四篇文章带你玩转springboot——4starter组件
第1章 starter组件简介
starter组件是SpringBoot的一个核心特性,Starter组件的出现极大简化了项目开发,例如在项目中使用的pom.xm文件下配置:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
SpringBoot就会自动关联web开发相关的依赖,如tomcat以及spring-webmvc等,进而对web开发进行支持,同时相关技术也将实现自动配置,避免了繁琐的配置文件。
Starter组件使开发者不需要关注各种依赖库的处理,不需要具体的配置信息,由SpringBoot自动完成class类发现并加载需要的Bean。
利用starter实现自动化配置需要两个条件:Maven依赖、配置文件,Maven依赖实质上就是导入jar包,SpringBoot启动的时候会找到Starter组件jar包中的resources/META-INF/spring.factories文件,根据spring.factories文件中的配置,找到需要自动配置的类。
starter组件理解总结:
-
每个不同的starter组件实际上完成自身的功能逻辑,然后对外提供一个bean对象让别人调用
-
对外提供的bean通过自动装配原理注入到提供方的IoC容器中
第2章 手写starter组件
要实现一个自己的starter组件其实也很简单,要完成一个starter组件的编写,首先要明确,我们要做的事有哪些:
-
通过配置类提供对外服务的bean对象
-
按照自动装配原理完成spring.factories的编写
-
starter自动属性配置
接下来我们就来手写一个starter组件,流程如下:
-
创建一个springboot项目:redisson-spring-boot-starter
-
引入依赖
4.0.0 com.gupao.redisson redisson-spring-boot-starter 1.0-SNAPSHOT redisson-spring-boot-starter http://www.example.com UTF-8 1.8 1.8 junit junit 4.11 test org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter 2.3.2.RELEASE true org.redisson redisson 3.16.1 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-configuration-processor 2.3.2.RELEASE maven-clean-plugin 3.1.0 maven-resources-plugin 3.0.2 maven-compiler-plugin 3.8.0 maven-surefire-plugin 2.22.1 maven-jar-plugin 3.0.2 maven-install-plugin 2.5.2 maven-deploy-plugin 2.8.2 maven-site-plugin 3.7.1 maven-project-info-reports-plugin 3.0.0 -
创建要注入的bean类和接口
package com.gupao.redisson; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2022/6/11 9:58 */ public interface Humen { String dancing(); } package com.gupao.redisson; import org.redisson.Redisson; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient; import org.redisson.config.Config; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.Properties; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2022/1/14 22:55 */ public class Girl implements Humen{ public static Girl create(String name){ return new Girl(name); } private String name; public Girl(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String dancing() { return name+"喜欢跳舞"; } } -
创建属性类
package com.gupao.redisson; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2021/8/11 11:28 */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "gp.girl") public class GirlProperties { private String name = "wentai"; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } -
创建配置类
package com.gupao.redisson; import org.redisson.Redisson; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient; import org.redisson.config.Config; import org.redisson.config.SingleServerConfig; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2021/8/11 11:05 */ @ConditionalOnClass(Girl.class)//条件装配 @EnableConfigurationProperties(GirlProperties.class) @Configuration public class GirlAutoConfiguration { @Bean Humen humen(GirlProperties girlProperties){ return Girl.create(girlProperties.getName()); } } -
实现自动装配流程,在META-INF目录下创建spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ com.gupao.redisson.RedissonAutoConfiguration,\ com.gupao.redisson.GirlAutoConfiguration -
在META-INF创建属性默认规范文件additional-spring-configuration-metadata.json
{ "properties": [ { "name": "gp.redisson.host", "type": "java.lang.String", "description": "Redis的服务器地址", "defaultValue": "localhost" }, { "name": "gp.redisson.port", "type": "java.lang.Integer", "description": "Redis的服务器端口", "defaultValue": 6379 }, { "name": "gp.redisson.pwd", "type": "java.lang.String", "description": "Redis的服务器密码", "defaultValue": "jingtian" }, { "name": "gp.redisson.datasource", "type": "java.lang.Integer", "description": "Redis的服务器库", "defaultValue": 0 }, { "name": "gp.girl.name", "type": "java.lang.String", "description": "默认女孩名", "defaultValue": "wentai" } ] } -
打包发布
-
测试
通过上面我们实现自己的starter组件案例来看,starter组件的实现其实逻辑并不复杂,核心思想就是在META-INF目录下创建spring.factories文件,然后配置自定义的配置类。只要按照这个逻辑配置,都可以做到自动注入到IoC容器中去,OK,那我们现在来看看我们的spring-boot-starter-data-redis这个starter组件,你会发现,这个组件里面居然没有spring.factories文件,为什么呢?没有这个文件,它是怎么自动装配的呢?
