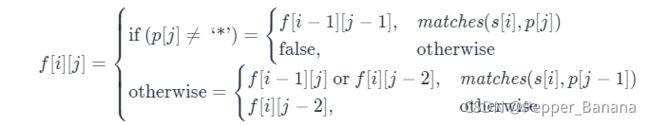数据结构算法与编程LeetCode题解
1-50
1. 两数之和
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector x, int y);
};
vector Solution::twoSum(vector nums, int y) {
vector twoSumVec;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.size(); j++) {
if (nums.at(i) + nums.at(j) == y) {
twoSumVec.push_back(i);
twoSumVec.push_back(j);
break;
}
}
}
return twoSumVec;
}
2. 两数相加
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2);
};
ListNode* Solution::addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* solution = new ListNode;
ListNode* r = solution;
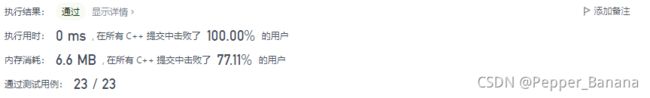
ListNode* p1 = l1;
ListNode* p2 = l2;
int sum = 0, flag = 0;
while (p1 != nullptr && p2 != nullptr) {
sum = p1->val + p2->val + flag;
if (sum > 9) {
sum -= 10;
flag = 1;
}
else
flag = 0;
ListNode* s = new ListNode;
s->val = sum;
r->next = s;
r = s;
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
while (p1 != nullptr) {
sum = p1->val + flag;
if (sum > 9) {
sum -= 10;
flag = 1;
}
else
flag = 0;
ListNode* s = new ListNode;
s->val = sum;
r->next = s;
r = s;
p1 = p1->next;
}
while (p2 != nullptr) {
sum = p2->val + flag;
if (sum > 9) {
sum -= 10;
flag = 1;
}
else
flag = 0;
ListNode* s = new ListNode;
s->val = sum;
r->next = s;
r = s;
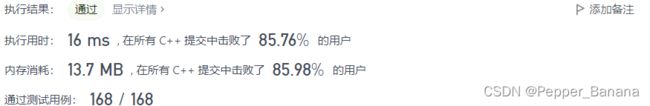
p2 = p2->next;
}
if (flag != 0) {
ListNode* s = new ListNode;
s->val = flag;
r->next = s;
r = s;
}
return solution->next;
}
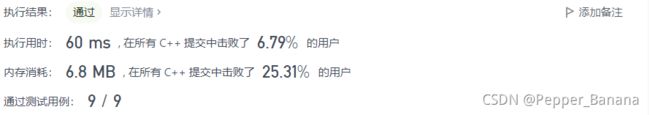
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
#ifndef MAX(X,Y)
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
#endif
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
if (s.length() < 1)
return 0;
unordered_set c;
int maxlen = 0;
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
while (c.find(s[i]) != c.cend())
c.erase(s[p++]);
c.insert(s[i]);
maxlen = MAX(maxlen, c.size());
}
return maxlen;
}
}; 其他的滑动窗口
76.最小覆盖子串。
209. 长度最小的子数组
904. 水果成篮
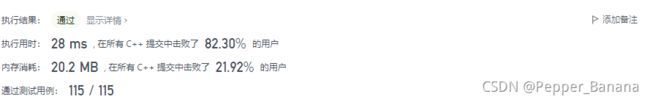
4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
执行用时:28 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了81.77%的用户
内存消耗:87.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了21.21%的用户
#define MIN(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
int findMedianSortedArrays(vector& nums1, vector& nums2, int k) {
int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size(), i = 0, j = 0;
while (k > 1 && i < m && j < n) {
int p = MIN(i + k / 2 - 1, m - 1), q = MIN(j + k / 2 - 1, n - 1);
if (nums1[p] <= nums2[q]) {
k -= (p - i + 1);
i = p + 1;
}
else {
k -= (q - j + 1);
j = q + 1;
}
}
if (k > 1) {
if (i < m && j >= n)
return nums1[i + k - 1];
if (i >= m && j < n)
return nums2[j + k - 1];
}
if (i < m && j >= n)
return nums1[i];
if (i >= m && j < n)
return nums2[j];
return MIN(nums1[i], nums2[j]);
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size();
float ans = 0.0;
if ((m + n) % 2)
ans = (float)findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2, (m + n + 1) / 2);
else {
int a = findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2, (m + n) / 2);
int b = findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2, (m + n) / 2 + 1);
ans = (float)(a + b) / 2;
}
return ans;
}
}; 5. 最长回文子(连续的)串
- 最优子结构:问题能写成状态转移方程的形式
- 重叠子问题:递归树中含有许多重复的结点
状态转移方程
重叠子问题
在比较s[j-1]和s[i+1]为起始点字符串时,有可能会进行
i+2和j-2位置的字符的比较。而在比较以 s[j]和s[i+1]为起始点字符串时,这些字符又会被比较一次。
/********************************************************
递归
执行结果:超出时间限制
最后执行的输入:"abbcccbbbcaaccbababcbcabca"
********************************************************/
class Solution {
public:
int lp(string& s, int i, int j, int& maxlen, int& p) {
if (i > j)
return 0;
if (j - i < 2 && s[i] == s[j]) {
if (j - i + 1 > maxlen) {
maxlen = max(j - i + 1, maxlen);
p = i;
}
return 1;
}
if (s[i] == s[j] && lp(s, i + 1, j - 1, maxlen, p)) {
if (j - i + 1 > maxlen) {
maxlen = max(j - i + 1, maxlen);
p = i;
}
return 1;
}
int a = lp(s, i + 1, j - 1, maxlen, p);
int b = lp(s, i + 1, j, maxlen, p);
int c = lp(s, i, j - 1, maxlen, p);
return a && b && c;
}
string longestPalindrome(string& s) {
int maxlen = 0, p = 0;
lp(s, 0, s.length() - 1, maxlen, p);
return maxlen < 1 ? "" : s.substr(p, maxlen);
}
};class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 1, p = 0;
vector> dp(n, vector(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][i] = 1;
if (i < n - 1 && s[i] == s[i + 1]) {
dp[i][i + 1] = 2;
ans = 2;
p = i;
}
}
for (int m = 3; m <= n; m++) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
int j = i + m - 1;
if (s[i] == s[j] && dp[i + 1][j - 1] > 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
ans = dp[i][j];
p = i;
}
}
}
return s.substr(p, ans);
}
}; 6. Z 字形变换
class Solution {
public:
string convert(string s, int numRows) {
int n = s.length(), loop = 2 * numRows - 2;
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (loop == 0 || j % loop == i || j % loop == loop - i)
ans.push_back(s[j]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};7. 整数反转
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:5.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.61%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int reverse(int x) {
int ans = 0;
while (x != 0) {
if (ans < INT_MIN / 10 || ans > INT_MAX / 10)
return 0;
int d = x % 10;
ans = ans * 10 + d;
x /= 10;
}
return x < 0 ? -ans : ans;
}
};8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
| 执行用时 | 内存消耗 | 语言 | 提交时间 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 通过 | 8 ms | 7 MB |
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
stringstream ss(s);
int x = 0;
ss >> x;
return x;
}
};9. 回文数
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了70.54%的用户
内存消耗:6.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了11.63%的用户
class Solution {
private:
bool isPalindromeInt(const long& x, const long& k, const long& p) {
if (p > k)
return true;
long a = pow(10, p);
long b = pow(10, p + 1);
long c = pow(10, k - p);
long d = pow(10, k - p + 1);
long m = (x % b) / a;
long n = (x % d) / c;
if (m != n)
return false;
else
return isPalindromeInt(x, k, p + 1);
}
public:
bool isPalindrome(const long& x) {
if (x < 0)
return false;
else if (x == 0)
return true;
else {
long k = 0;
long t = x;
while (t) {
t /= 10;
k++;
}
return isPalindromeInt(x, k - 1, 0);
}
}
};*10. 正则表达式匹配
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int m = s.length(), n = p.length();
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[j - 1] == '*') {
dp[i][j] |= dp[i][j - 2];
if (i > 0 && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] || p[j - 2] == '.'))
dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1][j];
}
else if (i > 0 && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == '.'))
dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}; 11. 盛最多水的容器
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
#define MIN(X,Y) ((X)>(Y)?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(const vector& h) {
int i = 0, j = h.size() - 1, ans = 0;
while (i < j) {
ans = MAX(ans, (j - i) * MIN(h[i], h[j]));
if (h[i] < h[j])
i++;
else
j--;
}
return ans;
}
}; 12. 整数转罗马数字
class Solution {
private:
const map> dic = {
{1, "I"},{4, "IV"},{5, "V"},{9, "IX"},{10, "X"},
{40, "XL"},{50, "L"},{90, "XC"},{100, "C"},
{400, "CD"},{500, "D"},{900, "CM"},{1000, "M"}
};
public:
string intToRoman(int num) {
string ro;
for (auto& it : dic) {
while (num >= it.first) {
num -= it.first;
ro += it.second;
}
if (num == 0) {
break;
}
}
return ro;
}
}; 13. 罗马数字转整数
class Solution {
private:
const vector > dic = {
{"M", 1000}, {"CM", 900},{"D", 500},{"CD", 400},{"C", 100},
{"XC", 90},{"L", 50},{"XL", 40},{"X", 10},
{"IX", 9},{"V", 5},{"IV", 4},{"I", 1}
};
public:
int romanToInt(string s) {
int p = 0, ans = 0;
string tmp;
while (p < s.length() - 1) {
tmp = s.substr(p, 2);
auto it = dic.begin();
for (; it < dic.end(); it++) {
if (it->first == tmp) {
ans += it->second;
p += 2;
break;
}
}
if (it < dic.end())
continue;
tmp = s.substr(p, 1);
it = dic.begin();
for (; it < dic.end(); it++) {
if (it->first == tmp) {
ans += it->second;
p++;
break;
}
}
}
while (p < s.length()) {
tmp = s[p];
for (auto it = dic.begin(); it < dic.end(); it++) {
if (it->first == tmp) {
ans += it->second;
p++;
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 14. 最长公共前缀
/*
取交集法
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了84.25%的用户
内存消耗:9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了56.55%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector& strs) {
if (strs.size() == 0)
return "";
if (strs.size() == 1)
return strs[0];
string ans = "", tmp = "", tmp1 = "";
int k = 0;
while (k < strs[0].length() && k < strs[1].length() && strs[0][k] - strs[1][k] == 0)
tmp.push_back(strs[0][k++]);
if (strs.size() == 2)
return tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++) {
int k = 0;
tmp1.clear();
while (k < tmp.length() && k < strs[i].length() && strs[i][k] - tmp[k] == 0)
tmp1.push_back(strs[i][k++]);
tmp = tmp1;
}
return tmp;
}
}; 349. 两个数组的交集
class Solution {
public:
vector intersection(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
vector ans;
unordered_set u, w;
for (auto i : nums1)
u.insert(i);
for (auto i : nums2)
if (u.find(i) != u.cend())
w.insert(i);
for (auto i : w)
ans.push_back(i);
return ans;
}
}; 350. 两个数组的交集 II
class Solution {
public:
vector intersect(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
vector ans;
sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
sort(nums2.begin(), nums2.end());
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < (int)nums1.size() && j < (int)nums2.size()) {
if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {
ans.push_back(nums1[i]);
i++;
j++;
}
else if (nums1[i] < nums2[j])
i++;
else
j++;
}
return ans;
}
}; 15. 三数之和
class Solution {
public:
vector> threeSum(vector& nums) {
vector> ans;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (!(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])) {
for (int j = i + 1, k = nums.size() - 1; j < k; j++, k--) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0) {
ans.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]});
while (j < k && nums[k] == nums[k - 1])
k--;
while (j < k && nums[j] == nums[j + 1])
j++;
}
else if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] > 0) {
while (j < k && nums[k] == nums[k - 1])
k--;
j--;
}
else {
while (j < k && nums[j] == nums[j + 1])
j++;
k++;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 16. 最接近的三数之和
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了98.34%的用户
内存消耗:9.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了75.49%的用户
#define ABS(X) ((X)<0 ? -(X):(X))
class Solution {
private:
static void qsort(const int& low, const int& high, vector& nums) {
if (low >= high)
return;
int i = low, j = high, t = 0, pivot = nums[low];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] >= pivot)
j--;
while (i < j && nums[i] <= pivot)
i++;
if (i < j) {
t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
}
nums[low] = nums[i];
nums[i] = pivot;
qsort(low, i - 1, nums);
qsort(j + 1, high, nums);
return;
}
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector& nums, int target) {
qsort(0, nums.size() - 1, nums);
int ans = 270094056, a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])
continue;
a = nums[i];
for (int j = i + 1, k = nums.size() - 1; j < k;) {
int sum3 = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];
if (sum3 == target)
return target;
if (ABS(target - sum3) < ABS(target - ans))
ans = sum3;
if (sum3 > target) {
int k0 = k;
while (j < k0 && nums[k0] == nums[k])
k0--;
k = k0;
}
else {
int j0 = j;
while (k > j0 && nums[j0] == nums[j])
j0++;
j = j0;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 17. 电话号码的字母组合
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:8.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.05%的用户
*/
class Solution {
private:
const unordered_map um = {
{'1', "!@#"}, {'2', "abc"}, {'3', "def"},
{'4', "ghi"}, {'5', "jkl"}, {'6', "mno"},
{'7', "pqrs"}, {'8', "tuv"}, {'9', "wxyz"}
};
private:
vector dfs(const string& d, string& t, int k) {
static vector ans;
if (k < 1)
ans.clear();
if (t.length() == d.length()) {
ans.push_back(t);
return ans;
}
else {
const string t0 = um.find(d[k])->second;
for (auto i = 0; i < t0.length(); i++) {
t.push_back(t0[i]);
dfs(d, t, k + 1);
t.pop_back();
}
return ans;
}
}
public:
vector letterCombinations(const string digits) {
vector ans;
if (digits.empty())
return ans;
string tmp = "";
ans = dfs(digits, tmp, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 18. 四数之和
/*
执行用时:56 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了72.62%的用户
内存消耗:19.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.01%的用户
*/
#define ABS(X) ((X)<0 ? -(X):(X))
class Solution {
private:
void qsort(vector& v, const int& low, const int& high) {
if (low >= high)
return;
int i = low, j = high, pivot = v[low], t = 0;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && v[j] >= pivot)
j--;
while (i < j && v[i] <= pivot)
i++;
if (i < j) {
t = v[i];
v[i] = v[j];
v[j] = t;
}
}
v[low] = v[i];
v[i] = pivot;
qsort(v, low, i - 1);
qsort(v, j + 1, high);
}
vector > dfs(const vector& nums, const int target, int sum, int low) {
static vector > ans;
static vector num4;
if (low < 1) {
num4.clear();
ans.clear();
}
if (num4.size() == 4 && sum == target)
ans.push_back(num4);
else {
for (int i = low; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums.size() - i < 4 - static_cast(num4.size()) || i < nums.size() - 1 && nums[i] + sum + (3 - static_cast(num4.size())) * nums[i + 1] > target)
break;
if (i > low && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] || i < nums.size() - 1 && nums[i] + sum + (3 - static_cast(num4.size())) * *(nums.cend() - 1) < target)
continue;
num4.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, target, sum + nums[i], i + 1);
num4.pop_back();
}
}
return ans;
}
public:
vector> fourSum(vector& nums, int target) {
vector> ans;
if (nums.size() < 4)
return ans;
if (ABS(nums[0] / 10.0 + nums[1] / 10.0 + nums[2] / 10.0 + nums[3] / 10.0) > INT_MAX / 10) {
if (nums.size() == 4 && nums[0] / 10.0 + nums[1] / 10.0 + nums[2] / 10.0 + nums[3] / 10.0 != target / 10.0)
return ans;
if (nums.size() == 4 && nums[0] / 10.0 + nums[1] / 10.0 + nums[2] / 10.0 + nums[3] / 10.0 == target / 10.0) {
ans.push_back(nums);
return ans;
}
}
if (nums.size() == 4 && nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] != target)
return ans;
if (nums.size() == 4 && nums[0] / 10 + nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] == target) {
ans.push_back(nums);
return ans;
}
qsort(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
return dfs(nums, target, 0, 0);
}
}; 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:10.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了74.92%的用户
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* p = head, * q = head;
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, q = q->next);
if (q == nullptr) {
head = head->next;
return head;
}
for (; q->next != nullptr; p = p->next, q = q->next);
p->next = p->next->next;
return head;
}
};20. 有效的括号
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了67.73%的用户
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.length() < 2)
return false;
stack st;
st.push('#');
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == ')' && st.top() == '('
|| s[i] == ']' && st.top() == '['
|| s[i] == '}' && st.top() == '{')
st.pop();
else
st.push(s[i]);
}
if (st.top() == '#')
return true;
else
return false;
}
}; 21. 合并两个有序链表
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了68.46%的用户
内存消耗:14.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了41.68%的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* p1 = l1, * p2 = l2;
ListNode* h = new ListNode;
ListNode* r = h;
while (p1 != nullptr && p2 != nullptr) {
if (p1->val < p2->val) {
ListNode* t = new ListNode(p1->val, r->next);
r->next = t;
r = t;
p1 = p1->next;
}
else {
ListNode* t = new ListNode(p2->val, r->next);
r->next = t;
r = t;
p2 = p2->next;
}
}
while (p1 != nullptr) {
ListNode* t = new ListNode(p1->val, r->next);
r->next = t;
r = t;
p1 = p1->next;
}
while (p2 != nullptr) {
ListNode* t = new ListNode(p2->val, r->next);
r->next = t;
r = t;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return h->next;
}
};
22. 括号生成
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了72.86%的用户
内存消耗:14.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了20.56%的用户
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(int n, int l, int r, string path, vector& ans) {
if (l == r && l == n) {
ans.push_back(path);
return;
}
if (l <= n && r <= n && r <= l) {
dfs(n, l + 1, r, path + "(", ans);
dfs(n, l, r + 1, path + ")", ans);
}
}
vector generateParenthesis(int n) {
vector ans;
dfs(n, 0, 0, "", ans);
return ans;
}
}; 23. 合并K个升序链表
/*
执行用时:40 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了34.77%的用户
内存消耗:31 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.00%的用户
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* p = list1, * q = list2;
ListNode* head = new ListNode;
ListNode* h = head;
while (p != nullptr && q != nullptr) {
if (p->val <= q->val) {
h->next = p;
h = h->next;
p = p->next;
}
else {
h->next = q;
h = h->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
while (p != nullptr) {
h->next = p;
h = h->next;
p = p->next;
