标签/TabActivity 深度研究
何谓标签 印象最深刻的应该是这个
现在 我们将通过一系列的扩展来研究之
写道
1. 自定义TabActivity 使得标签处于屏幕下方
2. 各个标签所用布局 既可在 *.xml 中定义 也可在 *.java 中定义
3. 更改标签布局
2. 各个标签所用布局 既可在 *.xml 中定义 也可在 *.java 中定义
3. 更改标签布局
1. 标签页 在 屏幕下方
写道
一个典型的标签Activity 是由2 部分构成的 且其id都有规定 即:
* TabWidget 用于展示标签页 id=tabs
* FrameLayout 用于展示隶属于各个标签的具体布局 id=tabcontent
* TabWidget 用于展示标签页 id=tabs
* FrameLayout 用于展示隶属于各个标签的具体布局 id=tabcontent
* 基本布局如下:
xml代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="200dip" >
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/view1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello to Johnny.Griffin!"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textStyle="bold|italic" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:src="@drawable/robot"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/text" />
</RelativeLayout>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
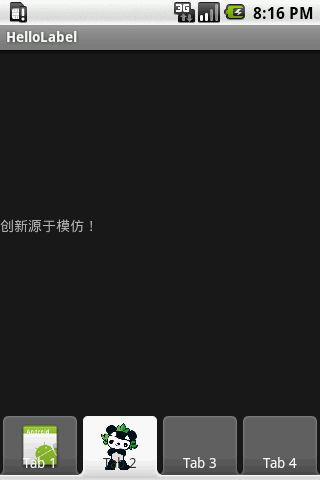
android:text="创新源于模仿!" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="欢迎进入 droid 世界!" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/view4"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:src="@drawable/robot" />
</FrameLayout>
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>
* 得到TabHost tHost 仅在TabActivity中有效
- tHost = this.getTabHost();
* 创建4个标签 并指定所使用的布局
Java代码
public static final String Tab1 = "Tab1";
public static final String Tab2 = "Tab2";
public static final String Tab3 = "Tab3";
public static final String Tab4 = "Tab4";
public static final String Tab5 = "Tab5";
tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab1).setIndicator("Tab 1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.icon)).setContent(R.id.view1));
tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab2).setIndicator("Tab 2", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.beijing_small)).setContent(R.id.view2));
tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab3).setIndicator("Tab 3").setContent(R.id.view3));
tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab4).setIndicator("Tab 4").setContent(R.id.view4));
* 设定监听器 用于监听 标签间切换事件
tHost.setOnTabChangedListener(new OnTabChangeListener(){
@Override
public void onTabChanged(String tabId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
* emulator 运行情况:
2. 在 *.java 中定义标签所需布局
Java代码
public class CustomLayout implements TabHost.TabContentFactory {
Activity activity;
LayoutInflater inflaterHelper;
LinearLayout layout;
public CustomLayout (Activity a) {
activity = a;
inflaterHelper = a.getLayoutInflater();
}
/** {@inheritDoc} *///tag 标记各个标签
public View createTabContent(String tag) {
return addCustomView(tag);
}
public View addCustomView(String id){
layout = new LinearLayout(activity);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
if(id.equals(Tab1)){
ImageView iv = new ImageView(activity);
iv.setImageResource(R.drawable.beijing_big);
layout.addView(iv,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
}
else if(id.equals(Tab2)){
EditText edit = new EditText(activity);
layout.addView(edit,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
Button btn = new Button(activity);
btn.setText("OK");
btn.setWidth(100);
layout.addView(btn,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
RadioGroup rGroup = new RadioGroup(activity);
rGroup.setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
RadioButton radio1 = new RadioButton(activity);
radio1.setText("Radio A");
rGroup.addView(radio1);
RadioButton radio2 = new RadioButton(activity);
radio2.setText("Radio B");
rGroup.addView(radio2);
layout.addView(rGroup,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
}
else if(id.equals(Tab3)){
LinearLayout.LayoutParams param3 =
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
layout.addView(inflaterHelper.inflate(R.layout.hello, null),param3);
}
else if(id.equals(Tab4)){
TextView tv = new TextView(activity);
tv.setText("HelloTags!");
tv.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
layout.addView(tv);
}
return layout;
}
}
* 如何使用:
- CustomLayout ct = new CustomLayout(this);
- tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab4).setIndicator("Tab 4").setContent(ct));
* emulator 运行结果:

3. 改变标签布局
写道
可能很多人对TabActivity 不满意 原因之一:其很不美观 而不美观的根源就是:标签的问题 其图像和文字相互覆盖 导致的
那么 我们可以自己扩展么? 当然
那么 我们可以自己扩展么? 当然
写道
TabWidget 理解:
1. TabWidget 为 horizontal 的 LinearLayout
2. 且 其包含的标签又是一个RelativeLayout
3. 每个标签RelativeLayout 里面包含2个View: TextView ImageView
1. TabWidget 为 horizontal 的 LinearLayout
2. 且 其包含的标签又是一个RelativeLayout
3. 每个标签RelativeLayout 里面包含2个View: TextView ImageView
因此 我们甚至可以推算出其布局为:
xml代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<RelativeLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView />
<TextView />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView />
<TextView />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView />
<TextView />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView />
<TextView />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
* 去掉系统默认的布局 即 在 setIndicator() 中置空 修改如下:
- tHost.addTab(tHost.newTabSpec(Tab1).setIndicator("").setContent(ct));
写道
可能有人会说:那我不调用setIndicator() 不久可以了么 不行 否则 会报错
* 自己定义布局 并 指定显示的内容
Java代码
public View composeLayout(String s, int i){
LinearLayout layout = new LinearLayout(this);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
tv.setSingleLine(true);
tv.setText(s);
layout.addView(tv,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
ImageView iv = new ImageView(this);
iv.setImageResource(i);
layout.addView(iv,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
return layout;
}
* 得到 TabWidget 实例 tw
- LinearLayout ll=(LinearLayout)tHost.getChildAt(0);
- tw =(TabWidget)ll.getChildAt(1);
* 得到 TabWidget 内的具体某个Layout 并使用上面的布局 composeLayout()
- public void updateWidgetView(int i,String text,int image){
- RelativeLayout rl =(RelativeLayout)tw.getChildAt(i);
- rl.addView(composeLayout(text,image));
- }
* emulator 运行截图 // 前面 3个是使用新布局 最后一个是使用TabActivity 默认的布局 哪个好看 大家自己选择之

that's all!