Java 多线程基础
1. 程序、线程、进程
| 定义 | |
|---|---|
| 程序 | 算法 + 数据结构;静态;只有将程序加载到内存中,系统为其分配资源才能执行 |
| 线程 | 进程的一个实体,是系统独立调度和分配的基本单位 |
| 进程 | 资源分配和调度的基本单位;动态 |
2. 线程的创建
1. 继承 Thread 类
/*
创建线程方式一:
继承 Thread 类
重写 run() 方法,调用 start 开启线程
*/
public class ThreadTest extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//run 方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("run 线程: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建一个线程对象
ThreadTest threadTest = new ThreadTest();
//2. 调用 start() 方法开启线程
threadTest.start();
// main线程,主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程: " + i);
}
}
}
主线程: 0
run 线程: 0
主线程: 1
主线程: 2
主线程: 3
主线程: 4
run 线程: 1
run 线程: 2
run 线程: 3
run 线程: 4
run 线程: 5
run 线程: 6
主线程: 5
run 线程: 7
主线程: 6
run 线程: 8
主线程: 7
run 线程: 9
run 线程: 10
主线程: 8
run 线程: 11
run 线程: 12
run 线程: 13
run 线程: 14
run 线程: 15
run 线程: 16
主线程: 9
run 线程: 17
run 线程: 18
run 线程: 19
主线程: 10
主线程: 11
主线程: 12
主线程: 13
主线程: 14
主线程: 15
主线程: 16
主线程: 17
主线程: 18
主线程: 19
Process finished with exit code 0
2. 实现 Runnable 接口(推荐使用)
//实现 Runnable 接口,重写 run 方法,执行线程需要丢入runnable接口实现类,并调用 start 方法
public class ThreadRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//run 方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("run 线程: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建一个 runnable 接口的实现类对象
ThreadRunnable threadRunnable = new ThreadRunnable();
//2. 创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程(代理)
// Thread thread = new Thread(threadRunnable);
// thread.start();
new Thread(threadRunnable).start();
// main线程,主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程: " + i);
}
}
}
结果和上面结果类似
3. 两种方法对比
| 继承 Thread 类 | 实现 Runnable 接口 |
|---|---|
| 子类继承 Thread 类具备多线程能力 | 实现接口 Runnable 具备多线程能力 |
| 启动线程:子类对象.start(); | 启动线程:new Thread(threadRunnable).start(); |
| 不建议使用,避免OOP单继承局限性 | 推荐使用:避免单继承的局限性,灵活方便,方便同一个对象被多个线程使用 |
4. 实现 Callable 接口
//线程创建方式三:实现 callable 接口
public class TestCallable implements Callable {
private String str;
public TestCallable(String str){
this.str = str;
}
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(str);
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建目标对象
TestCallable tc1 = new TestCallable("线程1");
TestCallable tc2 = new TestCallable("线程2");
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(tc1);
Future<Boolean> result2 = ser.submit(tc2);
//获取结果
boolean r1 = result1.get();
boolean r2 = result2.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdownNow();
System.out.println("线程1执行结果:" + r1);//打印结果
System.out.println("线程2执行结果:" + r2);//打印结果
}
}
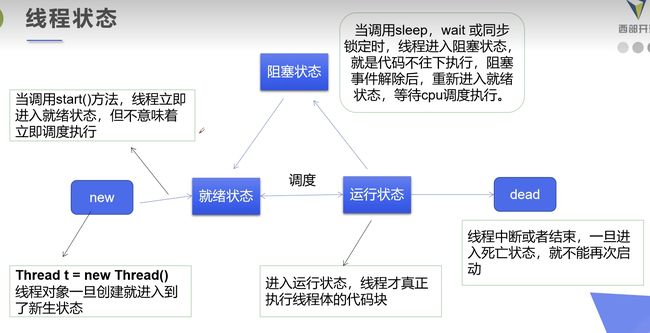
3. 线程状态
以后最好自己画
4. 线程操作
1. 线程停止
线程停止
- 建议线程正常停止—>利用次数,不建议死循环
- 建议使用标志位—>这只一个标志位
- 建议不要使用stop或者destroy等过时或者JDK不建议使用的方法
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
//1. 设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while(flag){
System.out.println("线程正在启动中....." + i++);
}
}
//2. 设置一个公共的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程:" + i);
//调用自定义方法停止线程
if(i == 90){
testStop.stop();
System.out.println("线程停止。。。。。");
}
}
}
}
2. 线程休眠_sleep
- sleep 指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数
- sleep存在异常InterruptedExceptionsleep
- 时间达到后线程进入就绪状态
- sleep可以模拟网络延时,倒计时等。
- 每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁;
模拟网络延时
//模拟网络延时:放大问题的发生性
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNum = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if(ticketNum <= 0){
break;
}
//模拟延时
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "抢到了第 " + ticketNum-- +" 票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSleep testSleep = new TestSleep();
//开启两个线程
new Thread(testSleep,"小明").start();
new Thread(testSleep,"黄牛").start();
}
}
运行结果:
小明抢到了第 10 票
黄牛抢到了第 9 票
小明抢到了第 8 票
黄牛抢到了第 8 票
黄牛抢到了第 7 票
小明抢到了第 7 票
小明抢到了第 6 票
黄牛抢到了第 5 票
小明抢到了第 4 票
黄牛抢到了第 3 票
小明抢到了第 1 票
黄牛抢到了第 2 票
模拟倒计时
public class TestSleep2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//打印系统时间
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());// 获取系统当前时间
while(true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新当前时间
}
}
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while(true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if(num <= 0) break;
}
}
}
3. 线程礼让_yield
- 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
