opencv图像像素算术运算+逻辑运算
1、像素的算术运算:
void QuickDemo::OperatorTest(Mat &image)
{
Mat res;
Mat m1 = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
m1 = Scalar(50, 50, 50);
add(image, m1, res);//加法
imshow("add",res);
subtract(image,m1,res);//减法
imshow("subtract",res);
m1 = Scalar(2,2,2);
multiply(image, m1, res);//乘法
imshow("multiply",res);
divide(image, m1, res);//除法
imshow("divide",res);
}
2、像素的逻辑运算:
void QuickDemo::bitwise_demo(Mat &image)
{
Mat m1 = Mat::zeros(Size(4, 4), CV_8UC1);
Mat m2 = Mat::zeros(Size(4, 4), CV_8UC1);
m1 = Scalar(0xFF);
m2 = Scalar(0x0F);
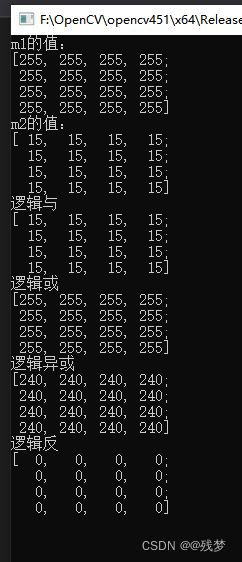
std::cout << "m1的值:" << std::endl;
std::cout << m1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "m2的值:" << std::endl;
std::cout << m2 << std::endl;
Mat dst = Mat::zeros(Size(4, 4), CV_8UC1);
bitwise_and(m1, m2, dst);
std::cout << "逻辑与\n" << dst<<std::endl;
bitwise_or(m1, m2, dst);
std::cout << "逻辑或\n" << dst << std::endl;
bitwise_xor(m1, m2, dst);
std::cout << "逻辑异或\n" << dst << std::endl;
bitwise_not(m1, dst);
std::cout << "逻辑反\n" << dst << std::endl;
}
void QuickDemo::bitwise_demo(Mat &image)
{
Mat m1 = Mat::zeros(Size(255, 255), CV_8UC3);
Mat m2 = Mat::zeros(Size(255, 255), CV_8UC3);
rectangle(m1, Rect(100, 100, 80, 80), Scalar(255, 255, 0), -1, LINE_8, 0);
rectangle(m2, Rect(150, 150, 80, 80), Scalar(0, 255, 255), -1, LINE_8, 0);
imshow("m1", m1); imshow("m2",m2);
Mat dst;
bitwise_and(m1, m2, dst);
imshow("bitwise_and", dst);
bitwise_or(m1,m2,dst);
imshow("bitwise_or",dst);
bitwise_xor(m1, m2, dst);
imshow("bitwise_xor", dst);
bitwise_not(image,dst);
imshow("bitwise_not", dst);
填充/绘边函数介绍:rectangle()
函数原型:
CV_EXPORTS_W void rectangle(InputOutputArray img, Rect rec,
const Scalar& color, int thickness = 1,
int lineType = LINE_8, int shift = 0);
功能:绘制一个简单的,粗的,或填充的右上矩形
矩形函数的作用是:绘制一个矩形的轮廓或填充矩形
@img:图像
@rec:填充位置/大小
@color:颜色
@thickness:组成矩形的线条的厚度。负值,比如# fill,意味着函数要画一个填充的矩形。-1代表全部填充,正值代表绘轮廓
@lineType:行类型。看LineTypes;这个是为了绘图防止轮廓锯齿现象,推荐LINE_8,LINE_AA 会很慢
/** types of line
@ingroup imgproc_draw
*/
enum LineTypes {
FILLED = -1,
LINE_4 = 4, //!< 4-connected line
LINE_8 = 8, //!< 8-connected line
LINE_AA = 16 //!< antialiased line
};
@shift:点坐标中的小数位数。