OpenCV(4)矩阵掩码操作/像素算数、逻辑操作 C++
1. 矩阵上的掩码操作
1.1.(cv :: filter2D)矩阵上的掩码操作
1.2.(cv :: CV_Assert) 确保输入图像数据是unsigned char格式
图像对比度增强方法的问题。基本上我们要为图像的每个像素应用以下公式:
I(i,j) = 5 * I(i,j) – [ I(i-1,j) + I(i+1,j) + I(i,j-1) + I(i,j+1)],
- I(i,j) :表示目标像素点;i :表示像素点的横坐标;j :表示像素点的纵坐标
- I(i-1,j) 、I(i+1,j) 、 I(i,j-1) 、 I(i,j+1):分别表示目标像素点周围的四个像素点
- 上面公式的作用就是:让自己增加4倍,然后减去周围像素点的值,所得到的值便是自己新的值。如果目标像素颜色很鲜艳,它周围的像素点颜色不鲜艳,那么通过公式,目标点会变得更加鲜艳。相反,目标像素点会变得更加不鲜艳。
#include #include 执行结果:
Hand written function, 自己写的代码耗时: 0.0022542
Built-in filter2D , filter2D耗时: 0.0005542
2.图像像素的算术操作
2.1.加:add (src1, src2, addResult);
2.2.减:subtract (src1, src2, subResult);
2.3.乘:multiply (src1, src2, mulResult);
2.4.除:divide (src1, src2, divResult);
还可以使用以下方式进行:像素之间的 加、减、乘法
saturateResult.at(row, col)[0] = saturate_cast(b1 * b2);
saturateResult.at(row, col)[1] = saturate_cast(g1 * g2);
saturateResult.at(row, col)[2] = saturate_cast(r1 * r2);
#include 执行结果:
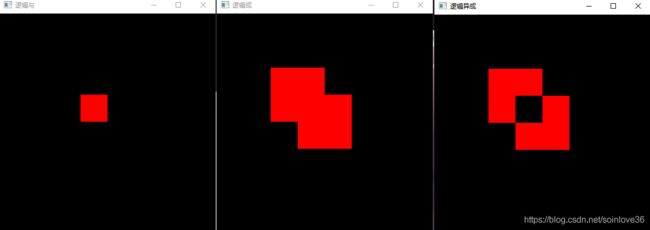
3.像素的逻辑操作
3.1.与:bitwise_and(src1, src2, dst1);
3.2.或:bitwise_or(src1, src2, dst2);
3.3.异或:bitwise_xor(src1, src2, dst3);
#include "opencv2\opencv.hpp"
#include