FFmpeg入门详解之119:FFmpeg的SDK编程回顾总结并操练
3.FFmpeg的SDK编程回顾总结并操练
参考课程:“FFmpeg4.3--系列5--SDK二次开发详解与实战”
FFmpeg主要框架
FFmpeg骨架:“八大金刚”核心开发库
1、libavformat:
2、libavcodec:
3、libavutil:
4、libswscale:
5、libpostproc:
6、libavdevice:
7、libswresmaple:
8、libavfilter:
FFmpeg SDK案例实战
数据结构
API
解封装
解码
显示
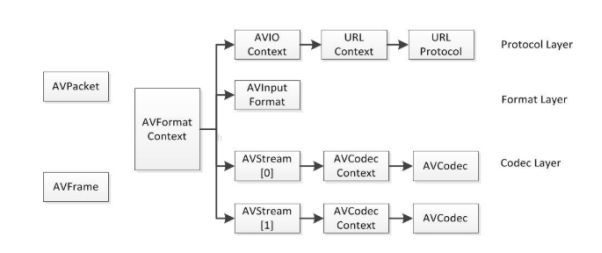
FFMPEG中结构体很多。
最关键的结构体可以分成以下几类:
AVPacket: 压缩后的音视频包:h264/265/mpeg4/...,, mp3/ac3/aac/...
AVFrame: 未压缩的音视频帧:RGB/YUV, PCM
a) 解协议(http,rtsp,rtmp,mms,hls,file,tcp,udp,......)
AVIOContext,URLContext,URLProtocol主要存储视音频使用的协议的类型以及状态。URLProtocol存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种协议都对应一个URLProtocol结构。(注意:FFMPEG中文件也被当做一种协议“file”)
Ffmpeg -i xxxInput -vcodec xx -acodec xxx -f flv -y rtmp://ip:port/.../channel/test1
xxxInput: rtsp, rtmp,http,file,.....
b)解封装(flv,avi,rmvb,mp4)
AVFormatContext主要存储视音频封装格式中包含的信息;AVInputFormat存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种视音频封装格式都对应一个AVInputFormat 结构。
c)解码(h264,mpeg2,aac,mp3)
每个AVStream存储一个视频/音频流的相关数据;
每个AVStream对应一个AVCodecContext,存储该视频/音频流使用解码方式的相关数据;
每个AVCodecContext中对应一个AVCodec,包含该视频/音频对应的解码器。
每种解码器都对应一个AVCodec结构。
d) 存数据
视频的话,每个结构一般是存一帧;音频可能有好几帧
解码前(压缩)数据: AVPacket
解码后(未压缩、原始)数据:AVFrame
三个结构体:AVFrame,AVPicture,AVPacket
解封装案例实战
源码参考:demuxer_test1.cpp
原理分析
最主要的API有如下几个。
FFmpeg中将编码帧及未编码帧均称作frame,本文为方便,将编码帧称作packet,未编码帧称作frame。
原始图片(yuv,rgb)或声音(pcm流):未压缩的,未编码的,
H264/265, aac/ac3/mp3:压缩的,编码的
读取本地文件:
读取rtsp流:
1)vlc模拟rtsp流
2)代码读取
3)测试:ffplay -i rtsp://127.0.0.1:8554/aabb
2.1 avformat_open_input()
这个函数会打开输入媒体文件,读取文件头,将文件格式信息存储在第一个参数AVFormatContext中。
文件、网络流(http,rtmp,rtsp,......)