}
while (q != nullptr) {
h->next = q;
h = h->next;
q = q->next;
}
return head->next;
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector& lists, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return nullptr;
if (i == j)
return lists[i];
if (i + 1 == j)
return mergeTwoLists(lists[i], lists[j]);
int mid = i + ((j - i) >> 1);
ListNode* p = mergeKLists(lists, i, mid);
ListNode* q = mergeKLists(lists, mid + 1, j);
return mergeTwoLists(p, q);
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector& lists) {
return mergeKLists(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
}; 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了54.05%的用户
内存消耗:7.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了93.84%的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* q = swapPairs(head->next->next);
ListNode* p = head->next;
head->next = q;
/*ListNode* p = head->next;
head->next = swapPairs(p->next);*/
p->next = head;
return p;
}
};25. K 个一组翻转链表
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了66.79%的用户
内存消耗:11.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了42.68%的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* r = reverse(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return r;
}
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* node = new ListNode(INT_MAX, head);
ListNode* newhead = node;
while (1) {
ListNode* l = node;
int i = 0;
while (l->next != nullptr && i < k) {
l = l->next;
i++;
}
if (l->next == nullptr && i < k)
break;
ListNode* p = l->next;
l->next = nullptr;
ListNode* h = reverse(node->next);
ListNode* t = node->next;
node->next = h;
node = t;
node->next = p;
}
return newhead->next;
}
};26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了59.15%的用户
内存消耗:17.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了74.44%的用户
class Solution {
public:
template
int removeDuplicates(vector& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 2)
return nums.size();
int i = 0;
while (i < nums.size() - 1) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
auto it = nums.begin();
for (int j = 0; j < i + 1; j++)
it++;
nums.erase(std::remove(it, nums.end(), nums[i]), nums.end());
}
i++;
}
return nums.size();
}
int removeDuplicates(vector& nums) {
int i = -1, j = 0;
while (j < nums.size()) {
while (j < nums.size() - 1 && nums[j] == nums[j + 1])
j++;
nums[++i] = nums[j++];
}
return i + 1;
}
}; 27. 移除元素
/*
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了55.38%的用户
内存消耗:8.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了48.53%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public:
int removeEle(vector& nums, int val) {
int i = -1, j = 0;
while (j < nums.size()) {
while (j < nums.size() && nums[j] == val)
j++;
while (j < nums.size() && nums[j] != val)
nums[++i] = nums[j++];
}
return i + 1;
}
int removeElement(vector& nums, int val) {
nums.erase(remove(nums.begin(), nums.end(), val), nums.end());
return nums.size();
}
}; class Solution {
public:
bool backspaceCompare(string s, string t) {
int i = s.length() - 1, j = t.length() - 1, cnts = 0, cntt = 0;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
while (i >= 0 && (s[i] == '#' || cnts > 0)) {
if (s[i] == '#')
cnts++;
else if (cnts > 0)
cnts--;
i--;
}
while (j >= 0 && (t[j] == '#' || cntt > 0)) {
if (t[j] == '#')
cntt++;
else if (cntt > 0)
cntt--;
j--;
}
if (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (s[i] != t[j]) {
return false;
}
}
else if (i >= 0 || j >= 0)
return false;
i--;
j--;
}
return true;
}
};977. 有序数组的平方
class Solution {
public:
vector sortedSquares(vector& nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1, k = nums.size() - 1;
vector ans(nums.size());
while (i <= j) {
if (nums[i] * nums[i] < nums[j] * nums[j]) {
ans[k] = nums[j] * nums[j];
j--;
}
else {
ans[k] = nums[i] * nums[i];
i++;
}
k--;
}
return ans;
}
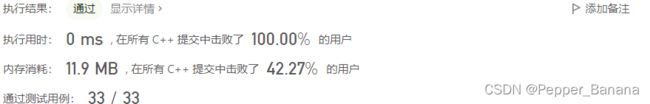
}; 28. 实现 strStr()
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.88%的用户
通过测试用例:79 / 79 */
class Solution {
public:
vector get_next(string s) {
int n = s.length();
vector next(n);
int i = 0, j = -1;
next[0] = j;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
while (j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1])
j = next[j];
if (s[i] == s[j + 1])
j++;
next[i] = j;
}
return next;
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int m = haystack.length(), n = needle.length();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
vector next = get_next(needle);
vector res;
int j = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
while (j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j + 1])
j = next[j];
if (haystack[i] == needle[j + 1])
j++;
if (j == n - 1) {
res.push_back(i - j);
i = i - j + 1;
j = -1;
}
}
return res.empty() ? -1 : res[0];
}
}; 相似
541. 反转字符串 II
class Solution {
public:
string reverseStr(string s, int k) {
string ans, str;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)s.length(); i += 2 * k) {
str = (i + k <= (int)s.length() ? s.substr(i, k) : s.substr(i, (int)s.length() - i));
reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
ans += str;
if (i + k >= (int)s.length())
break;
str = (i + 2 * k <= (int)s.length() ? s.substr(i + k, k) : s.substr(i + k, (int)s.length() - k));
ans += str;
}
return ans;
}
};05. 替换空格
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int len = s.length();
for (auto i : s)
if (i == ' ')
len += 2;
string ans(len, 0);
for (auto it1 = ans.rbegin(), it2 = s.rbegin(); it1 != ans.rend(); it1++, it2++) {
if (*it2 != ' ')
*it1 = *it2;
else {
*(it1++) = '0';
*(it1++) = '2';
*it1 = '%';
}
}
return ans;
}
};151. 颠倒字符串中的单词
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
s.push_back(' ');
reverse(s.begin(), s.end()); // 颠倒整个字符串
s.push_back(' ');
auto j = s.begin();
for (auto i = s.begin(); i < s.end(); i++) {
if (*i == ' ') {
reverse(j, i); // 颠倒每个单词
j = i + 1;
}
}
for (j = s.begin(); j < s.end(); j++) {
if (*j == ' ') {
auto b = j + 1;
while (b < s.end() && *(b) == ' ') // 删除单词中间和两端多余的空格
s.erase(b);
}
}
j = s.begin();
if (*j == ' ') // 删除前导空格
s.erase(j);
if (s.back() == ' ') // 删除尾随空格
s.pop_back();
return s;
}
};58 - II. 左旋转字符串
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
int i = 0, j = n, len = s.length();
auto it = s.begin();
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++, it++);
reverse(s.begin(), it);
reverse(it, s.end());
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
return s;
}
};459. 重复的子字符串
// KMP
class Solution {
public:
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
vector next(s.length(), -1);
int j = -1, i = 1, n = 0;
for (; i < (int)s.length(); i++) {
while (j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1])
j = next[j];
if (s[i] == s[j + 1]) {
n = i - j - 1;
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
if (n == 0 || (int)s.length() % n != 0)
return false;
if (i - j - 1 == n)
return true;
return false;
}
}; 29. 两数相除
/*
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了58.99%的用户
内存消耗:6.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.05%的用户
*/
#define ABS(X) ((X)<0?-(X):(X))
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
LL a = ABS((LL)dividend), b = ABS((LL)divisor);
vector exp;
for (auto i = b; i <= a; i = i + i)
exp.push_back(i);
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = (int)exp.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (a >= exp[i]) {
a -= exp[i];
ans += 1LL << i;
}
}
if (dividend < 0 && divisor > 0 || dividend > 0 && divisor < 0)
ans = -ans;
if (ans < INT_MIN || ans > INT_MAX)
ans = INT_MAX;
return ans;
}
}; 30. 串联所有单词的子串
/*
解法一:哈希表(时间复杂度:O(n²)空间复杂度:O(n))
执行用时:1240 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了9.17%的用户
内存消耗:453.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.05%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubstring(string s, int wordlen, unordered_map& m1) {
unordered_map m2;
string t = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i += wordlen) {
t = s.substr(i, wordlen);
m2[t]++;
}
if (m1.size() != m2.size())
return false;
for (auto it = m1.begin(); it != m1.end(); it++) {
auto iter = m2.find(it->first);
if (iter == m2.end() || iter->second != it->second)
return false;
}
return true;
}
vector findSubstring(string s, vector& words) {
vector ans;
int wordlen = words[0].length();
int wordslen = (wordlen) * ((int)(words.size()));
if (s.length() < words[0].length() || s.length() < wordslen)
return ans;
if (s.length() == 1 && wordslen == 1 && s[0] == words[0][0]) {
ans.push_back(0);
return ans;
}
unordered_map m;
for (auto w : words)
m[w]++;
string t = "";
for (int i = 0; i <= s.length() - wordslen; i++) {
t = s.substr(i, wordslen);
if (isSubstring(t, wordlen, m))
ans.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
}; 31. 下一个排列
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户(O(nlogn))
内存消耗:11.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了78.88%的用户(O(1))
*/
#define ABS(X) ((X) < 0? -(X) : (X))
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 2)
return;
int i = nums.size() - 1;
int j = i;
while (i > 0) {
if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i]) {
int p = nums.size() - 1;
/* 从后往前找第一个比后一个数字小的数字nums[i-1],一旦找到,
就再从后往前找与nums[i-1]距离最短且自身尽量大的数字nums[p],
最后交换它们并排序即为所得。
有两种特殊情况需要额外注意,一个是要跳过两数相等的情况(nums[i-1]==nums[p]),
因为虽然此时两数距离最短,但交换相等的两个数并不满足题意,所以此时要继续往前找;
一个是要跳过虽然nums[p-1]比nums[p]离nums[i-1]更远,但此时nums[i-1]大于nums[p]的
情况,比如输入[2,3,0,2,4,1],应该交换nums[3](==2)和nums[4](==4)从而得到正解
[2,3,0,4,1,2],但如果忽略这种情况就会交换nums[3]和nums[5]导致错误的[2,3,0,1,2,4]。 */
for (int k = nums.size() - 2; k > i - 1; k--)
if (ABS(nums[k] - nums[i - 1]) <= ABS(nums[i - 1] - nums[p])
|| nums[i - 1] == nums[p]
|| k + 1 == p && nums[i - 1] >= nums[p])
p = k;
int t = nums[i - 1];
nums[i - 1] = nums[p];
nums[p] = t;
break;
}
i--;
}
sort(nums.begin() + i, nums.begin() + j + 1);
}
};
/*
O(n)
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector& nums) {
int i = nums.size() - 2;
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1])
--i;
if (i >= 0) {
int j = nums.size() - 1;
while (nums[i] >= nums[j])
--j;
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
reverse(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end());
}
};
*/ *32. 最长有效括号
/*
解法一:栈,时间复杂度O(n³),空间复杂度O(n)
思路:产生所有可能的子串,并用栈依次判断有效
执行结果:超出时间限制
最后执行的输入:
"((())())(()))(()()(()(()))(()((((()))))))((()())()))()()(()(((((()()()())))()())(()()))((((((())))((()))()()))))(()))())))()))()())((()()))))(()(((((())))))()((()(()(())((((())(())((()()(()())))())(()(())()()))())(()()()))()(((()())(((()()())))(((()()()))(()()))()))()))))))())()()((()(())(()))()((()()()((())))()(((()())(()))())())))(((()))))())))()(())))()())))())()((()))((()))()))(((())((()()()(()((()((())))((()()))())(()()(()))))())((())))(()))()))))))()(()))())(()())))))(()))((())(()((())(((((()()()(()()())))(()())()((()(()()))(()(())((()((()))))))))(()(())()())()(()(()(()))()()()(()()())))(())(()((((()()))())))(())((()(())())))))())()()))(((())))())((()(()))(()()))((())(())))))(()(()((()((()()))))))(()()()(()()()(()(())()))()))(((()(())()())(()))())))(((()))())(()((()))(()((()()()(())()(()())()(())(()(()((((())()))(((()()(((()())(()()()(())()())())(()(()()((()))))()(()))))(((())))()()))(()))((()))))()()))))((((()(())()()()((()))((()))())())(()((()()())))))))()))(((()))))))(()())))...
解法二:动态规划,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:7.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了31.73%的用户
*/
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
vector dp(s.length(), 0);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == ')' && s[i - 1] == '(')
dp[i] = (i < 2 ? 0 : dp[i - 2]) + 2;
else if (s[i] == ')' && i - dp[i - 1] > 0 && s[i - dp[i - 1] - 1] == '(')
dp[i] = (i - dp[i - 1] < 2 ? 0 : dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2]) + dp[i - 1] + 2;
ans = MAX(dp[i], ans);
}
return ans;
}
}; 解析
@宝宝可乖了:
class Solution { public: int longestValidParentheses(string s) { int ans = 0; vectordp(s.length(), 0); for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s[i] == ')') { int j = i - dp[i - 1] - 1; if (j >= 0 && s[j] == '(') dp[i] = (i - j + 1) + ((j - 1) >= 0 ? dp[j - 1] : 0); } ans = max(ans, dp[i]); } return ans; } };
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:10.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了92.53%的用户
思路总结
将数组一分为二
如果右半部分有序,左半部分部分有序(nums[mid] < nums[j]),就按右半部分有序的标准来决定去哪半部分查找target(if nums[mid] < target < nums[j] 右 else 左)
如果左半部分有序,右半部分部分有序(nums[mid] > nums[j]),就按左半部分有序的标准来决定去哪半部分查找target(if nums[i] < target < nums[mid] 左 else 右)
*/
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector& nums, int target, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return -1;
int mid = i + ((j - i) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[i] == target)
return i;
if (nums[j] == target)
return j;
if (nums[mid] > nums[i]) {
if (nums[mid] > target && target > nums[i])
return search(nums, target, i, mid - 1);
else
return search(nums, target, mid + 1, j);
}
else if (nums[mid] < nums[j]) {
if (nums[mid] < target && target < nums[j])
return search(nums, target, mid + 1, j);
else
return search(nums, target, i, mid - 1);
}
return -1;
}
int search(vector& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
return search(nums, target, 0, n - 1);
}
}; 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了95.79%的用户
内存消耗:13.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.41%的用户
/*
思路总结
查找非递减数组中target的左边界,等价于查找非递减数组中从左向右第一个大于等于target的元素(的下标);查找非递减数组中target的右边界,等价于查找非递减数组中从左向右第一个大于target的元素
*/
#define lower int
#define upper int,int
#define GETMID(i,j) ((i) + (((j) - (i)) >> 1))
class Solution {
public:
template
void searchRange(vector& nums, int target, int i, int j, int& l) {
if (i > j)
return;
int mid = GETMID(i, j);
if (nums[mid] >= target) {
l = mid;
searchRange(nums, target, i, mid - 1, l);
}
else
searchRange(nums, target, mid + 1, j, l);
}
template
void searchRange(vector& nums, int target, int i, int j, int& r) {
if (i > j)
return;
int mid = GETMID(i, j);
if (nums[mid] > target) {
r = mid - 1;
searchRange(nums, target, i, mid - 1, r);
}
else
searchRange(nums, target, mid + 1, j, r);
}
vector searchRange(vector& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
int l = INT_MIN, r = INT_MIN;
searchRange(nums, target, 0, n - 1, l);
searchRange(nums, target, 0, n - 1, r);
if (l == INT_MIN || nums[l] != target)
return { -1, -1 };
if (r == INT_MIN)
r = n - 1;
vector ans = { l, r };
return ans;
}
}; 35. 搜索插入位置
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了83.15%的用户
内存消耗:9.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了92.59%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(vector& nums, int target, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return i;
int mid = i + ((j - i) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[mid] > target)
return searchInsert(nums, target, i, mid - 1);
return searchInsert(nums, target, mid + 1, j);
}
int searchInsert(vector& nums, int target) {
return searchInsert(nums, target, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
}; 相似
704. 二分查找
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector& nums, int target, int l, int r) {
if (l > r)
return -1;
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[mid] > target)
return search(nums, target, 0, mid - 1);
return search(nums, target, mid + 1, r);
}
int search(vector& nums, int target) {
return search(nums, target, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
}; 36. 有效的数独
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了61.12%的用户
内存消耗:19.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了15.35%的用户
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector>& board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
unordered_map mrow;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
mrow[board[i][j]]++;
if (mrow[board[i][j]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
unordered_map mcol;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[j][i] == '.')
continue;
mcol[board[j][i]]++;
if (mcol[board[j][i]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
unordered_map mgrid;
for (int h = 0; h < 3; h++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k] == '.')
continue;
mgrid[board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k]]++;
if (mgrid[board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}; 测试用例
vector > board = {
{'.','.','.','.','5','.','.','1','.'},
{'.','4','.','3','.','.','.','.','.'},
{'.','.','.','.','.','3','.','.','1'},
{'8','.','.','.','.','.','.','2','.'},
{'.','.','2','.','7','.','.','.','.'},
{'.','1','5','.','.','.','.','.','.'},
{'.','.','.','.','.','2','.','.','.'},
{'.','2','.','9','.','.','.','.','.'},
{'.','.','4','.','.','.','.','.','.'}
}; *37. 解数独
/* 在测试用例上正确输出 */
class Solution {
private:
bool isValidSudoku(vector>& board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
unordered_map mrow;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
mrow[board[i][j]]++;
if (mrow[board[i][j]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
unordered_map mcol;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[j][i] == '.')
continue;
mcol[board[j][i]]++;
if (mcol[board[j][i]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
unordered_map mgrid;
for (int h = 0; h < 3; h++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k] == '.')
