Python正则表达式详解
一、正则表达式详解
正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列,便于检查一个字符串是否与某种模式匹配。通过定义规则,使得从字符串中把符合规则的字符串提取出来。
正则表达式的作用:
- 在实际开发过程中经常会有查找符合某些复杂规则的字符串的需要,比如:手机号、邮箱、图片地址等,这时候想匹配或者查找符合某些规则的字符串就可以使用正则表达式了;
正则表达式的特点:
- 正则表达式的语法太多,可读性差;
- 正则表达式通用行很强,能够适用于很多编程语言;
正则表达式的应用场景:
- 判断一个字符串是否符合规则;
- 取出制定数据;
- 爬虫岗位较为核心的技术;
- 彩票网站匹配彩票信息;
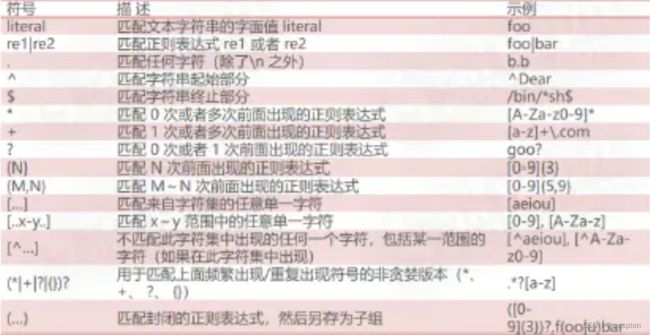
二、正则表达式符号匹配
1、正则表达式匹配语法
匹配单个字符:
正则表达式中的特殊字符:
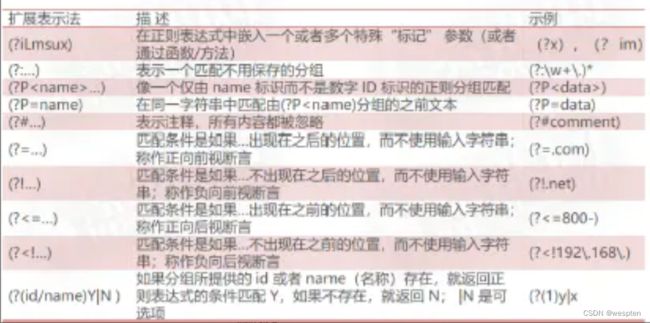
正则表达式的扩展表示法:
2、正则表达式的使用
|是或的关系,只要存在就会被捕获- 匹配到的数据只按字符串顺序返回,而不是按照匹配规则返回
In [18]: data = '[email protected]'
In [19]: print(re.findall('insane|com|loafer', data))
['insane', 'loafer', 'com']- ^ 等同于 \A
In [20]: print(re.findall('^insane',data))
['insane']
In [21]: print(re.findall('^insane1',data))
[]- $ 等同于 \Z
In [22]: print(re.findall('com$',data))
['com']
In [23]: print(re.findall('net$',data))
[]- * 匹配0次或多次
In [24]: print(re.findall('\w*',data))
['insane', '', 'loafer', '', 'com', '']- + 匹配1次或多次
- w+ 匹配1次或多次数字或字母
- @和.属于0次范围,不会被匹配出来
In [25]: print(re.findall('\w+',data))
['insane', 'loafer', 'com']- {3} 表示对于匹配到的数据只获取3次
In [31]: data = '[email protected]'
In [32]: print(re.findall('\w{3}',data))
['ins', 'ane', 'loa', 'com']
In [33]: print(re.findall('[a-z]{3}',data))
['ins', 'ane', 'loa', 'com'][a-zA-Z0-9] 基本上等同于 \w。
- {M, N} 表示对于匹配到的数据只获取M~N次
In [34]: data = '[email protected]'
In [35]: print(re.findall('\w{1,4}',data))
['insa', 'ne', 'loaf', 'com']- 反例:N 和 M 中间不能有空格
In [36]: print(re.findall('\w{1, 4}',data))
[]- [^...] 表示不匹配字符集中的字符
In [37]: data = '[email protected]'
In [38]: print(re.findall('[^insane]',data))
['@', 'l', 'o', 'f', '.', 'c', 'o', 'm']3、组的应用
In [42]: test = 'hello my name is insane'
In [43]: result = re.search('hello (.*) name is (.*)', test)
In [44]: result.groups()
Out[44]: ('my', 'insane')
In [45]: result.groups(1)
Out[45]: ('my', 'insane')
In [46]: result.group(1)
Out[46]: 'my'
In [47]: result.group(2)
Out[47]: 'insane'贪婪与非贪婪
- 0次或多次属于贪婪模式
- 通过?组合变成非贪婪模式
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/8/28 22:13
# @Author : InsaneLoafer
# @File : re_test2.py
import re
def check_url(url):
"""
判断url是否合法
:param url:
:return:
"""
result = re.findall('[a-zA-Z]{4,5}://\w*\.*\w+\.\w+', url)
if len(result) != 0:
return True
else:
return False
def get_url(url):
"""
通过组获取url中的某一部分
:param url:
:return:
"""
result = re.findall('[https://|http://](\w*\.*\w+\.\w+)', url)
if len(result) != 0:
return result[0]
else:
return ''
def get_email(data):
# result = re.findall('[0-9a-zA-Z_]+@[0-9a-zA-Z]+\.[a-zA-Z]+', data)
result = re.findall('.+@.+\.[a-zA-Z]+', data)
return result
html = ('')
def get_html_data(data):
"""
获取style中的display:
使用非贪婪模式
"""
result = re.findall('style="(.*?)"', data)
return result
def get_all_data_html(data):
"""
获取html中所有等号后双引号内的字符
:param data:
:return:
"""
result = re.findall('="(.+?)"', data)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
result = check_url('https://www.baidu.com')
print(result)
result = get_url('https://www.baidu.com')