2.2 avformat_find_stream_info()
这个函数会读取一段视频文件数据并尝试解码,将取到的流信息填入AVFormatContext.streams中。
AVFormatContext.streams是一个指针数组,数组大小是AVFormatContext.nb_streams
2.3 av_read_frame()
本函数用于解复用过程:读帧(AVFrame)是错误的,应该是读包AVPacket)
While(fp.eoef(...)){
//1. 解封装
av_read_frame(&AVPacket);
//2. 解码://AVFrame
//3. 大小调整,sws_scale, libyuv
/// yuv-->rgb,
}
本函数将存储在输入文件中的数据分割为多个packet,每次调用将得到一个packet。packet可能是视频帧、音频帧或其他数据,解码器只会解码视频帧或音频帧,非音视频数据并不会被扔掉、从而能向解码器提供尽可能多的信息。
对于视频来说,一个packet只包含一个视频帧;
对于音频来说,若是帧长固定的格式则一个packet可包含整数个音频帧,若是帧长可变的格式则一个packet只包含一个音频帧。
读取到的packet每次使用完之后应调用av_packet_unref(AVPacket *pkt)清空packet。否则会造成内存泄露。
2.4 av_write_frame()
本函数用于复用过程,将packet写入输出媒体。
packet交织是指:不同流的packet在输出媒体文件中应严格按照packet中dts递增的顺序交错存放。
本函数直接将packet写入复用器(muxer),不会缓存或记录任何packet。本函数不负责不同流的packet交织问题。由调用者负责。
如果调用者不愿处理packet交织问题,应调用av_interleaved_write_frame()替代本函数。
2.5 av_interleaved_write_frame()
本函数用于复用过程,将packet写入输出媒体。
本函数将按需在内部缓存packet,从而确保输出媒体中不同流的packet能按照dts增长的顺序正确交织。
2.6 avio_open()
创建并初始化一个AVIOContext,用于访问输出媒体文件。
2.7 avformat_write_header()
向输出文件写入文件头信息。
2.8 av_write_trailer()
向输出文件写入文件尾信息。
AV_TIME_BASE:时间基,时间刻度
每秒:分成25份, 或分成100份 , 90000份
Per : 1/25, 1/100, 1/90000
Fps: 25, 30, 60, 29.97,
1/25: 2份,占多少;把它转换成1/90000后,是多少份?
1/25 * 2 ==> 90000/25 * 2
代码:s26_chapter3_test1.cpp
1.分配解复用器上下文avformat_alloc_context
2.根据url打开本地文件或网络流avformat_open_input
3.读取媒体的部分数据包以获取码流信息avformat_find_stream_info
4.读取码流信息:循环处理
4.1 从文件中读取数据包av_read_frame
4.2 定位文件avformat_seek_file或av_seek_frame
5.关闭解复用器avformat_close_input
本例子实现的是将音视频分离,例如将封装格式为 FLV、MKV、MP4、AVI 等封装格式的文件,将音频、视频读取出来并打印。
实现的过程,可以大致用如下图表示:
音视频同步与AVPacket、PTS、DTS
FFmpeg里有两种时间戳:DTS(Decoding Time Stamp)和PTS(Presentation Time Stamp)。 顾名思义,前者是解码的时间,后者是显示的时间。
要仔细理解这两个概念,需要先了解FFmpeg中的packet和frame的概念。
FFmpeg中用AVPacket结构体来描述解码前或编码后的压缩包,用AVFrame结构体来描述解码后或编码前的原始未压缩信号帧。
对于视频来说,AVFrame就是视频的一帧图像。这帧图像什么时候显示给用户,就取决于它的PTS。
DTS是AVPacket里的一个成员,表示这个压缩包应该什么时候被解码。 如果视频里各帧的编码是按输入顺序(也就是显示顺序)依次进行的,那么解码和显示时间应该是一致的。可事实上,在大多数编解码标准(如H.264或HEVC)中,编码顺序和输入顺序并不一致。 于是才会需要PTS和DTS这两种不同的时间戳。
基本概念:
I frame :帧内编码帧 又称intra picture,I 帧通常是每个 GOP(MPEG 所使用的一种视频压缩技术)的第一个帧,经过适度地压缩,做为随机访问的参考点,可以当成图象。I帧可以看成是一个图像经过压缩后的产物。
P frame: 前向预测编码帧 又称predictive-frame,通过充分将低于图像序列中前面已编码帧的时间冗余信息来压缩传输数据量的编码图像,也叫预测帧;
B frame: 双向预测内插编码帧 又称bi-directional interpolated prediction frame,既考虑与源图像序列前面已编码帧,也顾及源图像序列后面已编码帧之间的时间冗余信息来压缩传输数据量的编码图像,也叫双向预测帧;
PTS:Presentation Time Stamp。PTS主要用于度量解码后的视频帧什么时候被显示出来
DTS:Decode Time Stamp。DTS主要是标识读入内存中的bit流在什么时候开始送入解码器中进行解码。
在没有B帧存在的情况下DTS的顺序和PTS的顺序应该是一样的。
摄像头:
I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, ..........I13, I14, I15.......(rgb, yuv)
编码器:时差
Fps:30 , width, height
GOP:
I1,P2, P3, P4, P5, .........., P12, I13, P14,P15,P16,......