continue;
mgrid[board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k]]++;
if (mgrid[board[i * 3 + h][j * 3 + k]] > 1)
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
public:
bool dfs(vector>& board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++) {
board[i][j] = k;
if (isValidSudoku(board) && dfs(board))
return true;
board[i][j] = '.';
}
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
void solveSudoku(vector>& board) {
dfs(board);
}
}; 测试用例
vector > board = {
{'5','3','.','.','7','.','.','.','.'},
{'6','.','.','1','9','5','.','.','.'},
{'.','9','8','.','.','.','.','6','.'},
{'8','.','.','.','6','.','.','.','3'},
{'4','.','.','8','.','3','.','.','1'},
{'7','.','.','.','2','.','.','.','6'},
{'.','6','.','.','.','.','2','8','.'},
{'.','.','.','4','1','9','.','.','5'},
{'.','.','.','.','8','.','.','7','9'}
}; 相同
HJ44 Sudoku
![]()
#include
using namespace std;
bool isValid(vector>& board, int x, int y) {
int cur = board[x][y];
/* 检查行和列 */
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
if (i != y && board[x][i] == cur || i != x && board[i][y] == cur)
return false;
/* 判断九宫格 */
int a = x / 3, b = y / 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if ((a * 3 + i != x) && (b * 3 + j != y) && board[a * 3 + i][b * 3 + j] == cur) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool dfs(vector>& board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
board[i][j] = k;
if (isValid(board, i, j) && dfs(board))
return true;
board[i][j] = 0;
}
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
vector> board(9, vector(9));
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
cin >> board[i][j];
dfs(board);
for_each(board.begin(), board.end(), [](const auto val)->void{
for_each(val.begin(), val.end(), [](const auto x)->void{
cout << x << " ";
});
cout << endl;
});
return 0;
} 38. 外观数列
class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
if (n < 2)
return "1";
string a = "11";
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
int len = a.length();
int p = 0, q = 0;
string t = "", tmp = "";
while (p < len) {
while (a[p] == a[q])
q++;
tmp = std::to_string(q - p);
t.append(tmp);
t.push_back(a[p]);
p = q;
}
a = t;
}
return a;
}
};39. 组合总和
class Solution {
public:
vector> ans;
vector tmp;
void dfs(vector& candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.push_back(tmp);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < (int)candidates.size() && candidates[i] + sum <= target; i++) {
tmp.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i);
tmp.pop_back();
}
}
vector> combinationSum(vector& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 40. 组合总和 II
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector& candidates, int target, int sum, vector& can, vector>& ans, int idx) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.push_back(can);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < (int)candidates.size() && candidates[i] + sum <= target; i++) {
if (!(i > idx && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1])) {
can.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], can, ans, i + 1);
can.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector> combinationSum2(vector& candidates, int target) {
vector> ans;
vector can;
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
dfs(candidates, target, 0, can, ans, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 相似
216. 组合总和 III
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(int k, int n, int idx, int sum, vector& res, vector>& ans) {
if (sum == n && res.size() == k) {
ans.push_back(res);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i <= 9 && i <= n - sum; i++) {
res.push_back(i);
dfs(k, n, i + 1, sum + i, res, ans);
res.pop_back();
}
}
vector> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
if (n < k)
return {};
vector res;
vector > ans;
dfs(k, n, 1, 0, res, ans);
return ans;
}
}; 131. 分割回文串
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(string s, int idx, vector& v, vector>& ans) {
if (idx == s.length()) {
ans.push_back(v);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < s.length(); i++) {
string a = s.substr(idx, i - idx + 1);
string b(a.rbegin(), a.rend());
if (a == b) {
v.push_back(a);
dfs(s, i + 1, v, ans);
v.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector> partition(string s) {
vector v;
vector> ans;
dfs(s, 0, v, ans);
return ans;
}
}; 41. 缺失的第一个正数
/* 腾讯2022光子后台暑期实习一面 */
class Solution {
public:
int firstMissingPositive(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] - 1 != i) {
if (nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i])
swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i] - 1]);
else
break;
}
}
int ans = n + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] <= 0 || nums[i] - 1 != i) {
ans = i + 1;
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 42. 接雨水
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
#define MIN(X,Y) ((X)>(Y)?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector& height) {
int hsize = height.size();
vector lm(hsize), rm(hsize);
int tmp = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < hsize; i++) {
lm[i] = MAX(tmp, height[i]);
tmp = lm[i];
}
tmp = INT_MIN;
for (int i = hsize - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
rm[i] = MAX(tmp, height[i]);
tmp = rm[i];
}
int rain = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < hsize; i++)
rain += MIN(lm[i], rm[i]) - height[i];
return rain;
}
}; 43. 字符串相乘
class Solution {
public:
string multiply(string num1, string num2) {
string rnum1(num1.rbegin(), num1.rend());
string rnum2(num2.rbegin(), num2.rend());
int len1 = rnum1.length(), len2 = rnum2.length();
vector res(len1 + len2, 0);
vector add(len1 + len2, 0);
int a = 0, b = 0, d = 0, f = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
a = rnum1[i] - 48;
k = i;
for (int j = 0; j < len2; j++, k++) {
b = rnum2[j] - 48;
res[k] = res[k] + a * b % 10;
add[k] = add[k] + a * b / 10;
if (res[k] > 9) {
d = res[k] % 10;
f = res[k] / 10;
res[k] = d;
add[k] += f;
}
}
}
f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < len1 + len2; i++) {
res[i] = res[i] + add[i - 1] + f;
if (res[i] > 9) {
f = res[i] / 10;
res[i] %= 10;
}
else
f = 0;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
k = 0;
while (k < len1 + len2 - 1 && res[k] < 1)
k++;
string ans(len1 + len2 - k, ' ');
for (int i = 0, j = k; j < len1 + len2; i++, j++)
ans[i] = res[j] + 48;
return ans;
}
}; *44. 通配符匹配
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int slen = s.length(), plen = p.length();
vector > dp(slen + 1, vector(plen + 1, 0));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= plen; i++) {
if (p[i - 1] == '*')
dp[0][i] = 1;
else
break;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= slen; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= plen; j++) {
if (p[j - 1] == '*')
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] | dp[i][j - 1];
else if (p[j - 1] == '?' || s[i - 1] == p[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[slen][plen];
}
}; 45. 跳跃游戏 II
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector& nums) {
int j = nums.size() - 1, ans = 0;
while (j > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (i + nums[i] >= j) {
ans++;
j = i;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 46. 全排列
![]()
class Solution {
private:
void dfs(vector& nums, vector>& ans, vector& t, vector& s, const int& lev, int f) {
if ((int)t.size() >= lev)
ans.push_back(t);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nums.size(); i++) {
if (!s[i]) {
s[i]++;
t.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, ans, t, s, lev, 0);
t.pop_back();
s[i]--;
}
}
}
public:
vector> permute(vector& nums) {
vector> ans;
vector t;
vector s(nums.size(), 0);
const int lev = nums.size();
dfs(nums, ans, t, s, lev, 1);
return ans;
}
}; 47. 全排列 II
![]()
inline void qsort(int lo, int hi, vector& v) {
if (lo >= hi)
return;
int i = lo, j = hi, t = 0, pivot = v[lo];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && v[j] >= pivot)
j--;
while (i < j && v[i] <= pivot)
i++;
if (i < j) {
t = v[i];
v[i] = v[j];
v[j] = t;
}
}
v[lo] = v[i];
v[i] = pivot;
qsort(lo, i - 1, v);
qsort(j + 1, hi, v);
}
class Solution {
private:
void dfs(vector& nums, vector>& ans, vector& t, vector& s, int lev) {
if ((int)t.size() >= (int)nums.size()) {
ans.push_back(t);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nums.size(); i++) {
if (!(s[i] || (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !s[i - 1]))) {
t.push_back(nums[i]);
s[i]++;
dfs(nums, ans, t, s, i + 1);
s[i]--;
t.pop_back();
}
}
}
public:
vector> permuteUnique(vector& nums) {
vector> ans;
vector t;
vector s(nums.size(), 0);
qsort(0, nums.size() - 1, nums);
dfs(nums, ans, t, s, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 48. 旋转图像
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector>& matrix) {
int tmp = 0, n = (int)matrix.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][n - j - 1]);
}
}; 49. 字母异位词分组
class Solution {
public:
vector> groupAnagrams(vector& strs) {
unordered_map > hm;
vector> ans;
for (auto i : strs) {
auto ts = i;
sort(ts.begin(), ts.end());
hm[ts].emplace_back(i);
}
for (auto i : hm) {
ans.emplace_back(i.second);
}
return ans;
}
}; 相似
242. 有效的字母异位词
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
return s == t ? true : false;
}
};383. 赎金信
class Solution {
public:
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine) {
unordered_map umm, umr;
for (auto i : magazine)
umm[i]++;
for (auto i : ransomNote)
umr[i]++;
for (auto i : umr)
if (i.second > umm[i.first])
return false;
return true;
}
}; 438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
class Solution {
public:
vector findAnagrams(string s, string p) {
vector ans;
if (s.length() < p.length())
return ans;
vector vs(26), vp(26);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)p.length(); i++) {
vs[s[i] - 97]++;
vp[p[i] - 97]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= (int)s.length() - (int)p.length(); i++) {
if (vs == vp)
ans.push_back(i);
if (i == (int)s.length() - (int)p.length())
break;
vs[s[i] - 97]--;
vs[s[i + p.length()] - 97]++;
}
return ans;
}
}; 202. 快乐数
class Solution {
public:
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_set u;
do {
int sum = 0, digit = 0;
while (n > 0) {
digit = n % 10;
sum += digit * digit;
n /= 10;
}
if (sum == 1)
return true;
if (u.find(sum) != u.cend())
return false;
u.insert(sum);
n = sum;
} while (1);
return false;
}
}; 50. Pow(x, n)
class Solution {
private:
double myPower(double x, int n) {
double ans = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
ans *= x;
n >>= 1;
x *= x;
}
return ans;
}
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
if (x == 0)
return 0;
if (n == INT_MIN) {
n++;
return 1 / x * (1 / myPower(x, -n));
}
return n < 0 ? 1 / myPower(x, -n) : myPower(x, n);
}
};51-100
51. N 皇后
![]()
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidNQueen(vector& board, int n) {
/* 行和列 */
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = 0, q = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.')
p++;
if (board[j][i] != '.')
q++;
if (p > 1 || q > 1)
return false;
}
}
/* 左上角 */
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = k; i < n && j >= 0; i++, j--) {
if (board[i][j] != '.')
p++;
if (p > 1)
return false;
}
}
/* 右下角 */
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = k, j = n - 1; i < n && j >= 0; i++, j--) {
if (board[i][j] != '.')
p++;
if (p > 1)
return false;
}
}
/* 左下角 */
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = k, j = 0; i < n && j < n; i++, j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.')
p++;
if (p > 1)
return false;
}
}
/* 右上角 */
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = k; i < n && j < n; i++, j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.')
p++;
if (p > 1)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void dfs(vector& board, vector >& tmp, int n, int index) {
if (index >= n && isValidNQueen(board, n)) {
tmp.emplace_back(board);
return;
}
int i = 0;
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (board[index][i] == '.') {
board[index][i] = 'Q';
if (isValidNQueen(board, n))
dfs(board, tmp, n, index + 1);
board[index][i] = '.';
}
}
if (i >= n)
return;
}
vector> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector > ans;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string row(n, '.');
vector board(n, row);
vector > t;
board[0][i] = 'Q';
dfs(board, t, n, 1);
ans.insert(ans.end(), t.begin(), t.end());
board[0][i] = '.';
}
return ans;
}
}; 52. N皇后 II
增加下面的
int totalNQueens(int n) {
return solveNQueens(n).size();
}53. 最大子序和
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:96 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了41.82%的用户
内存消耗:66.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了49.67%的用户
通过测试用例:209 / 209 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size(), sum = nums[0], ans = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
sum = sum > 0 ? sum + nums[i] : nums[i]; // 贪心
// sum = max(sum + nums[i], nums[i]); // 动归
ans = max(ans, sum);
}
return ans;
}
}; 54. 螺旋矩阵
class Solution {
public:
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
vector ans;
int k = 0, p1 = 0, p2 = matrix[0].size() - 1, p3 = 0, p4 = matrix.size() - 1;
while (p1 <= p2 && p3 <= p4) {
for (int i = p1; i <= p2; i++)
ans.push_back(matrix[p3][i]);
if (++p3 > p4)
break;
for (int i = p3; i <= p4; i++)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][p2]);
if (--p2 < p1)
break;
for (int i = p2; i >= p1; i--)
ans.push_back(matrix[p4][i]);
if (--p4 < p3)
break;
for (int i = p4; i >= p3; i--)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][p1]);
if (++p1 > p2)
break;
}
return ans;
}
}; 55. 跳跃游戏
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了79.78%的用户
内存消耗:47 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.15%的用户
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector& nums) {
if (nums.empty())
return true;
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nums.size(); i++) {
if (p < i)
return false;
p = p < i + nums[i] ? i + nums[i] : p;
}
return true;
}
}; 56. 合并区间
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
vector> merge(vector>& intervals) {
vector> ans;
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());
for (auto i = intervals.begin(); i < intervals.end(); i++) {
if (ans.empty() || *i->begin() > *ans.rbegin()->rbegin())
ans.emplace_back(*i);
else
*ans.rbegin()->rbegin() = MAX(*i->rbegin(), *ans.rbegin()->rbegin());
}
return ans;
}
}; #define MAX(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
vector> merge(vector>& intervals) {
vector> ans;
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());
ans.push_back(intervals[0]);
for (vector& i : intervals) {
vector* j = &ans.back();
if (i[0] <= j[0][1])
j[0][1] = MAX(j[0][1], i[1]);
else
ans.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
}; 57. 插入区间
执行用时:32 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了6.58%的用户
内存消耗:17.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了10.30%的用户
#define MAX(X,Y) ((X)<(Y)?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
vector> insert(vector>& intervals, vector& newInterval) {
intervals.emplace_back(newInterval);
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());
vector> ans;
for (auto i : intervals) {
if (ans.empty() || ans.back()[1] < i[0])
ans.emplace_back(i);
else
ans.back()[1] = MAX(i[1], ans.back()[1]);
}
return ans;
}
}; 58. 最后一个单词的长度
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了39.39%的用户
内存消耗:6.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了42.62%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {
int ans = 0;
auto i = s.rbegin();
while (i[0] == 32)
i++;
for (; i < s.rend() && i[0] != 32; i++)
ans++;
return ans;
}
};59. 螺旋矩阵 II
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了62.48%的用户
class Solution {
public:
vector> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector> ans(n, vector(n));
vector t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n * n; i++)
t.emplace_back(i);
int p1 = 0, p2 = n - 1, p3 = 0, p4 = n - 1, j = 0;
while (j < (int)t.size()) {
for (int i = p1; i <= p2; i++)
ans[p3][i] = t[j++];
if (++p3 > p4)
break;
for (int i = p3; i <= p4; i++)
ans[i][p2] = t[j++];
if (--p2 < p1)
break;
for (int i = p2; i >= p1; i--)
ans[p4][i] = t[j++];
if (--p4 < p3)
break;
for (int i = p4; i >= p3; i--)
ans[i][p1] = t[j++];
if (++p1 > p2)
break;
}
return ans;
}
}; *60. 排列序列
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-sequence/solution/di-kge-pai-lie-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。@大神:
class Solution { public: string getPermutation(int n, int k) { string result = ""; vectorvechash = { 1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880 }; vector vec; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { vec.push_back('1' + i - 1); } k--; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int t = k / vechash[n - i]; k %= vechash[n - i]; result += vec[t]; vec.erase(vec.begin() + t); } return result; } };
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:5.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了55.02%的用户
template struct _fac { static const int val = n * _fac::val; };
template <> struct _fac<0> { static const int val = 1; };
const int fac[10] = {_fac<0>::val, _fac<1>::val, _fac<2>::val, _fac<3>::val, _fac<4>::val,
_fac<5>::val, _fac<6>::val, _fac<7>::val, _fac<8>::val, _fac<9>::val};
class Solution {
public:
string getPermutation(int n, int k) {
vector nums;
string ans;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
nums.push_back(i);
k--;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
auto iter = nums.begin() + k / fac[i];
k %= fac[i];
ans += *iter + 48;
nums.erase(iter);
}
return ans;
}
}; 61. 旋转链表
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了62.06%的用户
内存消耗:11.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了74.05%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int getListLength(ListNode* head, ListNode*& tail) {
tail = head;
if (head == nullptr)
return 0;
int len = 1;
while (head->next != nullptr) {
++len;
head = head->next;
tail = tail->next;
}
return len;
}
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* tail;
int len = getListLength(head, tail);
if (len < 2)
return head;
k %= len;
if (k == 0)
return head;
k = len - k;
ListNode* b = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
b = b->next;
ListNode* p = b->next;
b->next = nullptr;
tail->next = head;
return p;
}
};测试用例
std::vector nums = { 1,2 };
ListNode* head = new ListNode;
ListNode* p = head;
for (auto i : nums) {
ListNode* t = new ListNode(i);
p->next = t;
p = t;
}
p = head->next;
while (p != nullptr) {
cout << "-->" << p->val;
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
p = head->next;
p = solution->rotateRight(p, 0);
while (p != nullptr) {
cout << "-->" << p->val;
p = p->next;
} 62. 不同路径
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:5.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.37%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
std::vector dp(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
return dp[n - 1];
}
}; 63. 不同路径 II
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:7.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了56.92%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector >& obg) {
int m = obg.size(), n = obg[0].size();
if (m < 1 || n < 1 || obg[0][0] > 0)
return 0;
vector > dp(m, vector(n, 1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[0][i] ^= obg[0][i];
if (i > 0)
dp[0][i] &= dp[0][i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] ^= obg[i][0];
if (i > 0)
dp[i][0] &= dp[i - 1][0];
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (obg[i][j] > 0)
dp[i][j] = 0;
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}; 64. 最小路径和
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了79.64%的用户
内存消耗:9.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了91.25%的用户
#define __min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
int minPathSum(vector>& grid) {
if (grid.empty() || grid[0].empty())
return 0;
vector> dp(move(grid));
int m = dp.size(), n = dp[0].size();
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
dp[i][0] += dp[i - 1][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
dp[0][i] += dp[0][i - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
dp[i][j] += __min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}; *65. 有效数字
// TODO
66. 加一
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.74%的用户
内存消耗:8.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了51.35%的用户
class Solution {
public:
vector plusOne(vector& digits) {
vector ans;
int flag = 0;
int t = digits.back() + 1;
digits.back() = t % 10;
flag = t / 10;
if ((int)digits.size() < 2) {
if (flag == 0)
return digits;
ans.push_back(flag);
ans.insert(ans.end(), digits.begin(), digits.end());
return ans;
}
for (int i = digits.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
t = digits[i] + flag;
digits[i] = t % 10;
flag = t / 10;
}
if (flag > 0)
ans.push_back(flag);
ans.insert(ans.end(), digits.begin(), digits.end());
return ans;
}
}; 67. 二进制求和
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了57.30%的用户
内存消耗:6.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了72.18%的用户
class Solution {
public:
string addBinary(string a, string b) {
string c = a.length() < b.length() ? b : a;
string d = a.length() >= b.length() ? b : a;
string res;
char f = '0';
for (auto i = d.rbegin(), j = c.rbegin(); i != d.rend(); i++, j++) {
char t = *i + *j + f - 96;
res.push_back(((t - 48) % 2) + 48);
f = (t - 48) / 2 + 48;
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)(c.length() - d.length()); i++) {
char t = c[(int)(c.length() - d.length()) - i - 1] + f - 48;
res.push_back(((t - 48) % 2) + 48);
f = (t - 48) / 2 + 48;
}
if (f > '0') {
res.push_back(f);
f = '0';
}
string ans(res.rbegin(), res.rend());
return ans;
}
};68. 文本左右对齐
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:7.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了42.59%的用户
class Solution {
public:
vector fullJustify(vector& words, int maxWidth) {
vector ans;
int sol = 0, lineCharCnt = 0;
for (int cur = 0; cur < (int)words.size(); cur++) {
lineCharCnt += words[cur].length() + 1;
if (cur == words.size() - 1 || lineCharCnt + words[cur + 1].length() > maxWidth) {
int lineWordCnt = cur - sol + 1;
int extroLineSpaceCnt = maxWidth - lineCharCnt + 1;
int extroLineSpaceAvg = lineWordCnt < 2 ? 1 : extroLineSpaceCnt / (lineWordCnt - 1);
int extroLineSpaceMod = lineWordCnt < 2 ? 0 : extroLineSpaceCnt % (lineWordCnt - 1);
string str = "";
for (int i = sol; i < cur; i++) {
str += words[i];
if (cur == words.size() - 1) {
str.push_back(0x20);
continue;
}
fill_n(back_inserter(str), extroLineSpaceAvg + (int)((i - sol) < extroLineSpaceMod) + 1, 0x20);
}
str += words[cur];
fill_n(back_inserter(str), maxWidth - (int)str.length(), 0x20);
ans.push_back(str);
sol = cur + 1;
lineCharCnt = 0;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 69. Sqrt(x)
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:5.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了89.03%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int mySqrt(int x) {
double res = (double)x;
while (res * res - x > 0.001)
res = res - 0.5 * res + (double)x * 0.5 / res;
return (int)res;
}
};70. 爬楼梯
class Solution1 {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int dp[3] = { 1, 1, 2 };
if (n < 3)
return dp[n];
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
dp[0] = dp[1];
dp[1] = dp[2];
dp[2] = dp[0] + dp[1];
}
return dp[2];
}
};
71. 简化路径
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.83%的用户
内存消耗:7.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了68.61%的用户
class Solution {
public:
string simplifyPath(string path) {
stringstream ss;
ss << path;
string str;
vector res;
while (getline(ss, str, '/')) {
if (str == "" || str == ".")