print(result, 'https')
result = get_url('http://www.baidu.com')
print(result, 'http')
result = get_email('[email protected]')
print(result)
result = get_html_data(html)
print(result)
result = get_all_data_html(html)
print(result)True
www.baidu.com https
www.baidu.com http
['[email protected]']
['display:none;']
['s-top-nav', 'display:none;', 's-center-box']
Process finished with exit code 04、正则表达式中的特殊字符
In [1]: import re
In [2]: data = 'hello insane you are 26 years old'
In [3]: print(re.findall('\d', data))
['2', '6']
In [4]: print(re.findall('\s', data))
[' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ']
In [5]: data = 'i am insane'
In [6]: print(re.findall('\w', data))
['i', 'a', 'm', 'i', 'n', 's', 'a', 'n', 'e']
In [7]: data = 'i am insane, i am 26'
In [8]: print(re.findall('\w', data))
['i', 'a', 'm', 'i', 'n', 's', 'a', 'n', 'e', 'i', 'a', 'm', '2', '6']
In [9]: data = 'hello insane you are 26 years old'
In [10]: print(re.findall('\Ahello', data))
['hello']
In [11]: print(re.findall('\Ahellos', data))
[]
In [12]: print(re.findall('old\Z', data))
['old']
In [13]: print(re.findall('aold\Z', data))
[]
In [14]: print(re.findall('.', data))
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'i', 'n', 's', 'a', 'n', 'e', ' ', 'y', 'o', 'u', ' ', 'a', 'r', 'e', ' ', '2', '6', ' ', 'y', 'e', 'a', 'r', 's', ' ', 'o', 'l', 'd']
实战
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/8/28 19:52
# @Author : InsaneLoafer
# @File : re_test1.py
import re
def had_number(data):
result = re.findall('\d', data)
print(result)
for i in result:
return True
return False
def remove_number(data):
result = re.findall('\D', data)
print(result)
return ''.join(result)
def startswith(sub, data):
_sub = '\A%s' % sub
result = re.findall(_sub, data)
for i in result:
return True
return False
def endswith(sub, data):
_sub = '%s\Z' % sub
result = re.findall(_sub, data)
if len(result) != 0:
return True
else:
return False
def real_len(data):
"""
去掉字符串空格,判断真实长度
:param data:
:return:
"""
result = re.findall('\S', data)
print(result)
return len(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = 'i am insane, i am 26'
result = had_number(data)
print(result)
result = remove_number(data)
print(result)
data = 'hello insane, i am loafer. i am 26 year\'s old'
print(re.findall('\W', data))
result = startswith('hello', data)
print(result)
result = endswith('old', data)
print(result)
print(len(data))
result = real_len(data)
print(result)['2', '6']
True
['i', ' ', 'a', 'm', ' ', 'i', 'n', 's', 'a', 'n', 'e', ',', ' ', 'i', ' ', 'a', 'm', ' ']
i am insane, i am
[' ', ',', ' ', ' ', ' ', '.', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', "'", ' ']
True
True
45
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'i', 'n', 's', 'a', 'n', 'e', ',', 'i', 'a', 'm', 'l', 'o', 'a', 'f', 'e', 'r', '.', 'i', 'a', 'm', '2', '6', 'y', 'e', 'a', 'r', "'", 's', 'o', 'l', 'd']
36
Process finished with exit code 0三、正则表达式re模块
1、re模块使用
import re
str_data = 'hello insane, this is a good day!'