I1, B3,B4,P2,
IPB帧的不同:
I frame:自身可以通过视频解压算法解压成一张单独的完整的图片。
P frame:需要参考其前面的一个I frame 或者B frame来生成一张完整的图片。
B frame:则要参考其前一个I或者P帧及其后面的一个P帧来生成一张完整的图片。
两个I frame之间形成一个GOP,在x264中同时可以通过参数来设定bf的大小,即:I 和p或者两个P之间B的数量。
通过上述基本可以说明如果有B frame 存在的情况下一个GOP的最后一个frame一定是P.
DTS和PTS的不同:
DTS主要用于视频的解码,在解码阶段使用.
PTS主要用于视频的同步和输出.在display的时候使用.
在没有B frame的情况下.DTS和PTS的输出顺序是一样的.
例子:
摄像头:
I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, ..........I13, I14, I15.......(rgb, yuv)
编码器:时差
Fps:30 , width, height
GOP:
I1,P2, P3, P4, P5, .........., P12, I13, P14,P15,P16,......
I1, B3,B4,P2,
下面给出一个GOP为15的例子,其解码的参照frame及其解码的顺序都在里面:
如上图:I frame 的解码不依赖于任何的其它的帧.
而p frame的解码则依赖于其前面的I frame或者P frame.
B frame的解码则依赖于其前的最近的一个I frame或者P frame 及其后的最近的一个P frame.
案例代码
#includeextern "C" { #include } /** * @brief 将一个AVRational类型的分数转换为double类型的浮点数 * @param r:r为一个AVRational类型的结构体变量,成员num表示分子,成员den表示分母,r的值即为(double)r.num / (double)r.den。用这种方法表示可以最大程度地避免精度的损失 * @return 如果变量r的分母den为0,则返回0(为了避免除数为0导致程序死掉);其余情况返回(double)r.num / (double)r.den */ static double r2d(AVRational r) { return r.den == 0 ? 0 : (double)r.num / (double)r.den; } int main001() { //需要读取的本地媒体文件相对路径为video1.mp4,这里由于文件video1.mp4就在工程目录下,所以相对路径为video1.mp4 const char *path = "ande_10s.mp4";// or : rtsp/rtmp:///...... //const char *path = "audio1.mp3"; ///av_register_all(); //初始化所有组件,只有调用了该函数,才能使用复用器和编解码器。否则,调用函数avformat_open_input会失败,无法获取媒体文件的信息 avformat_network_init(); //打开网络流。这里如果只需要读取本地媒体文件,不需要用到网络功能,可以不用加上这一句 AVDictionary *opts = NULL; // dictionary[key:value], json //AVFormatContext是描述一个媒体文件或媒体流的构成和基本信息的结构体 AVFormatContext *ic = NULL; //媒体打开函数,调用该函数可以获得路径为path的媒体文件的信息,并把这些信息保存到指针ic指向的空间中(调用该函数后会分配一个空间,让指针ic指向该空间) int re = avformat_open_input(&ic, path, NULL, &opts); if (re != 0) //如果打开媒体文件失败,打印失败原因。比如,如果上面没有调用函数av_register_all,则会打印“XXX failed!:Invaliddata found when processing input” { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); printf("open %s failed!:%s", path, buf); } else //打开媒体文件成功 { printf("打开媒体文件 %s 成功!\n", path); //调用该函数可以进一步读取一部分视音频数据并且获得一些相关的信息。 //调用avformat_open_input之后,我们无法获取到正确和所有的媒体参数,所以还得要调用avformat_find_stream_info进一步的去获取。 avformat_find_stream_info(ic, NULL); //调用avformat_open_input读取到的媒体文件的路径/名字 printf("媒体文件名称:%s\n", ic->filename); //视音频流的个数,如果一个媒体文件既有音频,又有视频,则nb_streams的值为2。