continue;
if (str == "..")
if (!res.empty())
res.pop_back();
else
continue;
else
res.push_back(str);
}
if (res.empty())
return "/";
string ans = "";
for_each(res.begin(), res.end(), [&ans](auto val)->void { ans.push_back('/'); ans += val; });
return ans;
}
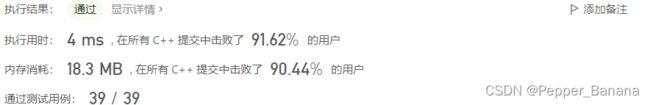
}; 72. 编辑距离
/*
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击了48.97%的用户
内存消耗:8.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了35.65%的用户
通过测试用例:1146 / 1146
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length();
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
dp[i][0] = i;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[0][i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1] - (int)(word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]));
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}; 73. 矩阵置零
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了77.82%的用户
内存消耗:12.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了43.85%的用户
class Solution {
public:
void setZeroes(vector>& m) {
int cr0 = 0, cr1 = 0, h = m.size(), w = m[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
if (m[0][i] == 0)
cr1 = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
if (m[i][0] == 0)
cr0 = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < w; j++)
if (m[i][j] == 0)
m[i][0] = m[0][j] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < w; j++)
if (m[i][0] == 0 || m[0][j] == 0)
m[i][j] = 0;
if (cr0 == 1)
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
m[i][0] = 0;
if (cr1 == 1)
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
m[0][i] = 0;
}
}; 74. 搜索二维矩阵
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了76.67%的用户
内存消耗:9.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了49.93%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int biSearch(vector>& m, int tar, int l, int r, int& lb) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (l <= r) {
if (m[mid][0] >= tar) {
lb = mid;
return biSearch(m, tar, l, mid - 1, lb);
}
else
return biSearch(m, tar, mid + 1, r, lb);
}
return mid;
}
int biSearch(vector>& m, int tar, int l, int r, int i, int& lb) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (l <= r) {
if (m[i][mid] >= tar) {
lb = mid;
return biSearch(m, tar, l, mid - 1, i, lb);
}
else
return biSearch(m, tar, mid + 1, r, i, lb);
}
return mid;
}
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector>& matrix, int target) {
int i = -1;
int mid = biSearch(matrix, target, 0, matrix.size() - 1, i);
if (i >= 0) {
if (matrix[i][0] == target)
return true;
if (i == 0)
return false;
if (i > 0)
i--;
}
else
i = matrix.size() - 1;
int j = -1;
mid = biSearch(matrix, target, 0, matrix[0].size() - 1, i, j);
if (j >= 0) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target)
return true;
if (j == 0)
return false;
if (j > 0)
j--;
}
else
j = matrix[0].size() - 1;
if (matrix[i][j] == target)
return true;
return false;
}
}; 75. 颜色分类
/**
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了78.37%的用户
通过测试用例:87 / 87
*/
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector& nums) {
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= r; i++) {
while (i <= r && nums[i] == 2) {
swap(nums[i], nums[r]);
r--;
}
while (l <= i && nums[i] == 0) {
swap(nums[i], nums[l]);
l++;
}
}
}
}; 76. 最小覆盖子串
class Solution {
public:
bool isCover(unordered_map& um1, unordered_map& um2) {
for (auto i : um2)
if (um1[i.first] < i.second)
return false;
return true;
}
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
string ans = "";
if (s.length() < t.length())
return ans;
unordered_map sm, tm;
for (auto i : t)
tm[i]++;
int len = INT_MAX, l = 0, r = 0;
while (r < s.length()) {
++sm[s[r++]];
while (l < r && isCover(sm, tm)) {
if (len > r - l) {
len = r - l;
ans = s.substr(l, len);
}
--sm[s[l]];
++l;
}
}
return len == INT_MAX ? "" : ans;
}
}; 77. 组合
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了65.30%的用户
内存消耗:8.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.82%的用户
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector>& ans, vector& nums, vector& t, int k, int r) {
if ((int)t.size() == k) {
ans.push_back(t);
return;
}
for (int i = r; i < nums.size(); i++) {
t.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(ans, nums, t, k, i + 1);
t.pop_back();
}
}
vector> combine(int n, int k) {
vector> ans;
vector nums, tmp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
nums.push_back(i);
dfs(ans, nums, tmp, k, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 78. 子集
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了90.74%的用户
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector& nums, vector& t, vector>& ans, int r) {
ans.push_back(t);
for (int i = r; i < nums.size(); i++) {
t.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, t, ans, i + 1);
t.pop_back();
}
}
vector> subsets(vector& nums) {
vector> ans;
vector tmp;
dfs(nums, tmp, ans, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 79. 单词搜索
执行用时:1484 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了8.51%的用户
内存消耗:233 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.19%的用户
class Solution {
public:
bool check(vector>& b, vector>& v, int i, int j, string& s, int k) {
if (b[i][j] != s[k])
return false;
if ((int)s.length() - 1 == k)
return true;
v[i][j] = 1;
vector> d{ {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
for (auto p : d) {
int m = i + p.first, n = j + p.second;
if (m >= 0 && m < b.size() && n >= 0 && n < b[0].size() && v[m][n] == 0 && check(b, v, m, n, s, k + 1))
return true;
}
v[i][j] = 0;
return false;
}
bool exist(vector>& board, string s) {
int h = board.size(), w = board[0].size();
vector> visited(h, vector(w, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
if (check(board, visited, i, j, s, 0))
return true;
return false;
}
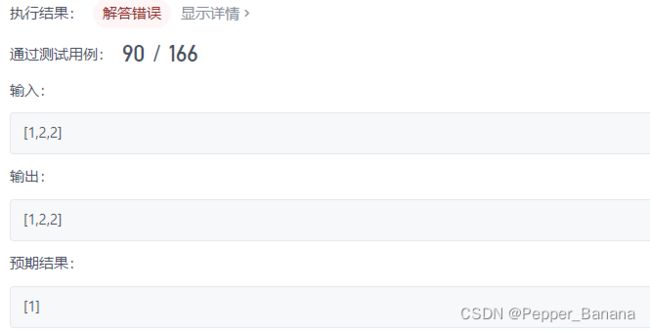
}; 80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.10%的用户
内存消耗:10.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了26.32%的用户
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 3)
return nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1] && nums[i] == nums[i + 2]) {
auto it = nums.begin();
for (int j = 0; j < i + 2; j++, it++);
nums.erase(remove(it, nums.end(), nums[i]), nums.end());
}
}
if (nums.size() < 3)
return nums.size();
auto it1 = nums.rbegin();
auto it2 = it1 + 1, it3 = it1 + 2;
if (*it1 == *it2 && *it1 == *it3)
nums.erase(nums.end() - 1, nums.end());
return nums.size();
}
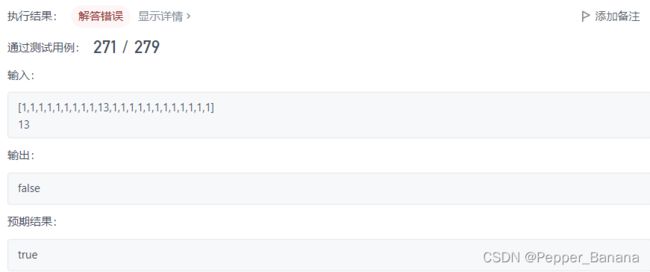
}; 81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
边界条件导致的一个错误用例
class Solution {
public:
int biSearch(vector& nums, int target, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return -1;
int mid = (i + j) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[i] == nums[mid] && nums[mid] == nums[j])
return biSearch(nums, target, i + 1, j - 1);
if (nums[mid] <= nums[j]) { //
if (nums[mid] < target && nums[j] >= target)
return biSearch(nums, target, mid + 1, j);
else
return biSearch(nums, target, i, mid - 1);
}
if (nums[i] <= target && nums[mid] > target)
return biSearch(nums, target, i, mid - 1);
else
return biSearch(nums, target, mid + 1, j);
}
bool search(vector& nums, int target) {
int pos = biSearch(nums, target, 0, nums.size() - 1);
return pos < 0 ? false : true;
}
}; 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
指针模拟错误
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* r = head;
while (r->next != nullptr)
r = r->next;
if (head->val == r->val)
return nullptr;
ListNode* l = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode* b = l;
ListNode* p = head, *q = head->next;
ListNode* t = q;
while (q != nullptr) {
while (q != nullptr && p->val != q->val) {
b = p;
p = q;
q = q->next;
t = q;
}
while (q != nullptr && p->val == q->val) {
t = q;
q = q->next;
}
if (t != nullptr && p->val == t->val) {
b->next = q;
p = q;
if (q == nullptr)
return l->next;
q = q->next;
t = q;
}
else
b = p;
}
return l->next;
}
};83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了98.69%的用户
内存消耗:11.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了96.18%的用户
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* p = head, *q = head->next;
while (q != nullptr) {
while (q != nullptr && p->val != q->val) {
p = q;
q = q->next;
}
while (q != nullptr && p->val == q->val) {
q = q->next;
}
p->next = q;
p = q;
if (q != nullptr)
q = q->next;
}
return head;
}
};84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
/*
执行用时:140 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了47.46%的用户
内存消耗:79.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了9.66%的用户
通过测试用例:98 / 98
*/
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector& heights) {
stack stk;
int n = heights.size();
vector l(n), r(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && heights[i] <= heights[stk.top()])
stk.pop();
l[i] = stk.empty() ? -1 : stk.top();
stk.push(i);
}
stk = stack();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stk.empty() && heights[i] <= heights[stk.top()])
stk.pop();
r[i] = stk.empty() ? n : stk.top();
stk.push(i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ans = max(ans, (r[i] - l[i] - 1) * heights[i]);
return ans;
}
}; 85. 最大矩形
#define MAX(X,Y) (((X)<(Y))?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector& heights) {
int res = 0, n = heights.size();
stack s;
vector l;
vector r(n, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!s.empty() && heights[i] <= heights[s.top()]) {
r[s.top()] = i;
s.pop();
}
l.push_back(s.empty() ? -1 : s.top());
s.push(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
res = MAX((r[i] - l[i] - 1) * heights[i], res);
return res;
}
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector>& matrix) {
int ans = 0;
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
if (!(m && n))
return ans;
vector hist(n, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (j > 0 && matrix[j][i] == matrix[j - 1][i])
hist[i] += matrix[j][i] - 48;
else
hist[i] = matrix[j][i] - 48;
}
ans = MAX(largestRectangleArea(hist), ans);
}
return ans;
}
}; 86. 分隔链表
备注
1、原链表中既有小于x又有不小于x的值,丢弃两个临时链表末尾的0
2、原链表中只有小于或只有不小于x的值,丢弃一个临时链表末尾的0和另一个临时链表
![]()
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* juni = new ListNode, * seni = new ListNode;
ListNode* p = juni, * q = seni, * t = head;
while (t != nullptr) {
ListNode* r = new ListNode;
if (t->val < x) {
p->val = t->val;
p->next = r;
p = r;
}
else {
q->val = t->val;
q->next = r;
q = r;
}
t = t->next;
}
ListNode* l = juni, * r = seni;
if (l->next == nullptr) {
while (r->next != q)
r = r->next;
r->next = nullptr;
return seni;
}
if (r->next == nullptr) {
while (l->next != p)
l = l->next;
l->next = nullptr;
return juni;
}
while (l->next != p)
l = l->next;
while (r->next != q)
r = r->next;
l->next = seni;
r->next = nullptr;
return juni;
}
};87. 扰乱字符串
// TODO
88. 合并两个有序数组
#define MAX(X,Y) (((X)<(Y))?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector& nums1, int m, vector& nums2, int n) {
int i = m - 1, j = n - 1, p = m + n - 1;
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 && p >= 0) {
nums1[p--] = MAX(nums1[i], nums2[j]);
nums1[i] < nums2[j] ? --j : --i;
}
while (i >= 0)
nums1[p--] = nums1[i--];
while (j >= 0)
nums1[p--] = nums2[j--];
}
}; 89. 格雷编码
class Solution {
public:
const char l[3] = { '0', '1' };
const char r[3] = { '1', '0' };
void dfs(string& tmp, vector& res, const char d[], int n) {
if ((int)tmp.length() == n) {
res.push_back(strtol(tmp.c_str(), nullptr, 2));
return;
}
tmp.push_back(d[0]);
dfs(tmp, res, l, n);
tmp.pop_back();
tmp.push_back(d[1]);
dfs(tmp, res, r, n);
tmp.pop_back();
}
vector grayCode(int n) {
string tmp = "";
vector res;
const char d[3] = { '0', '1' };
dfs(tmp, res, d, n);
return res;
}
}; 90. 子集 II
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector& nums, vector& res, vector>& ans, int idx) {
ans.push_back(res);
for (int i = idx; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (!(i > idx && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])) {
res.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, res, ans, i + 1);
res.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector> subsetsWithDup(vector& nums) {
vector res;
vector> ans;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dfs(nums, res, ans, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 91. 解码方法
法1:DFS
![]()
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(string s, int idx) {
if (idx >= s.length())
return 1;
int ans = 0;
int t = stoi(s.substr(idx, 1));
if (t > 0 && t < 10)
ans += dfs(s, idx + 1);
else
return ans;
if (idx < s.length() - 1) {
t = stoi(s.substr(idx, 2));
if (t > 9 && t < 27)
ans += dfs(s, idx + 2);
else
return ans;
}
return ans;
}
int numDecodings(string s) {
if (s.length() < 2 && s[0] == '0')
return 0;
return dfs(s, 0);
}
};法2:动态规划
![]()
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
vector dp = { 0, 1, 0 };
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); ++i) {
dp[2] = 0;
if (s[i - 1] != '0') {
dp[2] = dp[1];
}
if (i > 1 && (s[i - 2] == 49 || s[i - 2] == 50 && s[i - 1] < 55))
dp[2] += dp[0];
dp[0] = dp[1];
dp[1] = dp[2];
}
return dp[2];
}
}; 类似
491. 递增子序列
class Solution {
public:
bool dup(vector& nums, int idx, int i) {
for (int j = idx; j < i && j < nums.size(); j++)
if (nums[j] == nums[i])
return true;
return false;
}
void dfs(vector& nums, vector& res, vector>& ans, int idx) {
if (res.size() > 1)
ans.push_back(res);
for (int i = idx; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if ((res.empty() || nums[i] >= res.back()) && !(i > idx && dup(nums, idx, i))) {
res.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, res, ans, i + 1);
res.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector> findSubsequences(vector& nums) {
vector> ans;
vector res;
dfs(nums, res, ans, 0);
return ans;
}
}; 92. 反转链表 II
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseSingly(ListNode* head, ListNode*& tail) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* rhead = reverseSingly(head->next, tail);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
return rhead;
}
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || right <= left)
return head;
ListNode* pre = new ListNode(INT_MAX, head);
ListNode* p = pre, * q = pre;
ListNode* r = nullptr;
ListNode* rbeg = new ListNode;
ListNode* rtail = new ListNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++, p = p->next) {}
for (int i = 0; i < right; i++, q = q->next) {}
if (q->next != nullptr) {
r = q->next;
q->next = nullptr;
}
rbeg = reverseSingly(p->next, rtail);
p->next = rbeg;
if (r != nullptr)
rtail->next = r;
return pre->next;
}
};93. 复原 IP 地址
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(string s, int idx, int dot, string& str, vector& ans) {
if (idx == s.length() && dot == 4) {
str.pop_back();
int k = 0;
ans.push_back(str);
str.push_back('.');
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < s.length() && dot < 4; i++) {
string num = s.substr(idx, i - idx + 1);
if (num.length() == 1 || (num[0] != '0' && num.length() <= 3 && stoi(num) <= 255)) {
str += num;
str.push_back('.');
dfs(s, i + 1, dot + 1, str, ans);
str.pop_back();
for (int j = 0; j < num.size(); j++)
str.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
vector ans;
string str = "";
dfs(s, 0, 0, str, ans);
return ans;
}
}; 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
// Morris遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector ans;
vector inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* p = root;
while (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left == nullptr) {
ans.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
else {
p = root->left;
while (p->right != nullptr && p->right != root)
p = p->right;
if (p->right == nullptr) {
p->right = root;
root = root->left;
}
else /* if (p->right == root) */ {
p->right = nullptr;
ans.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 类似
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector ans;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left == nullptr) {
ans.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
else {
p = root->left;
while (p->right != nullptr && p->right != root)
p = p->right;
if (p->right == nullptr) {
ans.push_back(root->val);
p->right = root;
root = root->left;
}
else {
p->right = nullptr;
root = root->right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 145. 二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector ans;
stack stk;
while (root != nullptr || !stk.empty()) {
while (root != nullptr) {
ans.push_back(root->val);
stk.push(root);
root = root->right;
}
root = stk.top();
root = root->left;
stk.pop();
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
}; 95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
![]()
class Solution {
public:
vector generateTrees(int l, int r) {
if (l > r)
return { nullptr };
vector ans;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
vector left = generateTrees(l, i - 1);
vector right = generateTrees(i + 1, r);
for (auto j : left) {
for (auto k : right) {
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(i, j, k);
ans.push_back(node);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
vector generateTrees(int n) {
vector ans = generateTrees(1, n);
return ans;
}
}; 96. 不同的二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
int numTrees(int n, vector& f) {
if (n == 0)
f[0] = 1;
if (n == 1)
f[1] = 1;
if (f[n] > 0)
return f[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
f[n] += numTrees(i, f) * numTrees(n - 1 - i, f);
return f[n];
}
int numTrees(int n) {
vector f(n + 1);
return numTrees(n, f);
}
}; 97. 交错字符串
// TODO
98. 验证二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root, long long l, long long r) {
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
if (root->val <= l || root->val >= r)
return false;
return isValidBST(root->left, l, root->val) && isValidBST(root->right, root->val, r);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return isValidBST(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);
}
};99. 恢复二叉搜索树
// TODO
100. 相同的树
![]()
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (p == nullptr && q == nullptr)
return true;
if (p == nullptr && q != nullptr || q == nullptr && p != nullptr)
return false;
return p->val == q->val && isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
};101-150
101. 对称二叉树
// 递归
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (p == nullptr && q == nullptr)
return true;
if (p == nullptr || q == nullptr || p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSymmetric(p->left, q->right) && isSymmetric(p->right, q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