- 将线程从运行转态转为就绪状态
- 让 cpu 重新调度,礼让不一定成功
//礼让不一定成功
public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myyield myyield = new Myyield();
new Thread(myyield,"A").start();
new Thread(myyield,"B").start();
}
}
class Myyield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " start...");
Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " stop...");
}
}
礼让成功
A start...
B start...
B stop...
A stop...
礼让不成功
A start...
A stop...
B start...
B stop...
4. 线程强制执行_join
- join 合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
- 可以想象为插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("vip来了:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动线程
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i == 20){
thread.join();//插队
}
System.out.println("普通人来了:" + i);
}
}
}
5. 线程状态观测
线程的六种转态
代码演示
//观察线程状态
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//使用 Lamda 表达式创建线程
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("endinng-----");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); // NEW
//观察启动后
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);// Run
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){//线程不终止
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();// 观察线程状态
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
注意:线程停止后,不能再 start()。
6. 线程优先级
- 线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10
- Thread.MIN_PRIORITY =1
- Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10
- Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5
- 优先级低只是意味着获得调度的概率低.并不是优先级低就不会被调用了.这都是看CPU的调度
- 优先级的设定建议在start()调度前
//测试线程优先级
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印主线程
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority);
//先设置优先级,再启动
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(5);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(6);
t5.start();
t6.setPriority(8);
t6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
7. 守护线程
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 如,后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收等待.
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
//启动守护线程
thread.setDaemon(true);//默认为false,为false就是用户线程
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
//上帝
class God implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("上帝守护着你。。。");
}
}
}
//自己
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) {
System.out.println("开心活好每一天。。。");
}
System.out.println("幸福的来到天堂====");
}
}
5. 线程同步
1. 线程不安全的三个例子
车站买票
//不安全的买票
//线程不安全
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
syn.BuyTicket station = new syn.BuyTicket();
new Thread(station, "你").start();
new Thread(station, "我").start();
new Thread(station, "黄牛").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
//票
private int ticketNum = 10;
//标志位:外部停止方式
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
//买票
while (flag) {
buy();
}
}
private void buy() {
//判断是否有票
if (ticketNum <= 0) {
flag = false;
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到:" + ticketNum--);
}
}
银行取款
//不安全的取钱
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你");
Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account, 100, "girlFriend");
you.start();
girlFriend.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account {
int money; //余额
String name; //卡名
public Account(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行:模拟取款
class Drawing extends Thread {
Account account;//账户
//取了多少钱
int drawingMoney;
//手里多少钱
int nowMoney;
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
@Override
public void run() {
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "余额不足!!!");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);// 放大问题
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//卡余额
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//你手里的钱
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name + "余额为:" + account.money);
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱" + nowMoney);
}
}
线程不安全的集合
//线程不安全的集合
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
2. 同步方法及同步块(安全)
安全的买票(同步方法)
//安全的买票
//线程安全
public class SafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket1 station = new BuyTicket1();
new Thread(station, "你").start();
new Thread(station, "我").start();