如果媒体文件只有音频,则值为1 printf("视音频流的个数:%d\n", ic->nb_streams); //媒体文件的平均码率,单位为bps printf("媒体文件的平均码率:%lldbps\n", ic->bit_rate); printf("duration:%d\n", ic->duration); int tns, thh, tmm, tss; tns = (ic->duration) / AV_TIME_BASE; thh = tns / 3600; tmm = (tns % 3600) / 60; tss = (tns % 60); printf("媒体文件总时长:%d时%d分%d秒\n", thh, tmm, tss); //通过上述运算,可以得到媒体文件的总时长 printf("\n"); //通过遍历的方式读取媒体文件视频和音频的信息, //新版本的FFmpeg新增加了函数av_find_best_stream,也可以取得同样的效果,但这里为了兼容旧版本还是用这种遍历的方式 for (int i = 0; i < ic->nb_streams; i++) { AVStream *as = ic->streams[i]; if (AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO == as->codecpar->codec_type) //如果是音频流,则打印音频的信息 { printf("音频信息:\n"); printf("index:%d\n", as->index); //如果一个媒体文件既有音频,又有视频,则音频index的值一般为1。但该值不一定准确,所以还是得通过as->codecpar->codec_type判断是视频还是音频 printf("音频采样率:%dHz\n", as->codecpar->sample_rate); //音频编解码器的采样率,单位为Hz if (AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP == as->codecpar->format) //音频采样格式 { printf("音频采样格式:AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP\n"); } else if (AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P == as->codecpar->format) { printf("音频采样格式:AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P\n"); } printf("音频信道数目:%d\n", as->codecpar->channels); //音频信道数目 if (AV_CODEC_ID_AAC == as->codecpar->codec_id) //音频压缩编码格式 { printf("音频压缩编码格式:AAC\n"); } else if (AV_CODEC_ID_MP3 == as->codecpar->codec_id) { printf("音频压缩编码格式:MP3\n"); } int DurationAudio = (as->duration) * r2d(as->time_base); //音频总时长,单位为秒。注意如果把单位放大为毫秒或者微妙,音频总时长跟视频总时长不一定相等的 printf("音频总时长:%d时%d分%d秒\n", DurationAudio / 3600, (DurationAudio % 3600) / 60, (DurationAudio % 60)); //将音频总时长转换为时分秒的格式打印到控制台上 printf("\n"); } else if (AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO == as->codecpar->codec_type) //如果是视频流,则打印视频的信息 { printf("视频信息:\n"); printf("index:%d\n", as->index); //如果一个媒体文件既有音频,又有视频,则视频index的值一般为0。但该值不一定准确,所以还是得通过as->codecpar->codec_type判断是视频还是音频 printf("视频帧率:%lffps\n", r2d(as->avg_frame_rate)); //视频帧率,单位为fps,表示每秒出现多少帧 if (AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 == as->codecpar->codec_id) //视频压缩编码格式 { printf("视频压缩编码格式:MPEG4\n"); } printf("帧宽度:%d 帧高度:%d\n", as->codecpar->width, as->codecpar->height); //视频帧宽度和帧高度 int DurationVideo = (as->duration) * r2d(as->time_base); //视频总时长,单位为秒。注意如果把单位放大为毫秒或者微妙,音频总时长跟视频总时长不一定相等的 printf("视频总时长:%d时%d分%d秒\n", DurationVideo / 3600, (DurationVideo % 3600) / 60, (DurationVideo % 60)); //将视频总时长转换为时分秒的格式打印到控制台上 printf("\n"); } } //av_dump_format(ic, 0, path, 0); } if (ic) { avformat_close_input(&ic); //关闭一个AVFormatContext,和函数avformat_open_input()成对使用 } avformat_network_deinit(); getchar(); //加上这一句,防止程序打印完信息就马上退出了 return 0; } int main002(int argc, char **argv) { // 1. 