return isSymmetric(root->left, root->right);
}
};102. 二叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector > ans;
if (root == nullptr)
return ans;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
vector res;
int n = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res.push_back(q.front()->val);
if (q.front()->left != nullptr)
q.push(q.front()->left);
if (q.front()->right != nullptr)
q.push(q.front()->right);
q.pop();
}
ans.push_back(res);
}
return ans;
}
}; 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector > ans;
if (root == nullptr)
return ans;
int d = 0x0CCCCCCC;
deque q;
q.push_back(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
vector res;
int n = q.size();
if (d > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res.push_back(q.front()->val);
if (q.front()->left != nullptr)
q.push_back(q.front()->left);
if (q.front()->right != nullptr)
q.push_back(q.front()->right);
q.pop_front();
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res.push_back(q.back()->val);
if (q.back()->right != nullptr)
q.push_front(q.back()->right);
if (q.back()->left != nullptr)
q.push_front(q.back()->left);
q.pop_back();
}
}
d = ~d;
ans.push_back(res);
}
return ans;
}
}; 104. 二叉树的最大深度
#define MAX(X,Y) (((X)<(Y))?(Y):(X))
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int DepthLeft = 1 + maxDepth(root->left);
int DepthRight = 1 + maxDepth(root->right);
return MAX(DepthLeft, DepthRight);
}
};105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
![]()
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& pre, vector& inorder, int pl, int pr, int il, int ir) {
if (il > ir)
return nullptr;
int i = 0;
for (; i <= ir; i++)
if (inorder[i] == pre[pl])
break;
return new TreeNode(inorder[i],
buildTree(pre, inorder, pl + 1, pr - ir + i, il, i - 1),
buildTree(pre, inorder, pr - ir + i + 1, pr, i + 1, ir));
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& preorder, vector& inorder) {
return buildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1, 0, inorder.size() - 1);
}
}; 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
![]()
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& inorder, vector& postorder, int il, int ir, int pl, int pr) {
if (il > ir)
return nullptr;
int i = il;
for (; i <= ir; i++)
if (inorder[i] == postorder[pr])
break;
return new TreeNode(postorder[pr],
buildTree(inorder, postorder, il, i - 1, pl, pr - ir + i - 1),
buildTree(inorder, postorder, i + 1, ir, pr - ir + i, pr - 1));
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& inorder, vector& postorder) {
return buildTree(inorder, postorder, 0, inorder.size() - 1, 0, postorder.size() - 1);
}
}; 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
class Solution {
public:
vector> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return {};
vector> ans;
queue res;
res.push(root);
while (!res.empty()) {
int n = res.size();
vector lev;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* p = res.front();
res.pop();
lev.push_back(p->val);
if (p->left)
res.push(p->left);
if (p->right)
res.push(p->right);
}
ans.push_back(lev);
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
}; 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector& nums, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return nullptr;
int mid = i + ((j - i) >> 1);
return new TreeNode(nums[mid], sortedArrayToBST(nums, i, mid - 1), sortedArrayToBST(nums, mid + 1, j));
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector& nums) {
return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
}; 109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode*& head, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return nullptr;
int mid = i + ((j - i + 1) >> 1);
TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(INT_MAX);
p->left = sortedListToBST(head, i, mid - 1);
p->val = head->val;
head = head->next;
p->right = sortedListToBST(head, mid + 1, j);
return p;
}
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* t = head;
int len = 0;
for (; t; t = t->next, ++len);
return sortedListToBST(head, 0, len - 1);
}
};
110. 平衡二叉树
// 迭代
// 思路:通过后序遍历计算每个结点的高度,通过前序遍历判断每个结点是否平衡
#define MAX(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define ABS(a) (((a) < 0) ? -(a) : (a))
class Solution {
public:
int getHeight(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr, * cur = root;
int h = 1, mh = 0;
while (cur || !res.empty()) {
while (cur) {
res.push_back(cur);
++h;
cur = cur->left;
}
cur = res.back();
res.pop_back();
if (cur->right == nullptr || cur->right == pre) {
pre = cur;
cur = nullptr;
--h;
}
else {
res.push_back(cur);
cur = cur->right;
}
mh = MAX(mh, h);
}
return mh;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
TreeNode* cur = root;
vector res;
res.push_back(cur);
while (!res.empty()) {
cur = res.back();
res.pop_back();
int l = getHeight(cur->left);
int r = getHeight(cur->right);
if (ABS(l - r) > 1)
return false;
if (cur->left)
res.push_back(cur->left);
if (cur->right)
res.push_back(cur->right);
}
return true;
}
}; // 递归
#define MAX(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define ABS(a) (((a) < 0) ? -(a) : (a))
class Solution {
public:
int h(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int l = h(root->left);
if (l == -1)
return -1;
int r = h(root->right);
if (r == -1)
return -1;
if (ABS(l - r) > 1)
return -1;
return MAX(l, r) + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return h(root) >= 0;
}
};111. 二叉树的最小深度
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int depth = 0, n = 0;
if (root == nullptr)
return depth;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
depth++;
n = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
if (node->left)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
q.push(node->right);
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr)
return depth;
q.pop();
}
}
return depth;
}
}; 112. 路径总和
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int sum) {
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && sum + root->val == targetSum)
return true;
return dfs(root->left, targetSum, sum + root->val) || dfs(root->right, targetSum, sum + root->val);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
return dfs(root, targetSum, 0);
}
};113. 路径总和 II
114. 二叉树展开为链表
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
stack stk;
stk.push(root);
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
while (!stk.empty()) {
TreeNode* cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (pre) {
pre->left = nullptr;
pre->right = cur;
}
if (cur->right)
stk.push(cur->right);
if (cur->left)
stk.push(cur->left);
pre = cur;
}
}
}; 115. 不同的子序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:40 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了59.13%的用户
内存消耗:29.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了37.03%的用户
通过测试用例:64 / 64 */
class Solution {
public:
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int numDistinct(string s, string t) {
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
dp[i][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s[i - 1] == t[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}; 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:28 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了28.87%的用户
内存消耗:26.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了73.11%的用户
通过测试用例:94 / 94 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root, int& ans) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int l = max(0, maxPathSum(root->left, ans));
int r = max(0, maxPathSum(root->right, ans));
ans = max(ans, root->val + l + r);
return root->val + max(l, r);
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = INT_MIN;
maxPathSum(root, ans);
return ans;
}
};136. 只出现一次的数字
/* 提交结果 执行用时 内存消耗 语言 提交时间 备注通过
16 ms 16.4 MB C++ 2022/10/11 15:37 添加备注 */
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector& nums) {
int ans = 0;
for (auto& d : nums)
ans ^= d;
return ans;
}
}; 141. 环形链表
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了93.11%的用户
内存消耗:7.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了89.65%的用户
通过测试用例:22 / 22 */
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* p = head, * q = head;
while (q != nullptr && q->next != nullptr) {
p = p->next;
q = q->next->next;
if (p == q)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};142. 环形链表 II
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了97.99%的用户
内存消耗:7.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了87.37%的用户
通过测试用例:17 / 17 */
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* p = head, * q = head;
while (q != nullptr && q->next != nullptr) {
p = p->next;
q = q->next->next;
if (p == q)
break;
}
if (q == nullptr || q->next == nullptr)
return nullptr;
p = head;
while (p != q) {
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return p;
}
};
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
/* 贪心算法
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:120 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了30.65%的用户
内存消耗:91 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败78.76%的用户
通过测试用例:211 / 211 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int cheapest = INT_MAX, ans = 0, n = prices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cheapest = min(cheapest, prices[i]);
ans = max(ans, prices[i] - cheapest);
}
return ans;
}
}; /* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:108 ms, 在所有 C++ 提中击败了51.08%的用户
内存消耗:102.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了15.41%的用户
通过测试用例:211 / 211 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector> dp(2, vector(n));
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[1][0] = prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[0][i] = max(dp[0][i - 1], prices[i] - dp[1][i - 1]);
dp[1][i] = min(dp[1][i - 1], prices[i]);
}
return dp[0][n - 1];
}
}; 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了49.85%的用户
内存消耗:13 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了24.08%的用户
通过测试用例:200 / 200 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector> dp(2, vector(n));
if (n == 1)
return 0;
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[1][0] = prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[0][i] = max(dp[0][i - 1], prices[i] - dp[1][i - 1]);
dp[1][i] = min(dp[1][i - 1], prices[i] - dp[0][i - 1]);
}
return dp[0].back();
}
}; 123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:136 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了60.37%的用户
内存消耗:73.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.72%的用户
通过测试用例:214 / 214 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if (n == 1)
return 0;
vector dp(vector(5));
int ans = 0;
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = prices[0];
dp[2] = 0;
dp[3] = prices[0];
dp[4] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[1] = min(dp[1], prices[i] - dp[0]);
dp[2] = max(dp[2], prices[i] - dp[1]);
dp[3] = min(dp[3], prices[i] - dp[2]);
dp[4] = max(dp[4], prices[i] - dp[3]);
ans = max(dp[2], dp[4]);
}
return ans;
}
}; 134. 加油站
/* 用totalSum来判断是否存在这个点,用curSum来判断从当前点出发能否到达后面的加油站 */
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector& gas, vector& cost) {
int n = gas.size();
int curSum = 0, totoalSum = 0, startIdx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
totoalSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
if (curSum < 0) {
curSum = 0;
startIdx = i + 1;
}
}
return totoalSum < 0 ? -1 : startIdx;
}
}; 135. 分发糖果
#define MAX(X,Y) (((X)>(Y))?(X):(Y))
class Solution {
public:
int candy(vector& ratings) {
int n = ratings.size();
vector can(n, 1);
/* 从左往右,确保高级的比左边低级的糖多 */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1])
can[i] = can[i - 1] + 1;
/* 从右向左,确保高级的也比右边低级的糖多 */
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1])
can[i] = MAX(can[i], can[i + 1] + 1);
int ans = 0;
for (int i : can)
ans += i;
return ans;
}
}; 139. 单词拆分
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了28.56%的用
内存消耗:14.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了6.74%的用户
通过测试用例:45 / 45 */
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector& wordDict) {
unordered_set us(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
int n = s.size();
vector dp(n + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
string t = s.substr(j, i - j);
if (us.find(t) != us.end() && dp[j] == 1) {
dp[i] = 1;
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}; 146. LRU 缓存
struct DLinkList {
int key, value;
DLinkList* next;
DLinkList* prev;
DLinkList() : key(0), value(0), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}
DLinkList(int k, int v) : key(k), value(v), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}
DLinkList(int k, int v, DLinkList* n, DLinkList* p) : key(k), value(v), next(n), prev(p) {}
};
class LRUCache {
private:
unordered_map um;
DLinkList* head, * tail;
int size, cap;
void addHead(DLinkList* node) {
node->prev = head;
node->next = head->next;
head->next->prev = node;
head->next = node;
}
void removeNode(DLinkList* node) {
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
}
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) : cap(capacity), size(0) {
head = new DLinkList;
tail = new DLinkList;
head->next = tail;
tail->prev = head;
}
int get(int key) {
auto it = um.find(key);
if (it != um.end()) {
DLinkList* p = it->second;
removeNode(p);
addHead(p);
return p->value;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int val) {
auto it = um.find(key);
if (it != um.end()) {
DLinkList* p = it->second;
p->value = val;
removeNode(p);
addHead(p);
}
else {
DLinkList* p = new DLinkList(key, val);
um[key] = p;
addHead(p);
++size;
if (size > cap) {
DLinkList* t = tail->prev;
um.erase(t->key);
removeNode(t);
--size;
}
}
}
}; 148. 排序链表
/**
执行结果:超出时间限制
最后执行的输入:
[1,3,3,1,3,1,3,3,2,3,2,2,1,1,1,3,2,2,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,1,1,2,2,2,1,2,1,1,2,3,3,2,2,3,2,3,2,2,2,1,1,3,2,3,3,1,1,1,2,2,1,2,2,2,2,3,1,3,1,1,1,2,1,2,2,2,1,3,2,2,2,3,3,2,3,3,1,1,2,2,1,2,1,3,2,1,3,3,1,2,1,1,1,1,1,2,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,1,1,3,2,1,1,2,1,3,3,2,2,1,3,1,3,1,3,2,2,3,2,3,2,2,1,2,3,1,3,1,2,3,3,2,3,3,3,1,1,2,3,1,2,3,2,1,1,2,3,1,1,3,1,2,2,3,2,1,3,1,2,1,3,2,1,1,2,2,2,1,3,1,3,2,3,3,1,1,3,1,2,1,2,3,1,2,1,1,3,1,3,3,1,1,1,2,2,1,3,1,2,2,3,2,1,3,2,1,3,2,2,3,3,2,2,1,3,2,2,2,2,2,3,2,2,3,1,3,2,1,3,2,1,2,3,3,3,1,2,2,3,1,1,2,2,3,2,1,1,1,1,1,3,2,2,2,1,3,2,1,2,3,2,1,1,2,1,3,3,1,3,1,2,2,1,2,3,2,3,3,1,2,3,2,2,3,3,2,1,3,2,2,2,3,3,3,1,1,2,1,1,2,3,3,3,1,3,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,3,1,3,2,2,3,3,3,1,2,3,2,1,3,1,1,2,2,1,1,1,2,2,3,1,3,1,2,3,3,3,2,2,3,1,1,1,3,2,1,1,3,1,2,3,3,3,2,1,2,3,2,3,2,1,3,2,2,2,2,1,1,3,1,1,1,3,2,2,2,1,2,3,2,3,2,2,1,2,3,2,1,1,3,1,3,3,1,1,1,1,1,2,3,3,3,1,3,2,2,3,1,1,3,1,1,1,3,1,1,2,2,2,1,1,1,1,2,1,3,3,3,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,1,2,2,3,1,3,1,2,1,2,2,3,3,1,3,3,2,1,3,1,1,3,1,2,3,3,3,3,1,1,3,3,3,3,2,2,2,1,1,3,2,2,2,3,1,3查看全部
*/
/* 通过25/29个用例,待优化。转成数组归并后再转链表可AC */
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
#define GETMID(i,j) ((i) + (((j) - (i)) >> 1))
class Solution {
public:
void merge(ListNode*& head, int l, int mid, int r) {
ListNode* h = new ListNode;
ListNode* s = h;
ListNode* p = head, * q = head;
for (int u = 0; u < l; u++, p = p->next);
for (int u = 0; u < mid + 1; u++, q = q->next);
int k = 0, i = l, j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= r) {
if (p->val <= q->val) {
s->next = new ListNode(p->val);
p = p->next;
i++;
}
else {
s->next = new ListNode(q->val);
q = q->next;
j++;
}
s = s->next;
}
while (i <= mid) {
s->next = new ListNode(p->val);
p = p->next;
i++;
s = s->next;
}
while (j <= r) {
s->next = new ListNode(q->val);
q = q->next;
j++;
s = s->next;
}
p = head, q = head;
for (int u = 0; u < l - 1; u++, p = p->next);
for (int u = 0; u < r; u++, q = q->next);
if (p == head)
head = h->next;
else
p->next = h->next;
s->next = q->next;
}
void sortList(ListNode*& head, int l, int r) {
if (l == r)
return;
int mid = GETMID(l, r);
sortList(head, l, mid);
sortList(head, mid + 1, r);
merge(head, l, mid, r);
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode*& head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
int len = 0;
ListNode* p = head;
for (; p != nullptr; p = p->next, ++len);
sortList(head, 0, len - 1);
return head;
}
};150. 逆波兰表达式求值
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了42.80%的用户
内存消耗:12.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.33%的用户
通过测试用例:22 / 22 */
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector& tokens) {
int n = tokens.size();
vector ans;
for (string s : tokens) {
if (s == "+" || s == "-" || s == "*" || s == "/") {
int64_t x = stoll(ans.back());
ans.pop_back();
int64_t y = stoll(ans.back());
ans.pop_back();
int64_t res = 0;
switch (s[0]) {
case '+':
res = x + y;
break;
case '-':
res = y - x;
break;
case '*':
res = x * y;
break;
default:
res = y / x;
break;
}
ans.push_back(to_string(res));
}
else
ans.push_back(s);
}
return stoll(ans.back());
}
}; 152. 乘积最大子数组
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了58.83%的用户
内存消耗:13.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了66.89%的用户
通过测试用例:188 / 188 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector& nums) {
int m = nums[0], n = nums[0], ans = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int t = m;
m = max({nums[i], m * nums[i], n * nums[i]});
n = min({nums[i], t * nums[i], n * nums[i]});
ans = max(m, ans);
}
return ans;
}
}; 155. 最小栈
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:1388 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.12%的用户
内存消耗:15.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了82.19%的用户
通过测试用例:31 / 31 */
class MinStack {
public:
deque nums;
vector stk;
MinStack() {
nums.clear();
stk.clear();
}
void sift_down(deque& nums, int i, int n) {
int j = i, l = 2 * i + 1, r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l <= n && nums[l] < nums[j])
j = l;
if (r <= n && nums[r] < nums[j])
j = r;
if (j == i)
return;
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
sift_down(nums, j, n);
}
void make_heap(deque& nums) {
int lastidx = nums.size() - 1;
for (int i = (lastidx - 1) >> 1; i >= 0; i--)
sift_down(nums, i, lastidx);
}
void push(int val) {
stk.push_back(val);
nums.push_back(val);
make_heap(nums);
}
void pop() {
int val = stk.back();
stk.pop_back();
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nums.size(); i++) {
if (val == nums[i]) {
for (int j = i; j < (int)nums.size() - 1; j++)
nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
break;
}
}
nums.resize(stk.size());
make_heap(nums);
}
int top() {
if (stk.empty())
return -1;