new Thread(station, "黄牛").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket1 implements Runnable {
//票
private int ticketNum = 10;
//标志位:外部停止方式
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
//买票
while (flag) {
buy();
}
}
//synchronized 同步方法,锁的是 this
private synchronized void buy() {
//判断是否有票
if (ticketNum <= 0) {
flag = false;
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到:" + ticketNum--);
}
}
安全的取钱(同步块)
//安全的取钱
public class SafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SafeAccount account = new SafeAccount(100, "结婚基金");
SafeDrawing you = new SafeDrawing(account, 50, "你");
SafeDrawing girlFriend = new SafeDrawing(account, 100, "girlFriend");
you.start();
girlFriend.start();
}
}
//账户
class SafeAccount {
int money; //余额
String name; //卡名
public SafeAccount(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行:模拟取款
class SafeDrawing extends Thread {
SafeAccount account;//账户
//取了多少钱
int drawingMoney;
//手里多少钱
int nowMoney;
public SafeDrawing(SafeAccount account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(account){
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "余额不足!!!");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);// 放大问题
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//卡余额
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//你手里的钱
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name + "余额为:" + account.money);
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱" + nowMoney);
}
}
}
安全的集合(同步代码块)
//线程安全的集合
public class SafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (list) {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
3. CopyOnWriteArrayList(安全的集合)
//测试JUC 安全类型的集合
public class TestJUC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
6. 死锁
1. 死锁的定义
死锁是指两个或两个以上的进程在执行过程中,由于竞争资源或者由于彼此通信而造成的一种阻塞的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去。此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁,这些永远在互相等待的进程称为死锁进程。
2. 死锁的四个必要条件
- 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用。
- 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放。
- 不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在末使用完之前,不能强行剥夺。
- 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系。
上面列出了死锁的四个必要条件,我们只要想办法破其中的任意一个或多个条件就可以避免死锁发生
3. 代码举例
死锁举例
//死锁:多个进程互相抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup girl1 = new Makeup(0,"灰姑凉");
Makeup girl2 = new Makeup(1,"白雪公主");
girl1.start();
girl2.start();
}
}
//定义两种资源
//口红
class Lipstick{}
//镜子
class Mirror{}
//定义化妆类
class Makeup extends Thread{
//使用静态关键字保证资源只有一份
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;//选择哪一种资源
String girlName;
public Makeup(int choice,String girlName){
this.choice = choice;
this.girlName = girlName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if(choice == 0){
synchronized(lipstick){ //获得口红资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红资源");
Thread.sleep(1000);
//死锁产生原因
synchronized (mirror){ // 一秒钟后想要获取镜子资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获取镜子资源");
}
}
}else{
synchronized(mirror){ //获得镜子资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子资源");
Thread.sleep(1000);
//死锁产生原因
synchronized (lipstick){ // 一秒钟后想要获取口红资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获取口红资源");
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
白雪公主获得镜子资源
灰姑凉获得口红资源
解决死锁
//死锁:多个进程互相抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup girl1 = new Makeup(0,"灰姑凉");
Makeup girl2 = new Makeup(1,"白雪公主");
girl1.start();
girl2.start();
}
}
//定义两种资源
//口红
class Lipstick{}
//镜子
class Mirror{}
//定义化妆类
class Makeup extends Thread{
//使用静态关键字保证资源只有一份
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;//选择哪一种资源
String girlName;
public Makeup(int choice,String girlName){
this.choice = choice;
this.girlName = girlName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if(choice == 0){
synchronized(lipstick){ //获得口红资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红资源");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
synchronized (mirror){ // 一秒钟后想要获取镜子资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获取镜子资源");
}
}else{
synchronized(mirror){ //获得镜子资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子资源");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
synchronized (lipstick){ // 一秒钟后想要获取口红资源