打开文件 const char *ifilename = "ande_10s.mp4"; printf("in_filename = %s\n", ifilename); avformat_network_init(); // AVFormatContext是描述一个媒体文件或媒体流的构成和基本信息的结构体 AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx = NULL; // 输入文件的demux // 打开文件,主要是探测协议类型,如果是网络文件则创建网络链接 int ret = avformat_open_input(&ifmt_ctx, ifilename, NULL, NULL); if (ret < 0) { char buf[1024] = {0}; av_strerror(ret, buf, sizeof (buf) - 1); printf("open %s failed: %s\n", ifilename, buf); return -1; } // 2. 读取码流信息 ret = avformat_find_stream_info(ifmt_ctx, NULL); if (ret < 0) //如果打开媒体文件失败,打印失败原因 { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(ret, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); printf("avformat_find_stream_info %s failed:%s\n", ifilename, buf); avformat_close_input(&ifmt_ctx); return -1; } // 3.打印总体信息 printf_s("\n==== av_dump_format in_filename:%s ===\n", ifilename); av_dump_format(ifmt_ctx, 0, ifilename, 0); printf_s("\n==== av_dump_format finish =======\n\n"); printf("media name:%s\n", ifmt_ctx->url); printf("stream number:%d\n", ifmt_ctx->nb_streams); // nb_streams媒体流数量 printf("media average ratio:%lldkbps\n",(int64_t)(ifmt_ctx->bit_rate/1024)); // 媒体文件的码率,单位为bps/1000=Kbps // duration: 媒体文件时长,单位微妙 int total_seconds = (ifmt_ctx->duration) / AV_TIME_BASE; // 1000us = 1ms, 1000ms = 1秒 printf("audio duration: %02d:%02d:%02d\n", total_seconds / 3600, (total_seconds % 3600) / 60, (total_seconds % 60)); printf("\n"); // 4.读取码流信息 // 音频 int audioindex = av_find_best_stream(ifmt_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, -1, -1, NULL, 0); if (audioindex < 0) { printf("av_find_best_stream %s eror.", av_get_media_type_string(AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO)); return -1; } AVStream *audio_stream = ifmt_ctx->streams[audioindex]; printf("----- Audio info:\n"); printf("index: %d\n", audio_stream->index); // 序列号 printf("samplarate: %d Hz\n", audio_stream->codecpar->sample_rate); // 采样率 printf("sampleformat: %d\n", audio_stream->codecpar->format); // 采样格式 AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP:8 printf("audio codec: %d\n", audio_stream->codecpar->codec_id); // 编码格式 AV_CODEC_ID_MP3:86017 AV_CODEC_ID_AAC:86018 if (audio_stream->duration != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) { int audio_duration = audio_stream->duration * av_q2d(audio_stream->time_base); printf("audio duration: %02d:%02d:%02d\n", audio_duration / 3600, (audio_duration % 3600) / 60, (audio_duration % 60)); } // 视频 int videoindex = av_find_best_stream(ifmt_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1, NULL, 0); if (videoindex < 0) { printf("av_find_best_stream %s eror.", av_get_media_type_string(AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)); return -1; } AVStream *video_stream = ifmt_ctx->streams[videoindex]; printf("----- Video info:\n"); printf("index: %d\n", video_stream->index); // 序列号 printf("fps: %lf\n", av_q2d(video_stream->avg_frame_rate)); // 帧率 printf("width: %d, height:%d \n", video_stream->codecpar->width, video_stream->codecpar->height); printf("video codec: %d\n", video_stream->codecpar->codec_id); // 编码格式 AV_CODEC_ID_H264: 27 if (video_stream->duration != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) { int video_duration = video_stream->duration * av_q2d(video_stream->time_base); printf("audio duration: %02d:%02d:%02d\n", video_duration / 3600, (video_duration % 3600) / 60, (video_duration % 60)); } // 5.提取码流 AVPacket *pkt = av_packet_alloc(); int pkt_count = 0; int print_max_count = 100; printf("\n-----av_read_frame start\n"); while (1) { ret = av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, pkt); if (ret < 0) { printf("av_read_frame end\n"); break; } if(pkt_count++ < print_max_count) { if (pkt->stream_index == audioindex) { printf("audio pts: %lld\n", pkt->pts); printf("audio dts: %lld\n", pkt->dts); printf("audio size: %d\n", pkt->size); printf("audio pos: %lld\n", pkt->pos); printf("audio duration: %lf\n\n", pkt->duration * av_q2d(ifmt_ctx->streams[audioindex]->time_base)); } else if (pkt->stream_index == videoindex) { printf("video pts: %lld\n", pkt->pts); printf("video dts: %lld\n", pkt->dts); printf("video size: %d\n", pkt->size); printf("video pos: %lld\n", pkt->pos); printf("video duration: %lf\n\n", pkt->duration * av_q2d(ifmt_ctx->streams[videoindex]->time_base)); } else { printf("unknown stream_index:\n", pkt->stream_index); } } av_packet_unref(pkt); } // 6.结束 if(pkt) av_packet_free(&pkt); if(ifmt_ctx) avformat_close_input(&ifmt_ctx); avformat_network_deinit(); //getchar(); //加上这一句,防止程序打印完信息马上退出 return 0; }
解码案例实战
源码参考:demuxing_decoding.c
原理分析
/// av_read_frame
/// AVFormatContext, AVPacket
/// 1. avformat_open_input
/// 2. avformat_find_stream_info
/// 3. av_find_best_stream, return stream index for audio,or video,or subtitle
/// 4. read packet: while(1){ av_read_frame(...) }
/// 5. decoding : ......
avcodec_send_packet:把解封装出来的AVPacket压缩包,发给:解码器
avcodec_receive_frame:将解码器出来的未压缩的帧,存到AVFrame中
av_image_copy : 将真实的音视频数据复制出来
static uint8_t *video_dst_data[4] = {NULL};
static AVFrame *frame = NULL;
/// 解码器流程
AVFormatContext:大管家婆
static AVCodecContext *video_dec_ctx = NULL, *audio_dec_ctx;
avcodec_find_decoder
avcodec_alloc_context3
avcodec_parameters_to_context
avcodec_open2
案例代码
demuxing_decoding.c:注意后缀名是c
/**
* @file
* Demuxing and decoding example.
*
* Show how to use the libavformat and libavcodec API to demux and
* decode audio and video data.