result = re.search('h([a-zA-Z])s', str_data)
print(result.groups())
>>> ('i',)- search()只匹配一次
import re
str_data = '本期彩票结果为: 10, 20, 1, 5, 7, 21, 22'
result = re.findall('(\d+, \d+, \d+, \d+, \d+, \d+, \d+)', str_data)
print(result)
>>> ['10, 20, 1, 5, 7, 21, 22']- \d:匹配数字
- +:匹配一个或多个
2、re模块中的函数
1)findall()的使用
findall(pattern , string, [flags])- 查找字符串中所有(非重复)出现的正则表达式模式,并返回一个匹配列表
2)search()的使用
search(pattern , string , flags=0)- 使用可选标记搜索字符串中第一次出现的正则表达式模式。如果匹配成功,则返回匹配对象如果失败,则返回None
3)group()与groups()
- group(num)返回整个匹配对象,或者编号为num的特定子组
- groups():返回一个包含所有匹配子组的元组(如果没有成功匹配,则返回一个空元组)
In [1]: test = 'hello my name is insane'
In [2]: import re
In [3]: result = re.search('hello (.*) name is (.*)', test)
In [4]: result.groups()
Out[4]: ('my', 'insane')
In [5]: result.group(1)
Out[5]: 'my'
In [6]: result.group(2)
Out[6]: 'insane'4)split()正则替换
split(pattern, string , max=0)- 根据正则表达式的模式分隔符,split 函数将字符串分割为列表,然后返回成功匹配的列表,分隔最多操作max 次(默认分割所有匹配成功的位置)
In [7]: data = 'hello world'
In [8]: print(re.split('\W', data))
['hello', 'world']5)re模块-match
match(pattern , string , flags=0)- 尝试使用带有可选的标记的正则表达式的模式来匹配字符串。如果匹配成功,就返回匹配对象;如果失败,就返回None。
- match只会匹配字符串从头开始的信息,如果匹配成功,就返回匹配对象;如果失败,就返回None。
- match返回的对象也可以使用
group函数调用
In [10]: result = re.match('hello', data)
In [11]: result.groups()
Out[11]: ()
In [12]: result.group()
Out[12]: 'hello'6)re模块-compile
compile(pattern, flags=0)- 定义一个匹配规则的对象
In [13]: data='hello my email is [email protected] i like python'
In [14]: re_obj = re.compile('email is (.*?) i')
In [15]: result = re_obj.findall(data)
In [16]: result
Out[16]: ['[email protected]']7)re的额外匹配要求
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/8/28 22:13
# @Author : InsaneLoafer
# @File : re_test2.py
import re
def check_url(url):
"""
判断url是否合法
:param url:
:return:
"""
re_g = re.compile('[a-zA-Z]{4,5}://\w*\.*\w+\.\w+')
print(re_g)
result = re_g.findall(url)
if len(result) != 0:
return True
else:
return False
def get_url(url):
"""
通过组获取url中的某一部分
:param url:
:return:
"""
re_g = re.compile('[https://|http://](\w*\.*\w+\.\w+)')
result = re_g.findall(url)
if len(result) != 0:
return result[0]
else:
return ''
def get_email(data):
# result = re.findall('[0-9a-zA-Z_]+@[0-9a-zA-Z]+\.[a-zA-Z]+', data)
re_g = re.compile('.+@.+\.[a-zA-Z]+')
result = re_g.findall(data)
return result
html = ('')
def get_html_data(data):
"""
获取style中的display:
使用非贪婪模式
"""
re_g = re.compile('style="(.*?)"')