return stk.back();
}
int getMin() {
if (nums.empty())
return -1;
return nums.front();
}
}; 169. 多数元素
/*
43 / 43 个通过测试用例
状态:通过
执行用时: 8 ms
内存消耗: 19 MB
*/
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector& nums) {
int c, n = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (n == 0)
c = num;
n += (num == c) ? 1 : -1;
}
return c;
}
};
/*
43 / 43 个通过测试用例
状态:通过
执行用时: 32 ms
内存消耗: 19 MB
提交时间:29 分钟前
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector& nums, int i, int j) {
if (i == j)
return nums[i];
int mid = i + ((j - i) >> 1);
int l = majorityElement(nums, i, mid);
int r = majorityElement(nums, mid + 1, j);
int a = 0, b = 0;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
if (l == nums[k])
a++;
if (r == nums[k])
b++;
}
if (a > b) {
if (a > ((j - i + 1) >> 1))
return l;
else
return -1;
}
if (b > ((j - i + 1) >> 1))
return r;
return -1;
}
int majorityElement(vector& nums) {
return majorityElement(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};
*/ 188. 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了95.91%的用户
内存消耗:10.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了74.52%的用户
通过测试用例:211 / 211 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(int k, vector& prices) {
if (prices.empty())
return 0;
int n = prices.size();
vector dp(2 * k + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * k + 1; i++)
if (i & 1)
dp[i] = prices[0];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 2 * k + 1; j++) {
if (j & 1) {
dp[j] = min(dp[j], prices[i] - dp[j - 1]);
}
else {
dp[j] = max(dp[j], prices[i] - dp[j - 1]);
ans = max(ans, dp[j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 198. 打家劫舍
/*
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:7.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了81.08%的用户
通过测试用例:68 / 68
*/
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 1)
return nums[0];
if (n == 2)
return max(nums[0], nums[1]);
vector steal(3);
steal[0] = nums[0];
steal[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
steal[2] = max(steal[1], steal[0] + nums[i]);
ans = max(ans, steal[2]);
steal[0] = steal[1];
steal[1] = steal[2];
}
return ans;
}
}; 199. 二叉树的右视图
/*
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:11.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了79.96%的用户
通过测试用例:216 / 216
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return {};
queue que;
vector ans;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
ans.push_back(que.back()->val);
int n = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* p = que.front();
que.pop();
if (p->left != nullptr)
que.push(p->left);
if (p->right != nullptr)
que.push(p->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 200. 岛屿数量
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:28 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.10%的用户
内存消耗:12.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了32.08%的用户
通过测试用例:49 / 49 */
class DisjointSet {
private:
vector p;
public:
DisjointSet(int n) {
p.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
p[i] = i;
}
bool isp(int x) { return p[x] == x ? true : false; }
int find(int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : find(p[x]); }
void tounion(int x, int y) { p[find(x)] = find(y); }
int cntp() {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {
if (p[i] == i)
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
void setp(int i, int x) { p[i] = x; }
};
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
DisjointSet ds(m * n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
if (j > 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == '1')
ds.tounion(i * n + j, i * n + j - 1);
if (i > 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == '1')
ds.tounion(i * n + j, (i - 1) * n + j);
}
else
ds.setp(i * n + j, INT_MIN);
}
}
return ds.cntp();
}
}; 207. 课程表
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了89.13%的用户
内存消耗:12.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了95.91%的用户
通过测试用例:52 / 52 */
class Solution {
public:
bool topological_sort(vector>& g, vector& deg) {
int cnt = 0, n = g.size();
queue que;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (deg[i] == 0)
que.push(i);
while (!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front();
que.pop();
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)g[u].size(); i++) {
int v = g[u][i];
deg[v]--;
if (deg[v] == 0)
que.push(v);
}
}
return cnt == n;
}
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
vector> g(numCourses);
vector deg(numCourses, 0);
for(const auto& val : prerequisites) {
g[val[0]].push_back(val[1]);
deg[val[1]]++;
}
return topological_sort(g, deg);
}
}; 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:52 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了72.71%的用户
内存消耗:47.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了15.36%的用户
通过测试用例:16 / 16 */
class Trie {
public:
vector children;
bool end;
Trie() : children(26), end(false) {}
Trie* search_prefix(string s) {
Trie* p = this;
for (char c : s) {
c -= 'a';
if (p->children[c] == nullptr)
return nullptr;
p = p->children[c];
}
return p;
}
void insert(string word) {
Trie* p = this;
for (char c : word) {
c -= 'a';
if (p->children[c] == nullptr)
p->children[c] = new Trie;
p = p->children[c];
}
p->end = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
return search_prefix(word) != nullptr && search_prefix(word)->end;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
return search_prefix(prefix) != nullptr;
}
}; 209. 长度最小的子数组
#define MIN(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector& nums) {
if ((int)nums.size() < 1)
return 0;
int sum = 0, l = 0, r = 0, len = INT_MAX;
while (r < nums.size()) {
while (r < nums.size() && sum < target)
sum += nums[r++];
while (sum >= target && l < r) {
len = MIN(len, r - l);
sum -= nums[l++];
}
}
return len == INT_MAX ? 0 : len;
}
}; 213. 打家劫舍 II
/*执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:7.6 MB, 在所有C++ 提交中击败了63.52%的用户
通过测试用例:75 / 75 */
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vectordp(n);
dp[0] = nums[0];
if (n == 1)
return dp[0];
if (n == 2)
return max(nums[0], nums[1]);
dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n - 1; i++) {
dp[2] = max(dp[0] + nums[i], dp[1]);
dp[0] = dp[1];
dp[1] = dp[2];
}
ans = dp[1];
dp[0] = nums[1];
dp[1] = max(nums[1], nums[2]);
for (int i = 2; i < n - 1; i++) {
dp[2] = max(dp[0] + nums[i + 1], dp[1]);
dp[0] = dp[1];
dp[1] = dp[2];
}
ans = max(ans, dp[1]);
return ans;
}
}; 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:88 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了60.91%的用户
内存消耗:44.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了73.40%的用户
通过测试用例:39 / 39 */
class Solution {
public:
int quick_selection(vector& nums, int k, int l, int r) {
int pivot = nums[l], i = l, j = r;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] <= pivot)
j--;
while (i < j && nums[i] >= pivot)
i++;
if (i < j)
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
swap(nums[i], nums[l]);
if (i == k - 1)
return pivot;
if (i > k - 1)
return quick_selection(nums, k, l, i - 1);
return quick_selection(nums, k, i + 1, r);
}
int findKthLargest(vector& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
assert(n >= k);
return quick_selection(nums, k, 0, n - 1);
}
}; 257. 二叉树的所有路径
// 迭代:前序遍历,用两个栈分别保存结点和其对应路径
class Solution {
public:
vector binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector ans;
TreeNode* cur = root;
vector res;
vector path;
path.push_back(to_string(cur->val));
res.push_back(cur);
string str;
while (!res.empty()) {
cur = res.back();
res.pop_back();
str = path.back();
path.pop_back();
if (cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr)
ans.push_back(str);
if (cur->left) {
res.push_back(cur->left);
path.push_back(str + "->" + to_string(cur->left->val));
}
if (cur->right) {
res.push_back(cur->right);
path.push_back(str + "->" + to_string(cur->right->val));
}
}
return ans;
}
}; // 递归:回溯
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode* root, string str, vector& ans) {
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
if (str.length() < 3) {
ans.push_back(to_string(root->val));
return;
}
string s = str.substr(2, str.length() - 2);
ans.push_back(s + "->" + to_string(root->val));
return;
}
if (root->left)
dfs(root->left, str + "->" + to_string(root->val), ans);
if (root->right)
dfs(root->right, str + "->" + to_string(root->val), ans);
}
vector binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector ans;
dfs(root, "", ans);
return ans;
}
}; 279. 完全平方数
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:236 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了14.57%的用户
内存消耗:9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了19.88%的用户
通过测试用例:588 / 588 */
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector dp(n + 1, INT_MAX);
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; j++) {
if (dp[i - j * j] < INT_MAX)
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j] + 1);
}
}
return dp[n] == INT_MAX ? 0 : dp[n];
}
}; 283. 移动零
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector& nums) {
int i = -1, j = 0;
while (j < nums.size()) {
while (j < nums.size() && nums[j] == 0)
j++;
while (j < nums.size() && nums[j] != 0)
nums[++i] = nums[j++];
}
for (int k = i + 1; k < nums.size(); k++)
nums[k] = 0;
}
}; 287. 寻找重复数
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:104 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中了43.58%的用户
内存消耗:59.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了30.32%的用户
通过测试用例:58 / 58 */
class Solution {
public:
void findDuplicate(vector& nums, int l, int r, int& ans) {
if (l > r)
return;
int m = l + ((r - l) >> 1), cnt = 0;
for (auto& val : nums)
cnt += (int)(val <= m);
if (cnt <= m)
findDuplicate(nums, m + 1, r, ans);
else if (cnt > m) {
ans = m;
findDuplicate(nums, l, m - 1, ans);
}
}
int findDuplicate(vector& nums) {
int ans = -1;
findDuplicate(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1, ans);
return ans;
}
};
class Solution1 {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector& nums) {
int p = nums[0], q = nums[nums[0]];
while (p != q) {
p = nums[p];
q = nums[nums[q]];
}
p = 0;
while (p != q) {
p = nums[p];
q = nums[q];
}
return p;
}
}; 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了52.09%的用户
内存消耗:29.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.23%的用户
通过测试用例:52 / 52 */
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string s = "";
if (root != nullptr) {
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t != nullptr)
s += to_string(t->val) + ",";
else
s += "#,";
if (t != nullptr) {
q.push(t->left);
q.push(t->right);
}
}
}
return s;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if (data.length() < 2)
return nullptr;
stringstream ss;
ss << data;
string str;
vector nums;
while (getline(ss, str, ',')) {
if (str.length() > 0) {
if (str[0] == '#')
nums.push_back(INT_MAX);
else
nums.push_back(stoi(str));
}
}
int n = nums.size();
assert(n > 0);
queue q;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[0]);
q.push(root);
int i = 1;
while (!q.empty() && i < n) {
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t == nullptr)
continue;
if (i < n && nums[i] != INT_MAX)
t->left = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
q.push(t->left);
i++;
if (i < n && nums[i] != INT_MAX)
t->right = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
q.push(t->right);
i++;
}
return root;
}
}; 300. 最长递增子序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:288 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了24.29%的用户
内存消耗:10.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了78.28%的用户
通过测试用例:54 / 54 */
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size(), ans = 1;
vector dp(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 301. 删除无效的括号
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.92%的用户
内存消耗:7.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了83.29%的用户
通过测试用例:127 / 127 */
class Solution {
public:
bool is_valid(string& s) {
int cnt = 0;
for (auto& c : s) {
if (c == '(')
cnt++;
if (c == ')') {
cnt--;
if (cnt < 0)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void dfs(string s, int idx, int lr, int rr, vector& ans) {
if (lr == 0 && rr == 0 && is_valid(s)) {
ans.push_back(s);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (!(i > idx && s[i] == s[i - 1]) && !(lr + rr > s.length() - i)) {
if (lr > 0 && s[i] == '(')
dfs(s.substr(0, i) + s.substr(i + 1), i, lr - 1, rr, ans);
if (rr > 0 && s[i] == ')')
dfs(s.substr(0, i) + s.substr(i + 1), i, lr, rr - 1, ans);
}
}
}
vector removeInvalidParentheses(string s) {
vector ans;
int n = s.length(), lr = 0, rr = 0;
for (auto& c : s) {
if (c == '(')
lr++;
if (c == ')') {
if (lr == 0)
rr++;
else
lr--;
}
}
dfs(s, 0, lr, rr, ans);
return ans;
}
}; 309. 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:11 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了71.49%的用户
通过测试用例:210 / 210 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector dp(3, 0);
dp[1] = prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int dp0 = max(dp[0], dp[2]);
int dp1 = min(dp[1], prices[i] - dp[0]);
dp[2] = prices[i] - dp[1];
dp[0] = dp0;
dp[1] = dp1;
}
return max(dp[0], dp[2]);
}
}; 312. 戳气球
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注执行用时:392 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了
69.29%的用户内存消耗:10.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了39.74%的用户通过测试用例:73 / 73 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxCoins(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector> dp(n + 2, vector(n + 2, 0));
vector val(n + 2, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
val[i] = nums[i - 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 2; j < n + 2; j++) {
for (int k = i + 1; k < j; k++)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + val[i] * val[k] * val[j] + dp[k][j]);
}
}
return dp[0][n + 1];
}
}; 322. 零钱兑换
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:120 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了11.81%的用户
内存消耗:14.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了34.28%的用户
通过测试用例:189 / 189 */
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector& coins, int amount) {
int n = coins.size();
vector dp(amount + 1, INT_MAX);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i >= coins[j] && dp[i - coins[j]] != INT_MAX)
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] == INT_MAX ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}; 332. 重新安排行程
给你一份航线列表 tickets ,其中 tickets[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点。请你对该行程进行重新规划排序。所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。如果存在多种有效的行程,请你按字典排序返回最小的行程组合。例如,行程 ["JFK", "LGA"] 与 ["JFK", "LGB"] 相比就更小,排序更靠前。假定所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程。且所有的机票 必须都用一次 且 只能用一次。
输入:tickets = [["MUC","LHR"],["JFK","MUC"],["SFO","SJC"],["LHR","SFO"]]
输出:["JFK","MUC","LHR","SFO","SJC"]
输入:tickets = [["JFK","SFO"],["JFK","ATL"],["SFO","ATL"],["ATL","JFK"],["ATL","SFO"]]
输出:["JFK","ATL","JFK","SFO","ATL","SFO"]
解释:另一种有效的行程是 ["JFK","SFO","ATL","JFK","ATL","SFO"] ,但是它字典排序更大更靠后。
/* 回溯 */
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(vector& x, vector& y) {
return x[1] > y[1];
}
void dfs(vector>& tickets, vector& ans, int backup_size) {
/* 用到所有机票,即找到一条合理的行程 */
if (tickets.size() == 0)
return;
/* 否则,找所有指定起点的机票 */
vector> dep;
for (auto i : tickets) {
if (i[0] == ans.back()) {
dep.push_back(i);
}
}
/* 如果找不到任何指定起点的机票,撤销上次的安排 */
if (dep.empty()) {
string desstr = ans.back();
ans.pop_back();
string depstr = ans.back();
tickets.push_back({ depstr, desstr });
return;
}
/* 按字典序给所有指定起点的机票排序 */
sort(dep.begin(), dep.end(), &cmp);
/* 保证必须用到所有机票,否则继续枚举其余指定起点的机票 */
while (!dep.empty() && ans.size() != backup_size + 1) {
/* 从字典序最小的指定起点机票开始枚举。不需要for循环,用if即可 */
for (auto i = dep.rbegin(); i < dep.rend(); i++) {
ans.push_back(i[0][1]);
for (auto it = tickets.begin(); it < tickets.end(); it++) {
if (i[0][0] == it[0][0] && i[0][1] == it[0][1]) {
tickets.erase(it, it + 1);
break;
}
}
dfs(tickets, ans, backup_size);
break;
}
if (!dep.empty())
dep.pop_back();
}
/* 如果已枚举完当前指定起点的机票集仍无法找到一条行程,撤销上次的安排 */
if (dep.empty() && ans.size() != backup_size + 1) {
string bstr = ans.back();
ans.pop_back();
string tstr = ans.back();
tickets.push_back({ tstr, bstr });
}
}
vector findItinerary(vector>& tickets) {
vector ans;
vector> jfk;
vector> backup = tickets;
int backup_size = backup.size();
/* 把所有以“JFK”为起点的机票按字典序排序。为便于操作我按倒序排序,即最小的排在最后 */
for (auto i : tickets)
if (i[0] == "JFK")
jfk.push_back(i);
sort(jfk.begin(), jfk.end(), &cmp);
/* 保证必须用到所有机票,否则继续枚举任何以“JFK”为起点的机票 */
while (ans.size() != backup.size() + 1) {
tickets = backup;
ans.clear();
/* 从以“JFK”为起点的字典序最小的机票开始枚举。不需要for循环,用if即可 */
for (auto i = jfk.rbegin(); i < jfk.rend(); i++) {
if (ans.empty()) {
ans.push_back("JFK");
ans.push_back(i[0][1]); // 暂时加入结果集
for (auto it = tickets.begin(); it < tickets.end(); it++) {
if (i[0][0] == it[0][0] && i[0][1] == it[0][1]) {
tickets.erase(it, it + 1); // 在未使用机票集里删除该票
break;
}
}
dfs(tickets, ans, backup_size); // 以该票终点为起点开始递归
break;
}
}
/* 从以“JFK”为起点的机票集里删除该以“JFK”为起点的机票 */
if (!jfk.empty())
jfk.pop_back();
}
return ans;
}
}; 337. 打家劫舍 III
/* 记忆化递归
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了60.03%的用户
内存消耗:24.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了75.00%的用户
通过测试用例:124 / 12 */
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map um;
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
if (um[root] > 0)
return um[root];
int ans = 0, res = root->val;
if (root->left)
res += rob(root->left->left) + rob(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
res += rob(root->right->left) + rob(root->right->right);
ans += rob(root->left) + rob(root->right);
ans = max(ans, res);
um[root] = ans;
return ans;
}
};
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了60.03%的用户
内存消耗:31.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.39%的用户
通过测试用例:124 / 124 */
class Solution1 {
public:
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
vector ans = rob(root, true);
return max(ans[0], ans[1]);
}
vector rob(TreeNode* root, bool k) {
if (root == nullptr)
return { 0, 0 };
vector l = rob(root->left, true);
vector r = rob(root->right, true);
int a = max(l[0], l[1]) + max(r[0], r[1]);
int b = root->val + l[0] + r[0];
return { a, b };
}
}; 343. 整数拆分
/* 难度中等929收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了11.23%的用户
通过测试用例:50 / 50 */
class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
vector dp(n + 1, 0);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
dp[i] = max({dp[i], j * (i - j), j * dp[i - j]});
return dp[n];