* @example demuxing_decoding.c
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
static AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx = NULL;
static AVCodecContext *video_dec_ctx = NULL, *audio_dec_ctx;
static int width, height;
static enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt;
static AVStream *video_stream = NULL, *audio_stream = NULL;
static const char *src_filename = NULL;
static const char *video_dst_filename = NULL;
static const char *audio_dst_filename = NULL;
static FILE *video_dst_file = NULL;
static FILE *audio_dst_file = NULL;
static uint8_t *video_dst_data[4] = {NULL};
static int video_dst_linesize[4];
static int video_dst_bufsize;
static int video_stream_idx = -1, audio_stream_idx = -1;
static AVFrame *frame = NULL;
static AVPacket pkt;
static int video_frame_count = 0;
static int audio_frame_count = 0;
static int output_video_frame(AVFrame *frame)
{
if (frame->width != width || frame->height != height ||
frame->format != pix_fmt) {
/* To handle this change, one could call av_image_alloc again and
* decode the following frames into another rawvideo file. */
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Width, height and pixel format have to be "
"constant in a rawvideo file, but the width, height or "
"pixel format of the input video changed:\n"
"old: width = %d, height = %d, format = %s\n"
"new: width = %d, height = %d, format = %s\n",
width, height, av_get_pix_fmt_name(pix_fmt),
frame->width, frame->height,
av_get_pix_fmt_name(frame->format));
return -1;
}
printf("video_frame n:%d coded_n:%d\n",
video_frame_count++, frame->coded_picture_number);
/* copy decoded frame to destination buffer:
* this is required since rawvideo expects non aligned data */
av_image_copy(video_dst_data, video_dst_linesize,
(const uint8_t **)(frame->data), frame->linesize,
pix_fmt, width, height);
/* write to rawvideo file */
fwrite(video_dst_data[0], 1, video_dst_bufsize, video_dst_file);
return 0;
}
static int output_audio_frame(AVFrame *frame)
{
size_t unpadded_linesize = frame->nb_samples * av_get_bytes_per_sample(frame->format);
printf("audio_frame n:%d nb_samples:%d pts:%s\n",
audio_frame_count++, frame->nb_samples,
av_ts2timestr(frame->pts, &audio_dec_ctx->time_base));
/* Write the raw audio data samples of the first plane. This works
* fine for packed formats (e.g. AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16). However,
* most audio decoders output planar audio, which uses a separate
* plane of audio samples for each channel (e.g. AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P).
* In other words, this code will write only the first audio channel
* in these cases.
* You should use libswresample or libavfilter to convert the frame
* to packed data. */
fwrite(frame->extended_data[0], 1, unpadded_linesize, audio_dst_file);
return 0;
}
static int decode_packet(AVCodecContext *dec, const AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret = 0;
// submit the packet to the decoder
ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error submitting a packet for decoding (%s)\n", av_err2str(ret));
return ret;
}
// get all the available frames from the decoder
while (ret >= 0) {
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec, frame);
if (ret < 0) {
// those two return values are special and mean there is no output
// frame available, but there were no errors during decoding
if (ret == AVERROR_EOF || ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return 0;
fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding (%s)\n", av_err2str(ret));
return ret;
}
// write the frame data to output file
if (dec->codec->type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
ret = output_video_frame(frame);
else
ret = output_audio_frame(frame);
av_frame_unref(frame);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
static int open_codec_context(int *stream_idx,
AVCodecContext **dec_ctx,
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx,
enum AVMediaType type)
{
int ret, stream_index;
AVStream *st;
AVCodec *dec = NULL;
AVDictionary *opts = NULL;
ret = av_find_best_stream(fmt_ctx, type, -1, -1, NULL, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find %s stream in input file '%s'\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type), src_filename);
return ret;
} else {
stream_index = ret;
st = fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index];
/* find decoder for the stream */
dec = avcodec_find_decoder(st->codecpar->codec_id);
if (!dec) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to find %s codec\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
/* Allocate a codec context for the decoder */
*dec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(dec);
if (!*dec_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate the %s codec context\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* Copy codec parameters from input stream to output codec context */
if ((ret = avcodec_parameters_to_context(*dec_ctx, st->codecpar)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to copy %s codec parameters to decoder context\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return ret;
}
/* Init the decoders */
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(*dec_ctx, dec, &opts)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open %s codec\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return ret;
}
*stream_idx = stream_index;
}
return 0;
}
static int get_format_from_sample_fmt(const char **fmt,
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt)
{
int i;
struct sample_fmt_entry {
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; const char *fmt_be, *fmt_le;
} sample_fmt_entries[] = {
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8, "u8", "u8" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, "s16be", "s16le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32, "s32be", "s32le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT, "f32be", "f32le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL, "f64be", "f64le" },
};
*fmt = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(sample_fmt_entries); i++) {
struct sample_fmt_entry *entry = &sample_fmt_entries[i];
if (sample_fmt == entry->sample_fmt) {
*fmt = AV_NE(entry->fmt_be, entry->fmt_le);
return 0;
}
}
fprintf(stderr,
"sample format %s is not supported as output format\n",
av_get_sample_fmt_name(sample_fmt));
return -1;
}