System.out.println(this.girlName + "获取口红资源");
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
灰姑凉获得口红资源
白雪公主获得镜子资源
灰姑凉获取镜子资源
白雪公主获取口红资源
7. Lock 锁
1. 背景
- 从DK 5.0开始( Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制——通过显式定义同步锁对象来实现同步。同步锁使用Lock对象充当
- java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具。锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象
- ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显式加锁、释放锁。
2. 代码演示
//测试Lock
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义三个线程
Ticket t1 = new Ticket();
new Thread(t1).start();
new Thread(t1).start();
new Thread(t1).start();
}
}
//买票
class Ticket implements Runnable {
int ticketNum = 1000;
//定义可重入锁(Lock锁的实现类)
private final ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
//推荐是用try catch 来加解锁
try {
//加锁
reentrantLock.lock();
while (true) {
if (ticketNum > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(ticketNum--);
} else {
break;
}
}
} finally {
//解锁
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
3. synchronized 和 Lock 的对比
| synchronized | Lock |
|---|---|
| 隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放 | 显式锁(手动开启和关闭锁,别忘记关闭锁) |
| 代码块锁和方法锁 | 只有代码块锁 |
| ----- | JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,并且具有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类) |
优先使用顺序
Lock > 同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配」怕应负际) > 同步方法(在方法体之外)
8. 线程通信
1. 线程通信的方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| wait() | 表示线程一直等待,直到其他线程通知,与sleep不同,会释放锁 |
| wait(long timeout) | 指定等待的毫秒数 |
| notify() | 唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程 |
| notifyAll() | 唤醒同一个对象上所有调用wait()方法的线程,优先级别高的线程优先调度 |
注意:均是Object类的方法,都只能在同步方法或者同步代码块中使用.否则会抛出异常llleaalMonitorStateException
2. 生产者消费者问题
管程法(缓冲区)
//测试生产者消费者模型----> 利用缓冲区来解决
// 生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区
public class TestPC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynContainer container = new SynContainer();
new Productor(container).start();
new Cusumer(container).start();
}
}
//生产者
class Productor extends Thread {
SynContainer container;
public Productor(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
//生产
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
container.push(new Product(i));
System.out.println("生产了第" + i + "个产品");
}
}
}
//消费者
class Cusumer extends Thread {
SynContainer container;
public Cusumer(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
//消费
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("消费了第" + container.pop().id + "个产品");
}
}
}
//产品
class Product {
int id;
public Product(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//缓冲区
class SynContainer {
//需要一个容器大小
Product[] products = new Product[10];
//容器计数器
int count = 0;
//生产者放入产品
public synchronized void push(Product product) {
//容器满了,需要等待消费者消费
if (count == products.length) {
//通知消费者消费,生产者等待
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//如果没有满,则放入产品
products[count++] = product;
//通知消费者消费
this.notifyAll();
}
//消费者消费产品
public synchronized Product pop() {
//判断是否可以消费
if (count == 0) {
//等待生产者生产,消费者等待
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//可以消费
System.out.println(count);
count--; //要在前,因为count不满足条件
Product product = products[count];
//通知生产者生产
this.notifyAll();
return product;
}
}
信号灯(标志位)
设置一个标志位控制线程等待或者唤醒
9. 线程池
1. 线程池的好处
- 背景:经常创建和销毁、使用量特别大的资源,比如并发情况下的线程,对性能影响很大。
- 思路:提前创建好多个线程,放入线程池中,使用时直接获取,使用完放回池中。可以避免频繁创建销毁、实现重复利用。类似生活中的公共交通工具。
- 好处:
- 提高响应速度(减少了创建新线程的时间)
- 降低资源消耗(重复利用线程池中线程,不需要每次都创建)
- 便于线程管理(…….)
- corePoolSize:核心池的大小
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
- keepAliveTime:线程没有任务时最多保持多长时间后会终止
2. 线程池API
-
ExecutorService:真正的线程池接口。常见子类ThreadPoolExecutor
- void execute(Runnable command)∶执行任务/命令,没有返回值,一般用来执行Runnable
Future submit(Callable task):执行任务,有返回值,一般又来执行Callable - void shutdown()∶关闭连接池
-
Executors:工具类、线程池的工厂类,用于创建并返回不同类型的线程池
3. 代码演示
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建服务,创建线程池,参数是线程池大小
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
//2. 关闭连接
service.shutdown();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
参考
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1V4411p7EF/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=25b05e9bd8b4bdac16ca2f47bbeb7990