}
}; 347. 前 K 个高频元素
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了45.69%的用户
内存消耗:13.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了76.54%的用户
通过测试用例:21 / 21 */
class Solution {
public:
vector topKFrequent(vector& nums, int k) {
auto cmp = [](const pair& x, const pair& y)->bool { return x.second > y.second; };
unordered_map um;
priority_queue, vector>, decltype(cmp)> q(cmp);
vector ans(k);
for (auto& a : nums)
um[a]++;
for (auto& p : um) {
q.push(p);
if (q.size() > k)
q.pop();
}
for (auto& a : ans) {
a = q.top().first;
q.pop();
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
}; 376. 摆动序列
class Solution {
public:
int wiggleMaxLength(vector& nums) {
int ans = 1;
if (nums.size() == 1)
return ans;
if (nums.size() == 2)
return nums[0] != nums[1] ? 2 : 1;
int cur = 0, pre = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
cur = nums[i] - nums[i + 1];
if (cur > 0 && pre <= 0 || cur < 0 && pre >= 0) {
ans++;
pre = cur;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 377. 组合总和 Ⅳ
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.47%的用户
内存消耗:7.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.01%的用户
通过测试用例:15 / 15 */
class Solution {
public:
int combinationSum4(vector& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(target + 1, 0));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= target; j++) {
if (j >= nums[i - 1] && dp[i][j - nums[i - 1]] < INT_MAX - dp[i][j]) {
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
if (j >= nums[k] && dp[i][j - nums[k]] < INT_MAX - dp[i][j])
dp[i][j] += dp[i][j - nums[k]];
}
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
return dp[n][target];
}
}; 392. 判断子序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了97.63%的用户
通过测试用例:18 / 18 */
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int i = 0, j = 0, m = s.length(), n = t.length();
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (s[i] == t[j])
i++;
j++;
}
return i == m;
}
};
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了42.15%的用户
内存消耗:7.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了20.90%的用户
通过测试用例:18 / 18 */
class Solution1 {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s[i - 1] == t[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[m][n] == m;
}
}; 406. 根据身高重建队列
class Solution {
public:
vector> reconstructQueue(vector>& people) {
vector> ans(people.size(), vector(2, -1));
sort(people.begin(), people.end(), [](vector& x, vector& y)->bool {
if (x[0] == y[0])
return x[1] < y[1];
return x[0] > y[0];
});
for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++) {
int j = people[i][1];
/* 插入操作 */
if (ans[j][0] == -1) {
ans[j][0] = people[i][0];
ans[j][1] = people[i][1];
}
else {
int a = ans[j][0], b = ans[j][1];
ans[j][0] = people[i][0];
ans[j][1] = people[i][1];
for (int k = j + 1; k < people.size(); k++) {
int c = ans[k][0], d = ans[k][1];
ans[k][0] = a;
ans[k][1] = b;
a = c;
b = d;
if (a == -1)
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; /* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:452 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.13%的用户
内存消耗:83.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.11%的用户
通过测试用例:139 / 139 */
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector& nums) {
int sum = 0, n = nums.size();
for (auto& num : nums)
sum += num;
if (sum & 1)
return false;
int target = sum / 2;
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(target + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= target; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= nums[i - 1])
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - nums[i - 1]] + nums[i - 1]);
}
}
return dp[n][target] == target;
}
}; 417.太平洋大西洋水流问题
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(vector>& heights, int i, int j, int m, int n, int f) {
if (f == 0) {
if (j <= 0 || i <= 0)
return 1;
}
else {
if (j >= n - 1 || i >= m - 1)
return 1;
}
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0;
if (i >= 1 && heights[i][j] >= heights[i - 1][j]) {
int t = heights[i][j];
heights[i][j] = INT_MAX;
a = dfs(heights, i - 1, j, m, n, f);
heights[i][j] = t;
if (a > 0)
return 1;
}
if (j >= 1 && heights[i][j] >= heights[i][j - 1]) {
int t = heights[i][j];
heights[i][j] = INT_MAX;
b = dfs(heights, i, j - 1, m, n, f);
heights[i][j] = t;
if (b > 0)
return 1;
}
if (i <= m - 2 && heights[i][j] >= heights[i + 1][j]) {
int t = heights[i][j];
heights[i][j] = INT_MAX;
c = dfs(heights, i + 1, j, m, n, f);
heights[i][j] = t;
if (c > 0)
return 1;
}
if (j <= n - 2 && heights[i][j] >= heights[i][j + 1]) {
int t = heights[i][j];
heights[i][j] = INT_MAX;
d = dfs(heights, i, j + 1, m, n, f);
heights[i][j] = t;
if (d > 0)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
vector> pacificAtlantic(vector>& heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
vector> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int pac = dfs(heights, i, j, m, n, 0);
int atl = dfs(heights, i, j, m, n, 1);
if (pac > 0 && atl > 0) {
vector res = { i, j };
ans.push_back(res);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 427. 建立四叉树
class Solution {
public:
Node* dfs(vector>& grid, int x, int y, int m, int n) {
for (int i = x; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = y; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] != grid[x][y]) {
return new Node(true, false,
dfs(grid, x, y, (x + m) / 2, (y + n) / 2),
dfs(grid, x, (y + n) / 2, (x + m) / 2, n),
dfs(grid, (x + m) / 2, y, m, (y + n) / 2),
dfs(grid, (x + m) / 2, (y + n) / 2, m, n));
}
}
}
return new Node(grid[x][y], true);
}
Node *construct(vector> &grid) {
return dfs(grid, 0, 0, grid.size(), grid.size());
}
}; 435. 无重叠区间
![]()
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector>& intervals) {
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector& x, vector& y)->bool {
if (x[0] == y[0])
return x[1] < y[1];
return x[0] < y[0];
});
int cnt = 1, l = intervals.back()[0];
for (auto it = intervals.rbegin(); it != intervals.rend(); it++) {
if (it[0][1] <= l) {
cnt++;
l = it[0][0];
}
}
return intervals.size() - cnt;
}
}; 450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
TreeNode* tar = root;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
while (tar) {
if (tar->val < key) {
pre = tar;
tar = tar->right;
}
else if (tar->val > key) {
pre = tar;
tar = tar->left;
}
else
break;
}
if (tar == nullptr)
return root;
if (tar == root) {
TreeNode* p = root->left;
if (p == nullptr)
return root->right;
while (p->right)
p = p->right;
p->right = root->right;
return root->left;
}
TreeNode* q = tar->left;
if (q == nullptr) {
if (tar->val > pre->val)
pre->right = tar->right;
else if (tar->val < pre->val)
pre->left = tar->right;
return root;
}
while (q->right)
q = q->right;
q->right = tar->right;
if (tar->val > pre->val)
pre->right = tar->left;
else if (tar->val < pre->val)
pre->left = tar->left;
return root;
}
};452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
class Solution {
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector>& points) {
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](vector& x, vector& y)->bool {
return x[1] < y[1];
});
int ans = 1, r = points[0][1];
for (vector& i : points) {
if (i[0] > r) {
r = i[1];
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; class Solution {
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector>& points) {
sort(points.begin(), points.end()); // 按xstart排序
int ans = 1, l = points.back()[0];
for (auto i = points.rbegin(); i != points.rend(); i++) {
if (i[0][1] < l) {
ans++;
l = i[0][0];
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 455. 分发饼干
class Solution {
public:
int findContentChildren(vector& g, vector& s) {
int idx = s.size() - 1, ans = 0;
if (idx < 0)
return ans;
sort(g.begin(), g.end());
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
for (int i = g.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (g[i] <= s[idx]) {
ans++;
idx--;
if (idx < 0)
return ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 461. 汉明距离
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:5.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了67.69%的用户
通过测试用例:149 / 149 */
class Solution {
public:
int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int num = x ^ y, ans = 0;
while (num != 0) {
ans += num & 1;
num >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};474. 一和零
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:512 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了8.42%的用户
内存消耗:100.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了10.20%的用户
通过测试用例:72 / 72 */
class Solution {
public:
pair cntzeroone(string str) {
int tot = 0, ones = 0;
for (char& c : str) {
tot++;
if (c == '1')
ones++;
}
return make_pair(tot, ones);
}
int findMaxForm(vector& strs, int m, int n) {
int a = strs.size();
vector>> dp(a + 1, vector>(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0)));
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
pair cnts = cntzeroone(strs[i - 1]);
int ones = cnts.second, zeros = cnts.first - cnts.second;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
dp[i][j][k] = dp[i - 1][j][k];
if (j >= zeros && k >= ones)
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j - zeros][k - ones] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[a][m][n];
}
}; 494. 目标和
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了45.28%的用户
内存消耗:12 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败15.06%的用户
通过测试用例:139 / 139 */
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetSumWays(vector& nums, int target) {
int sum = 0, n = nums.size();
for (int& num : nums)
sum += num;
int tar = sum + target;
if (tar & 1 || abs(sum) < abs(target))
return 0;
tar /= 2;
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(tar + 1, 0));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= tar; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= nums[i - 1])
dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - nums[i - 1]];
}
}
return dp[n][tar];
}
}; 516. 最长回文子序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:120 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了22.68%的用户
内存消耗:71.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了34.13%的用户
通过测试用例:86 / 86 */
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindromeSubseq(string s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0;
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][i] = 1;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s[i - 1] == s[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
else
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j]);
}
}
return dp[1].back();
}
}; 518. 零钱兑换 II
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了9.02%的用户
内存消耗:18 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了12.15%的用户
通过测试用例:28 / 28 */
class Solution {
public:
int change(int amount, vector& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(amount + 1));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= amount; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= coins[i - 1])
dp[i][j] += dp[i][j - coins[i - 1]]; // 此处为完全背包与01背包在排列组合问题上的区别
}
}
return dp[n][amount];
}
}; 538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
stack stk;
TreeNode* cur = root;
int sum = 0;
while (cur || !stk.empty()) {
while (cur) {
stk.push(cur);
cur = cur->right;
}
cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
cur->val += sum;
sum = cur->val;
cur = cur->left;
}
return root;
}
}; 572. 另一棵树的子树
// 递归:前序遍历root,判断每个结点为根时是否与subRoot相同
class Solution {
public:
bool isSame(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) {
if (a == nullptr && b == nullptr)
return true;
if (a == nullptr || b == nullptr)
return false;
return (a->val == b->val) && isSame(a->left, b->left) && isSame(a->right, b->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
vector res;
res.push_back(root);
while (!res.empty()) {
TreeNode* cur = res.back();
res.pop_back();
if (cur->val == subRoot->val && isSame(cur->left, subRoot->left) && isSame(cur->right, subRoot->right)) {
return true;
}
if (cur->left)
res.push_back(cur->left);
if (cur->right)
res.push_back(cur->right);
}
return false;
}
}; 583. 两个字符串的删除操作
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.65%的用户
内存消耗:11.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了45.29%的用户
通过测试用例:1306 / 1306 */
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length();
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
dp[i][0] = i;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[0][i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
}
else {
dp[i][j] = min({dp[i][j - 1] + 1, dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 2});
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}; 647. 回文子串
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了56.19%的用户
内存消耗:19.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.88%的用户
通过测试用例:130 / 130 */
class Solution {
public:
int countSubstrings(string s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0;
vector> dp(n + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (s[i - 1] == s[j - 1]) {
if (j - i <= 1) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
ans++;
}
else if (dp[i + 1][j - 1] > 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
ans++;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 654. 最大二叉树
// 递归:前序遍历
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector& nums, int i, int j) {
if (i > j)
return nullptr;
int m = INT_MIN, k = -1;
for (int a = i; a <= j; a++) {
if (nums[a] > m) {
m = nums[a];
k = a;
}
}
return new TreeNode(m, constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums, i, k - 1), constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums, k + 1, j));
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector& nums) {
return constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
}; 669. 修剪二叉搜索树
![]()
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
while (root != nullptr && (root->val < low || root->val > high)) {
if (root->val < low)
root = root->right;
else if (root->val > high)
root = root->left;
}
TreeNode* node = root;
while (node != nullptr) {
while (node->left && node->left->val < low)
node->left = node->left->right;
node = node->left;
}
node = root;
while (node != nullptr) {
while (node->right && node->right->val > high)
node->right = node->right->left;
node = node->right;
}
return root;
}
};674. 最长连续递增序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了77.77%的用户
内存消耗:10.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了89.11%的用户
通过测试用例:35 / 35 */
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector& nums) {
int ans = 1, m = 1, n = nums.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int t = m;
m = 1;
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
m += t;
ans = max(ans, m);
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 707. 设计链表
struct SinglyListNode {
int val;
SinglyListNode* next;
SinglyListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
SinglyListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
SinglyListNode(int x, SinglyListNode* next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class MyLinkedList {
private:
SinglyListNode* head;
SinglyListNode* tail;
int _size;
public:
MyLinkedList() : head(nullptr), tail(nullptr), _size(0) {
}
MyLinkedList(int x) : head(new SinglyListNode(0)), tail(head), _size(1) {
}
MyLinkedList(int x, SinglyListNode* next) : head(new SinglyListNode(0, next)), tail(head), _size(1) {
}
int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= _size)
return -1;
SinglyListNode* p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++, p = p->next) {}
return p->val;
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
SinglyListNode* p = head;
head = new SinglyListNode(val, p);
if (p == nullptr)
tail = head;
++_size;
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
SinglyListNode* p = tail;
tail = new SinglyListNode(val);
if (p == nullptr) {
head == nullptr ? head = tail : head->next = tail;
++_size;
return;
}
p->next = tail;
++_size;
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index < 0 || index > _size)
return;
SinglyListNode* p = head;
if (index < 1) {
addAtHead(val);
return;
}
if (index == _size) {
addAtTail(val);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++, p = p->next) {}
SinglyListNode* q = p->next;
p->next = new SinglyListNode(val, q);
++_size;
}
int deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= _size)
return -1;
SinglyListNode* p = head;
if (index < 1) {
head = head->next;
--_size;
if (_size < 1)
tail = head;
return _size;
}
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++, p = p->next) {}
SinglyListNode* q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
if (q->next == nullptr) {
tail = p;
--_size;
return _size;
}
--_size;
return _size;
}
};714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
#define MIN(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices, int fee) {
/* @param m 记录一个今天买股票的最小成本,这样才能使利润最大 */
int ans = 0, m = prices[0] + fee;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) {
m = MIN(m, prices[i] + fee); // 假如m的较小值没变说明不买今天的股票而保持昨天的状态成本更低
if (prices[i] - m > 0) { // 如果有利可图
ans += prices[i] - m; // 假设先卖出去手里的股票
m = prices[i]; // 再买今天的股票,假如明天m的较小值选这个说明今天其实没买卖,因此不用手续费
}
}
return ans;
}
}; /* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:76 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了89.91%的用户
内存消耗:53.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了69.67%的用户
通过测试用例:44 / 44 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices, int fee) {
vector dp(2, 0);
int n = prices.size();
dp[1] = prices[0] + fee;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[0] = max(dp[0], prices[i] - dp[1]);
dp[1] = min(dp[1], prices[i] + fee - dp[0]);
}
return dp[0];
}
}; 718. 最长重复子数组
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:276 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了70.25%的用户
内存消耗:106.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了60.43%的用户
通过测试用例:57 / 57 */
class Solution {
public:
int findLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
int ans = 0, n0 = nums1.size(), n1 = nums2.size();
vector> dp(n0 + 1, vector(n1 + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n0; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n1; j++) {
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution1 {
public:
int findLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
int ans = 0, n0 = nums1.size(), n1 = nums2.size();
vector dp(n1 + 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n0; i++) {
for (int j = n1; j > 0; j--) {
dp[j] = 0;