result = re_g.findall(data)
return result
def get_all_data_html(data):
"""
获取html中所有等号后双引号内的字符
:param data:
:return:
"""
re_g = re.compile('="(.+?)"')
result = re_g.findall(data)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
result = check_url('https://www.baidu.com')
print(result)
result = get_url('https://www.baidu.com')
print(result, 'https')
result = get_url('http://www.baidu.com')
print(result, 'http')
result = get_email('[email protected]')
print(result)
result = get_html_data(html)
print(result)
result = get_all_data_html(html)
print(result)
re_g = re.compile('\s')
result = re_g.split(html)
print(result)
re_g = re.compile('
re.compile('[a-zA-Z]{4,5}://\\w*\\.*\\w+\\.\\w+')
True
www.baidu.com https
www.baidu.com http
['[email protected]']
['display:none;']
['s-top-nav', 'display:none;', 's-center-box']
['
四、常用的正则表达式汇总
1、校验数字的表达式
- 数字:
^[0-9]*$ - n位的数字:
^\d{n}$ - 至少n位的数字:
^\d{n,}$ - m-n位的数字:
^\d{m,n}$ - 零和非零开头的数字:
^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$ - 非零开头的最多带两位小数的数字:
^([1-9][0-9]*)+(\.[0-9]{1,2})?$ - 带1-2位小数的正数或负数:
^(\-)?\d+(\.\d{1,2})$ - 正数、负数、和小数:
^(\-|\+)?\d+(\.\d+)?$ - 有两位小数的正实数:
^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]{2})?$ - 有1~3位小数的正实数:
^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]{1,3})?$ - 非零的正整数:
^[1-9]\d*$或^([1-9][0-9]*){1,3}$ 或 ^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$ - 非零的负整数:
^\-[1-9][]0-9"*$或^-[1-9]\d*$
-非负整数:^\d+$或^[1-9]\d*|0$ - 非正整数:
^-[1-9]\d*|0$或^((-\d+)|(0+))$ - 非负浮点数:
^\d+(\.\d+)?$或^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$ - 非正浮点数:
^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$或^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$ - 正浮点数:
^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$或^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$ - 负浮点数:
^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$或^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$ - 浮点数:
^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$或^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$
2、校验字符的表达式
- 汉字:
^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,}$ - 英文和数字:
^[A-Za-z0-9]+$或^[A-Za-z0-9]{4,40}$ - 长度为3-20的所有字符:
^.{3,20}$ - 由26个英文字母组成的字符串:
^[A-Za-z]+$ - 由26个大写英文字母组成的字符串:
^[A-Z]+$ - 由26个小写英文字母组成的字符串:
^[a-z]+$ - 由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串:
^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ - 由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串:
^\w+$或^\w{3,20}$ - 中文、英文、数字包括下划线:
^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9_]+$ - 中文、英文、数字但不包括下划线等符号:
^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]+$或^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]{2,20}$ - 可以输入含有
^%&',;=?$\"等字符:[^%&',;=?$\x22]+ - 禁止输入含有~的字符:
[^~\x22]+
3、特殊需求表达式
- Email地址:
^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$ - 域名:
[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62}(\.[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62})+\.? - InternetURL:
[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]* 或 ^http://([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+(/[\w-./?%&=]*)?$ - 手机号码:
^(13[0-9]|14[5|7]|15[0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9]|18[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9])\d{8}$ - 电话号码("XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXXXXXX"和"XXXXXXXX):
^(\(\d{3,4}-)|\d{3.4}-)?\d{7,8}$ - 国内电话号码(0511-4405222、021-87888822):
\d{3}-\d{8}|\d{4}-\d{7} - 电话号码正则表达式(支持手机号码,3-4位区号,7-8位直播号码,1-4位分机号):
((\d{11})|^((\d{7,8})|(\d{4}|\d{3})-(\d{7,8})|(\d{4}|\d{3})-(\d{7,8})-(\d{4}|\d{3}|\d{2}|\d{1})|(\d{7,8})-(\d{4}|\d{3}|\d{2}|\d{1}))$) - 身份证号(15位、18位数字),最后一位是校验位,可能为数字或字符X:
(^\d{15}$)|(^\d{18}$)|(^\d{17}(\d|X|x)$) - 帐号是否合法(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线):
^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$ - 密码(以字母开头,长度在6~18之间,只能包含字母、数字和下划线):
^[a-zA-Z]\w{5,17}$ - 强密码(必须包含大小写字母和数字的组合,不能使用特殊字符,长度在 8-10 之间):
^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])[a-zA-Z0-9]{8,10}$ - 强密码(必须包含大小写字母和数字的组合,可以使用特殊字符,长度在8-10之间):
^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,10}$ - 日期格式:
^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2} - 一年的12个月(01~09和1~12):
^(0?[1-9]|1[0-2])$ - 一个月的31天(01~09和1~31):
^((0?[1-9])|((1|2)[0-9])|30|31)$ - 钱的输入格式:
- 有四种钱的表示形式我们可以接受:"10000.00" 和 "10,000.00", 和没有 "分" 的 "10000" 和 "10,000":
^[1-9][0-9]*$ - 这表示任意一个不以0开头的数字,但是,这也意味着一个字符"0"不通过,所以我们采用下面的形式:
^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$ - 一个0或者一个不以0开头的数字.我们还可以允许开头有一个负号:
^(0|-?[1-9][0-9]*)$ - 这表示一个0或者一个可能为负的开头不为0的数字.让用户以0开头好了.把负号的也去掉,因为钱总不能是负的吧。下面我们要加的是说明可能的小数部分:
^[0-9]+(.[0-9]+)?$ - 必须说明的是,小数点后面至少应该有1位数,所以"10."是不通过的,但是 "10" 和 "10.2" 是通过的:
^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$ - 这样我们规定小数点后面必须有两位,如果你认为太苛刻了,可以这样:
^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$ - 这样就允许用户只写一位小数.下面我们该考虑数字中的逗号了,我们可以这样:
^[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*(.[0-9]{1,2})?$ - 1到3个数字,后面跟着任意个 逗号+3个数字,逗号成为可选,而不是必须:
^([0-9]+|[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*)(.[0-9]{1,2})?$ - 备注:这就是最终结果了,别忘了"+"可以用"*"替代如果你觉得空字符串也可以接受的话(奇怪,为什么?)最后,别忘了在用函数时去掉去掉那个反斜杠,一般的错误都在这里
- 有四种钱的表示形式我们可以接受:"10000.00" 和 "10,000.00", 和没有 "分" 的 "10000" 和 "10,000":
- xml文件:
^([a-zA-Z]+-?)+[a-zA-Z0-9]+\\.[x|X][m|M][l|L]$ - 中文字符的正则表达式:
[\u4e00-\u9fa5] - 双字节字符:
[^\x00-\xff](包括汉字在内,可以用来计算字符串的长度(一个双字节字符长度计2,ASCII字符计1)) - 空白行的正则表达式:
\n\s*\r(可以用来删除空白行) - HTML标记的正则表达式:
<(\S*?)[^>]*>.*?|<.*? />( 首尾空白字符的正则表达式:^\s*|\s*$或(^\s*)|(\s*$)(可以用来删除行首行尾的空白字符(包括空格、制表符、换页符等等),非常有用的表达式) - 腾讯QQ号:
[1-9][0-9]{4,}(腾讯QQ号从10000开始) - 中国邮政编码:
[1-9]\d{5}(?!\d)(中国邮政编码为6位数字) - IPv4地址:
((2(5[0-5]|[0-4]\d))|[0-1]?\d{1,2})(\.((2(5[0-5]|[0-4]\d))|[0-1]?\d{1,2})){3}
4、不以xx开头或结尾
不以某个字符开头:
^(?!-):表示不以-开头
不以某个字符结尾:
(?:表示不以-结尾,注意有个<
域名校验:
- 域名只能包含英文、数字和中英文连接线
-,并且不以中英文连接线-开头或结尾 ^(?!-)(^[a-zA-Z0-9-]+$)(?