第3章 自身与第三方维护
其实针对springboot的starter组件分为两类
-
springboot自身维护的starter组件
@ConditionalOnBean(仅仅在当前上下文中存在某个对象时,才会实例化一个Bean) @ConditionalOnClass(某个class位于类路径上,才会实例化一个Bean) @ConditionalOnExpression(当表达式为true的时候,才会实例化一个Bean) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(仅仅在当前上下文中不存在某个对象时,才会实例化一个Bean) @ConditionalOnMissingClass(某个class类路径上不存在的时候,才会实例化一个Bean) @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication(不是web应用)
-
所有的starter组件自身不带spring.factories文件,集中在spring都是-boot-autoconfigure包下的EnableAutoConfiguration
-
springboot装配这些配置类是需要条件的,不可能所有的configuration都注入,假设我没用到redis的话就不会引包,这样就根据@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class)在class path下找不到RedisOperation类,这样就不会加载该配置类
-
自身维护的starter组件的命名:spring-boot-starter-XXX
-
-
第三方维护的starter组件
-
自己维护spring.factories文件
-
命名方式:XXX-spring-boot-starter
-
-
这里有个小知识:@ConditionalOnClass(XXX.class)在我们本地用的时候,如果XXX.class不存在的话压根编译不能通过,但是为什么springboot自身维护的能编译通过呢?
其实原因也简单,因为在starter组件编译的时候是引入了@ConditionnalOnClass里面的那个类了的,然后在pom文件引入的这个XXX类所在的jar包时加了
true,等starter组件编译打包之后不会将XXX类所在的jar包传递依赖给别的项目。 这里就可以将spring-boot-autoconfigure包理解成一个starter组件,它在编译的过程中引入了很多jar包,比如说引入Redis的相关jar包,然后加入了
true,当autoconfigure编译打成jar包之后是没问题的,但是别的项目依赖autoconfigure之后,必须要引入redis的jar包才能通过@ConditionalOnClass注解。
现在我们会手写自己的starter组件了,也明白了不同组件的区别,那么接下来让我们一起来看看springboot中的一个比较重要的组件——spring-boot-starter-web组件,为什么要看它呢?因为它帮我们完成了容器的内置以及启动。
第4章 内置容器
4.1 starter-web
-
Springboot整合Spring MVC只需要在pom.xml文件中引入
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web -
配置文件
server: port: 8080 # web服务端口号 servlet: multipart: enabled: true # 启用文件上传 location: # 上传文件临时保存位置 max-file-size: 50MB # 单个文件上传最大大小限制 max-request-size: 100MB # 单次请求主体最大大小限制 mvc: format: date: yyyy-MM-dd # 日期格式 date-time: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss # 日期时间格式 time: HH:mm:ss # 时间格式 servlet: path: / # servlet路径 static-path-pattern: # 匹配静态资源路径 view: prefix: # view前缀 suffix: # view后缀,如:.jsp以上是Spring MVC常用配置,更多配置可参见Common Application properties
我们只配置最简单的
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/ -
service
package com.example.springbootvipjtdemo.mvcdemo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2022/6/11 16:03 */ @Service public class JspService { public String sayHello(String name){ return "你真棒!"+name; } } -
controller
package com.example.springbootvipjtdemo.mvcdemo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; /** * @author Eclipse_2019 * @create 2022/6/11 16:03 */ @RestController public class JspController { @Autowired private JspService jspService; @RequestMapping("/jsp") public ModelAndView hello(@RequestParam String name){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("version","2.X版本"); modelAndView.addObject("name",name); modelAndView.addObject("msg",jspService.sayHello(name)); modelAndView.setViewName("a"); return modelAndView; } } -
jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>${version}
${name}:${msg}
上面的案例实现了Springboot集成springmvc,但是现在还没有哪里用到了容器,那容器是怎么启动的呢?
先来看看spring-boot-starter-web包里面有啥
-
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration配置类中Import了ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class
当容器启动的时候也会自动装配该类,在该配置类中创建了TomcatServletWebServerFactory()
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration类完成了InternalResourceViewResolver解析器的注入
然后再来看看springboot启动的时候是怎么去创建内置容器的
4.2 onRefresh
spring容器启动代码就不说了,这里主要看一下onRefresh() 这个方法。转到定义发现这个方法里面啥都没有,这明显是一个钩子方法,它会钩到它子类重写onRefresh()方法。所以去看子类里面的onRefresh()
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
//这是一个空方法,AbstractApplicationContext 这个类是一个抽象类,
//所以我们要找到集成AbstractApplicationContext的子类,去看子类里面的onRefresh()
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
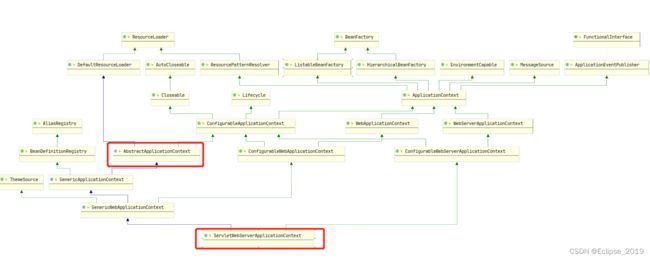
}我们这里是一个Web项目,所以我们就去看 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 这个类 ,我还是把类的关系图贴一下
我们就去看 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 这个类下面的 onRefresh() 方法
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
//看到内置容器的影子了,进去看看
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}4.3 createWebServer
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//1、这个获取webServerFactory还是要进去看看
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}我们继续看下getWebServletFactory() 这个方法,这个里面其实就是选择出哪种类型的web容器了
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory()
.getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : "
+ StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}4.4 getWebServer
我们再回头去看factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()) ,转到定义就会看到很熟悉的名字tomcat
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//tomcat这位大哥出现了
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}内置的Servlet容器就是在onRefresh() 方法里面启动的,至此一个Servlet容器就启动OK了。