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
ans = max(ans, dp[j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 738. 单调递增的数字
/* 两次遍历:第一次从前往后找第一个不单调递增的位置,第二次从这个位置倒着找减1还不小于前一位的位置 */
class Solution {
public:
int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
string ans = to_string(n);
int i = 0;
char ch = ans[0];
for (char c : ans) {
if (c >= ch) {
i++;
ch = c;
}
else
break;
}
if (i == ans.length())
return stoi(ans);
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0) {
if (j > 0 && ans[j] <= ans[j - 1])
j--;
else
break;
}
ans[j]--;
for (int k = j + 1; k < ans.length(); k++)
ans[k] = '9';
return stoi(ans);
}
}; ![]()
/* 直接倒着遍历 */
class Solution {
public:
int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
string ans = to_string(n);
for (int i = ans.length() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (ans[i] < ans[i - 1]) {
for (int k = i; k < ans.length() && ans[k] != '9'; k++)
ans[k] = '9';
ans[i - 1]--;
}
}
return stoi(ans);
}
};739. 每日温度
/*
执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:116 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了95.54%的用户
内存消耗:84.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了78.46%的用户
通过测试用例:47 / 47
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector dailyTemperatures(vector& temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.size();
vector stk, ans(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && temperatures[stk.back()] < temperatures[i]) {
ans[stk.back()] = i - stk.back();
stk.pop_back();
}
stk.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
}; 746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.00%的用户
内存消耗:13.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了52.34%的用户
通过测试用例:283 / 283 */
class Solution {
public:
int minCostClimbingStairs(vector& cost) {
int n = cost.size();
vector dp(n + 1, 0);
dp[1] = cost[0];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = cost[i - 1] + min(dp[i - 2], dp[i - 1]);
}
return min(dp[n - 1], dp[n]);
}
}; 763. 划分字母区间
#define MAX(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
vector partitionLabels(string s) {
int idx[27];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
idx[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
vector ans;
int j = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
k = MAX(k, idx[s[i] - 'a']);
if (i == k) {
string str = s.substr(j, i - j + 1);
ans.push_back(str);
j = i + 1;
}
}
vector res;
for (string x : ans)
res.push_back(x.length());
return res;
}
}; 860. 柠檬水找零
class Solution {
public:
bool lemonadeChange(vector& bills) {
int five = 0, ten = 0, twenty = 0;
for (int cash : bills) {
switch(cash) {
case 5:
five++;
break;
case 10:
if (five > 0) {
five--;
ten++;
}
else
return false;
break;
case 20:
if (five > 0 && ten > 0) {
five--;
ten--;
twenty++;
}
else if (five >= 3) {
five -= 3;
twenty++;
}
else
return false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return true;
}
}; 904. 水果成篮
#define MAX(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
int totalFruit(vector& fruits) {
int ans = 0;
int l = 0, r = 0;
unordered_map um;
while (r < fruits.size()) {
++um[fruits[r++]];
while (l < r && um.size() > 2) {
--um[fruits[l]];
if (um[fruits[l]] == 0)
um.erase(fruits[l]);
l++;
}
ans = MAX(ans, r - l);
}
return ans;
}
}; 968. 监控二叉树
class Solution {
public:
int post(TreeNode* root, int& cnt) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 2;
int left = post(root->left, cnt);
int right = post(root->right, cnt);
if (left == 2 && right == 2)
return 0;
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
cnt++;
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
int state = post(root, ans);
if (state == 0)
ans++;
return ans;
}
};#define MIN(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
class Solution {
public:
vector post(TreeNode* root) {
/* 0表示监控节点,1表示节点有覆盖,2表示节点无覆盖 */
vector dp(3);
if (root == nullptr)
return { INT_MAX >> 2, 0, 0 };
vector left = post(root->left);
vector right = post(root->right);
/* 该节点是监控 */
dp[0] = 1 + MIN(MIN(left[0], left[1]), left[2]) + MIN(MIN(right[0], right[1]), right[2]);
/* 该节点有覆盖,要求左右节点一个是监控另一个已覆盖或者是监控 */
dp[1] = MIN(left[0]+MIN(right[0],right[1]), right[0]+MIN(left[0],left[1]));
/* 该节点无覆盖,要求左右节点都已覆盖到 */
dp[2] = left[1] + right[1];
return dp;
}
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
vector dp = post(root);
return MIN(dp[0], dp[1]);
}
}; 1005. K 次取反后最大化的数组和
#define ABS(X) (((X)<0)?-(X):(X))
class Solution {
public:
/* 先让绝对值大的负数变为正数,如果K用不完,再让绝对值最小的数即nums右端的数用完K */
int largestSumAfterKNegations(vector& nums, int k) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int& x, int& y)->bool { return ABS(x) > ABS(y); });
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() && k > 0; i++) {
if (nums[i] < 0) {
nums[i] = -nums[i];
k--;
}
}
while (k > 0) {
nums.back() *= -1;
k--;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i : nums)
ans += i;
return ans;
}
}; 1035. 不相交的线
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:24 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了7.10%的用户
内存消耗:12.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了17.51%的用户
通过测试用例:74 / 74 */
class Solution {
public:
int maxUncrossedLines(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size(), ans = 0;
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1] ? dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1 : max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 1143. 最长公共子序列
/* 执行结果:通过显示详情添加备注
执行用时:24 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了49.60%的用户
内存消耗:12.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了77.54%的用户
通过测试用例:45 / 45 */
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int m = text1.length(), n = text2.length(), ans = 0;
vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1] ? dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1 : max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}; HJ50 四则运算
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Stage Zero: Input String
vector rpe;
stack stk;
stack ansstk;
string rawstr, tmpstr, eq;
stringstream ss;
getline(cin, rawstr);
ss << rawstr;
while (getline(ss, tmpstr, ' '))
eq += tmpstr;
int len = eq.length();
// Stage One: Construct Reverse Polish Expression
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = eq[i];
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
string a;
int j = i;
while (j < len && eq[j] >= '0' && eq[j] <= '9')
a.push_back(eq[j++]);
rpe.push_back(a);
i = j - 1;
}
else if (c == '{' || c == '[' || c == '(' || c == '*' || c == '/') {
stk.push(c);
}
else if (c == '}') {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() != '{') {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
stk.pop();
}
else if (c == ']') {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() != '[') {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
stk.pop();
}
else if (c == ')') {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() != '(') {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
stk.pop();
}
else if (c == '+') {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() != '(' && stk.top() != '[' && stk.top() != '{') {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
stk.push(c);
}
else if (c == '-') {
if (i == 0 || eq[i - 1] == '(' || eq[i - 1] == '[' || eq[i - 1] == '{')
rpe.push_back("0");
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() != '(' && stk.top() != '[' && stk.top() != '{') {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
stk.push(c);
}
}
while (!stk.empty()) {
string b;
b.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
rpe.push_back(b);
}
// Stage Two: Generate Results via RPE
len = rpe.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int isnum = 1;
string numstr = rpe[i];
if (numstr[0] < '0' || numstr[0] > '9')
isnum = 0;
if (isnum > 0)
ansstk.push(stoi(numstr));
else {
int x = ansstk.top();
ansstk.pop();
int y = ansstk.top();
ansstk.pop();
switch (numstr[0]) {
case '+':
ansstk.push(x + y);
break;
case '-':
ansstk.push(y - x);
break;
case '*':
ansstk.push(x * y);
break;
case '/':
ansstk.push(y / x);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
cout << ansstk.top() << endl;
return 0;
} 草稿本
最长公共子串
问题描述
- 即Longest Common Substring,子串需要在原字符串中是连续的
状态转移方程
- 设
![C[i, j] = |LCS(x[1...i],y[1...j])|,](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ea8ef03cd781481b98e48f86b4ff5628.gif) ,即C[i, j]表示序列X[1...i]和Y[1...j]的最长公共子串的长度,则可得到式(1)的状态转移方程,
,即C[i, j]表示序列X[1...i]和Y[1...j]的最长公共子串的长度,则可得到式(1)的状态转移方程,
int LongestCommomSubstring(string x, string y, vector >& dp) {
int maxlen = 0;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i <= x.length(); i++) {
for (unsigned int j = 1; j <= y.length(); j++) {
if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
maxlen = MAX(maxlen, dp[i][j]);
}
else
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return maxlen;
} 最长公共子序列
问题描述
- 与最长公共子串相比,最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence)只需保持相对位置而不需要是连续的
状态转移方程
- 设
![C[i, j] = |LCS(x[1...i],y[1...j])|,](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ea8ef03cd781481b98e48f86b4ff5628.gif) ,即C[i, j]表示序列X[1...i]和Y[1...j]的最长公共子序列的长度,则可得到式(2)的状态转移方程,
,即C[i, j]表示序列X[1...i]和Y[1...j]的最长公共子序列的长度,则可得到式(2)的状态转移方程,
int LongestCommomSubsequence(string x, string y, vector >& dp) {
for (unsigned int i = 1; i <= x.length(); i++) {
for (unsigned int j = 1; j <= y.length(); j++) {
if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = MAX(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return dp[x.length()][y.length()];
} 最大子段和
问题描述
- 给出一序列a,选出其中连续且非空的一段使得这段和最大,求这个和。
状态转移方程
- 设c[i]表示a[0...i]的最大子段和,
![C[i] = max(0,\ C[i - 1]+a[i])](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2f44a70d433242daaffa229713e14d3f.gif) (3)
(3)
int MaxSubSeqSum(int a[], int size) {
int tmp = 0, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (tmp > 0)
tmp += a[i];
else
tmp = a[i];
if (tmp > sum)
sum = tmp;
}
return sum;
}输出所有最大子串
问题描述
- 因为最大子串往往有多个,现在要输出所有的最大子串
- 比如设得出的最大子串长度为len_of_lcs,之前为了计算len_of_lcs判断条件是x[i] == y[j],现在需要反过来,判断一下dp[i][j] == len_of_lcs(x[i - 1]==y[j - 1]), 然后把x[i - 1](或y[j - 1])这个字符填进结果字符串
- 这样得出的最大子串(之一)是逆序的,要字符串反转一下
/*******************************************************************************
*函数体为回溯的过程:若dp表某个格的值等于lcs_str_all*
*说明这里的x[i-1]等于y[j-1],又因为字串是连续的,所以沿着对角线往左上角走都是子串, *
* 从而使用while循环把字符都填入结果字符串; 填完以后,放入结果集 *
******************************************************************************/
void GetAllLCString(int len_of_lcs, string x, string y, vector > dp, set& lcs_str_all) {
string str;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i <= x.length(); i++) {
for (unsigned int j = 1; j <= y.length(); j++) {
if (dp[i][j] == len_of_lcs) {
int dx = i, dy = j;
while (dp[dx][dy] > 0) {
str.push_back(x[dx - 1]);
dx--;
dy--;
}
string tmp(str.rbegin(), str.rend());
if (tmp.length() == len_of_lcs) {
lcs_str_all.insert(tmp);
str.clear();
}
}
}
}
} 输出所有最大子序列
问题描述
- 与输出所有最大子串类似,输出所有最大子序列
void GetAllLCSequence(int i, int j, int len_of_lcs, string x, string y, string str, vector > dp, set& lcs_str_all) {
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]) {
str.push_back(x[i - 1]);
i--;
j--;
}
else {
if (dp[i - 1][j] > dp[i][j - 1])
i--;
else if (dp[i - 1][j] < dp[i][j - 1])
j--;
else {
GetAllLCSequence(i - 1, j, len_of_lcs, x, y, str, dp, lcs_str_all);
GetAllLCSequence(i, j - 1, len_of_lcs, x, y, str, dp, lcs_str_all);
return;
}
}
}
string tmp(str.rbegin(), str.rend());
if (tmp.length() == len_of_lcs)
lcs_str_all.insert(tmp);
} 最大子矩阵(方阵)的大小
AKA面积最大的全1子矩阵
问题描述
在一个M * N的矩阵中,所有的元素只有0和1,从这个矩阵中找出一个面积最大的全1子矩阵,所谓最大是指元素1的个数最多,给出边长。
1、首先对行向量[1, 0, 1, 1, 1]来说,这个向量的分量如果是1,就往同一列的上面看有多少连续的1,然后记录在数组histgram[]里。所以这轮迭代后histgram[] = { 1, 0, 2, 2, 1};
void GenHistgram(char mat[101][101], int histgram[], int i, int size) {
for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) {
if (mat[i][k] == '0')
continue;
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
if (mat[j][k] != mat[i][k])
break;
histgram[k]++;
}
}
}2、求histgram[]的最大值:如果找到一个一般意义下的histgram的最大值m,看一下往右的连续子串长度len是不是大于等于最大值m(为了确保子矩阵的宽要大于等于高),比如histgram[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 2};最大值是3,但是边长不是3;若为真,则m即为一个全1子矩阵的边长(不一定是最终的面积最大的全1子矩阵的边长)。以这种方法查找出histgram[]的最大值m1。
int DeformedMax(int arr[], int size) {
int max = -1, tmpmax = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] > tmpmax)
tmpmax = arr[i];
for (int j = i; j < i + tmpmax; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) {
tmpmax = -1;
break;
}
}
if (tmpmax != -1)
max = tmpmax > max ? tmpmax : max;
}
return max;
}3、同样的方法处理(**)的下一个行向量[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],查找出histgram[]的最大值m2;
最后从mi里查找出最大值M即为面积最大的全1子矩阵的边长。
int main() {
/* 维度 */
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
/* Initialize */
char mat[101][101];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
cin >> mat[i][j];
int max = -1;
/* 从第二行的向量开始 */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
/* 每个向量打一次表 */
/* histgram[]初始化 */
int histgram[500] = { -1 };
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
histgram[j] = 0;
/* 打表 */
GenHistgram(mat, histgram, i, n);
/* 求当前向量下的最大值 */
int tmpmax = DeformedMax(histgram, n);
/* 求全局最大值 */
max = tmpmax > max ? tmpmax : max;
}
cout << max << endl;
}
return 0;
}1559 最大子矩阵
问题描述
- 给你一个m×n的整数矩阵,在上面找一个x×y的子矩阵,使子矩阵中所有元素的和最大。
状态转移方程
![]() (4)
(4)
式(4)的原理类似于图像积分,C[i, j]代表之前矩形里所有元素的和。
/* m、n、x、y同题目意义 */
int MaxSubMatrixSum(int m, int n, int x, int y) {
vector > dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1, 0));
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> dp[i][j];
dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1] - dp[i - 1][j - 1];
if (i >= x && j >= y)
ans = MAX(ans, dp[i][j] - dp[i - x][j] - dp[i][j - y] + dp[i - x][j - y]);
}
}
return ans;
} 最大公约数
- gcd怎么求呢?像下面这样把它辗转相除——啊,还没除呢~像下面这样把它辗转相除
int gcd(int x, int y) {
int r = x % y;
while (r) {
x = y;
y = r;
r = x % y;
}
return y;
}最小公倍数
int lcm(int x, int y) {
int g = gcd(x, y);
return x * y / g;
}判断质数和互质
bool IsPrime(int a) {
int i;
for (i = 2; i * i <= a; i++)
if ((a % i) == 0)
break;
return i * i > a ? true : false;
}bool IsInterprime(int x, int y) {
int g = gcd(x, y);
return g == 1 ? true : false;
}- 获取所有因数
int GetAllFactors(int a, int factors[]) {
int k = 0, i;
for (i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
if (!(a % i))
factors[k++] = i;
}
return k; // 这是数a的因数个数
}闰年判断
bool isLeapYear(int year) {
return year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0);
}M进制转10进制
/* M进制转10进制 */
int RadixM2Dec(char str[], int size, int radix) {
int ans = 0, t;
for (int i = (str[0] == '-' ? 1 : 0); i < size; i++) {
if (str[i] < '9')
t = str[i] - '0';
else if ('A' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'F')
t = str[i] - 'A' + 10;
else
t = str[i] - 'a' + 10;
ans = ans * radix + t; /* (I) */
}
return str[0] == '-' ? -ans : ans;
}10进制转M进制(返回值类型是string)
stack Dec2Radix(int m, int r) {
stack s;
if (m < 0)
m = -m; // 输出的时候别忘额外加上负号
do {
s.push(m % r);
m /= r;
} while (m);
return s;
}
string Trans2String(stack s) {
string str = "";
while (!s.empty()) {
if (s.top() < 10)
str.push_back(s.top() + 48);
else
str.push_back(s.top() + 55);
s.pop();
}
return str;
} 实例
2005
#include
#include
const int dattab[2][12] = { {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31},
{31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31} };
bool IsLeapYear(int y) {
return (y % 400 == 0) || ((y % 4 == 0) && (y % 100 != 0));
}
int main() {
int y, m, d;
while (~scanf("%d/%d/%d", &y, &m, &d)) {
int r = IsLeapYear(y) ? 1 : 0;
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++)
n += dattab[r][i];
n += d;
printf("%d\n", n);
}
return 0;
}
由以上讨论,k位m进制数的任意位之和 ![]()
-
1062 Text Reverse
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[1001];
int case_num;
cin >> case_num;
getchar();
while (case_num--) {
cin.getline(str, 1000);
int len = strlen(str);
int i = 0, j = 0;
char tmp;
/* 注意这里有等于,处理'\0'的情况 */
while (j <= len) {
/* 遇到子串结尾 */
if (str[j] == ' ' || str[j ] == '\0') {
/* 字符串反转 */
int a = i, b = j - 1;
while (a < b) {
tmp = str[a];
str[a] = str[b];
str[b] = tmp;
a++;
b--;
}
/* 子串指针头移至下一节 */
i = j + 1;
}
/* 子串指针尾后移 */
j++;
}
cout << str << endl;
}
return 0;
} -
1005 Number Sequence
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int A, B, n;
while (cin >> A && A != 0) {
cin >> B >> n;
int f[100];
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
f[2] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i < 50; i++)
f[i] = (A * f[i - 1] + B * f[i - 2]) % 7;
cout << f[n % 48] << endl;
}
return 0;
} -
1097 A hard puzzle
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b;
while (cin >> a >> b) {
int a_singles = a % 10;
int b_singles = b % 4;
int ans = 1;
if (b == 0) { /* 情况1:若指数为0,则结果为1 */
cout << 1 << endl;
continue;
}
else if (b_singles == 0) /* 情况2:若指数个位数为0,则令个位数为4 */
b_singles = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < b_singles; i++)/* 情况3:若指数个位数为1~3,平凡的情况 */
ans *= a_singles;
cout << ans % 10 << endl;
}
return 0;
} -
2072单词数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* 使用STL中的set可以去重,最后集合大小即为不同单词数 */
int CountWords(char str[], int size) {
set words;
int i = 0, j;
string s;
while (i < size) {
for (j = i; j < size; j++) {
if (str[j] != ' ')
s.push_back(str[j]);
else
break;
}
i = j + 1;
if (!s.empty())
words.insert(s);
s.clear();
}
return words.size();
}
int main() {
char a[999];
while (1) {
cin.getline(a, 999);
int len = strlen(a);
if (a[0] == '#' && len == 1)
break;
int words_count = CountWords(a, len);
cout << words_count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
-
2091空心三角形
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
char t;
int n;
bool dirty = false; // 这就是避免PE的方法
while (cin >> t && t != '@' && cin >> n) {
if (dirty) // 这就是避免PE的方法
cout << endl; // 这就是避免PE的方法
dirty = true; // 这就是避免PE的方法
int split_point = (2 * n - 1) / 2 + 1; // (I)
int sp = 0; // (II)
/* State 1 */
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= split_point + sp; i++) {
if ((i == split_point - sp) || (i == split_point + sp))
cout << t;
else
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sp++;
}
/* State 2 */
for (int j = 0; j < 2 * n - 1; j++)
cout << t;
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} 分析
1005
f[0] = 1; // by the way
f[1] = 1; // 等价于递归终止条件一
f[2] = 1; // 等价于递归终止条件二
for (int i = 3; i < 50; i++) // 等价于递归过程
f[i] = (A * f[i - 1] + B * f[i - 2]) % 7;1097
- 0~9的幂个位数是一个循环,比如9的若干次幂个位数永远是1、9、1、9……循环长度只可能是0、1、2或4,故所有的幂次直接模4;
- 根据网上人的说法分成3种情况:
- 指数为0,结果为懒惰的人类规定的特殊情况(简称懒惰情况);
- 指数为4的倍数,由于此时指数模4会变为0,为了防止错误得出懒惰情况,赋指数为4;
- 指数不是4的倍数,指数模4。
2001,牛顿法开平方,用C格式化输出。
2091,分2种情况:是否到达最后一行。(I)代表中点,(II)代表字符与中点之间的空格数。