char* name, string sex); // 自定义带参构造重载函数 Student(const Student& other); // 拷贝构造函数 Student& operator=(const Student& other); // 赋值拷贝构造函数 void describion(); private: // 类内初始化 int age = 12; char* name; string sex = "男"; };
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
// 自定义默认构造函数
Student::Student() {
// 使用类内初始化数据来初始化
// 其实这种就是编译器合成默认构造函数
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义默认构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, "bian");
this->sex = "未知";
}
// 自定义带参构造函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
}
// 自定义带参构造重载函数
Student::Student(int age, const char* name, string sex) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "自定义带参构造重载函数" << endl;
this->age = age;
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, name);
this->sex = sex;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Student::Student(const Student& other) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "拷贝构造函数" << endl;
// 浅拷贝,堆区地址还是以前的
//this->age = other.age;
//this->name = other.name;
//this->sex = other.sex;
// 深拷贝部分主要是堆区空间重新开辟
this->age = other.age;
// 重新开辟堆区
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, other.name);
this->sex = other.sex;
}
// 赋值拷贝构造函数
Student& Student::operator=(const Student& other) {
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
cout << "赋值拷贝构造函数" << endl;
if (this == &other) {
return *this; // 防止出现f1=f1
}
// 浅拷贝,堆区地址还是以前的
//this->age = other.age;
//this->name = other.name;
//this->sex = other.sex;
// 深拷贝部分主要是堆区空间重新开辟
this->age = other.age;
// 重新开辟堆区
this->name = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->name, 20, other.name);
this->sex = other.sex;
return *this;
}
void Student::describion() {
cout << this->name << " " << this->sex << " " << this->age << endl;
cout << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student s1(14, "gao", "女"); // 调用自定义带参构造函数(重载)
s1.describion();
// 调用赋值拷贝构造函数
Student s2;
s2.describion();
s2 = s1;
s2.describion();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
Student::Student
自定义带参构造重载函数
gao 女 14Student::Student
自定义默认构造函数
bian 未知 12Student::operator =
赋值拷贝构造函数
gao 女 14请按任意键继续. . .
特别注意
1、当存在类内初始值的时候,除了赋值拷贝构造函数外,其他的构造函数(默认构造函数、自定义参数构造函数、拷贝构造函数)在执行构造函数前都会先执行下数据初始值。
2、初始化列表只存在构造函数中(成员数据、父类对象可以使用初始化列表初始化)
到此这篇关于C++面向对象中构造函数使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++构造函数内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!